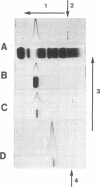
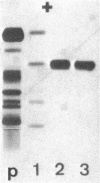
Abstract
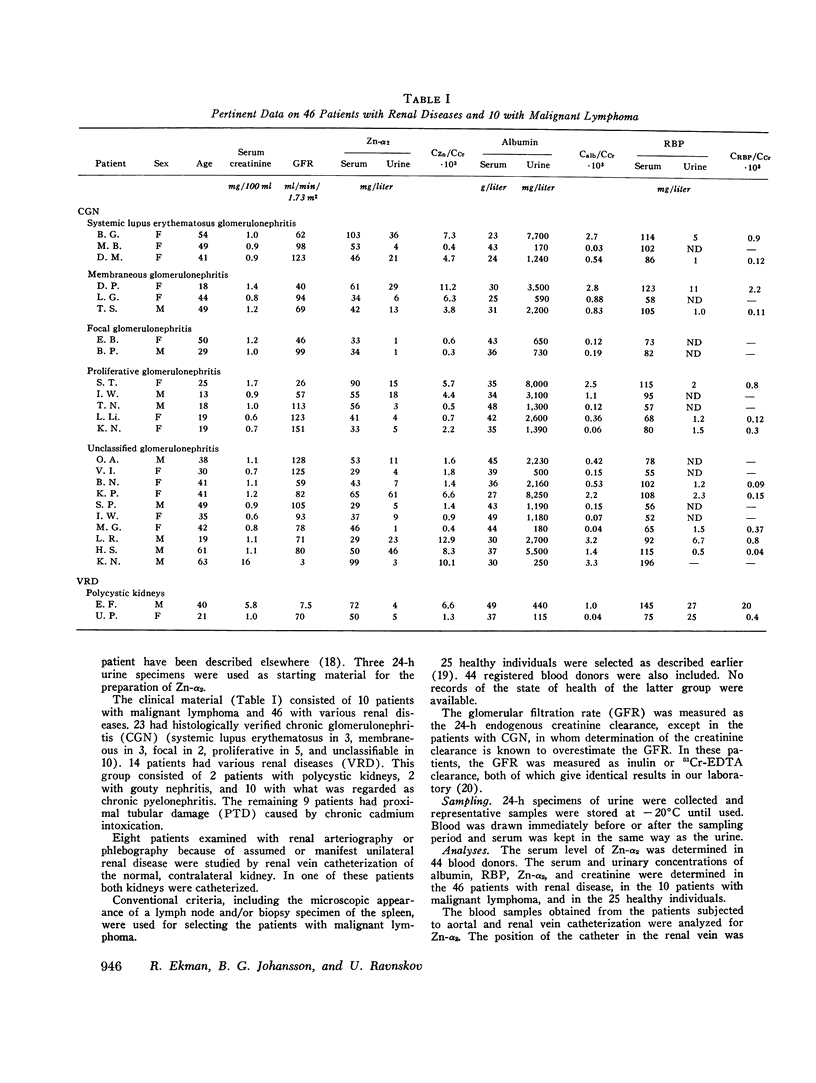
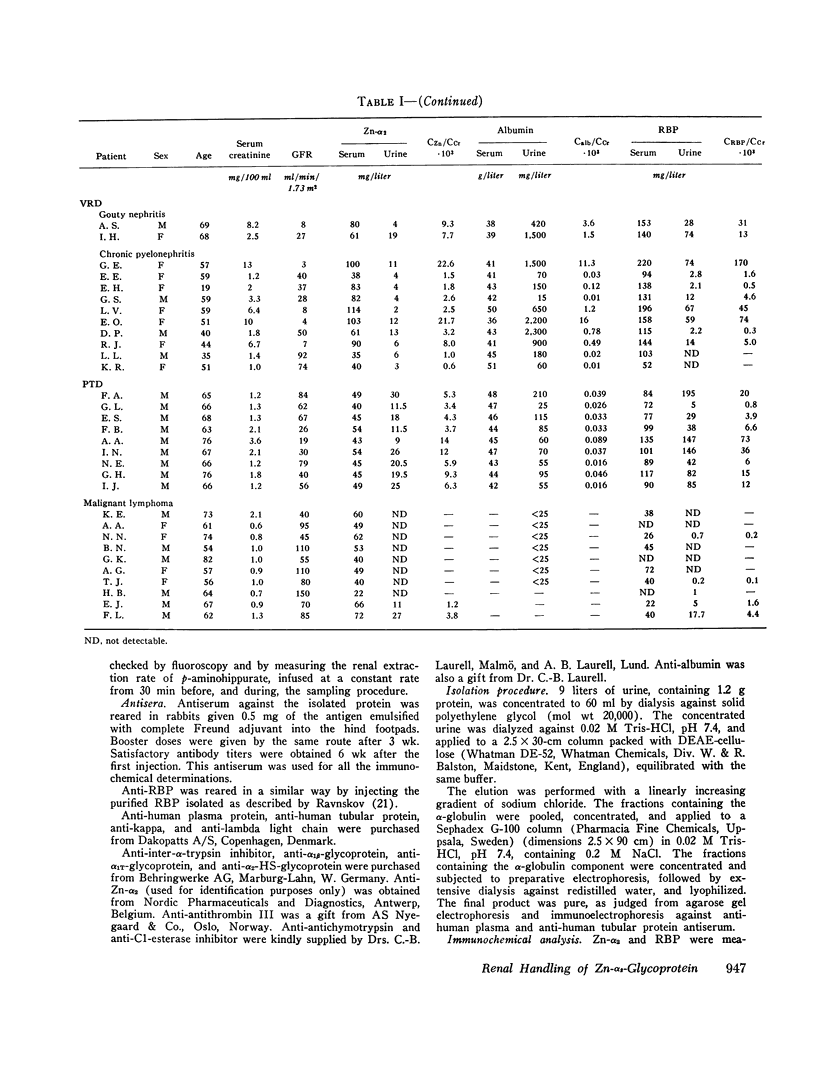
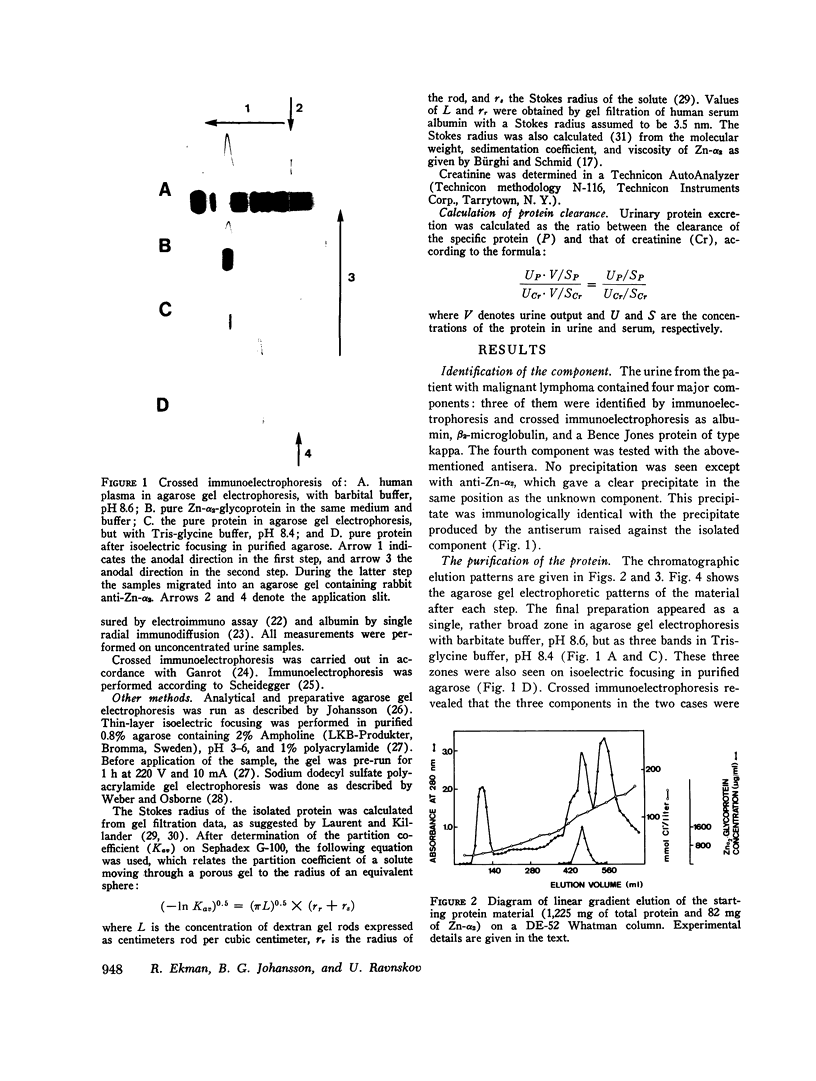
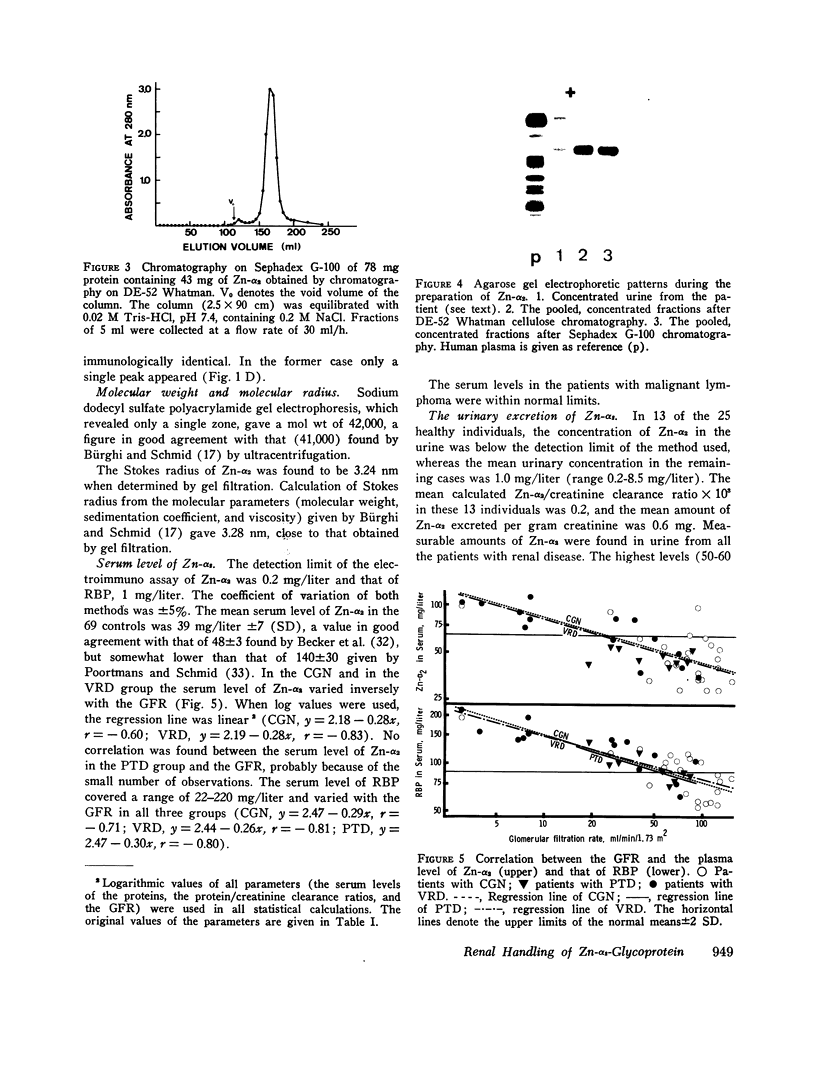
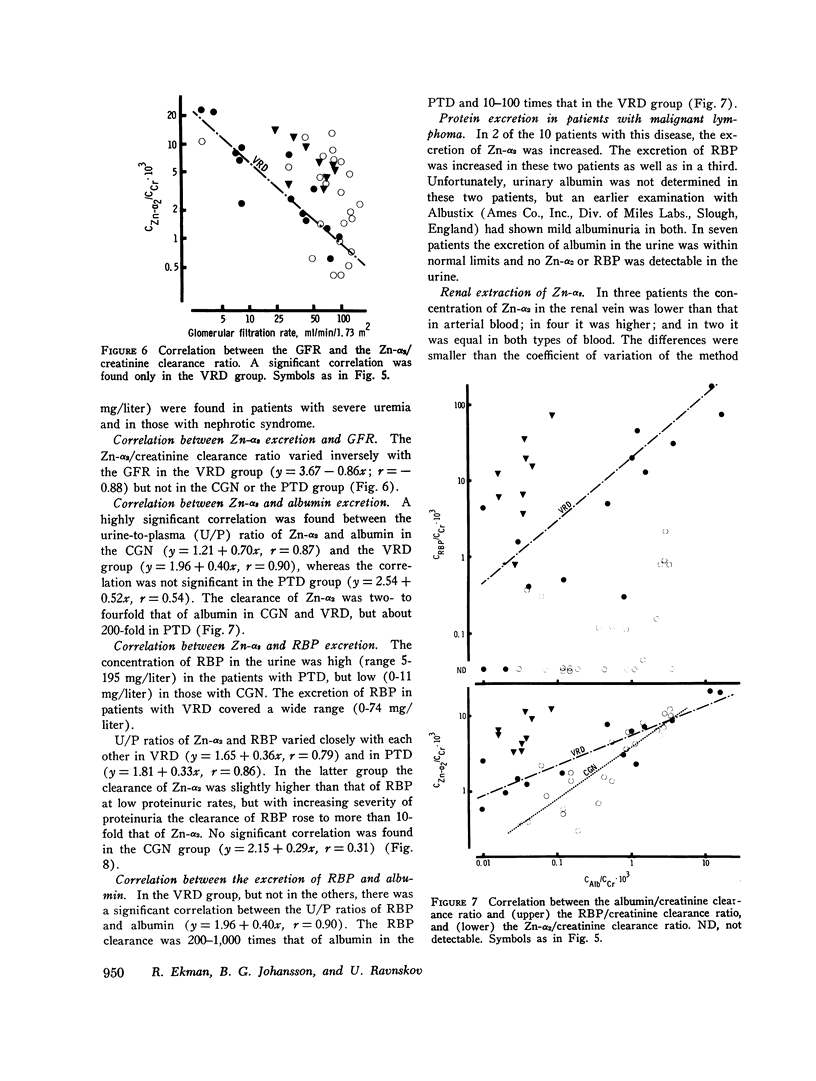
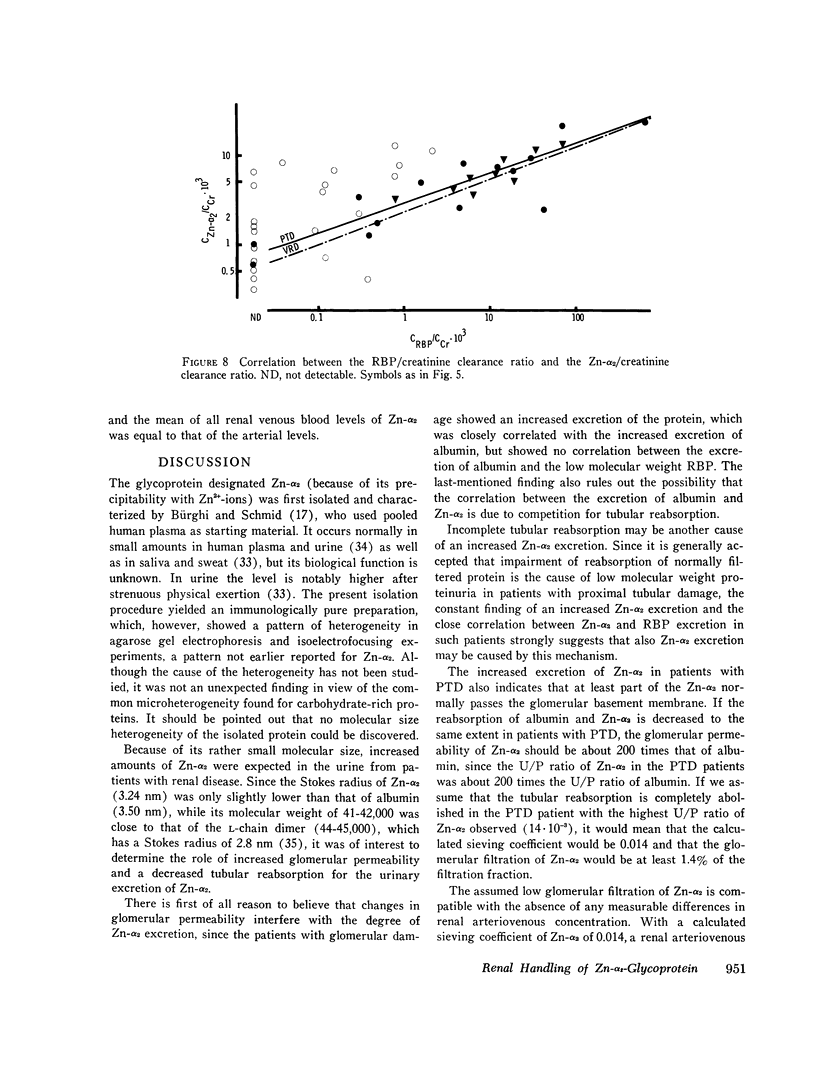
An unusual electrophoretic pattern of the urine from a patient with malignant lymphoma was observed. One of the major proteins, identified Zn-alpha2-glycoprotein (Zn-alpha2), was isolated from the urine and partly characterized. The Stokes radius was found to be 3.24 nm and the molecular weight, determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide electrophoresis, 42,000. The plasma level in healthy individuals was 39 +/- 7 (SD) mg/liter. In 12 of 25 healthy individuals, Zn-alpha2 was measurable in the urine and was found to be 1.0 +/- 1.1 mg/liter. In 23 patients with chronic glomerulonephritis (CGN), in 9 with proximal tubular dysfunction (PTD), in 23 with various renal diseases (VRD), and in 10 with malignant lymphoma, the plasma level and the urinary excretion were compared with those of albumin (mol wt 67,000) and of the retinol-binding protein (RBP, mol wt 21,000). A close correlation was found between the urine-to-plasma (U/P) ratios of Zn-alpha2 and albumin in the patients with CGN, whereas in the PTD patients the U/P ratios of Zn-alpha2 and RBP were correlated. No significant renal arteriovenous difference in Zn-alpha2 could be demonstrated. The Zn-alpha2 excretion was increased also in two patients with malignant lymphoma and proteinuria of a tubular pattern. The plasma Zn-alpha2 varied inversely with the glomerular filtration rate in the patients with renal