Abstract
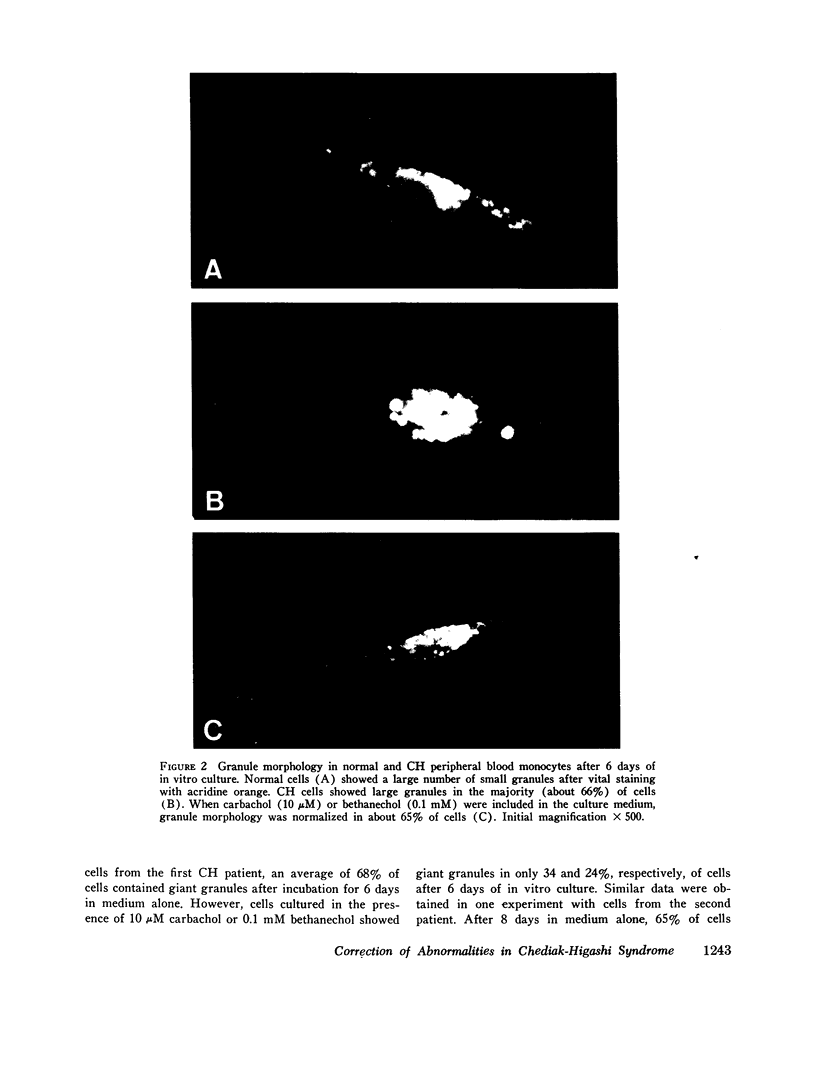
Chediak-Higashi (CH) syndrome is a genetic disorder of children and certain animal species including the beige mouse. We have previously described a membrane abnormality in CH mouse polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMH). Whereas normal mouse PMN do not form surface caps with concanavalin A except after treatment with agents such as colchicine that inhibit microtubule assembly, CH mouse PMN show spontaneous cap formation. This capping is inhibited by 3',5 cyclic guanosine monophosphate and by the cholinergic agonists carbamylcholine and carbamyl beta-methylcholine that increase 3',5' cyclic guanosine monophosphate generation. These data suggested that microtubule function may be impaired in CH syndrome perhaps secondary to an abnormality in 3',5' cyclic guanosine monophosphate generation. The cholinergic agonists were also shown to prevent development of the giant granules that are pathognomonic of CH syndrome in embryonic fibroblasts isolated from CH mice and cultured in vitro. In this report it is shown that an extreme degree of spontaneous concanavalin A cap formation is also characteristic of peripheral blood PMN from two patients with CH syndrome. This indicates an abnormality of microtubule function in CH syndrome in man. 3',5' cyclic guanosine monophasphate, carbamylcholine, and carbamyl beta-methylcholine reduce spontaneous capping in CH cells. In addition, it is shown that monocytes isolated from the patients' blood and incubated in tissue culture generate a large complement of abnormal granules. When the same cells mature in vitro in the presence of carbamylcholine or carbamyl beta-methylcholine, the proportion of cells containing morphologically normal granules is significantly increased. These responses can be reproduced in vivo in the beige (CH) mouse. Animals treated for 3 wk and longer with carbamylcholine or carbamyl beta-methylcholline show normal granule morphology and a normal degree of concanavalin A cap formation in peripheral blood PMN leukocytes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod F. B., Nachtigal R., Dancis J. Familial dysautonomia: diagnosis, pathogenesis and management. Adv Pediatr. 1974;21:75–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandmann U., Rydgren L., Norberg B. The difference between random movement and chemotaxis. Effects of antitubulins on neutrophil granulocyte locomotion. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Sep;88(1):63–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90618-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. E., Cohn Z. A. The isolation and selected properties of blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):145–160. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume R. S., Bennett J. M., Yankee R. A., Wolff S. M. Defective granulocyte regulation in the Chediak-Higashi syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1968 Nov 7;279(19):1009–1015. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196811072791901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume R. S., Glade P. R., Chessin L. N. Euchrysine, a supravital fluorescent lysosomal stain: technic and application for hematologic investigation. Blood. 1969 Jan;33(1):87–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume R. S., Wolff S. M. The Chediak-Higashi syndrome: studies in four patients and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1972 Jul;51(4):247–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyum A. Separation of blood leucocytes, granulocytes and lymphocytes. Tissue Antigens. 1974;4(4):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEDIAK M. M. Nouvelle anomalie leucocytaire de caractère constitutionnel et familial. Rev Hematol. 