Abstract
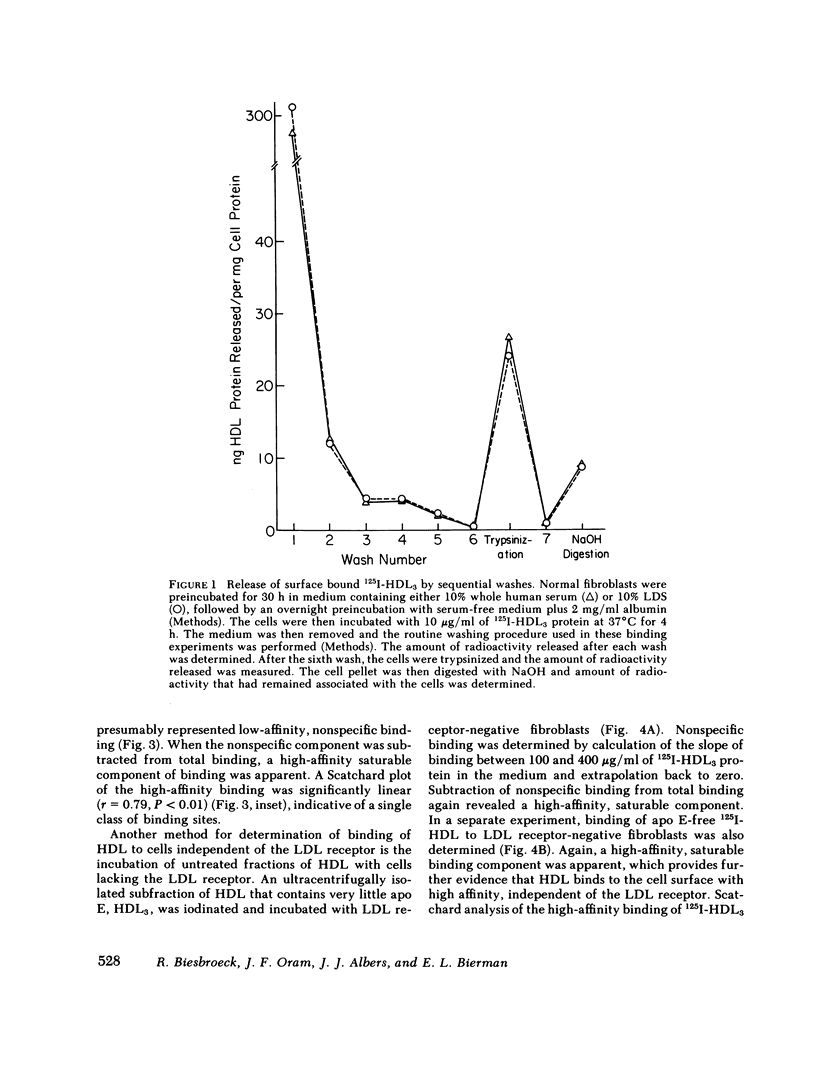
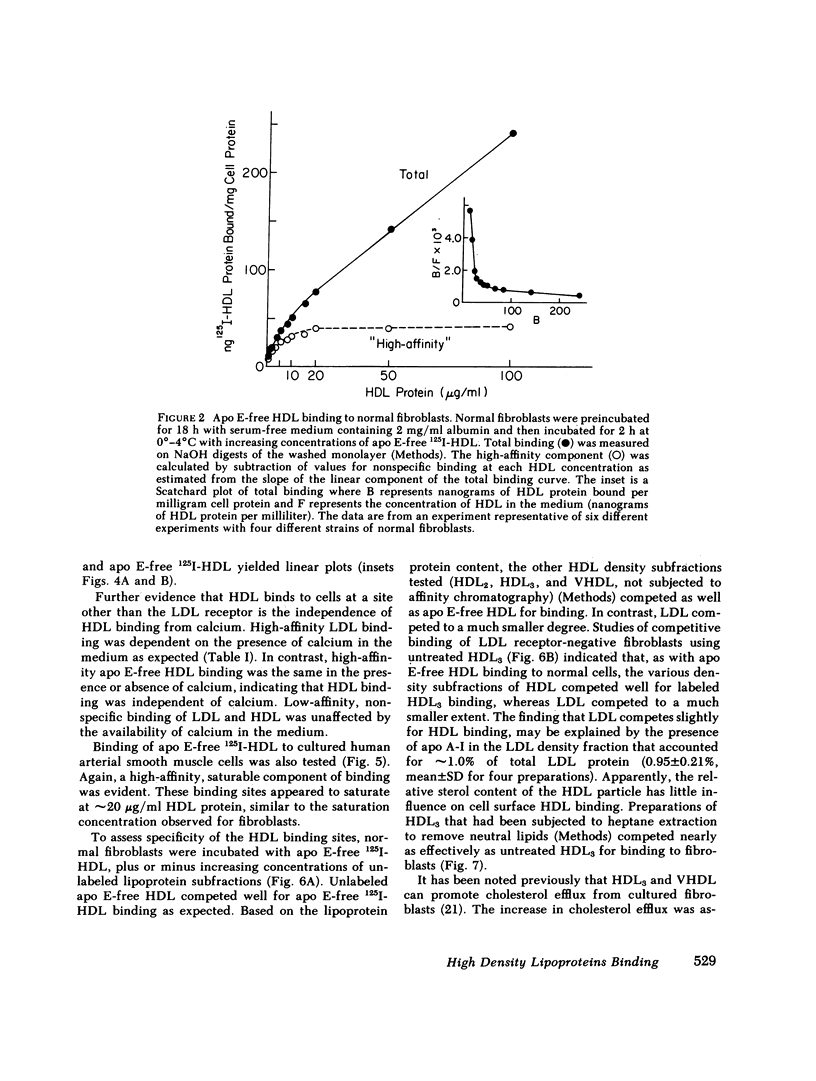
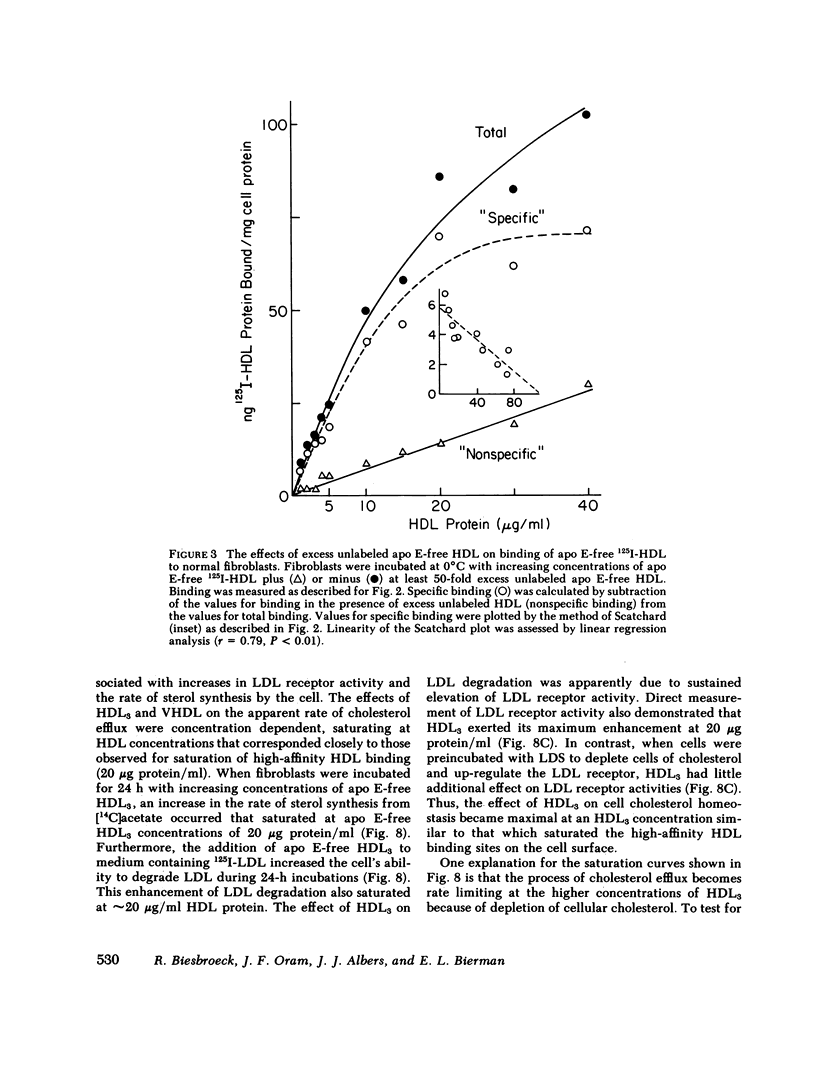
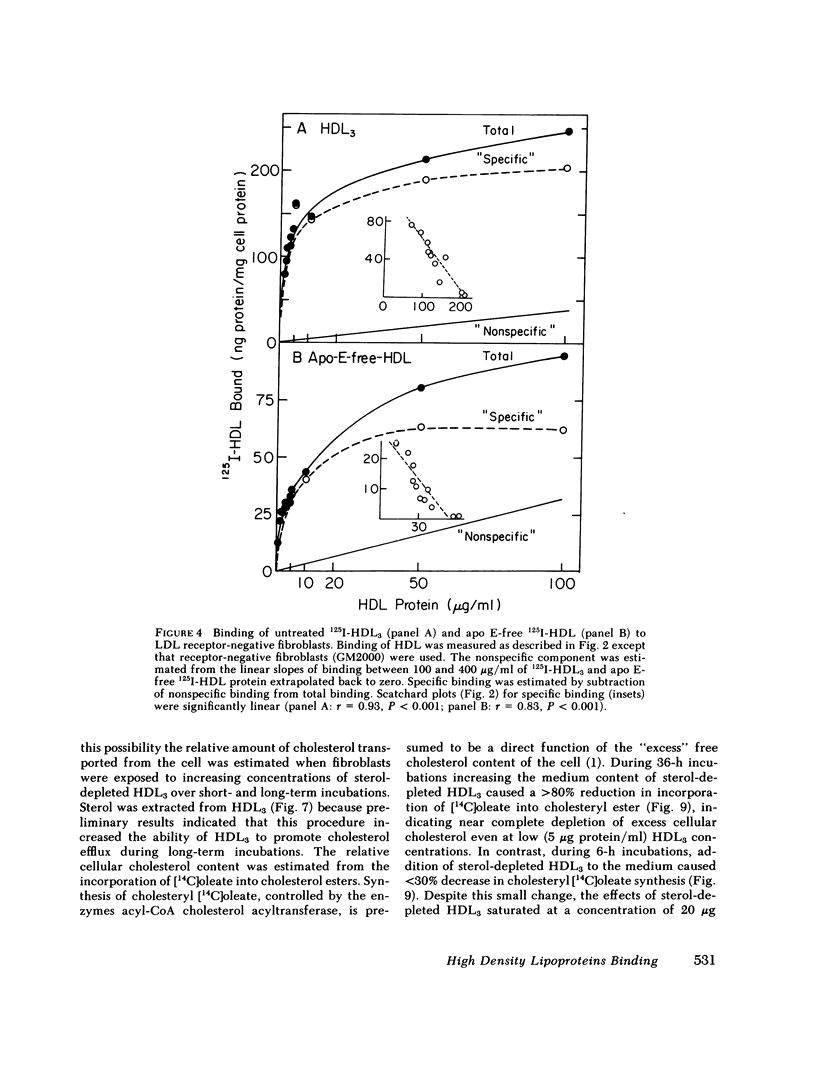
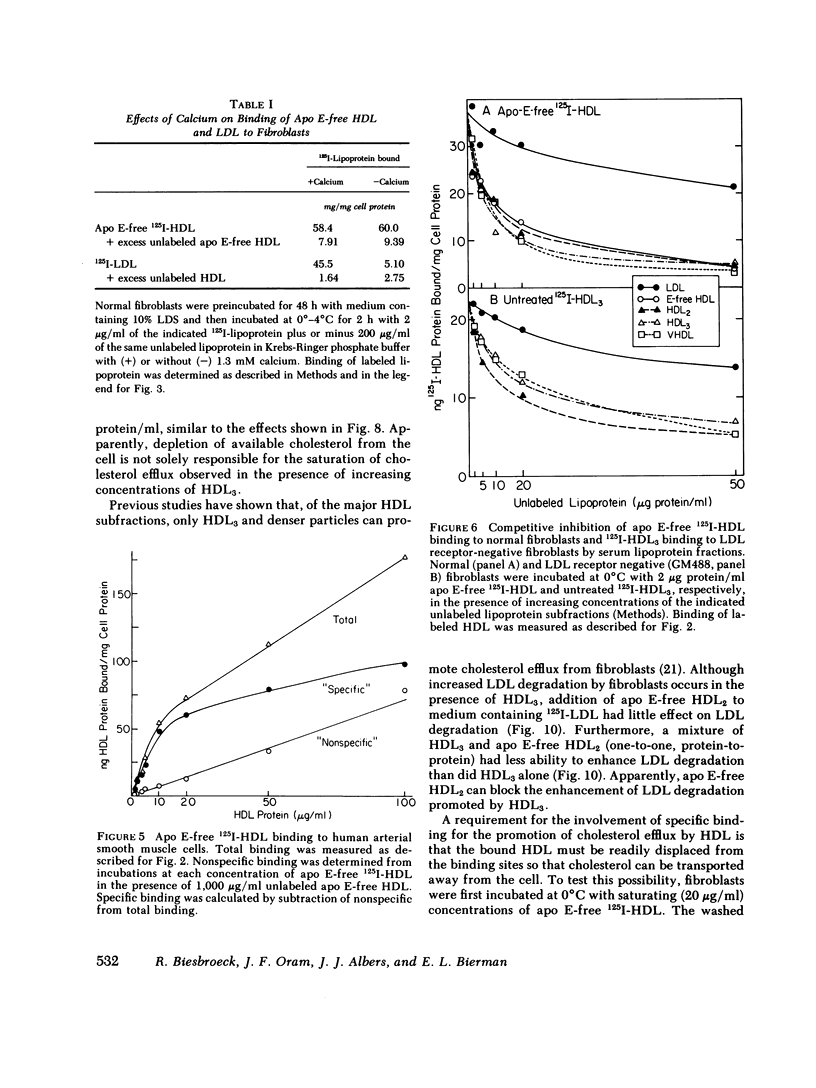
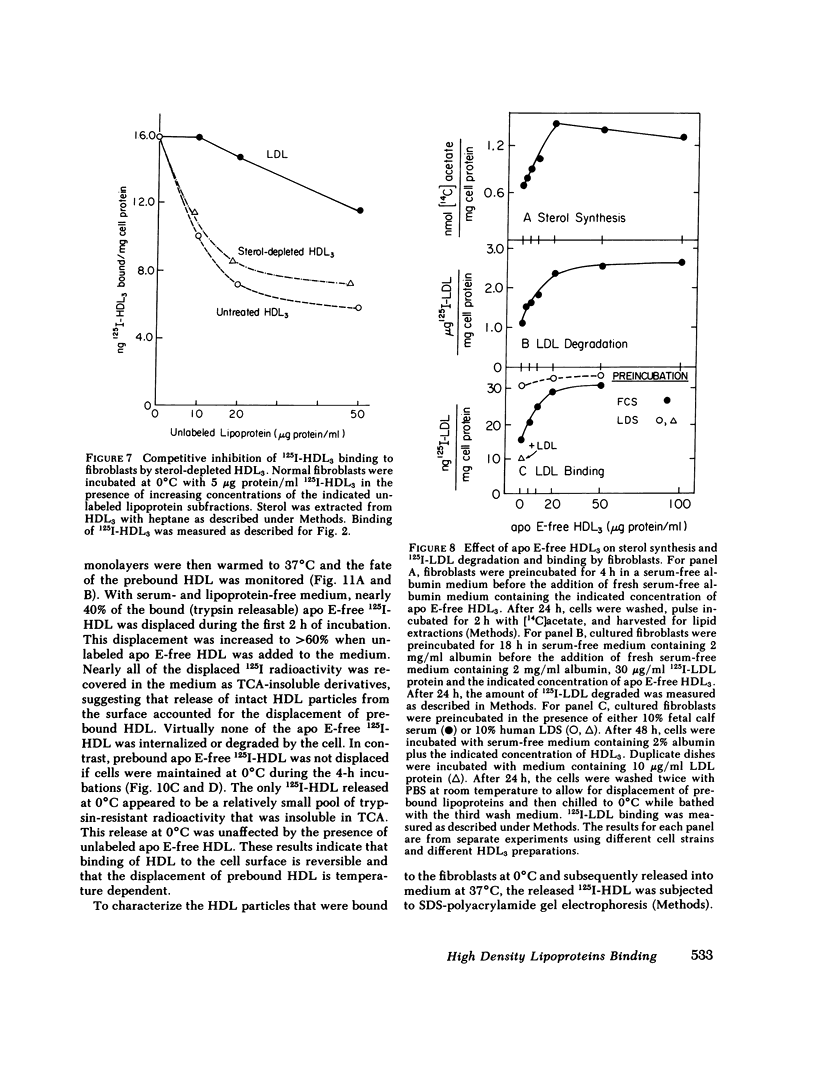
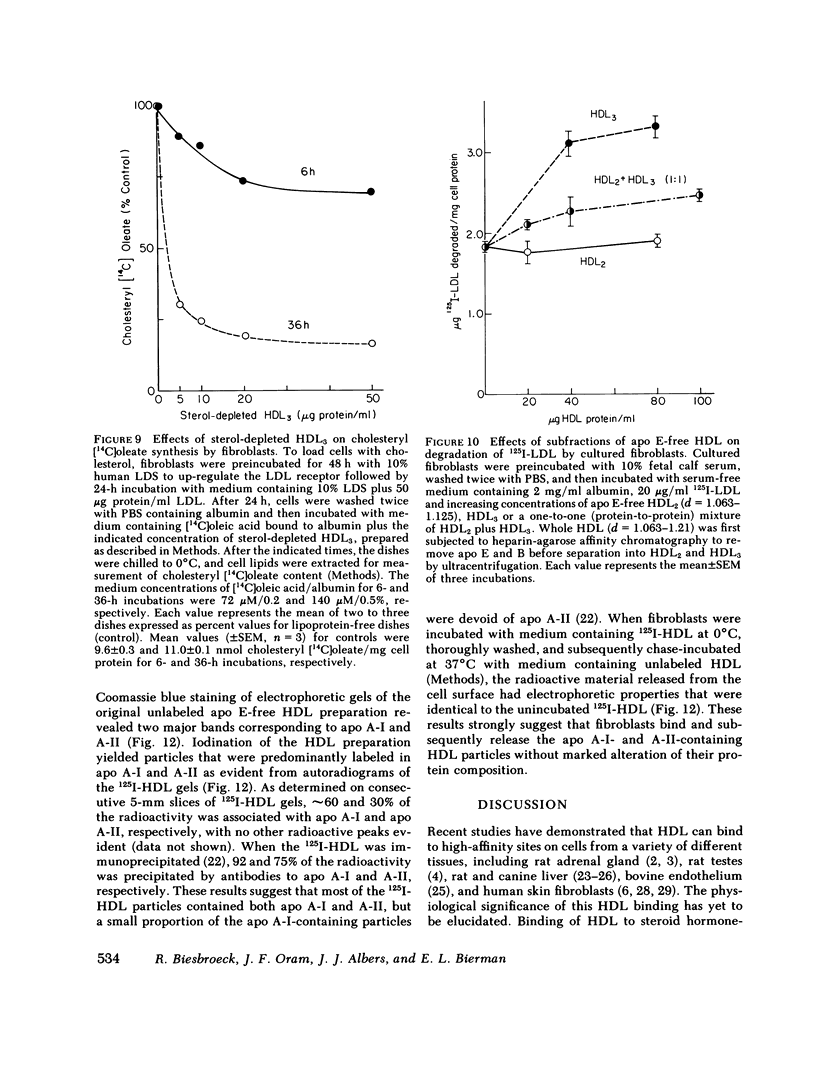
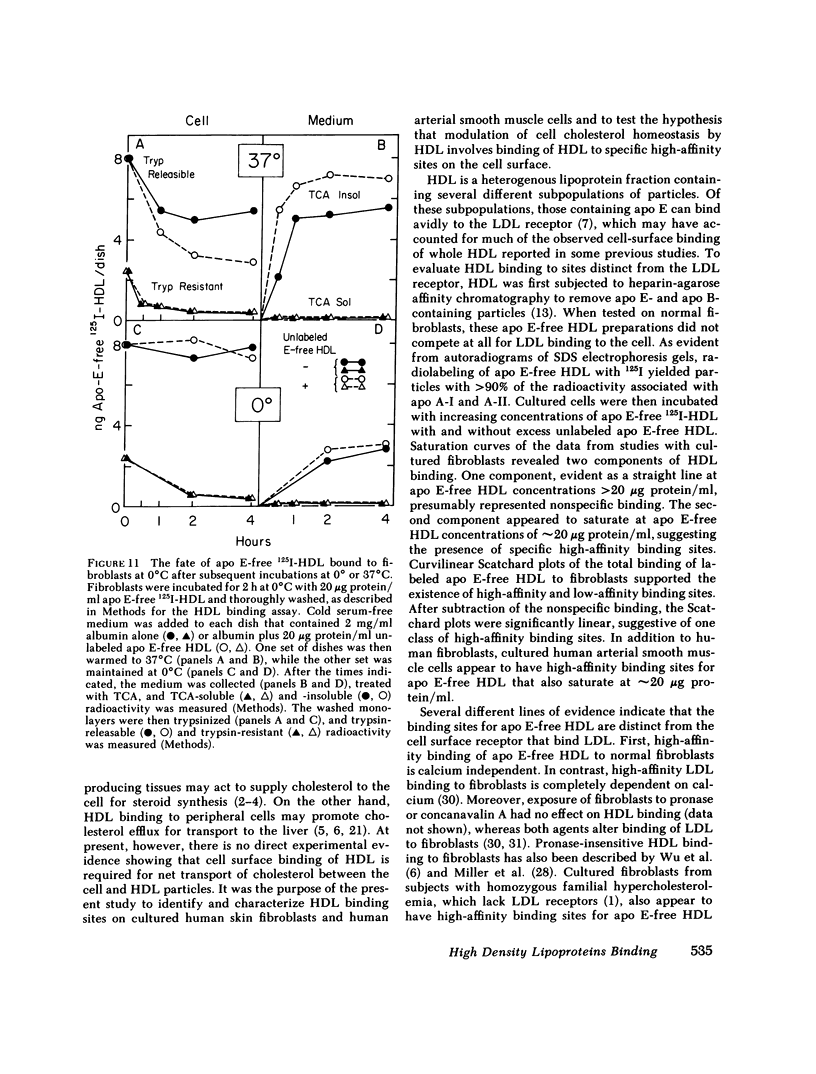
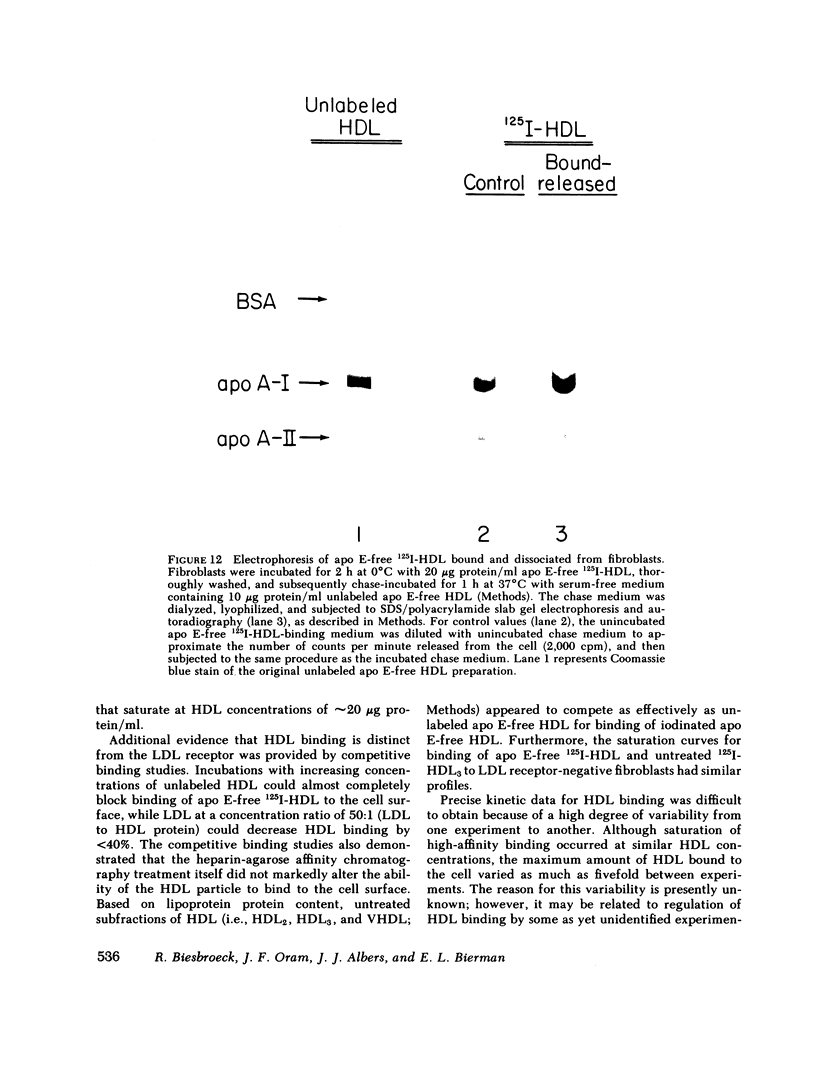
Binding of human high density lipoproteins (HDL, d = 1.063-1.21) to cultured human fibroblasts and human arterial smooth muscle cells was studied using HDL subjected to heparin-agarose affinity chromatography to remove apoprotein (apo) E and B. Saturation curves for binding of apo E-free 125I-HDL showed at least two components: low-affinity nonsaturable binding and high-affinity binding that saturated at approximately 20 micrograms HDL protein/ml. Scatchard analysis of high-affinity binding of apo E-free 125I-HDL to normal fibroblasts yielded plots that were significantly linear, indicative of a single class of binding sites. Saturation curves for binding of both 125I-HDL3 (d = 1.125-1.21) and apo E-free 125I-HDL to low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-negative fibroblasts also showed high-affinity binding that yielded linear Scatchard plots. On a total protein basis, HDL2 (d = 1.063-1.10), HDL3 