disease, but was normal in those with malignant lymphoma. The results are consistent with the assumption of a sieving coefficient of Zn-alpha2, substantially exceeding that of albumin, but notably lower than that of smaller low-molecular-weight proteins. An increased excretion of Zn-alpha2 may be due to increased glomerular permeability as well as to defective proximal tubular reabsorption.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURGI W., SCHMID K. Preparation and properties of Zn-alpha 2-glycoprotein of normal human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1961 Apr;236:1066–1074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER E. A., FLYNN F. V. The proteinuria of renal tubular disorders. Lancet. 1958 Nov 8;2(7054):978–980. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker W., Schwick H. G., Störiko K. Immunologic determination of proteins found in low concentrations in human serum. Clin Chem. 1969 Aug;15(8):649–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggård I., Bearn A. G. Isolation and properties of a low molecular weight beta-2-globulin occurring in human biological fluids. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 10;243(15):4095–4103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggård I., Peterson P. A. Polymeric forms of free normal kappa and lambda chains of human immunoglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4299–4307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier G. M., Cohen R. J., Conrad M. E. Microglobulinaemia in renal failure. Nature. 1968 May 11;218(5141):598–599. doi: 10.1038/218598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier G. M., Conrad M. E. Catabolsm of human beta-2-microglobulin by the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1969 Nov;217(5):1359–1362. