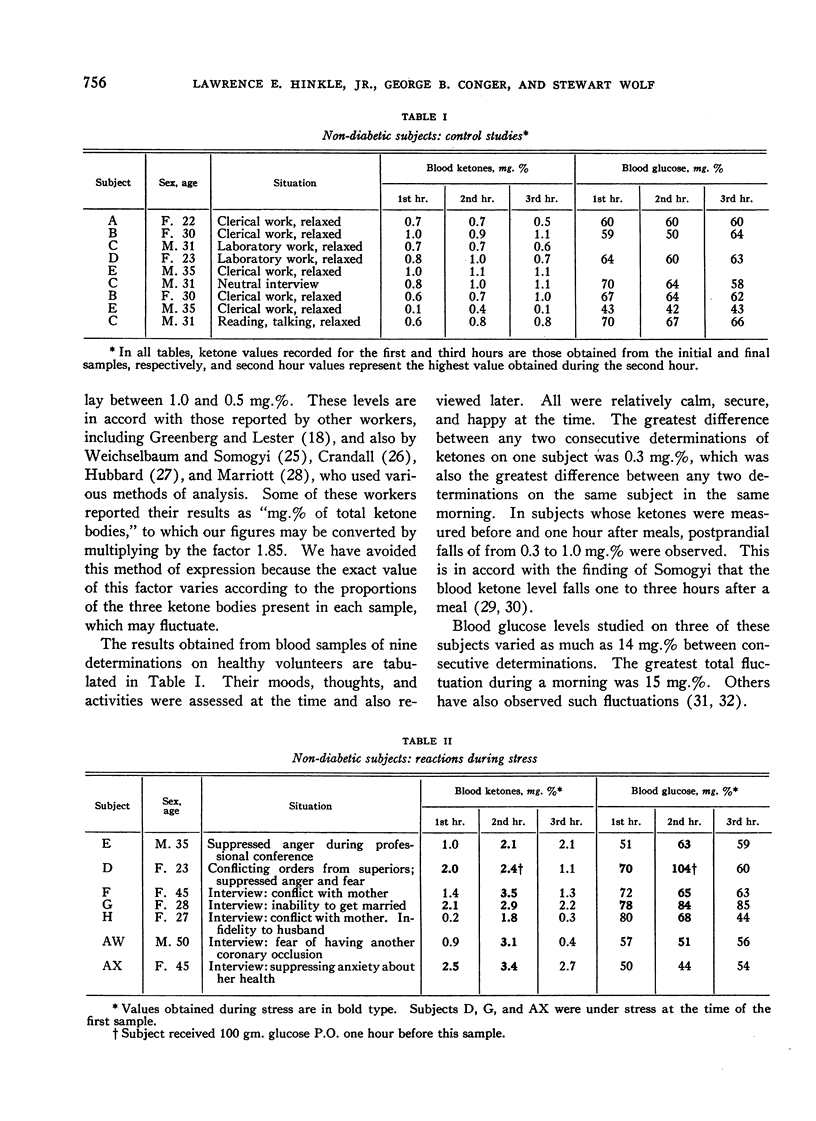
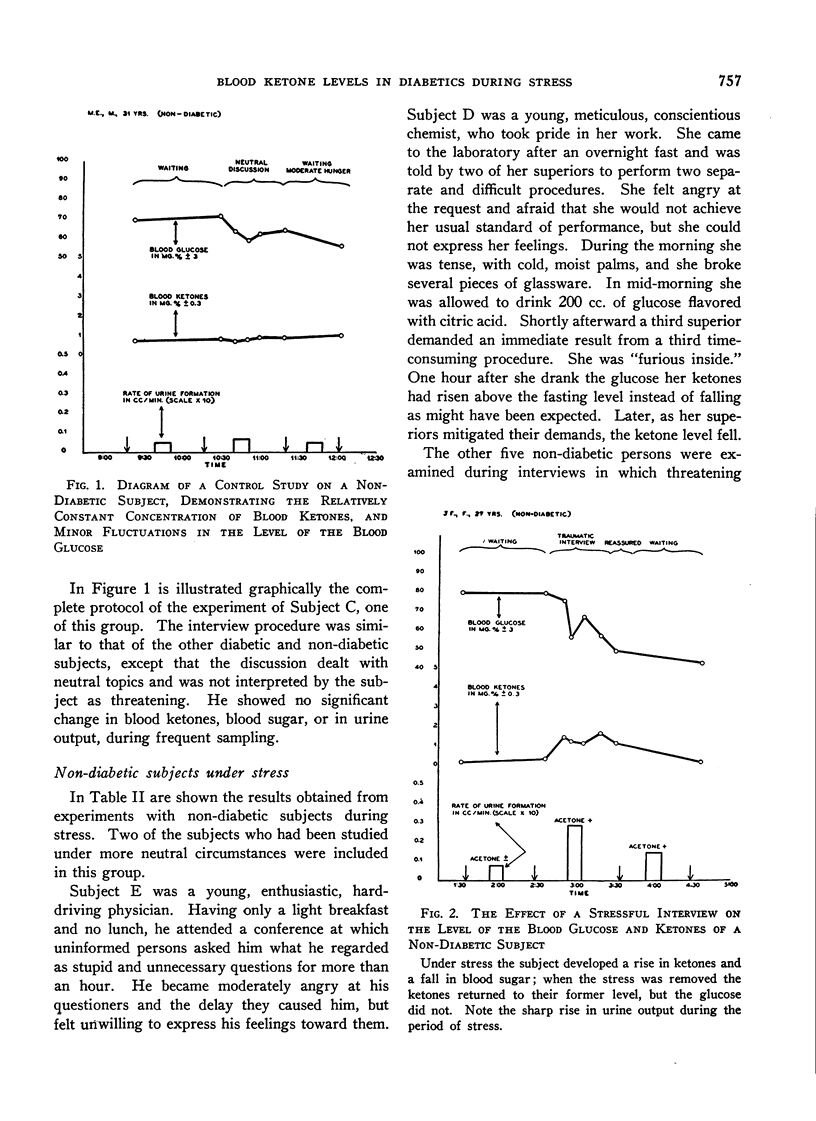
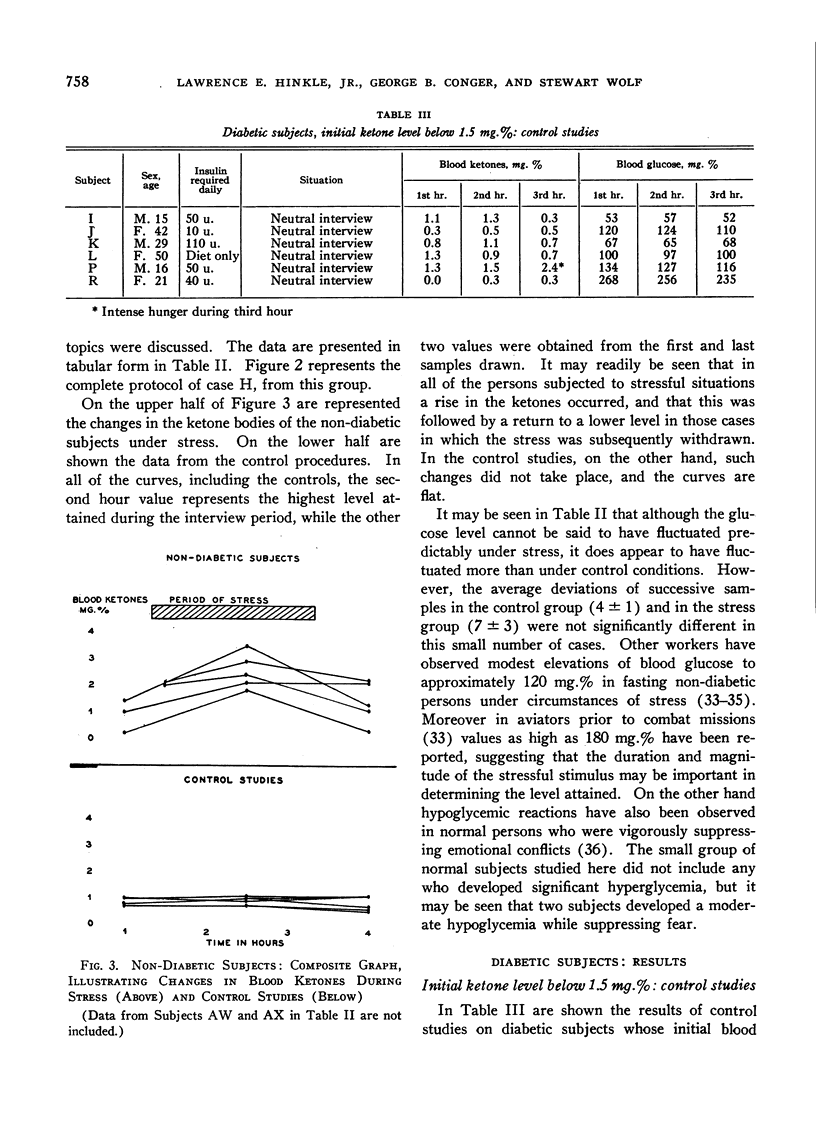
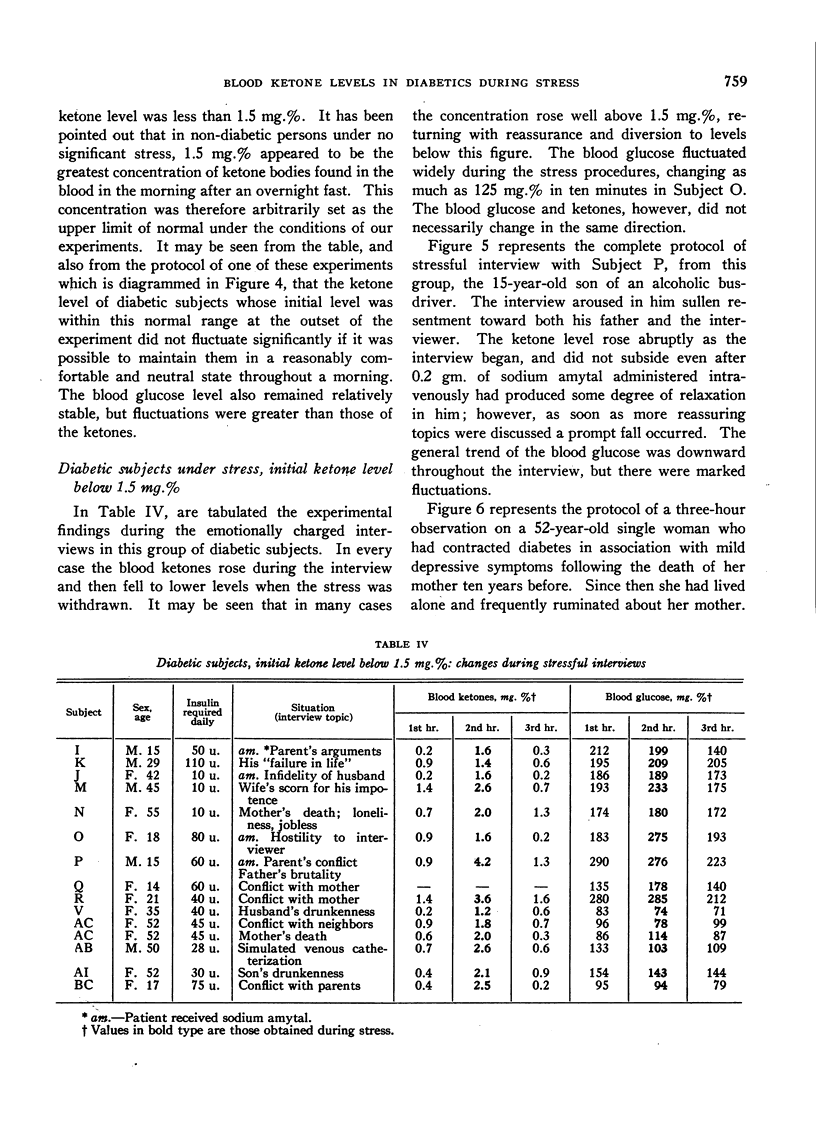
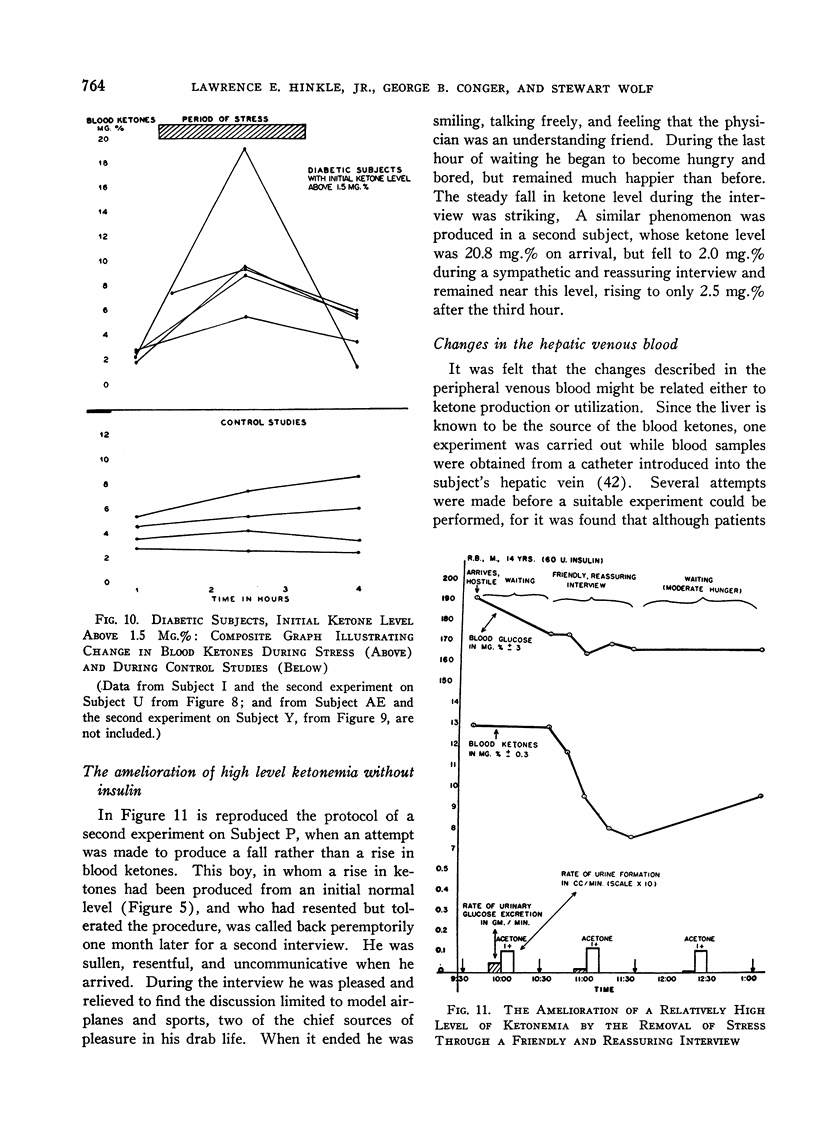
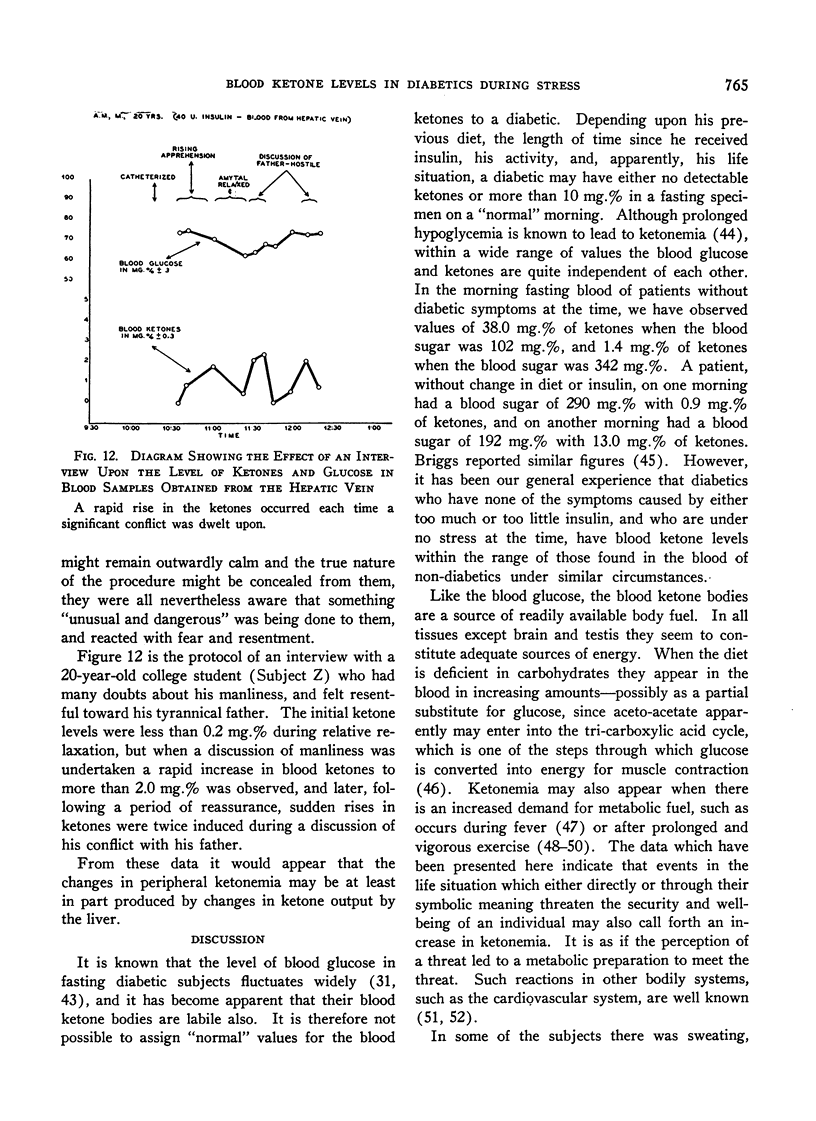
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Herbert F. K., Bourne M. C. The non-sugar reducing substances of human blood in pathological conditions. Biochem J. 1930;24(6):1787–1793. doi: 10.1042/bj0241787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert F. K., Bourne M. C. The non-sugar reducing substances of human blood, with special reference to glutathione. Biochem J. 1930;24(2):299–309. doi: 10.1042/bj0240299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kety S. S., Polis B. D., Nadler C. S., Schmidt C. F. THE BLOOD FLOW AND OXYGEN CONSUMPTION OF THE HUMAN BRAIN IN DIABETIC ACIDOSIS AND COMA. J Clin Invest. 1948 Jul;27(4):500–510. doi: 10.1172/JCI101997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN H., LIDZ T. Emotional factors in the precipitation of recurrent diabetic acidosis. Psychosom Med. 1949 Jul-Aug;11(4):211–215. doi: 10.1097/00006842-194907000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


