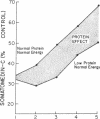
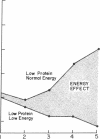
Abstract
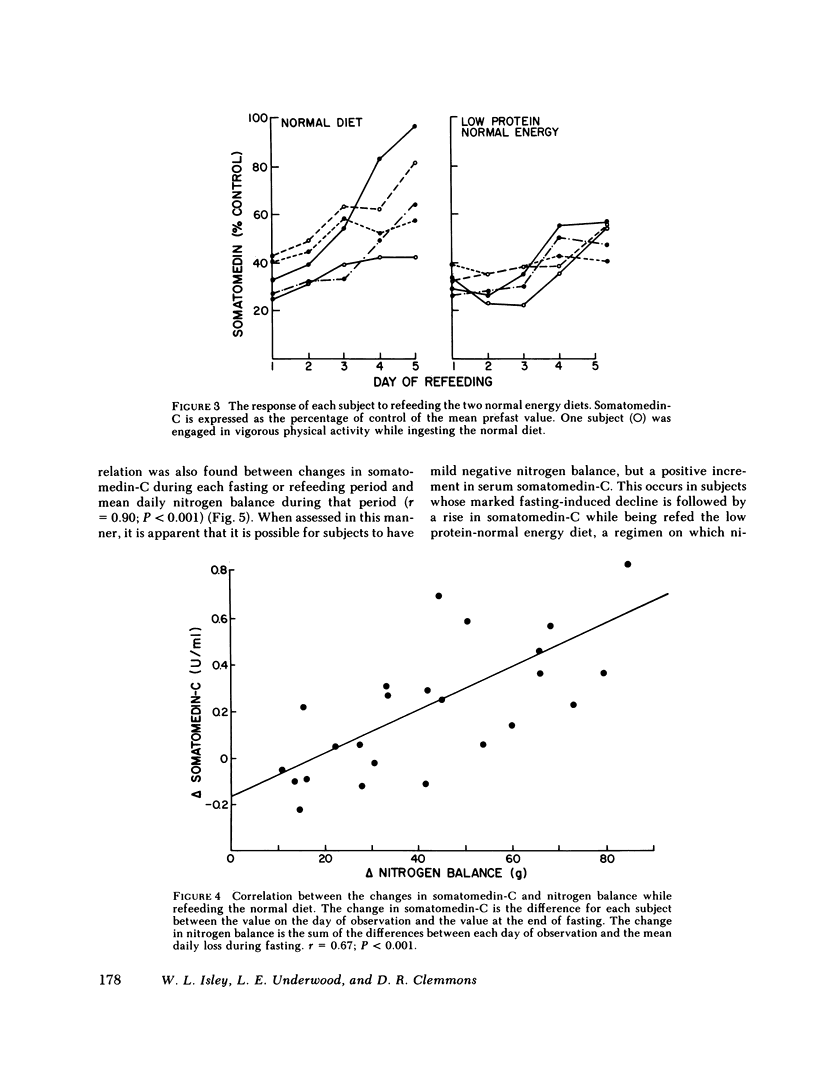
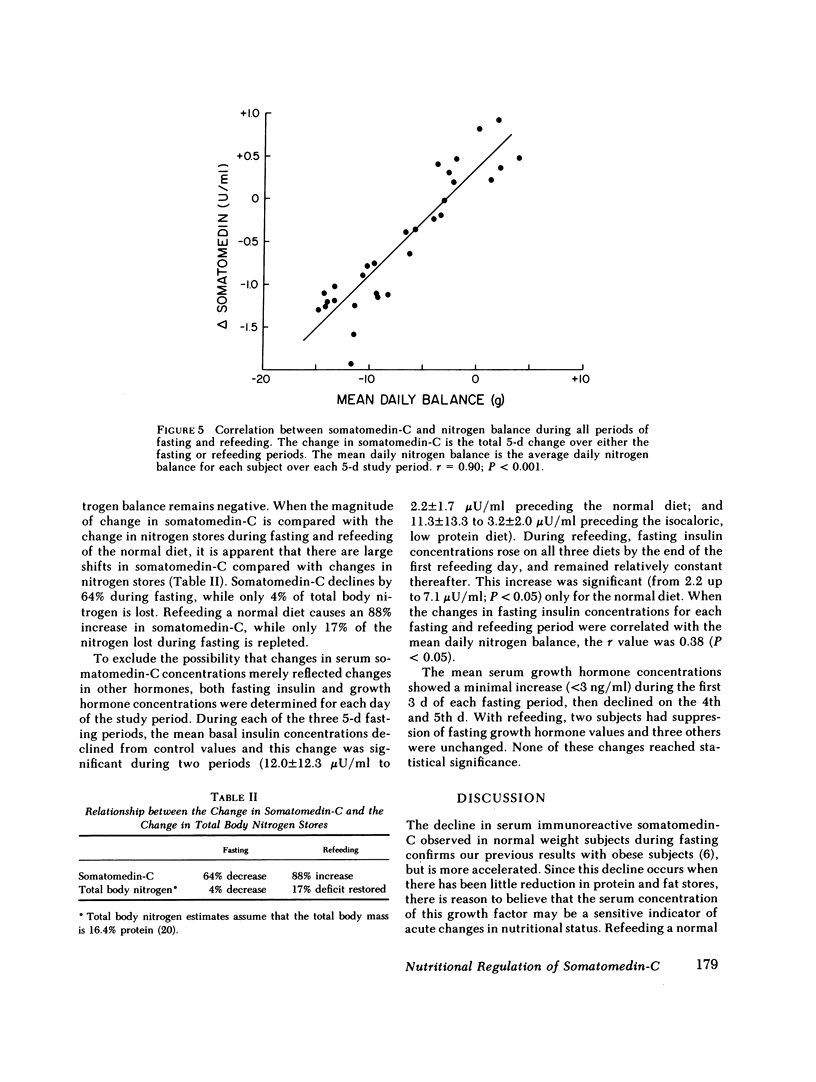
Dietary components responsible for the regulation of somatomedin-C in humans were assessed in five adult volunteers of normal weight who were fasted for 5 d on three occasions, then refed three diets of differing composition. The serum somatomedin-C decreased from a mean prefasting value of 1.85 +/- 0.39 U/ml (+/- 1 SD) to 0.67 +/- 0.16 U/ml at the end of fasting (P less than 0.005). After refeeding for 5 d with a normal diet, the mean serum somatomedin-C increased to 1.26 +/- 0.20 U/ml. A protein-deficient (32% of control), isocaloric diet resulted in a significantly smaller increase, to a mean value of 0.90 +/- 0.24 U/ml (P less than 0.05). A diet deficient in both protein and energy led to a further fall 0.31 +/- 0.06 U/ml. The changes in somatomedin-C during fasting and refeeding correlated significantly with mean daily nitrogen balance (r = 0.90). We conclude that both protein and energy intake are regulators of serum somatomedin-C concentrations in adult humans, and energy intake may be of greater importance. The correlation between changes in somatomedin-C and nitrogen balance suggests that the former are directly related to changes in protein synthesis and may be helpful in assessing the response to nutritional therapy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROZEK J., GRANDE F., ANDERSON J. T., KEYS A. DENSITOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF BODY COMPOSITION: REVISION OF SOME QUANTITATIVE ASSUMPTIONS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Sep 26;110:113–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb17079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benotti P., Blackburn G. L. Protein and caloric or macronutrient metabolic management of the critically ill patient. Crit Care Med. 1979 Dec;7(12):520–525. doi: 10.1097/00003246-197912000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Klibanski A., Underwood L. E., McArthur J. W., Ridgway E. C., Beitins I. Z., Van Wyk J. J. Reduction of plasma immunoreactive somatomedin C during fasting in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Dec;53(6):1247–1250. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-6-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland K. C., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J. Induction of immunoreactive somatomedin C human serum by growth hormone: dose-response relationships and effect on chromatographic profiles. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Apr;50(4):690–697. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-4-690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Mariz I. K., Blethen S. L. Inhibition of access of bound somatomedin to membrane receptor and immunobinding sites: a comparison of radioreceptor and radioimmunoassay of somatomedin in native and acid-ethanol-extracted serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Oct;51(4):781–788. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-4-781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Phillips L. S., Mueller M. C. The effects of insulin and growth hormone on the release of somatomedin by the isolated rat liver. Endocrinology. 1976 May;98(5):1214–1219. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-5-1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edozien J. C., Niehaus N., Mar M. H., Makoui T., Switzer B. R. Diet-hormone interrelationships in the rat. J Nutr. 1978 Nov;108(11):1767–1776. doi: 10.1093/jn/108.11.1767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elders M. J., Wingfield B. S., McNatt M. L., Clarke J. S., Hughes E. R. Glucocorticoid therapy in children. Effect on somatomedin secretion. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Dec;129(12):1393–1396. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120490011005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER J., FETTER M. C., MAST R. L., FREE A. H. STUDIES WITH A SIMPLIFIED NITROPRUSSIDE TEST FOR KETONE BODIES IN URINE, SERUM, PLASMA, AND MILK. Clin Chim Acta. 1965 Apr;11:372–378. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(65)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J., D'Ercole A. J. Estimation of somatomedin-C levels in normals and patients with pituitary disease by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):648–657. doi: 10.1172/JCI108816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalan C., Rao B. S. Effect of protein depletion on urinary nitrogen excretion in undernourished subjects. J Nutr. 1966 Nov;90(3):213–218. doi: 10.1093/jn/90.3.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D. B., Hambley J., Becker D., Pimstone B. L. Reduced sulphation factor in undernourished children. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Aug;48(8):596–600. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.8.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Suskind R., Amatayakul K., Thanangkul O., Olson R. Plasma somatomedin and growth hormone values in children with protein-calorie malnutrition. J Pediatr. 1978 Jan;92(1):153–156. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau R. L., Rochman H., Blix-Gruber P., Rubenstein A. H. The protein-sparing action of protein feeding: absence of relationship to insulin secretion. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Jul;34(7):1300–1304. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.7.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH W. H., FINGERHUT B., MILLER H. AUTOMATED AND MANUAL DIRECT METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF BLOOD UREA. Clin Chem. 1965 Jun;11:624–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicol B. M., Phillips P. G. Endogenous nitrogen excretion and utilization of dietary protein. Br J Nutr. 1976 Mar;35(2):181–193. doi: 10.1079/bjn19760022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. S., Orawski A. T., Belosky D. C. Somatomedin and nutrition. IV. Regulation of somatomedin activity and growth cartilage activity by quantity and composition of diet in rats. Endocrinology. 1978 Jul;103(1):121–127. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. S., Vassilopoulou-Sellin R. Somatomedins (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 21;302(8):438–446. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002213020805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. S., Young H. S. Nutrition and somatomedin. I. Effect of fasting and refeeding on serum somatomedin activity and cartilage growth activity in rats. Endocrinology. 1976 Jul;99(1):304–314. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-1-304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powanda M. C. Changes in body balances of nitrogen and other key nutrients: description and underlying mechanisms. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977 Aug;30(8):1254–1268. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.8.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prewitt T. E., D'Ercole A. J., Switzer B. R., Van Wyk J. J. Relationship of serum immunoreactive somatomedin-C to dietary protein and energy in growing rats. J Nutr. 1982 Jan;112(1):144–150. doi: 10.1093/jn/112.1.