1952;7(3):362–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Kimball H. R. Defective granulocyte chemotaxis in the Chediak-Higashi syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2645–2652. doi: 10.1172/JCI106765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. C., Douglas S. D. Defective granule formation and function in the Chediak-Higashi syndrome in man and animals. Semin Hematol. 1972 Oct;9(4):431–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. C., Spicer S. S., Greene W. B., Padgett G. A. Ultrastructure of bone marrow granulocytes in normal mink and mink with the homolog of the Chediak-Higashi trait of humans. I. Origin of the abnormal granules present in the neutrophils of mink with the C-HS trait. Lab Invest. 1971 Apr;24(4):303–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Yahara I., Wang J. L. Receptor mobility and receptor-cytoplasmic interactions in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1442–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Bujak J. S., Patten E., Wolff S. M. Granulocyte function in the Chediak-Higashi syndrome of mice. Blood. 1974 Feb;43(2):201–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRITZLER R. A., TERNER J. Y., LINDENBAUM J., MAGIDSON J., WILLIAMS R., PRESIG R., PHILLIPS G. B. CHEDIAK-HIGASHI SYNDROME. CYTOLOGIC AND SERUM LIPID OBSERVATIONS IN A CASE AND FAMILY. Am J Med. 1964 Apr;36:583–594. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball H. R., Ford G. H., Wolff S. M. Lysosomal enzymes in normal and Chediak-Higashi blood leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Oct;86(4):616–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEADER R. W., PADGETT G. A., GORHAM J. R. STUDIES OF ABNORMAL LEUKOCYTE BODIES IN THE MINK. Blood. 1963 Oct;22:477–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutzner M. A., Lowrie C. T., Jordan H. W. Giant granules in leukocytes of the beige mouse. J Hered. 1967 Nov-Dec;58(6):299–300. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a107620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Rosenthal A. S., Balestra D. J. Abnormal bactericidal, metabolic, and lysosomal functions of Chediak-Higashi Syndrome leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):649–665. doi: 10.1172/JCI106854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblith J. Z., Ukena T. E., Yin H. H., Berlin R. D., Karnovsky M. J. A comparative evaluation of the distribution of concanavalin A-binding sites on the surfaces of normal, virally-transformed, and protease-treated fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1625–1629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenszajn L. A., Radnay J. The lysosomal nature of the anomalous granules and chromosome aberrations in cultures of peripheral blood in Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jun;18(6):683–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Root R. K., Vaughan M. Phagocytosis in chronic granulomatous disease and the Chediak-Higashi syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jan 20;286(3):120–123. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197201202860302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Goldstein I., Hoffstein S., Tsung P. K. Reciprocal effects of cAMP and cGMP on microtubule-dependent release of lysosomal enzymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:750–762. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L., Bamburg J. R., Mizel S. B., Grisham L. M., Creswell K. M. Interaction of drugs with microtubule proteins. Fed Proc. 1974 Feb;33(2):158–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S. M. The Chediak-Higashi syndrome: studies of host defenses. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Feb;76(2):293–306. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Weissmann G., Hoffstein S., Kammerman S., Tai H. H. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. II. Effects of cAMP and cGMP, autonomic agonists, and agents which affect microtubule function. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):297–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI107550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]