Abstract
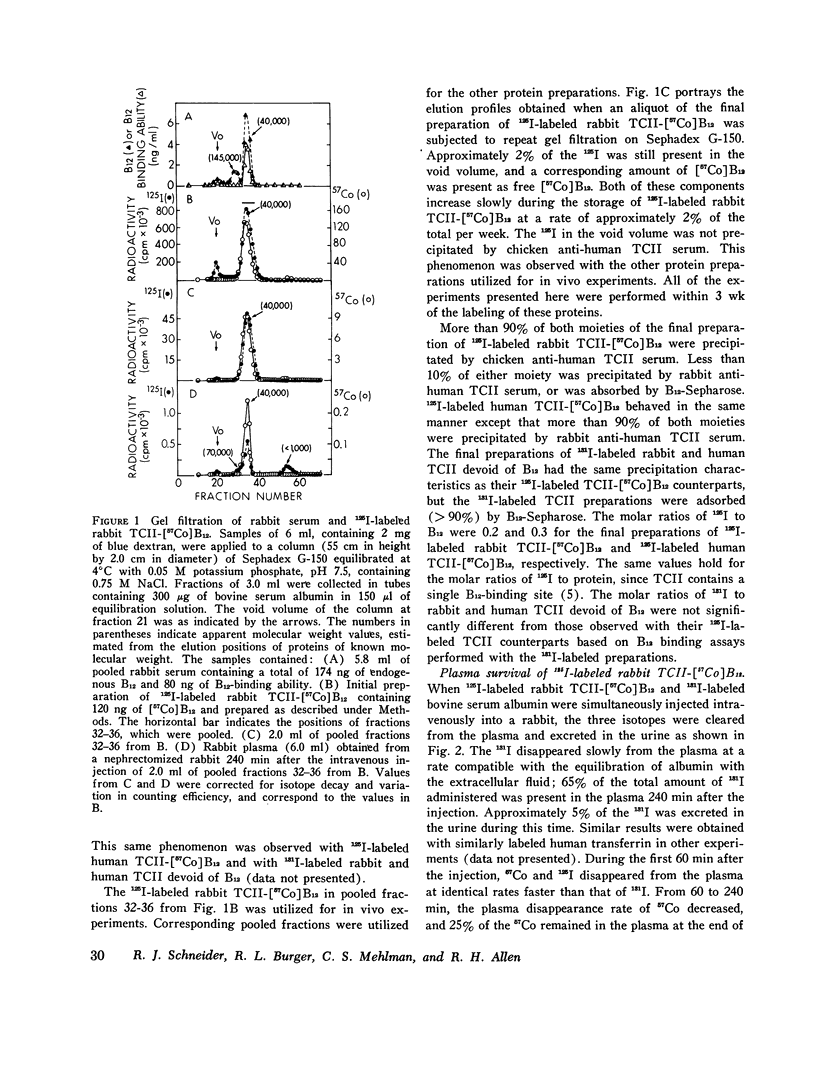
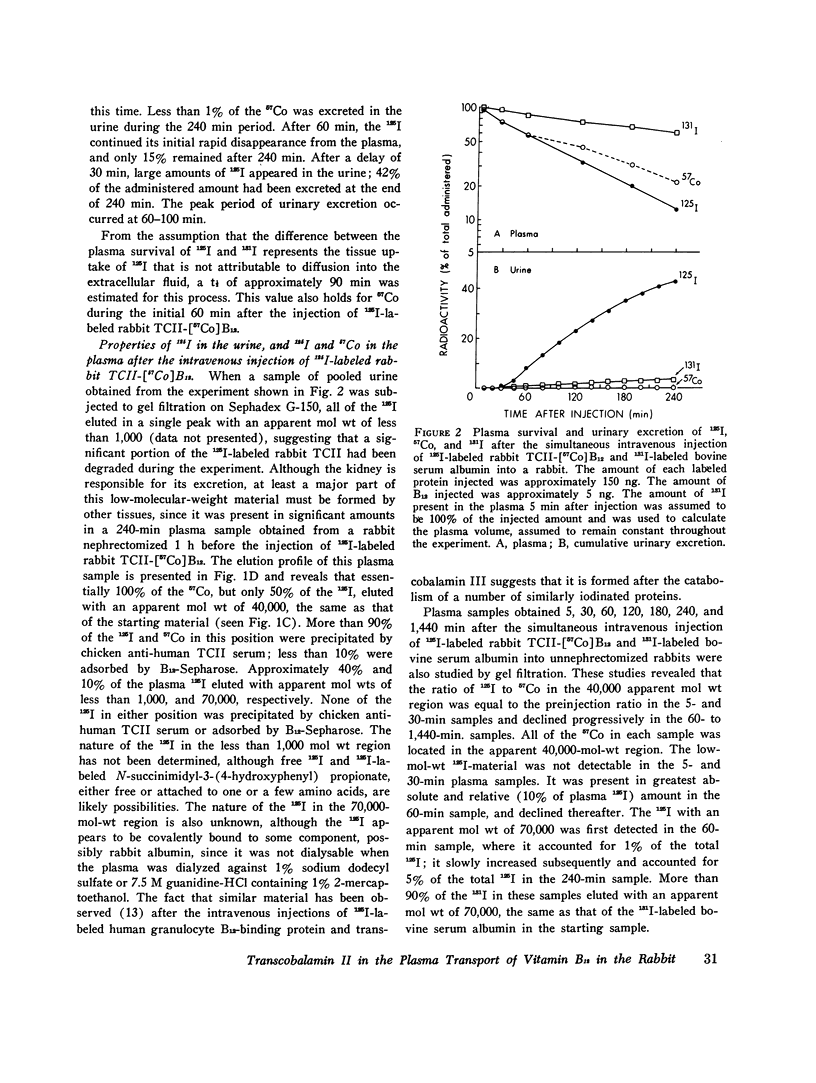
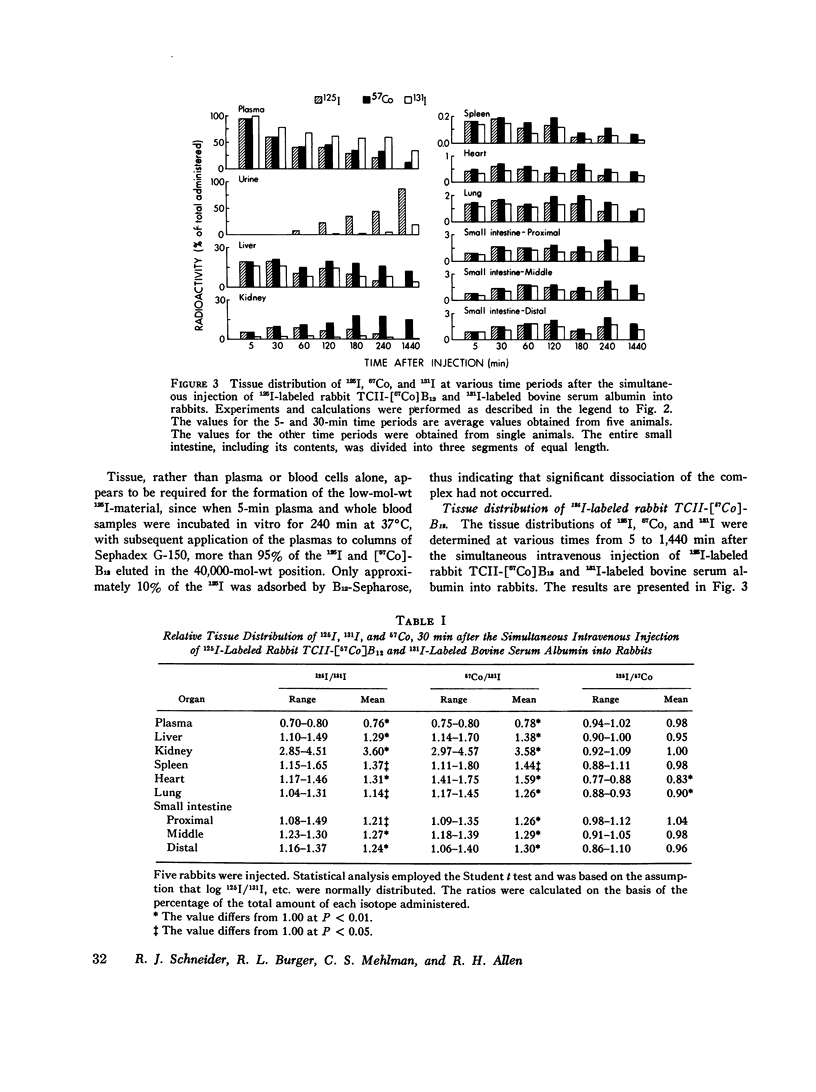
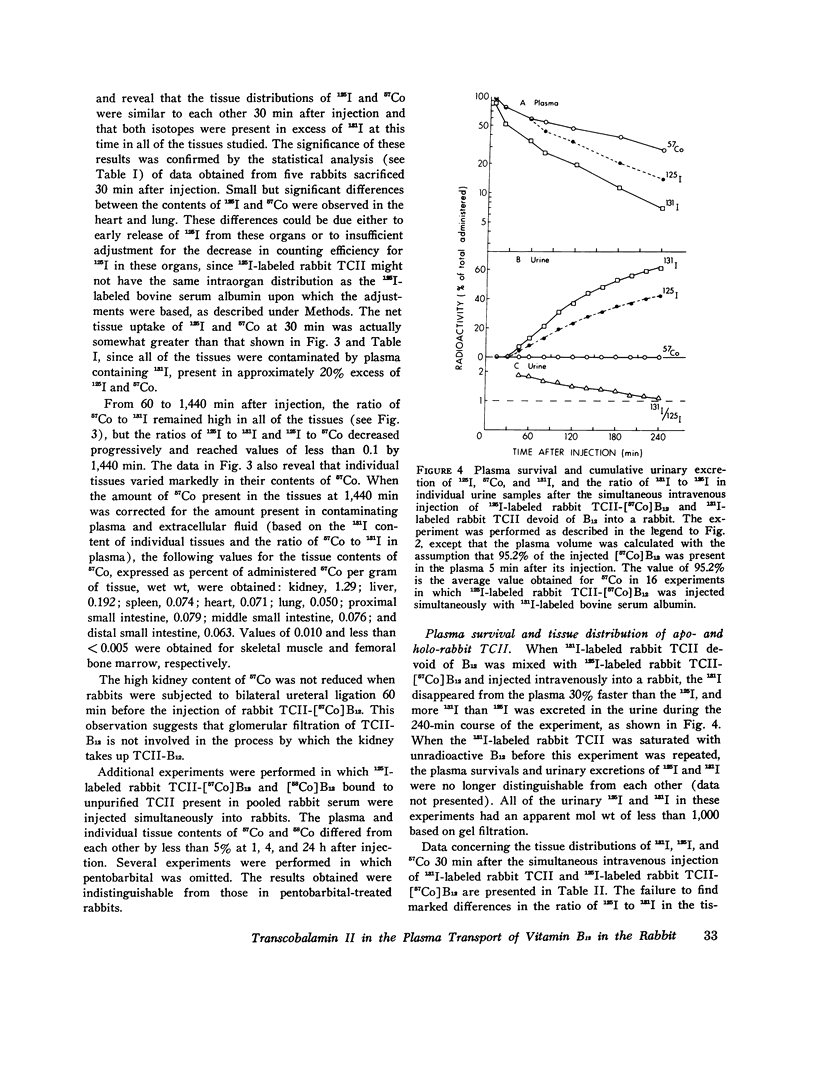
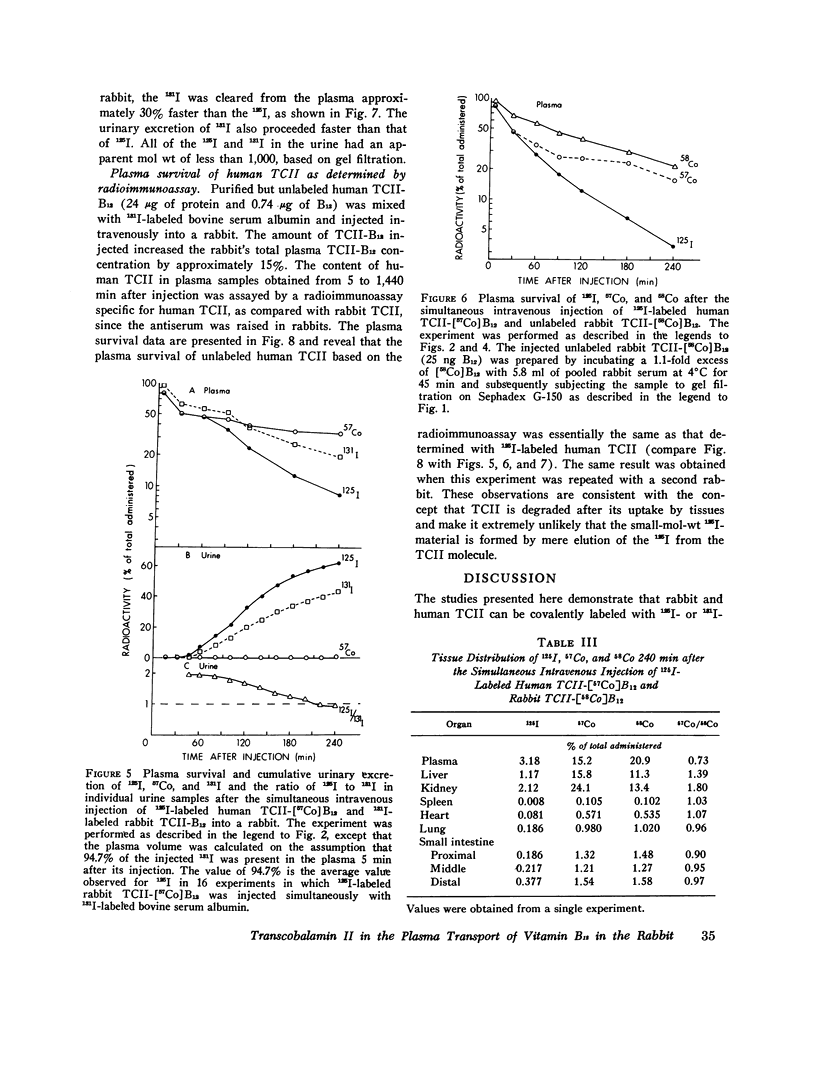
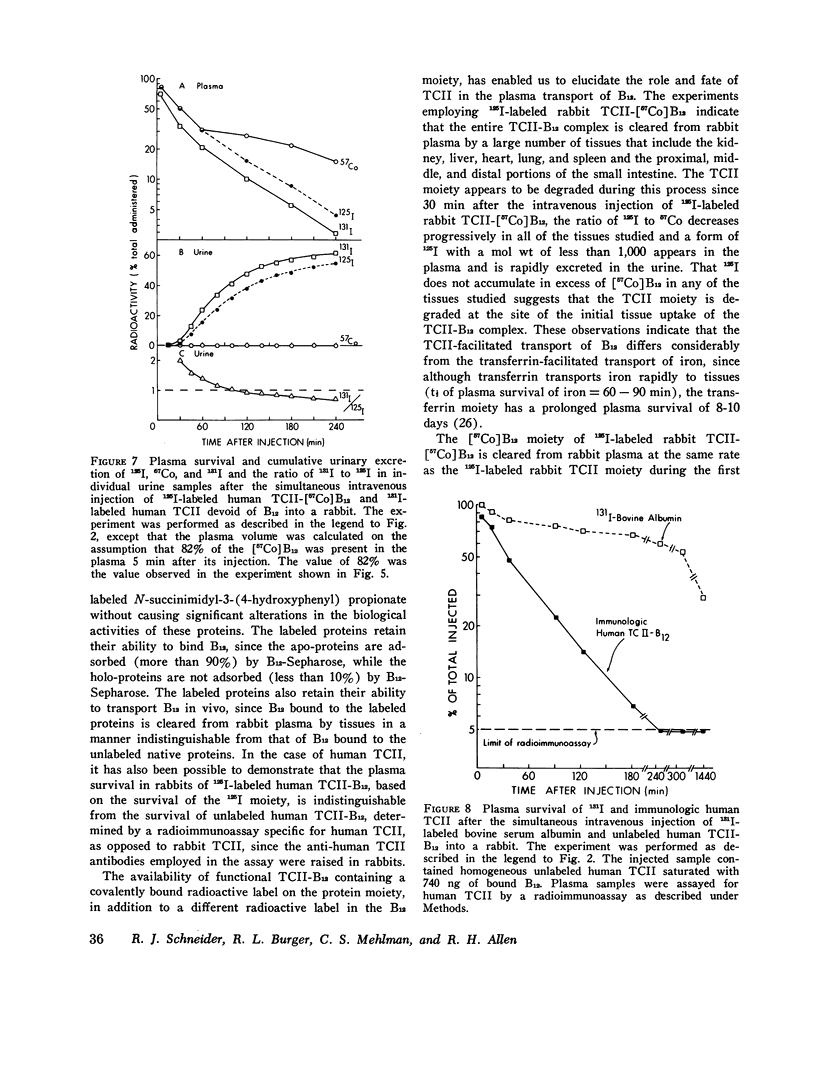
Previous studies have shown that plasma transcobalamin II (TCII) facilitates the cellular uptake of [57Co] vitamin B12 (B12) by a variety of tissues, but the lack of an intrinsic label on the protein moiety of the TCII-B12 complex has made it impossible to determine the role and fate of TCII during this process. We have labeled homogensous rabbit and human TCII with 125I-labeled N-succinimidyl-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate and have performed in vivo experiments in rabbits. When 125I-labeled rabbit TCII-[57Co] B12 and 131I-labeled bovine albumin were simultaneously injected intravenously, we observed that 125Iand 57Co were cleared from plasma at a faster rate (t1/2 = 1 1/2 h) than 131I and that 125I and 57Co were present in excess of 131I in the kidney, liver, spleen, heart, lung, and small intestine 1/2 h after injection. Later, 57Co remained in excess of 131I, but the ratio of 125I to 131I decreased progressively in all of these plasma and were rapidly excreted in the urine. After 1 h following injection, 57Co was present in excess of 125I in the plasma...
