Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERMAN L., AXELROD A. R., GOODMAN H. L., McCLAUGHRY R. I. So-called "lupus erythematosus inclusion phenomenon" of bone marrow and blood. Am J Clin Pathol. 1950 May;20(5):403–418. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/20.5.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., RUFFIER N. K. Elaboration of desoxyribonuclease by streptococci in the resting state and inhibition of the enzyme by a substance extractable from the cocci. J Exp Med. 1951 Apr 1;93(4):399–413. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.4.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN K. D., JACOBS G., LASKOWSKI M. The distribution of nucleode polymerases it calf thymus fractions. J Biol Chem. 1952 Jan;194(1):445–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASERICK J. R., LEWIS L. A., BORTZ D. W. Blood factor in acute disseminated lupus erythematosus; determination of gamma globulin as specific plasma fraction. Am J Med Sci. 1950 Jun;219(6):660–663. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195006000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENSTELL H. H., FREEDMAN R. I., GINSBURG B. An inhibitor of desoxyribonuclease in human white blood and bone marrow cells, and its relationship to cellular maturity. Cancer Res. 1952 May;12(5):346–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENSTELL H. H., FREEDMAN R. I. The viscosimetric determination of desoxyribonuclease inhibition. Cancer Res. 1952 May;12(5):341–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
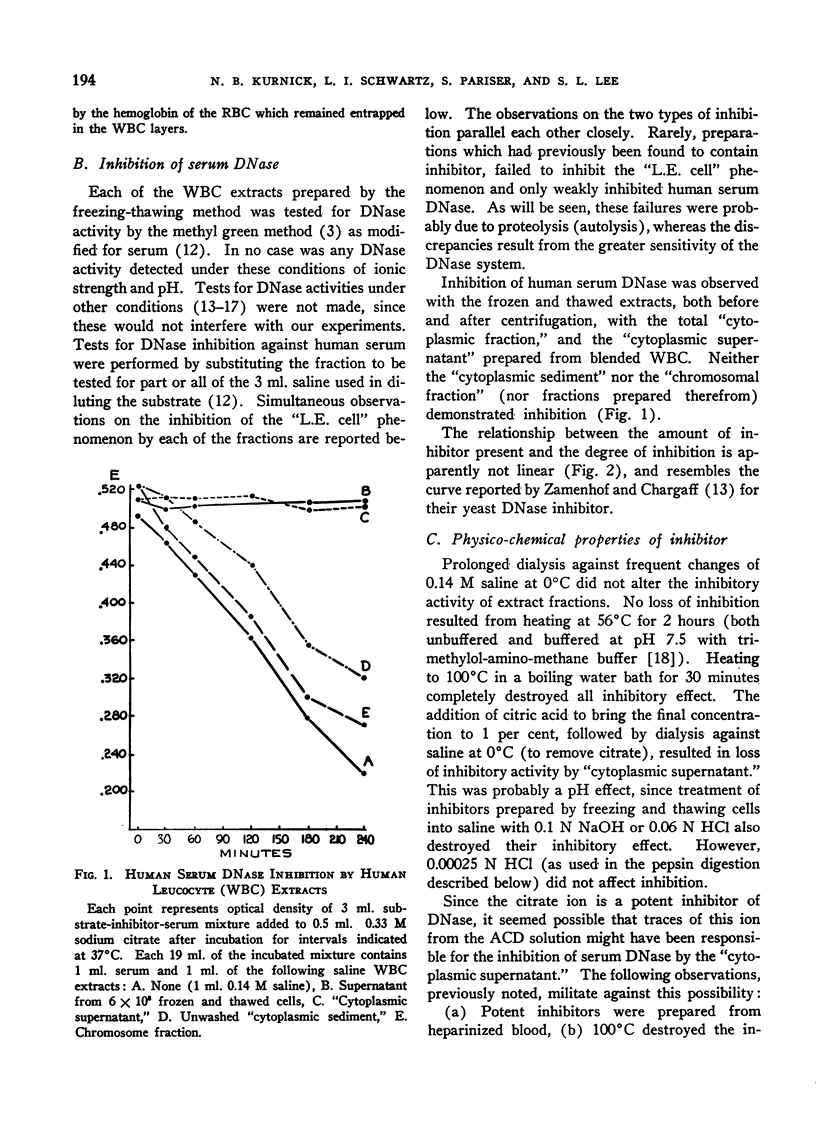
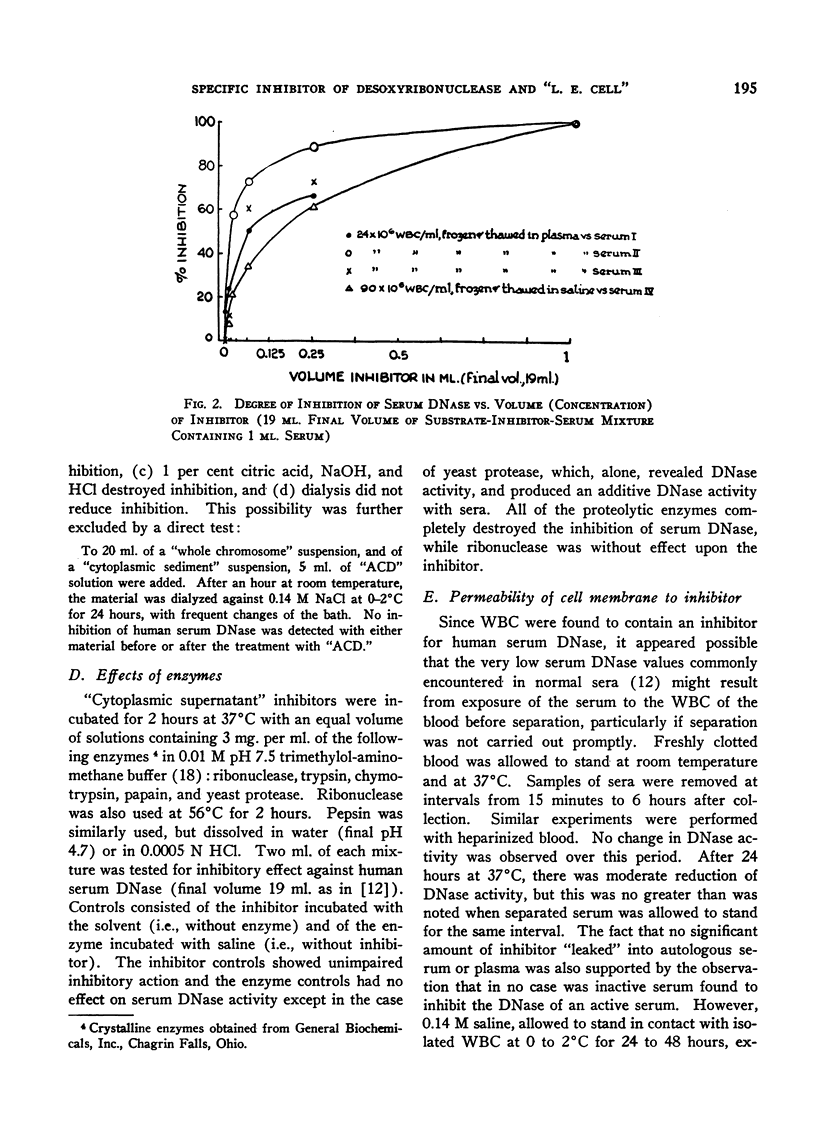
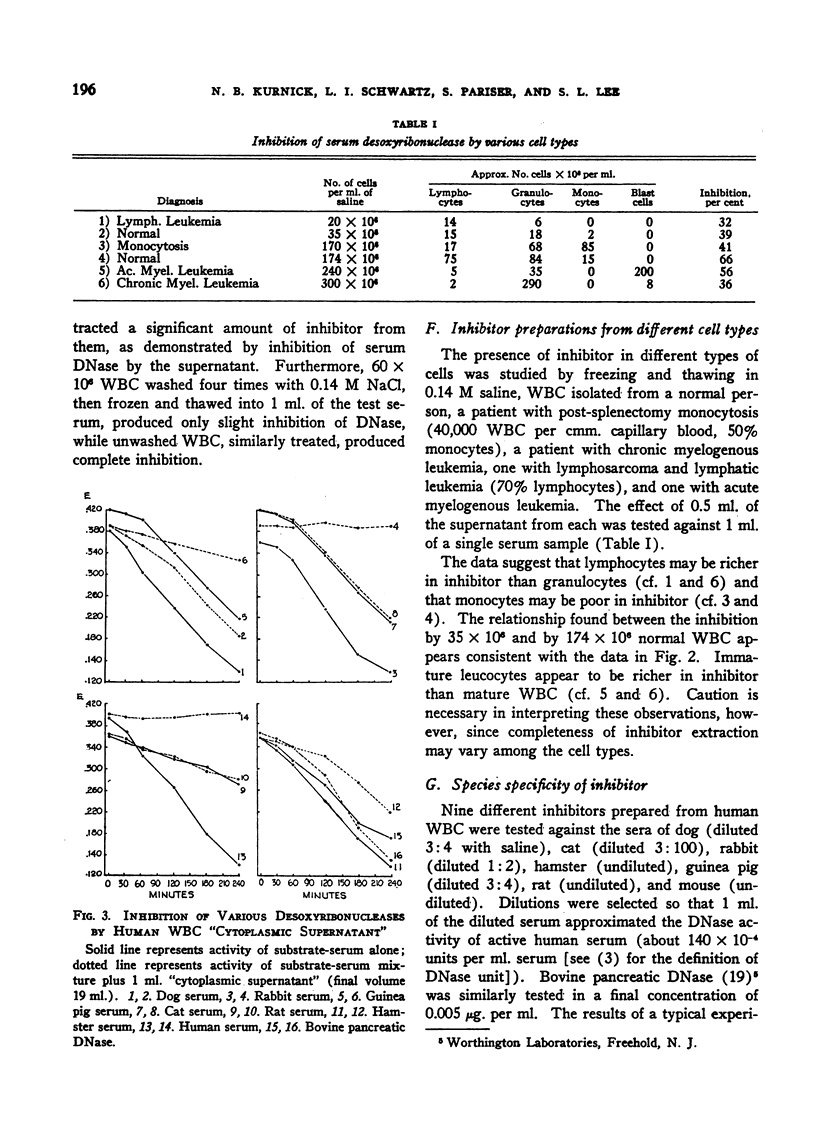
- KURNICK N. B., PARISER S., SCHWARTZ L. I., LEE S. L., IRVINE W. Studies on desoxyribonuclease in systemic lupus erythematosus; non-participation of serum desoxyribonuclease in the L.E. phenomenon. J Clin Invest. 1952 Dec;31(12):1036–1041. doi: 10.1172/JCI102696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURNICK N. B. The determination of desoxyribonuclease activity by methyl green; application to serum. Arch Biochem. 1950 Nov;29(1):41–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunitz M. Isolation of Crystalline Desoxyribonuclease From Beef Pancreas. Science. 1948 Jul 2;108(2792):19–20. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2792.19-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE S. L., MICHAEL S. R., VURAL I. L. The L.E. (lupus erythematosus) cell; clinical and chemical studies. Am J Med. 1951 Apr;10(4):446–451. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(51)90289-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAVER M. E., GRECO A. E. The nuclease activities of cathepsin preparations from calf spleen and thymus. J Biol Chem. 1949 Dec;181(2):861–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROHN R. J., BOND W. H. Some supravital observations on the L.E. phenomenon. Am J Med. 1952 Apr;12(4):422–432. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(52)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB M. Use of deoxyribonuclease inhibitors in the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acids. Nature. 1952 Mar 8;169(4297):417–417. doi: 10.1038/169417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


