Abstract
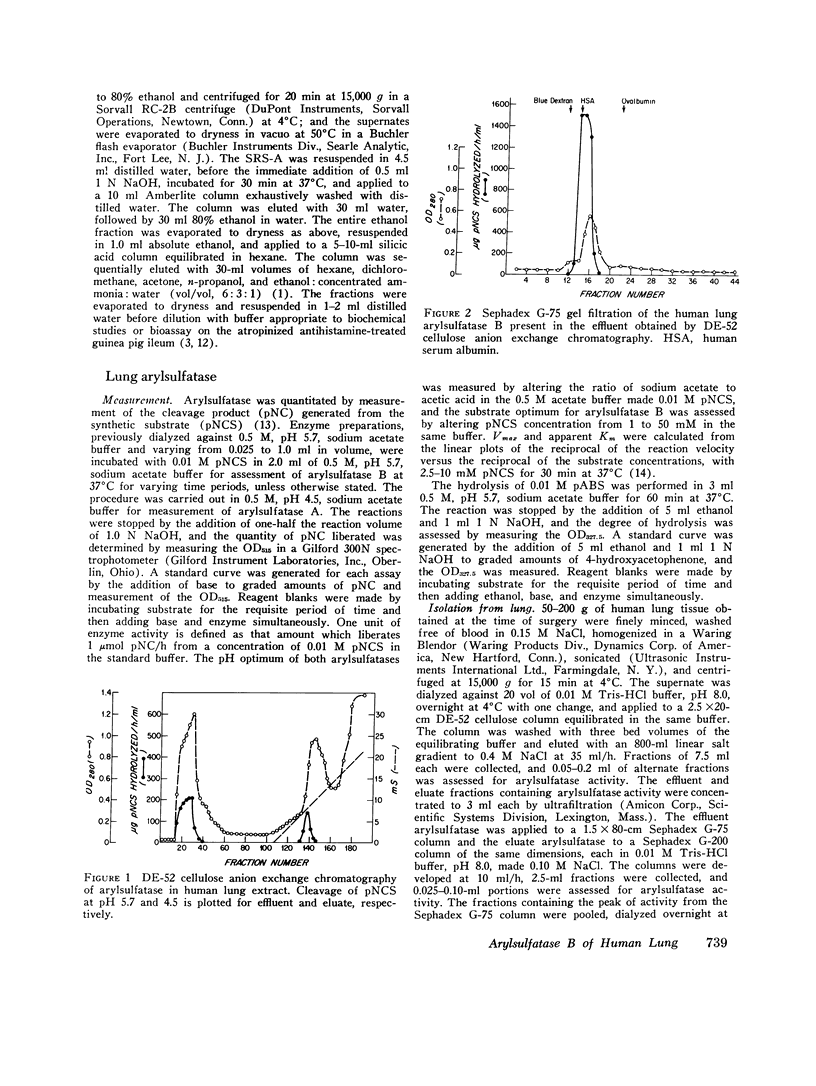
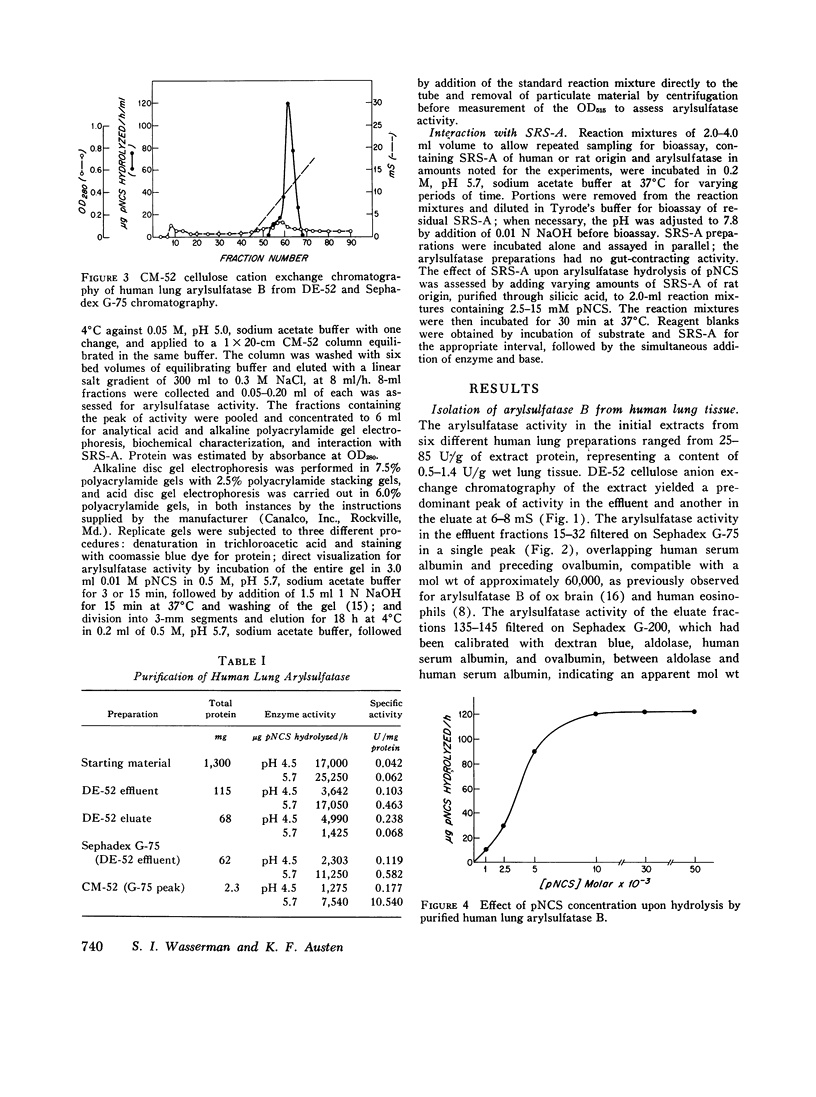
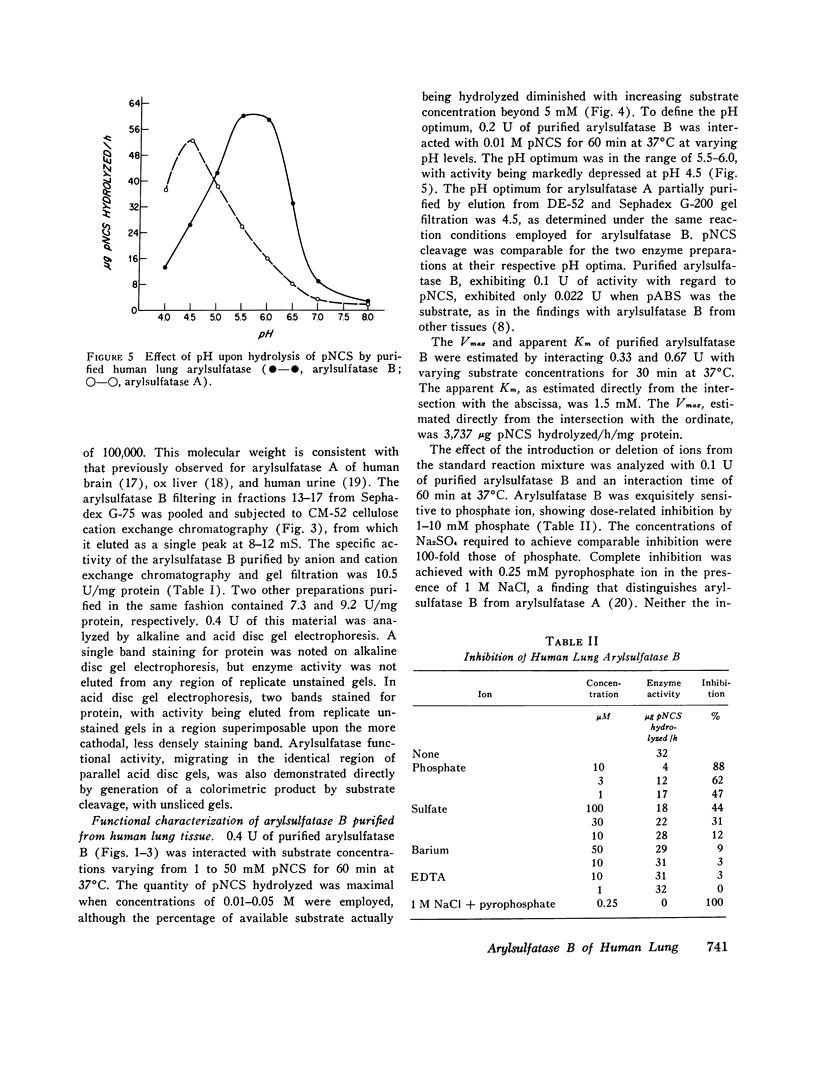
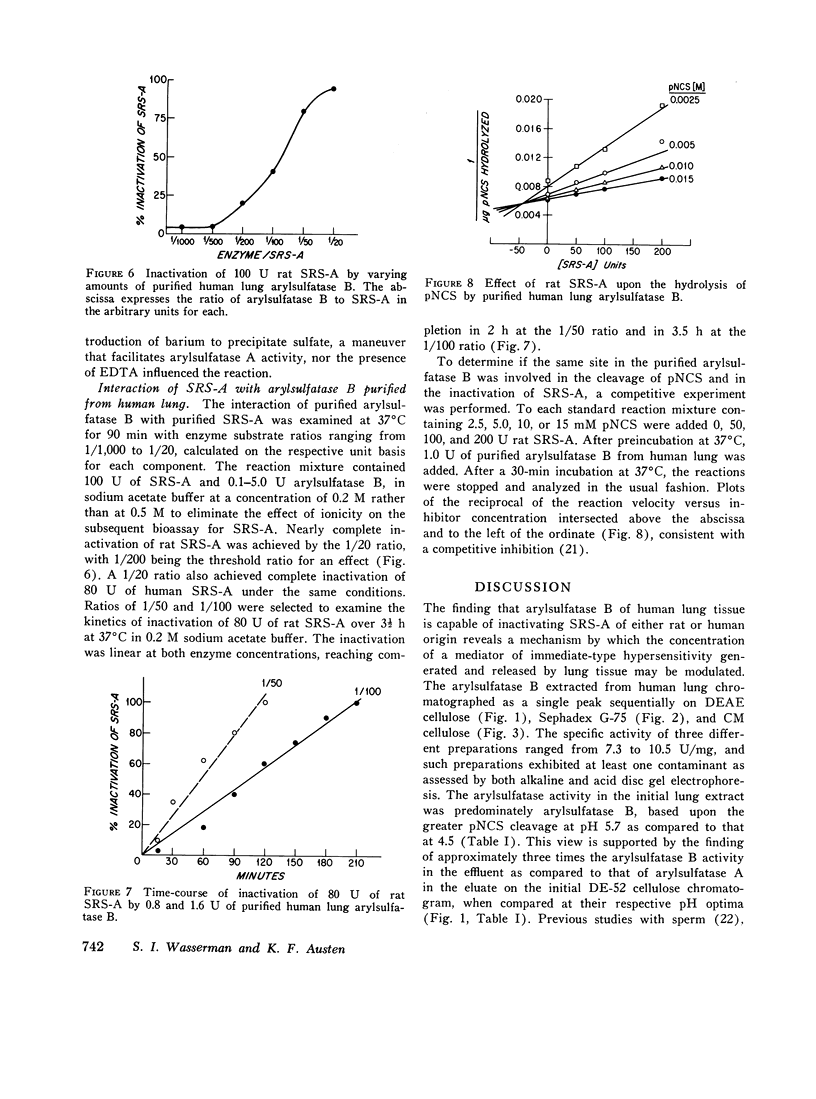
Arylsulfatase B was separated from arylsulfatase A in extracts of human lung tissue by anion exchange chromatography and further purified by gel filtration and cation exchange chromatography. Arylsulfatase B of human lung was similar to that enzyme in other tissues and species, exhibiting an apparent mol wt of approximately 60,000, a pH optimum for cleavage of 4-nitrocatechol sulfate (pNCS) of 5.5-6.0, and a sensitivity to inhibition by phosphate ions and especially pyrophosphate in the presence of NaCl. Human lung arylsulfatase B inactivated slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxix (SRS-A) in a linear time-dependent reaction in which the rate was determined by the enzyme-to-substrate ratio. Cleavage of pNCS by human lung arylsulfatase B was competitively suppressed by SRS-A. The finding that human lung tissue contains predominately arylsulfatase B discloses a potential regulatory mechanism for inactivation of SRS-A at or near the site of its generation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAUM H., DODGSON K. S., SPENCER B. The assay of arylsulphatases A and B in human urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1959 May;4(3):453–455. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(59)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKLEHURST W. E. The release of histamine and formation of a slow-reacting substance (SRS-A) during anaphylactic shock. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151:416–435. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleszynski W. S., Roy A. B. Some properties of the sulphatase B of ox brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 12;317(1):164–171. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90209-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., SPENCER B., WYNN C. H. Studies on sulphatases. 12. The arylsulphatases of human tissues. Biochem J. 1956 Mar;62(3):500–507. doi: 10.1042/bj0620500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiAugustine R. P. Lung concentric laminar organelle. Hydrolase activity and compositional analysis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):584–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Purification and synthesis of eosinophilotactic tetrapeptides of human lung tissue: identification as eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant J. A., Lichtenstein L. M. Release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis from human leukocytes. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):897–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harinath B. C., Robins E. Arylsulphatases in human brain: separation, purification, and certain properties of the two soluble arylsulphatases. J Neurochem. 1971 Feb;18(2):245–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaliner M., Wasserman S. I., Austen K. F. Immunologic release of chemical mediators from human nasal polyps. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 9;289(6):277–281. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197308092890601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Austen K. F. The IgE-mediated release of an eosinophil leukocyte chemotactic factor from human lung. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):899–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Wasserman S. I., Goetzi E. J., Austen K. F. Formation of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis in human lung tissue and cells before release. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1133–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichol L. W., Roy A. B. The sulfatase of ox liver. X. Some observations on the intermolecular bonding in sulfatase A. Biochemistry. 1966 Apr;5(4):1379–1388. doi: 10.1021/bi00868a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Austen W. G., Austen K. F. Immunological release of histamine and slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis from human lung. I. Modulation by agents influencing cellular levels of cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):136s–148s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Murphy R. C., Austen K. F. Inactivation of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxins (SRS-A) by arylsulfatases. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):316–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Murphy R. C., Karnovsky M. L., Austen K. F. The physicochemical characteristics and purification of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):760–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Valentine M. D., Austen K. F. Antigen-induced release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A rat) in rats prepared with homologous antibody. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):767–782. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. J., Fitzgerald J. W., Dodgson K. S. Methods for visualization of enzymes in polyacrylamide gels. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):154–158. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.154-158.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROY A. B. The sulphatase of ox liver. I. The complex nature of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):12–15. doi: 10.1042/bj0530012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. B. The type II arylsulphatases of the red kangaroo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 13;227(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F., Bloch K. J. Antibodies involved in antigen-induced release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) in the guinea pig and rat. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):127–147. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Fluharty A. L., Skokut M. H., Kihara H. Purification and properties of arylsulfatase. A from human urine. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2495–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORTMAN B. Arylsulfatase activity in beef and rabbit corneal extracts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Apr;97:70–74. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I., Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Inactivation of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis by human eosinophil arylsulfatase. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):645–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I., Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Preformed eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (ECF-A). J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):351–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. H., Srivastava P. N., Williams W. L. Purification and properties of aryl sulfatases from rabbit sperm acrosomes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Feb;145(2):721–725. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-37882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


