Abstract
The distribution, blood transport, and metabolic clearance of physiological concentrations of antidiuretic hormone were studied in 10 hydrated normal subjects with radioiodinated arginine vasopressin (125I-AVP). At 37 degrees C no binding of 125I-AVP to plasma proteins could be demonstrated, but some metabolites were associated with plasma proteins. 125I-AVP was rapidly distributed into a space approximating the extracellular fluid volume. Metabolic breakdown products became demonstrable within minutes after injection. The mean metabolic clearance rate of 125I-AVP was 4.1 ml/min/kg and the mean plasma half-life 24.1 min. Renal clearance had a mean value of 80 ml/min and accounted for 27% of the total metabolic clearance. It is concluded that in man antidiuretic hormone circulates as a free (non-protein bound) peptide, diffuses readily into the extracellular fluid space, and is metabolized within minutes. A plasma half-life of 24 min is consistent with the duration of antidiuresis after hormone administration or release.
Full text
PDF
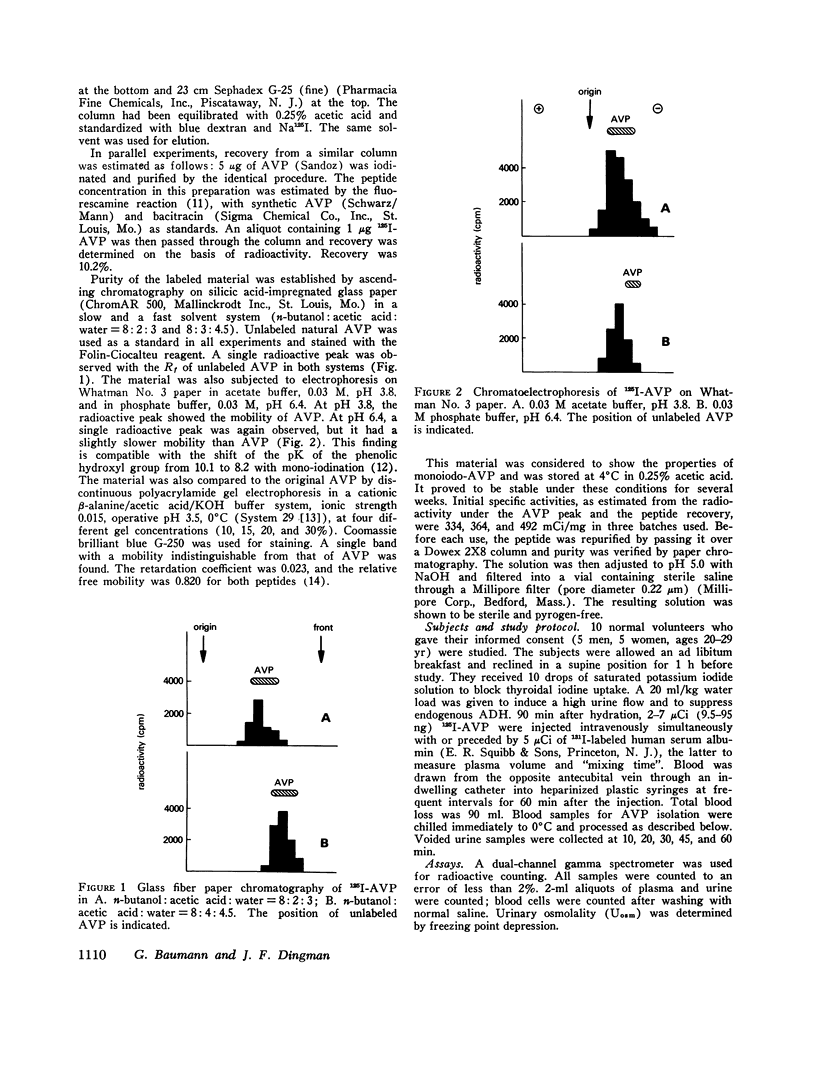
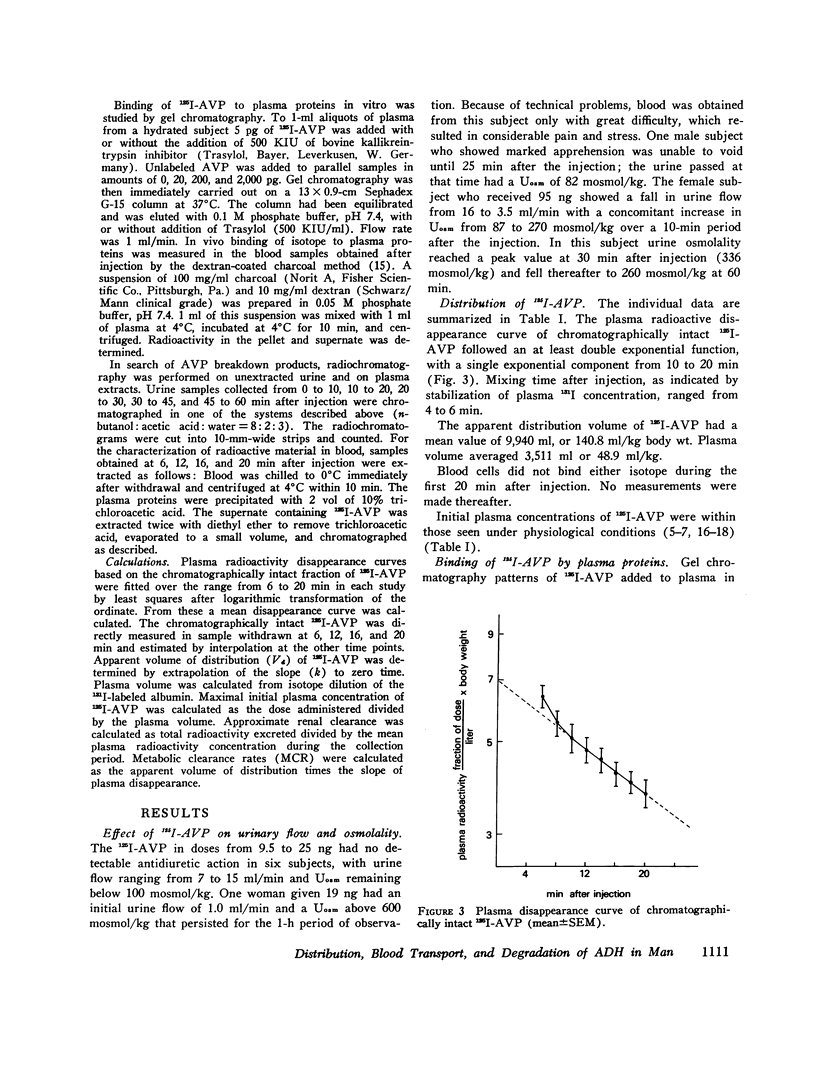
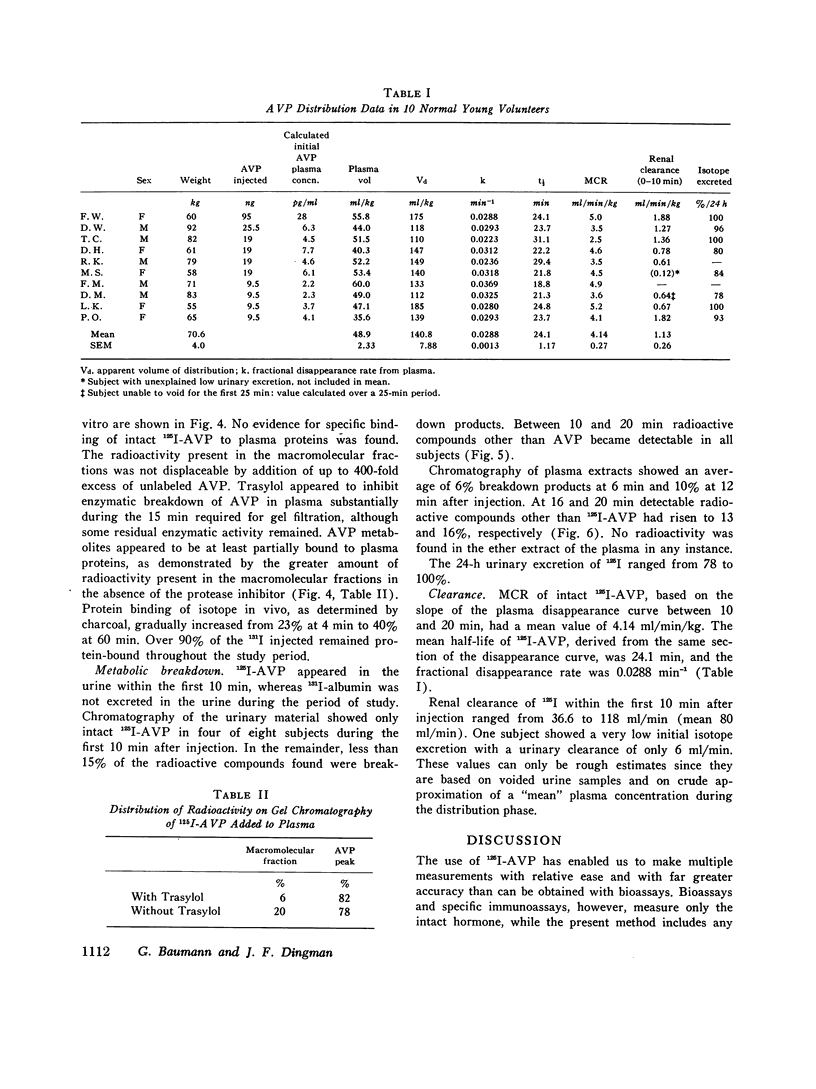
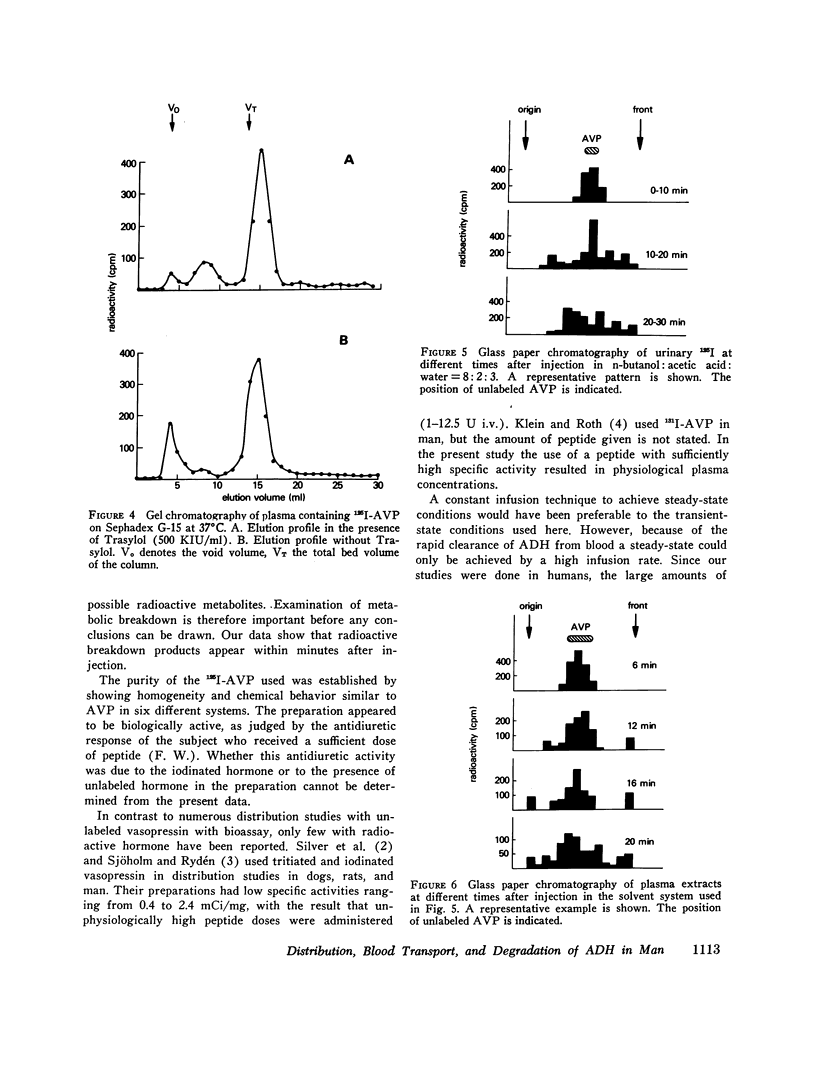



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed A. B., George B. C., Gonzalez-Auvert C., Dingman J. F. Increased plasma arginine vasopressin in clinical adrenocortical insufficeincy and its inhibition by glucosteroids. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):111–123. doi: 10.1172/JCI105504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beardwell C. G. Radioimmunoassay of arginine vasopressin in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Aug;33(2):254–260. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-2-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CZACZKES J. W., KLEEMAN C. R., KOENIG M. PHYSIOLOGIC STUDIES OF ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE BY ITS DIRECT MEASUREMENT IN HUMAN PLASMA. J Clin Invest. 