Abstract
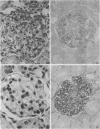
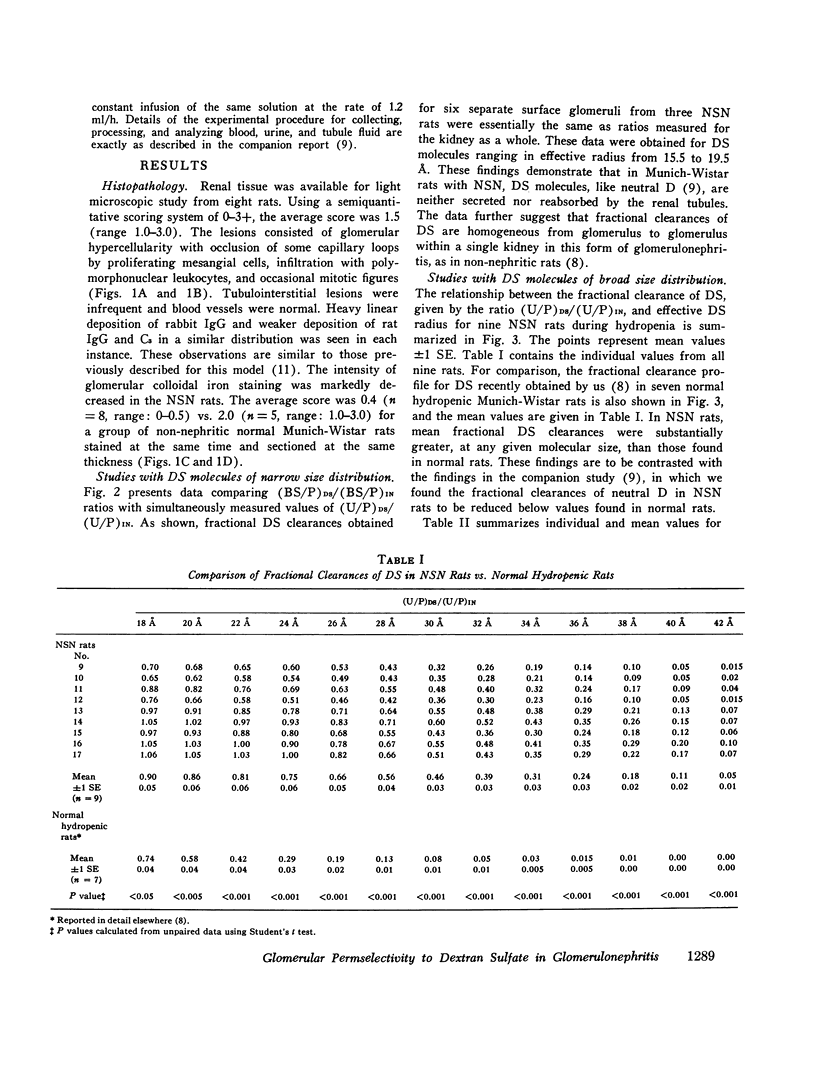
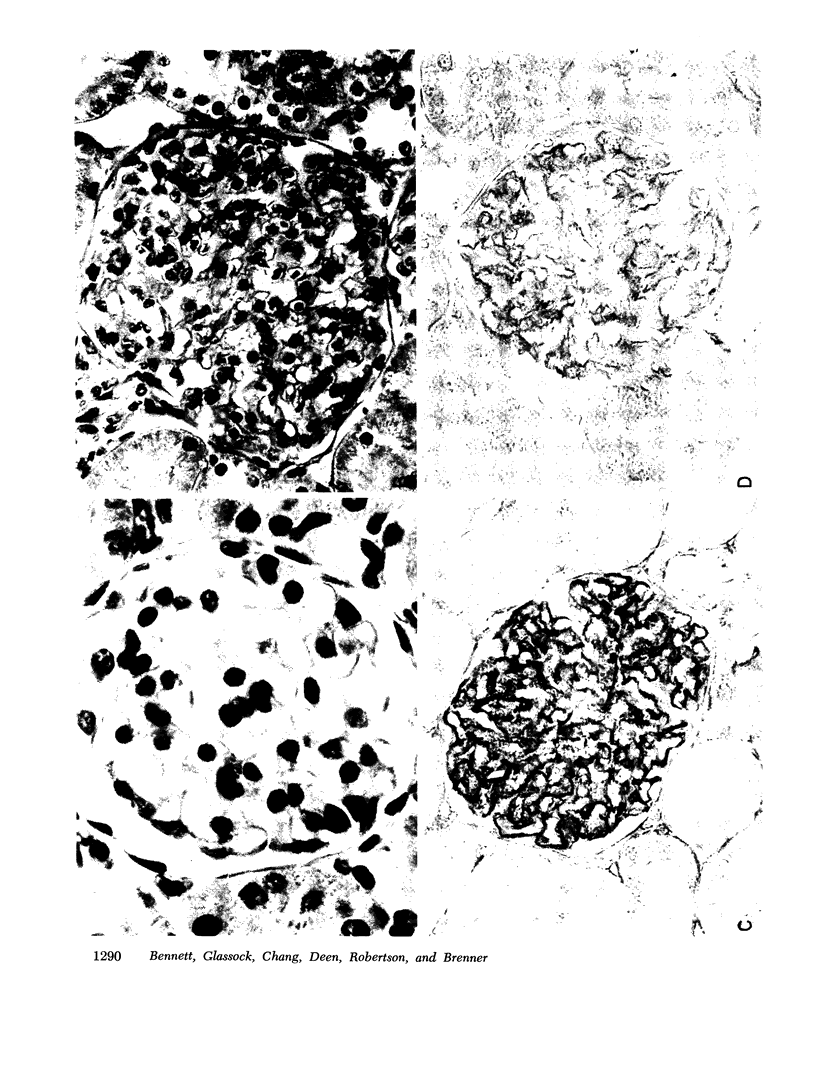
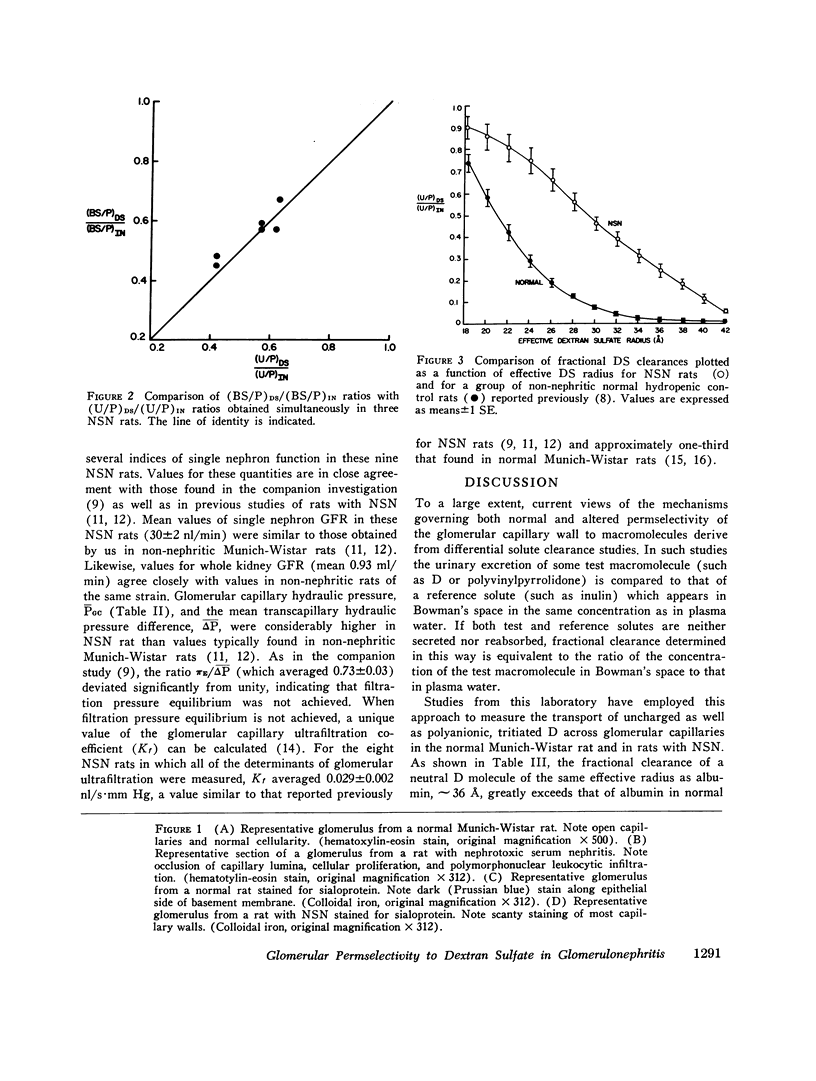
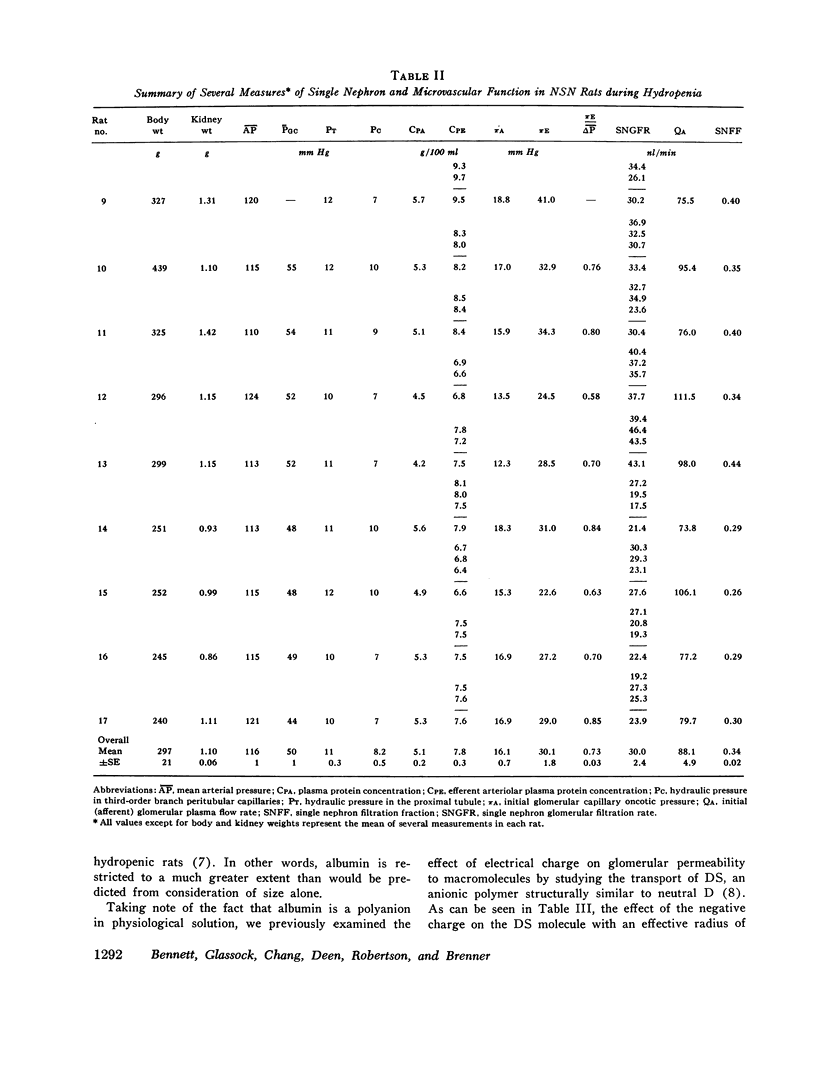
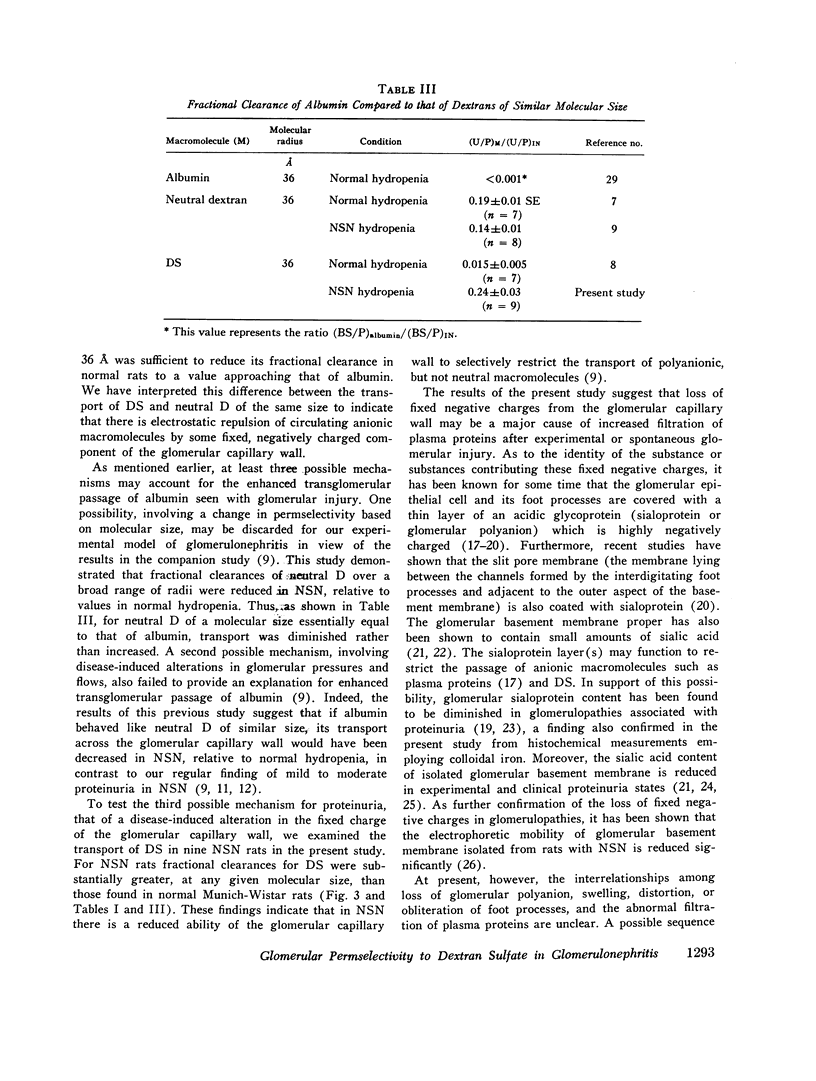
To determine whether the increased filtration of serum proteins after glomerular injury is the consequence of altered electrostatic properties of the glomerular capillary wall, we measured fractional clearances of the anionic polymer, dextran sulfate, in nine Munich-Wistar rats in the early autologous phase of nephrotoxic serum nephritis (NSN). In agreement with previous studied from this laboratory, whole kidney and single nephron glomerular filtration rates were normal in NSN rats despite histological evidence of glomerular injury, and despite a marked reduction in the glomerular capillary ultrafiltration coefficient to approximately one-third of normal. In the companion study (9), it was shown that in NSN rats the mean fractional clearances of neutral dextrans over the range of effective molecular radii from 18 to 42 A were reduced, compared to normla. In contrast, in the present study the mean fractional clearances for dextran sulfate over the same range of molecular radii were significantly greater than those found previously for normal Munich-Wistar rats. The fractional clearance of dextran sulfate molecules of the same molecular radius as serum albumin (approximately 36 A) was increased markedly, from 0.015 +/- 0.005 (SEM) in nonnephritic controls to 0.24 +/- 0.03 in NSN (P less than 0.001). The sialoprotein content of glomeruli, estimated by the colloidal iron reaction, was reduced in NSN rats as compared to normal controls. It is concluded that the abnormal filtration of anionic serum proteins, such as albumin, seen in glomerulopathies is, at least in part, the consequence of loss of fixed negative charges from the glomerular capillary wall.