Abstract
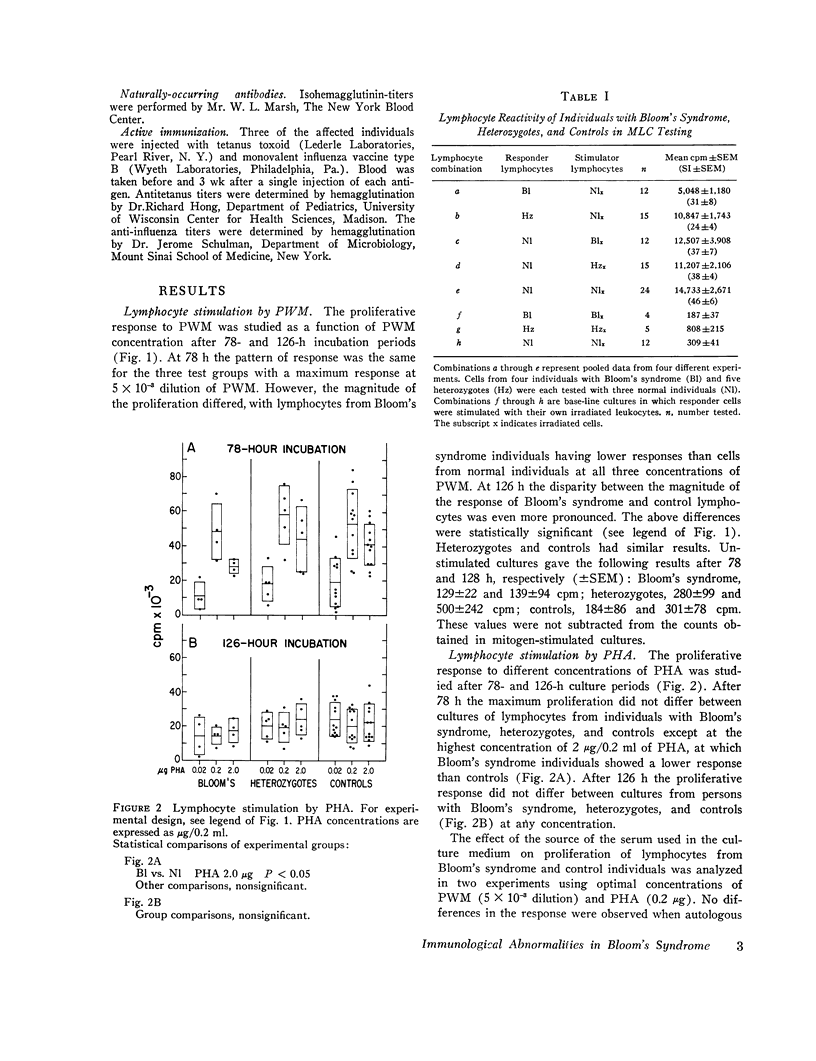
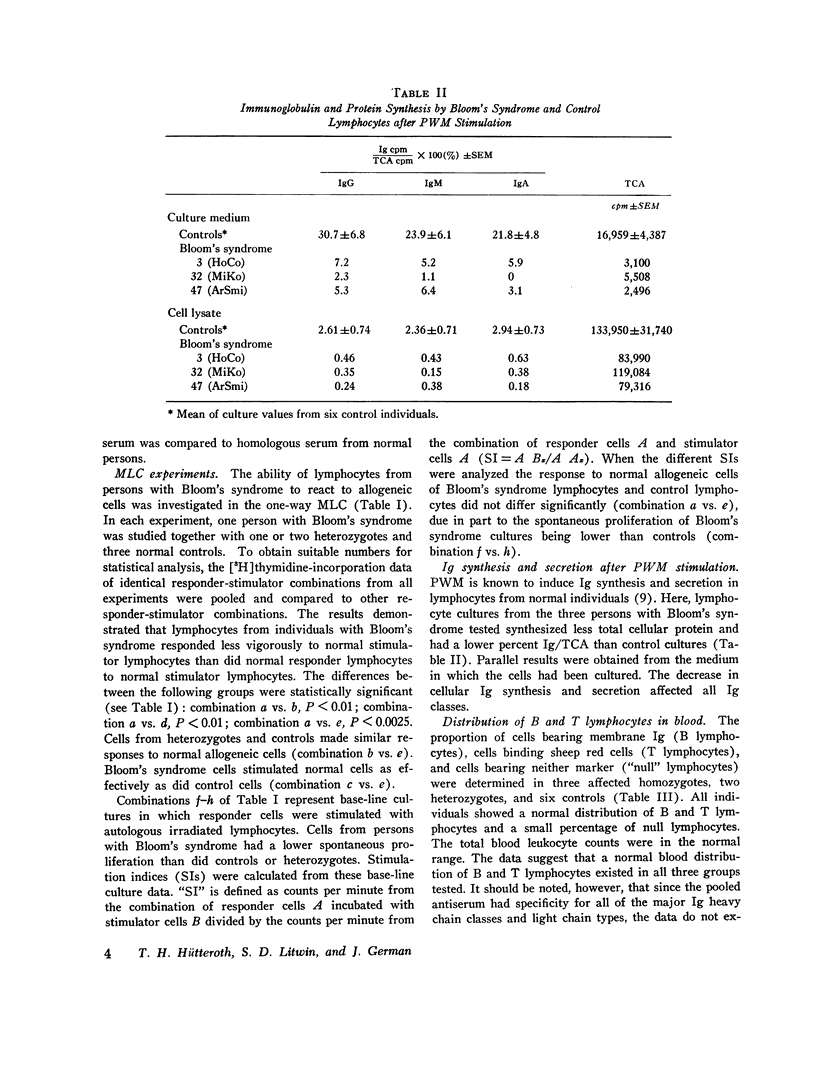
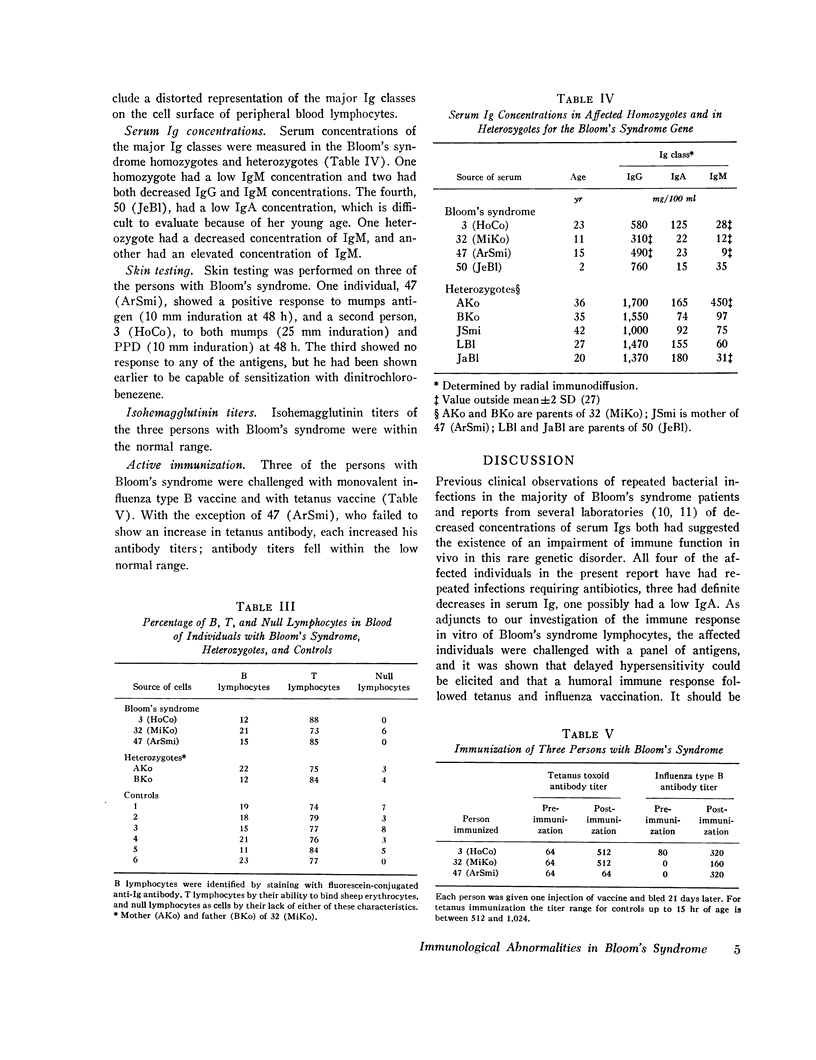
Bloom's syndrome is a rare autosmal recessive disorder, first characterized by growth retardation and asum-sensitive facial telangiectasia and more recently demonstarted to have increased chromosome instability, a predisposition to malignancy, and increased susecptibitily to infection. The present report ocncern the immune function of Bloom's syndrom lymphoctes in vitro. Four affected homozgotes and five heterozygotes were studied. An abnormal serum concentartion of at least one class of immunoglobin was present in three out of four homozgotes. Affected homozgotes were shown capable of both a humoral and cellular response after antigenic challenge, the responses in general being weak but detectable. Blood lymphocytes from Bloom's syndrome individuals were cultured in impaired proliferavite response and synthesized less immunoglobulin at the end of 5 days than did normal controls. In contrast, they had a normal proliferative response to phytohemagglutinin except at highest concentrations of the mitogen. In the mixed lymphocte culture, Bloom's syndrome lymphocytes proved to be poor responder cells but normal stimulator cells. Lmyphoctes from the heterozgotes produced normal responses in these three systems. Distrubed immunity appears to be on of several major consequences of homozygosity for the Bloom's syndrome gene. Although the explanation for this pleiotropism is at present obscure, the idea was advanced that the aberrant immune function is, along with the major clincial feature-small body size, amanifestation of defect in cellular proliferation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach F. H., Bach M. L., Sondel P. M., Sundharadas G. Genetic control of mixed leukocyte culture reactivity. Transplant Rev. 1972;12:30–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. C., Stites D. P., Fudenberg H. H. Dissociation of responses to phytohaemagglutinin and adult allogeneic lymphocytes in human foetal lymphoid tissues. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):279–281. doi: 10.1038/newbio241279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. S., Biggar W. D., Good R. A. Biosynthesis and secretion of immunoglobulins by peripheral-blood lymphocytes in severe hypogammaglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1972 May 27;1(7761):1149–1152. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. D., Hoffman P. F., Borjeson J., Chessin L. N. Studies on human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. 