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. N., Morrison A. B. Evaluation of protein in foods. XII. Effects of calorie restriction. Can J Biochem. 1966 Oct;44(10):1365–1375. doi: 10.1139/o66-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP G. S., LASSEN S., SHANKMAN S., HAZLET J. W., KENDIS M. S. Studies of protein retention and turnover using nitrogen-15 as a tag. J Nutr. 1957 Sep 10;63(1):155–162. doi: 10.1093/jn/63.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon W. D., Jr, DuVall M. R. In vitro stimulation of leucine incorporation into muscle and cartilage protein by a serum fraction with sulfation factor activity: differentiation of effects from those of growth hormone and insulin. Endocrinology. 1970 Dec;87(6):1168–1180. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-6-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrimshaw N. S., Perera W. D., Young V. R. Protein requirements of man: obligatory urinary and fecal nitrogen losses in elderly women. J Nutr. 1976 May;106(5):665–670. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.5.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. W., Payne P. R., Picou D., Waterlow J. C. Energy balance during recovery from malnutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1976 Oct;29(10):1073–1088. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/29.10.1073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessler R. H., Salmon W. D., Jr Glucocorticoid inhibition of sulfate incorporation by cartilage of normal rats. Endocrinology. 1975 Apr;96(4):898–902. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-4-898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uthne K., Reagan C. R., Gimpel L. P., Kostyo J. L. Effects of human somatomedin preparations on membrane transport and protein synthesis in the isolated rat diaphragm. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Sep;39(3):548–554. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-3-548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk J. J., Svoboda M. E., Underwood L. E. Evidence from radioligand assays that somatomedin-C and insulin-like growth factor-I are similar to each other and different from other somatomedins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jan;50(1):206–208. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-1-206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter R. M., Dudl R. J., Palmer J. P., Ensinck J. W. The effect of adrenergic blockade on the glucagon responses to starvation and hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1214–1220. doi: 10.1172/JCI107864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead R. G., Lunn P. G. Endocrines in protein-energy malnutrition. Proc Nutr Soc. 1979 May 1;38(1):69–76. doi: 10.1079/pns19790010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. A. Nutritional assessment. JAMA. 1980 Aug 8;244(6):559–560. doi: 10.1001/jama.1980.03310060015012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young V. R., Steffee W. P., Pencharz P. B., Winterer J. C., Scrimshaw N. S. Total human body protein synthesis in relation to protein requirements at various ages. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):192–194. doi: 10.1038/253192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Kaufmann U., Eigenmann E. J., Froesch E. R. Determination of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity in human serum by a sensitive protein-binding assay. Clin Chem. 1977;23(4):677–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]