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arturson G., Groth T., Grotte G. Human glomerular membrane porosity and filtration pressure: dextran clearance data analysed by theoretical models. Clin Sci. 1971 Feb;40(2):137–158. doi: 10.1042/cs0400137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau E. B., Haas J. E. Glomerular sialic acid and proteinuria in human renal disease. Lab Invest. 1973 Apr;28(4):477–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau E. B., Michael A. F. Rat glomerular glycoprotein composition and metabolism in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Oct;141(1):164–172. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. L., Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Bennett C. M., Glassock R. J., Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Ueki I. F., Rasmussen B. Permselectivity of of the glomerular capillary wall. Studies of experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat using neutral dextran. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1272–1286. doi: 10.1172/JCI108395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. L., Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. Permselectivity of the glomerular capillary wall: III. Restricted transport of polyanions. Kidney Int. 1975 Oct;8(4):212–218. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. L., Ueki I. F., Troy J. L., Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. Permselectivity of the glomerular capillary wall to macromolecules. II. Experimental studies in rats using neutral dextran. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):887–906. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85863-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Robertson C. R., Deen W. M., Brenner B. M. Permselectivity of the glomerular capillary wall to macromolecules. I. Theoretical considerations. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):861–886. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85862-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bats A., Gordon A. H., Rhodes E. L. Variation in glomerular sialic acid content in diabetes and as the result of ageing. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Jul;47(1):93–95. doi: 10.1042/cs0470093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. A model of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1178–1183. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen W. M., Troy J. L., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. IV. Determination of the ultrafiltration coefficient. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1500–1508. doi: 10.1172/JCI107324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbach G. M., Liew J. B., Boylan J. W., Manz N., Muir P. Effect of angiotensin on the filtration of protein in the rat kidney: a micropuncture study. Kidney Int. 1975 Aug;8(2):80–87. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalant N., Misra R. P., Manley R. S., Wilson J. Glomerular basement membrane in experimental nephrosis: x-ray diffraction and electrophoretic studies. Nephron. 1966;3(3):167–174. doi: 10.1159/000179473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Structure and biosynthesis of basement membranes. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1973;6:63–104. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363706-2.50008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMBERT P. P., GREGOIRE F. Hémodynamique glomérulaire et excrétion de l'hémoglobine. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1955 Feb;63(1):7–34. doi: 10.3109/13813455509150857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. P., Verniory A., Gassee J. P., Ficheroulle P. Sieving equations and effective glomerular filtration pressure. Kidney Int. 1972 Sep;2(3):131–146. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latta H., Johnston W. H., Stanley T. M. Sialoglycoproteins and filtration barriers in the glomerular capillary wall. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 Jun;51(3):354–376. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)80100-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lui S., Kalant N. Carbohydrate of the glomerular basement membrane in normal and hephrotic rats. Exp Mol Pathol. 1974 Aug;21(1):52–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(74)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox D. A., Bennett C. M., Deen W. M., Glassock R. J., Knutson D., Brenner B. M. Control of proximal tubule fluid reabsorption in experimental glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1315–1325. doi: 10.1172/JCI108051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox D. A., Bennett C. M., Deen W. M., Glassock R. J., Knutson D., Daugharty T. M., Brenner B. M. Determinants of glomerular filtration in experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):305–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI107934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael A. F., Blau E., Vernier R. L. Glomerular polyanion. Alteration in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Lab Invest. 1970 Dec;23(6):649–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohos S. C., Skoza L. Glomerular sialoprotein. Science. 1969 Jun 27;164(3887):1519–1521. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3887.