3. Fine structural features of lymphocyte transformation by pokeweed mitogen. J Immunol. 1967 Jan;98(1):17–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuy J. M., Lafforet D. A defect of cellular immunity in Xeroderma pigmentosum. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Sep;3(1):52–58. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German J. Bloom's syndrome. I. Genetical and clinical observations in the first twenty-seven patients. Am J Hum Genet. 1969 Mar;21(2):196–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German J., Crippa L. P., Bloom D. Bloom's syndrome. III. Analysis of the chromosome aberration characteristic of this disorder. Chromosoma. 1974;48(4):361–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00290993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Janossy G. Elicitation of selective T and B lymphocyte responses by cell surface binding ligands. Transplant Rev. 1972;11:87–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R., German J. A retarded rate of DNA chain growth in Bloom's syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):758–762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzman R. J., Bach M. L., Bach F. H., Thurman G. B., Sell K. W. Precipitation of radioactively labeled samples: a semi-automatic multiple-sample processor. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jun;4(2):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Immunodeficiency disease and malignancy. Various immunologic deficiencies of man and the role of immune processes in the control of malignant disease. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Oct;77(4):605–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Greaves M. F. Lymphocyte activation. I. Response of T and B lymphocytes to phytomitogens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Oct;9(4):483–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keutel J., Marghescu S., Teller W. Bloom-Syndrom. Bericht über einen Fall mit dermatohistologischen, endokrinologischen, immunologischen und cytogenetischen Untersuchungen. Z Kinderheilkd. 1967;101(2):165–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers F., Andersson J. Synthesis, surface deposition and secretion of immunoglobulin M in bone marrow-derived lymphocytes before and after mitogenic stimulation. Transplant Rev. 1973;14:76–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen H. J., Bach F. H., Hong R., Good R. A. Lymphocyte studies in congenital thymic dysplasia: The one-way stimulation test. J Pediatr. 