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.5.1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHINARD F. P., LAUSON H. D., EDER H. A., GREIF R. L., HILLER A. A study on the mechanism of proteinuria in patients with the nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1954 Apr;33(4):621–628. doi: 10.1172/JCI102933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEVE H., BEARN A. G. THE EXCRETION OF FIVE PLASMA PROTEINS PREVIOUSLY UNIDENTIFIED IN NORMAL HUMAN URINE. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Jul;10:1–11. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREETH J. M., KEKWICK R. A., FLYNN F. V., HARRIS H., ROBSON E. B. An ultracentrifuge study of urine proteins with particular reference to the proteinuria of renal tubular disorders. Clin Chim Acta. 1963 May;8:406–414. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(63)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain M. J., Stimmler L. The renal handling of insulin. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jun;46(6):911–919. doi: 10.1172/JCI105597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clendinnen B. G., Davidson W. D., Reeder D. D., Jackson B. M., Thompson J. C. Renal uptake and excretion of gastrin in the dog. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1971 Jun;132(6):1039–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIBERG L. Health hazards in the manufacture of alkaline accumulators with special reference to chronic cadmium poisoning; a clinical and experimental study. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1950;240:1–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann T., Håkansson C. H., Levan A., Möller T. Multiple chromosome aberrations in a lymphosarcomatous tumor. Hereditas. 