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AASA R., MALMSTROEM B. G., SALTMAN P. THE SPECIFIC BINDING OF IRON(III) AND COPPER(II) TO TRANSFERRIN AND CONALBUMIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 24;75:203–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90599-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AWAI M., BROWN E. B. Studies of the metabolism of I-131-labeled human transferrin. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Mar;61:363–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Majerus P. W. Isolation of vitamin B12-binding proteins using affinity chromatography. 3. Purification and properties of human plasma transcobalamin II. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7709–7717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Majerus P. W. Isolation of vitamin B12-binding proteins using affinity chromatography. I. Preparation and properties of vitamin B12-sepharose. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7695–7701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Majerus P. W. Isolation of vitamin B12-binding proteins using affinity chromatography. II. Purification and properties of a human granulocyte vitamine B12-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7702–7708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Mehlman C. S. Isolation of gastric vitamin B 12 -binding proteins using affinity chromatography. I. Purification and properties of human intrinsic factor. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3660–3669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell G., Morell A. G. The role of surface carbohydrates in the hepatic recognition and transport of circulating glycoproteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):99–128. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson R. E., Rappazzo M. E., Hall C. A. Late transport of vitamin B 12 by transcobalamin II. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Oct;80(4):488–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. L., Allen R. H. Characterization of vitamin B12-binding proteins isolated from human milk and saliva by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7220–7227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. L., Mehlman C. S., Allen R. H. Human plasma R-type vitamin B12-binding proteins. I. Isolation and characterization of transcobalamin I. TRANSCOBALAMIN III. and the normal granulocyte vitamin B12-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7700–7706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. L., Schneider R. J., Mehlman C. S., Allen R. H. Human plasma R-type vitamin B12-binding proteins. II. The role of transcobalamin I, transcobalamin III, and the normal granulocyte vitamin B12-binding protein in the plasma transport of vitamin B12. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7707–7713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. L., Waxman S., Gilbert H. S., Mehlman C. S., Allen R. H. Isolation and characterization of a novel vitamin B12-binding protein associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1262–1270. doi: 10.1172/JCI108202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A., PARANCHYCH W. Selective uptake of specifically bound cobalt-58 vitamin B12 by human and mouse tumour cells. Nature. 1961 Jul 22;191:393–395. doi: 10.1038/191393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmel R., Herbert V. Deficiency of vitamin B12-binding alpha globulin in two brothers. Blood. 1969 Jan;33(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkler A. E., Hall C. A. Nature of the relationship between vitamin B12 binding and cell uptake. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Apr;120(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90600-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gräsbeck R. Intrinsic factor and the other vitamin B12 transport proteins. Prog Hematol. 1969;6:233–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL C. A., FINKLER A. E. THE DYNAMICS OF TRANSCOBALAMIN II. A VITAMIN B12 BINDING SUBSTANCE IN PLASMA. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Mar;65:459–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakami N., Neiman P. E., Canellos G. P., Lazerson J. Neonatal megaloblastic anemia due to inherited transcobalamin II deficiency in two siblings. N Engl J Med. 1971 Nov 18;285(21):1163–1170. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197111182852103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hippe E., Olesen H. Nature of vitamin B 12 binding. 3. Thermodynamics of binding to human intrinsic factor and transcobalamins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 25;243(1):83–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom B. L., Olesen H. A. Plasma clearance of 57cobalt-labelled vitamin B12 bound in vitro and in vivo to transcobalamin I and II. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1969 May;23(3):201–211. doi: 10.3109/00365516909077650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletsch Q. A., Coffey J. W. Properties of the proteins that bind vitamin B 12 in subcellular fractions of rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jul;151(1):157–167. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90484-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retief F. P., Gottlieb C. W., Herbert V. Mechanism of vitamin B12 uptake by erythocytes. J Clin Invest. 1966 Dec;45(12):1907–1915. doi: 10.1172/JCI105495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryel E. M., Meyer L. M., Gams R. A. Uptake and subcellular distribution of vitamin B12 in mouse L1210 leukemic lymphoblasts. Blood. 1974 Sep;44(3):427–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. M., Bloomfield F. J., Stebbins R., Herbert V. Studies on derivation of transcobalamin 3 from granulocytes. Enhancement by lithium and elimination by fluoride of in vitro increments in vitamin B12-binding capacity. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):228–239. doi: 10.1172/JCI107543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenman U. H. Amniotic fluid vitamin B12-binding protein. Purification and characterization with isoelectric focusing and other techniques. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 14;342(1):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