1968 Feb;72(2):177–185. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paty D. W., Hughes D. Lymphocyte transformation using whole blood cultures: an analysis of responses. J Immunol Methods. 1972 Nov;2(1):99–114. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(72)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoen E. J., Shearn M. A. Immunoglobulin deficiency in Bloom's syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1967 May;113(5):594–596. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1967.02090200126017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. M., German J. Bloom's syndrome and Fanconi's anemia: demonstration of two distinctive patterns of chromosome disruption and rearrangement. Humangenetik. 1974;25(4):299–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00336905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Griscelli C., Preud'homme J. L., Sasportes M., Herzog C., Brouet J. C. A variant of severe combined immunodeficiency with normal in vitro response to allogeneic cells and an increase in circulating B lymphocytes persisting several months after successful bone marrow graft. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jun;17(2):245–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Serum levels of immune globulins in health and disease: a survey. Pediatrics. 1966 May;37(5):715–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockman G. D., Gallagher M. T., Heim L. R., South M. A., Trentin J. J. Differential stimulation of mouse lymphoid cells by phytohemagglutinin and pokeweed mitogen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Mar;136(3):980–982. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler M. E., Hütteroth T. H. Impaired lymphocyte function in aged humans. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):99–104. doi: 10.1172/JCI107565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. M., Benacerraf B. Comparison of T lymphocyte-dependent and B lymphocyte-dependent mitogen-stimulated DNA synthesis in serum-free medium with spleen cells from animals chosen for broad variation in genetically determined differences in T lymphocyte mitogen responsiveness. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1844–1849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. Y., Lawton A. R., Cooper M. D. Differentiation capacity of cultured B lymphocytes from immunodeficient patients. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3180–3189. doi: 10.1172/JCI107518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