1972;70(2):243–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1972.tb01383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGOIRE F., MALMENDIER C., LAMBERT P. P. The mechanism of proteinuria, and a study of the effects of hormonal therapy in the nephrotic syndrome. Am J Med. 1958 Oct;25(4):516–531. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:39–47. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDWICKE J., SQUIRE J. R. The relationship between plasma albumin concentration and protein excretion in patients with proteinuria. Clin Sci. 1955 Aug;14(3):509–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagstam K. E., Nordenfelt I., Svensson L., Svensson S. E. Comparison of different methods for determination of glomerular filtration rate in renal disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1974 Sep;34(1):31–36. doi: 10.3109/00365517409061818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. F., Barnes A. D. The urinary excretion of lysozyme in dogs. Clin Sci. 1970 Apr;38(4):533–547. doi: 10.1042/cs0380533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. G. Agarose gel electrophoresis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:7–19. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. G., Hjertén S. Electrophoresis, crossed immunoelectrophoresis, and isoelectric focusing in agarose gels with reduced electroendosmotic flow. Anal Biochem. 1974 May;59(1):200–213. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. G., Ravnskov U. The serum level and urinary excretion of 2 -microglobulin, 2 -microglobulin and lysozyme in renal disease. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1972;6(3):249–256. doi: 10.3109/00365597209132096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ J., ROSENFELD S., SELLERS A. L. Role of the kidney in plasma albumin catabolism. Am J Physiol. 1960 Apr;198:814–818. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.4.814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai M., Raz A., Goodman D. S. Retinol-binding protein: the transport protein for vitamin A in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2025–2044. doi: 10.1172/JCI105889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogielnicki R. P., Waldmann T. A., Strober W. Renal handling of low molecular weight proteins. I. L-Chain metabolism in experimental renal disease. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):901–909. doi: 10.1172/JCI106562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCKOP D. J., DAVIDSON W. D. A STUDY OF URINARY AND SERUM LYSOZYME IN PATIENTS WITH RENAL DISEASE. N Engl J Med. 1964 Feb 6;270:269–274. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196402062700602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Berggård I. Isolation and properties of a human retinol-transporting protein. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):25–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Evrin P. E., Berggård I. Differentiation of glomerular, tubular, and normal proteinuria: determinations of urinary excretion of beta-2-macroglobulin, albumin, and total protein. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1189–1198. doi: 10.1172/JCI106083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poortmans J. R., Schmid K. The level of Zn-alpha 2-glycoprotein in normal human body fluids and kidney extract. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 May;71(5):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabkin R., Simon N. M., Steiner S., Colwell J. A. Effect of renal disease on renal uptake and excretion of insulin in man. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jan 22;282(4):182–187. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197001222820402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravnskov U., Johansson B. G., Göthlin J. Renal extraction of 2 -microglobulin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972 Sep;30(1):71–75. doi: 10.3109/00365517209081093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A., WALDMANN T. A., FAHEY J. L., MCFARLANE A. S. METABOLISM OF BENCE JONES PROTEINS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jan;43:103–117. doi: 10.1172/JCI104884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Strober W., Mogielnicki R. P. The renal handling of low molecular weight proteins. II. Disorders of serum protein catabolism in patients with tubular proteinuria, the nephrotic syndrome, or uremia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2162–2174. doi: 10.1172/JCI107023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wochner R. D., Strober W., Waldmann T. A. The role of the kidney in the catabolism of Bence Jones proteins and immunoglobulin fragments. J Exp Med. 1967 Aug 1;126(2):207–221. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaharko D. S., Beck L. V., Blankenbaker R. Role of the kidney in the disposal of radioiodinated and nonradioiodinated insulin in dogs. Diabetes. 1966 Sep;15(9):680–685. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.9.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]