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohos S. C., Skoza L. Histochemical demonstration and localization of sialoproteins in the glomerulus. Exp Mol Pathol. 1970 Jun;12(3):316–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(70)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers B. D., Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. VIII. Effects of hematocrit. Circ Res. 1975 Mar;36(3):425–435. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER J. R. Passage of molecules through capillary wals. Physiol Rev. 1953 Jul;33(3):387–423. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1953.33.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENKIN E. M. Filtration, diffusion, and molecular sieving through porous cellulose membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Nov 20;38(2):225–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RINEHART J. F., ABUL-HAJ S. K. An improved method for histologic demonstration of acid mucopolysaccharides in tissues. AMA Arch Pathol. 1951 Aug;52(2):189–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson A. M., Giangiacomo J., Kienstra R. A., Naqvi S. T., Ingelfinger J. R. Normal glomerular permeability and its modification by minimal change nephrotic syndrmone. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1190–1199. doi: 10.1172/JCI107862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy L. P., Vernier R. L., Michael A. F. Effect of protein-load proteinuria on glomerular polyanion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Dec;141(3):870–874. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler M. W., Venkatachalam M. A., Cotran R. S. Glomerular epithelium: structural alterations induced by polycations. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):390–393. doi: 10.1126/science.1145209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]