Abstract
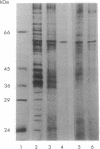
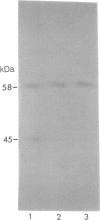
Active opioid binding proteins were solubilized from rat brain membranes in high yield with sodium deoxycholate in the presence of NaCl. Purification of opioid binding proteins was accomplished by opioid antagonist affinity chromatography. Chromatography using the delta-opioid antagonist N,N-diallyl-Tyr-D-Leu-Gly-Tyr-Leu attached to omega-aminododecyl-agarose (Affi-G) (procedure A) yielded a partially purified protein that binds selectively the delta-opioid agonist [3H]Tyr-D-Ser-Gly-Phe-Leu-Thr ([3H]DSLET), with a Kd of 19 +/- 3 nM and a Bmax of 5.1 +/- 0.4 nmol/mg of protein. Subsequently, Lens culinaris agglutinin-Sepharose 4B chromatography of the Affi-G eluate resulted in isolation of an electrophoretically homogeneous protein of 58 kDa that binds selectively [3H]DSLET with a Kd of 21 +/- 3 nM and a Bmax of 16.5 +/- 1.0 nmol/mg of protein. Chromatography using the nonselective antagonist 6-aminonaloxone coupled to 6-aminohexanoic acid-Sepharose 4B (Affi-NAL) (procedure B) resulted in isolation of a protein that binds selectively [3H]DSLET with a Kd of 32 +/- 2 nM and a Bmax of 12.4 +/- 0.5 nmol/mg of protein, and NaDodSO4/PAGE revealed a major band of apparent molecular mass 58 kDa. Polyclonal antibodies (Anti-R IgG) raised against the Affi-NAL protein inhibit the specific [3H]DSLET binding to the Affi-NAL eluate and to the solubilized membranes. Moreover, the Anti-R IgG inhibits the specific binding of radiolabeled Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-N-methyl-Phe-Gly-ol (DAMGO; mu-agonist), DSLET (delta-agonist), and naloxone to homogenates of rat brain membranes with equal potency. Furthermore, immunoaffinity chromatography of solubilized membranes resulted in the retention of a major protein of apparent molecular mass 58 kDa. In addition, immunoblotting of solubilized membranes and purified proteins from the Affi-G and Affi-NAL matrices revealed that the Anti-R IgG interacts with a protein of 58 kDa.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Lawson-Wendling K., Pugsley T. A. A rapid filtration assay for soluble receptors using polyethylenimine-treated filters. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D. J., DeCosta B., Jacobson A. E., Bost K. L., Rice K. C., Blalock J. E. Immunoaffinity-purified opiate receptor specifically binds the delta-class opiate receptor ligand, cis-(+)-3-methylfentanylisothiocyanate, SUPERFIT. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 30;224(2):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80468-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho T. M., Hasegawa J., Ge B. L., Loh H. H. Purification to apparent homogeneity of a mu-type opioid receptor from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4138–4142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa T., Herz A. Antagonists with negative intrinsic activity at delta opioid receptors coupled to GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7321–7325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. J., Keith D. E., Jr, Morrison H., Magendzo K., Edwards R. H. Cloning of a delta opioid receptor by functional expression. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1952–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.1335167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgoussi Z., Zioudrou C. Effect of delta-opioid antagonists on the functional coupling between opioid receptors and G-proteins in rat brain membranes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Jun 22;45(12):2405–2410. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90220-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gioannini T. L., Howard A. D., Hiller J. M., Simon E. J. Purification of an active opioid-binding protein from bovine striatum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15117–15121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomathi K. G., Sharma S. K. Purification and reconstitution of the delta opioid receptor. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 13;330(2):146–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80261-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard A. D., de La Baume S., Gioannini T. L., Hiller J. M., Simon E. J. Covalent labeling of opioid receptors with radioiodinated human beta-endorphin. Identification of binding site subunit. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10833–10839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J. B., Hanson R. N., Portoghese P. S., Takemori A. E. Stereochemical studies on medicinal agents. 23. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 6-amino derivatives of naloxone and naltrexone. J Med Chem. 1977 Aug;20(8):1100–1102. doi: 10.1021/jm00218a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer B. L., Befort K., Gaveriaux-Ruff C., Hirth C. G. The delta-opioid receptor: isolation of a cDNA by expression cloning and pharmacological characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12048–12052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh H. H., Smith A. P. Molecular characterization of opioid receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:123–147. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loukas S., Varoucha D., Zioudrou C., Streaty R. A., Klee W. A. Opioid activities and structures of alpha-casein-derived exorphins. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4567–4573. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. A practical computer-based approach to the analysis of radioligand binding experiments. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Aug-Oct;17(1-2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. L., Barnard E. A. Identification of an opioid receptor subunit carrying the mu binding site. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5385–5389. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofri D., Simon E. J. Sulfhydryl groups on opioid receptors revisited. Evidence for two sulfhydryl groups at or near the active site of the mu opioid receptor. Receptor. 1992 Summer;2(2):109–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson S. J., Robson L. E., Kosterlitz H. W. Classification of opioid receptors. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):31–36. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisine T., Bell G. I. Molecular biology of opioid receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Dec;16(12):506–510. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90194-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Burke T. R., Jr, Rice K. C., Jacobson A. E., Klee W. A. Purification of the opiate receptor of NG108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4974–4978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szücs M., Belcheva M., Simon J., Benyhe S., Tóth G., Hepp J., Wollemann M., Medzihradszky K. Covalent labeling of opioid receptors with 3H-D-Ala2-Leu5-enkephalin chloromethyl ketone. I. Binding characteristics in rat brain membranes. Life Sci. 1987 Jul 13;41(2):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90491-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ternynck T., Avrameas S. Polyacrylamide-protein immunoadsorbents prepared with glutaraldehyde. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):24–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Harada H., Misawa H., Nozaki M., Takagi H. Purified opioid mu-receptor is of a different molecular size than delta- and kappa-receptors. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Apr 10;75(3):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90546-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollemann M. Recent developments in the research of opioid receptor subtype molecular characterization. J Neurochem. 1990 Apr;54(4):1095–1101. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]