and very high density lipoproteins (VHDL, d = 1.21-1.25) competed as effectively as apo E-free HDL for binding of apo E-free 125I-HDL to normal fibroblasts. Also, HDL2, HDL3, and VHDL competed similarly for binding of 125I-HDL3 to LDL receptor-negative fibroblasts. In contrast, LDL was a weak competitor for HDL binding. These results indicate that both human fibroblasts and arterial smooth muscle cells possess specific high affinity HDL binding sites. As indicated by enhanced LDL binding and degradation and increased sterol synthesis, apo E-free HDL3 promoted cholesterol efflux from fibroblasts. These effects also saturated at HDL3 concentrations of 20 micrograms/ml, suggesting that promotion of cholesterol efflux by HDL is mediated by binding to the high-affinity cell surface sites.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Cabana V. G., Hazzard W. R. Immunoassay of human plasma apolipoprotein B. Metabolism. 1975 Dec;24(12):1339–1351. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates S. R. Accumulation and loss of cholesterol esters in monkey arterial smooth muscle cells exposed to normal and hyperlipemic serum lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis. 1979 Feb;32(2):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(79)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierman E. L., Stein O., Stein Y. Lipoprotein uptake and metabolism by rat aortic smooth muscle cells in tissue culture. Circ Res. 1974 Jul;35(1):136–150. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.1.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-mediated control of cholesterol metabolism. Science. 1976 Jan 16;191(4223):150–154. doi: 10.1126/science.174194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. The cholesteryl ester cycle in macrophage foam cells. Continual hydrolysis and re-esterification of cytoplasmic cholesteryl esters. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9344–9352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. D., Kraemer F. B., Reaven G. M. Identification of specific high density lipoprotein-binding sites in rat testis and regulation of binding by human chorionic gonadotropin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9162–9167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung M. C., Albers J. J. Distribution of high density lipoprotein particles with different apoprotein composition: particles with A-I and A-II and particles with A-I but no A-II. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jul;23(5):747–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung M. C., Albers J. J. The measurement of apolipoprotein A-I and A-II levels in men and women by immunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):43–50. doi: 10.1172/JCI108767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daerr W. H., Gianturco S. H., Patsch J. R., Smith L. C., Gotto A. M., Jr Stimulation and suppression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in normal human fibroblasts by high density lipoprotein subclasses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 11;619(2):287–301. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels R. J., Guertler L. S., Parker T. S., Steinberg D. Studies on the rate of efflux of cholesterol from cultured human skin fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4978–4983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Release of low density lipoprotein from its cell surface receptor by sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Binding and degradation of low density lipoproteins by cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5153–5162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Inhibition of proteolytic degradation of low density lipoprotein in human fibroblasts by chloroquine, concanavalin A, and Triton WR 1339. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7854–7862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynne J. T., Mahaffee D., Brewer H. B., Jr, Ney R. L. Adrenal cholesterol uptake from plasma lipoproteins: regulation by corticotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4329–4333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Lipoprotein binding to canine hepatic membranes. Metabolically distinct apo-E and apo-B,E receptors. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5646–5655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Increased binding of low density lipoprotein to liver membranes from rats treated with 17 alpha-ethinyl estradiol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11367–11373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Schneider W. J., Hillman G. M., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Separate mechanisms for the uptake of high and low density lipoproteins by mouse adrenal gland in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5498–5505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger M., Brown M. S., Faust J. R., Goldstein J. L. Replacement of endogenous cholesteryl esters of low density lipoprotein with exogenous cholesteryl linoleate. Reconstitution of a biologically active lipoprotein particle. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4093–4101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N. E. Induction of low density lipoprotein receptor synthesis by high density lipoprotein in cultures of human skin fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 28;529(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N. E., Weinstein D. B., Carew T. E., Koschinsky T., Steinberg D. Interaction between high density and low density lipoproteins uptake and degradation by cultured human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):78–88. doi: 10.1172/JCI108772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N. E., Weinstein D. B., Steinberg D. Binding, internalization, and degradation of high density lipoprotein by cultured normal human fibroblasts. J Lipid Res. 1977 Jul;18(4):438–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. D., King W. C., Applegate K. R., Forte T., Glomset J. A., Norum K. R., Gjone E. Characterization of apolipoprotein E-rich high density lipoproteins in familial lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jul;21(5):625–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Otto P. S., Kennedy D. L., Whayne T. F., Jr Rat high density lipoprotein subfraction (HDL3) uptake and catabolism by isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4914–4921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. F., Albers J. J., Bierman E. L. Rapid regulation of the activity of the low density lipoprotein receptor of cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):475–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. F., Albers J. J., Cheung M. C., Bierman E. L. The effects of subfractions of high density lipoprotein on cholesterol efflux from cultured fibroblasts. Regulation of low density lipoprotein receptor activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8348–8356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ose L., Røken I., Norum K. R., Drevon C. A., Berg T. The binding of high density lipoproteins to isolated rat hepatocytes. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1981 Feb;41(1):63–73. doi: 10.3109/00365518109092016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Cell surface receptor binding of phospholipid . protein complexes containing different ratios of receptor-active and -inactive E apoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5454–5460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichl D., Simons L. A., Myant N. B., Pflug J. J., Mills G. L. The lipids and lipoproteins of human peripheral lymph, with observations on the transport of cholesterol from plasma and tissues into lymph. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Sep;45(3):313–329. doi: 10.1042/cs0450313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Vanderhoek J., Stein Y. Cholesterol content and sterol synthesis in human skin fibroblasts and rat aortic smooth muscle cells exposed to lipoprotein-depleted serum and high density apolipoprotein/phospholipid mixtures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 27;431(2):347–358. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber J. P., Goldminz D., Gospodarowicz D. Up-regulation in vascular endothelial cells of binding sites of high density lipoprotein induced by 25-hydroxycholesterol. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(2):327–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Subfractionation of human high density lipoproteins by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1980 Mar;21(3):316–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. D., Butler J., Bailey J. M. Lipid metabolism in cultured cells. XVIII. Comparative uptake of low density and high density lipoproteins by normal, hypercholesterolemic and tumor virus-transformed human fibroblasts. J Lipid Res. 1979 May;20(4):472–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]