1964 Aug;43:1625–1640. doi: 10.1172/JCI105038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron D. P., Burger H. G., Catt K. J., Doig A. Metabolic clearance rate of radioiodinated human growth hormone in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Sep;48(9):1600–1608. doi: 10.1172/JCI106125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Rodbard D. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Science. 1971 Apr 30;172(3982):440–451. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3982.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong C. T., Silver L., Christman D. R., Schwartz I. L. ON THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF THE ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE (VASOPRESSIN). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Oct;46(10):1273–1277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.10.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG M. The clearance of vasopressin from the splanchnic vascular area and the kidneys. J Endocrinol. 1957 Dec;16(2):217–226. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0160217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey N., Jones J. J., Lee J. The renal clearance and plasma binding of vasopressin in the dog. J Endocrinol. 1967 Jun;38(2):163–171. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0380163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain M. K., Fernando N., Shapiro M., Kagan A., Glick S. M. Radioimmunoassay of arginine vasopressin in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Oct;37(4):616–625. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-4-616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Frandsen P., Nielsen A. T. Comparative experiments on the urinary excretion of exogenous oxytocin and vasopressin. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1973 Aug;73(4):643–650. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0730643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauson H. D. Metabolism of antidiuretic hormones. Am J Med. 1967 May;42(5):713–744. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L., Fisch L., Kleeman C. R. Relative potency of arginine-8-vasopressin and lysine-8-vasopressin in humans. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Feb;69(2):270–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOBLE R. L., TAYLOR N. B. Antidiuretic substances in human urine after haemorrhage, fainting, dehydration and acceleration. J Physiol. 1953 Nov 28;122(2):220–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson G. L., Klein L. A., Roth J., Gorden P. Immunoassay of plasma vasopressin in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1298–1305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson G. L., Mahr E. A., Athar S., Sinha T. Development and clinical application of a new method for the radioimmunoassay of arginine vasopressin in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2340–2352. doi: 10.1172/JCI107423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHALLY A. V., LIPSCOMB H. S., GUILLEMIN R. Chromatographic separation of oxytocin and vasopressin on carboxymethylcellulose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jan;31(1):252–254. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90465-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHROEDER R., ROTT D. [On the determination and behavior of ADH in human plasma]. Klin Wochenschr. 1959 Nov 15;37:1175–1181. doi: 10.1007/BF01491358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVER L., SCHWARTZ I. L., FONG C. T., DEBONS A. F., DAHL L. K. Disappearance of plasma radioactivity after injection of H3- or I-131-labeled arginine vasopressin. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Nov;16:1097–1099. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.6.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowsky W. R., Rosenbloom A. A., Fisher D. A. Radioimmunoassay measurement of arginine vasopressin in serum: development and application. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Feb;38(2):278–287. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-2-278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORN N. A., SMITH W. M. RENAL EXCRETION OF SYNTHETIC ARGININE-VASOPRESSIN INJECTED INTO DOGS. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1965 Jul;49:388–392. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0490388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORN N. A., WILLUMSEN N. B. INACTIVATION OF ARGININE- AND LYSINE-VASOPRESSIN BY SLICES FROM DIFFERENT ZONES OF THE RAT KIDNEY AND BY RAT LIVER SLICES. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1963 Dec;44:545–562. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0440545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. E., Freychet P., Roth J. Monoido-oxytocin: demonstration of its biological activity and specific binding to isolated fat cells. Endocrinology. 1972 Nov;91(5):1199–1205. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-5-1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter R., Bowman R. H. Mechanism of inactivation of vasopressin and oxytocin by the isolated perfused rat kidney. Endocrinology. 1973 Jan;92(1):189–193. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-1-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter R., Shlank H. Differences in the enzymatic inactivation of arginine vasopressin and oxytocin by rat kidney homogenate. Endocrinology. 1975 Mar;96(3):811–814. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-3-811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIDA S., MOTOHASHI K., IBAYASHI H., OKINAKA S. METHOD FOR THE ASSAY OF ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE IN PLASMA WITH A NOTE ON THE ANTIDIURETIC TITER OF HUMAN PLASMA. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Aug;62:279–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


