Abstract
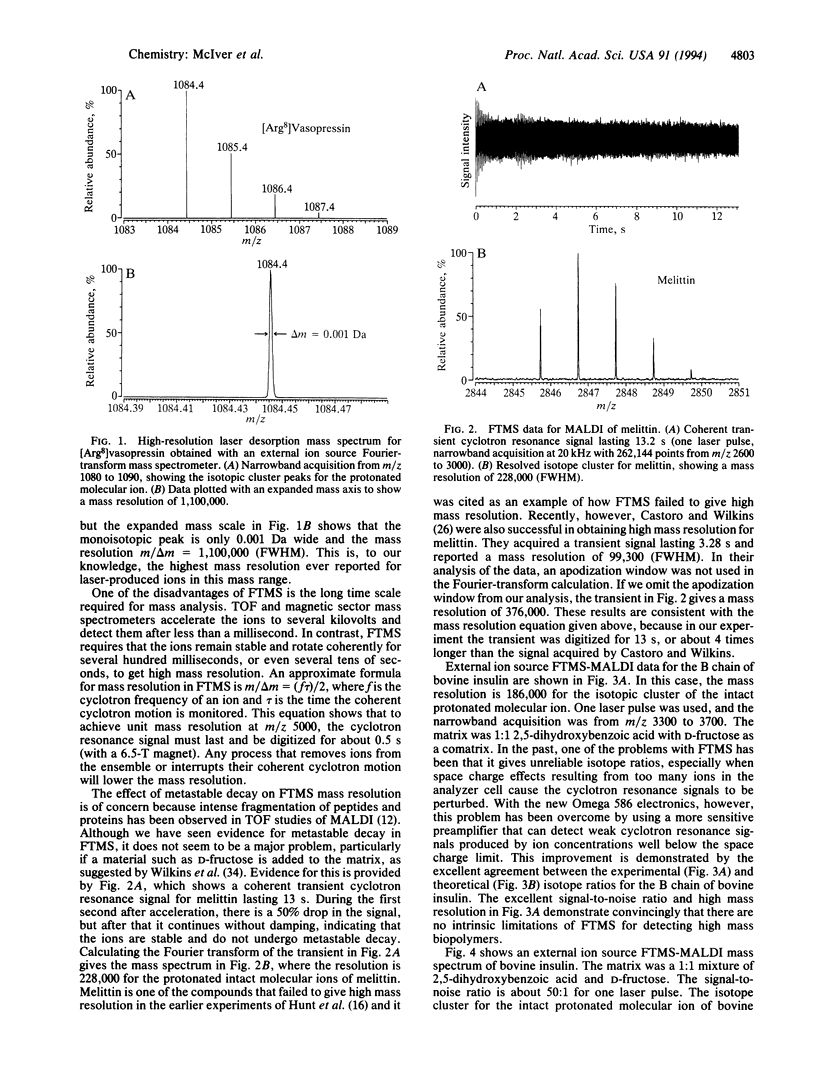
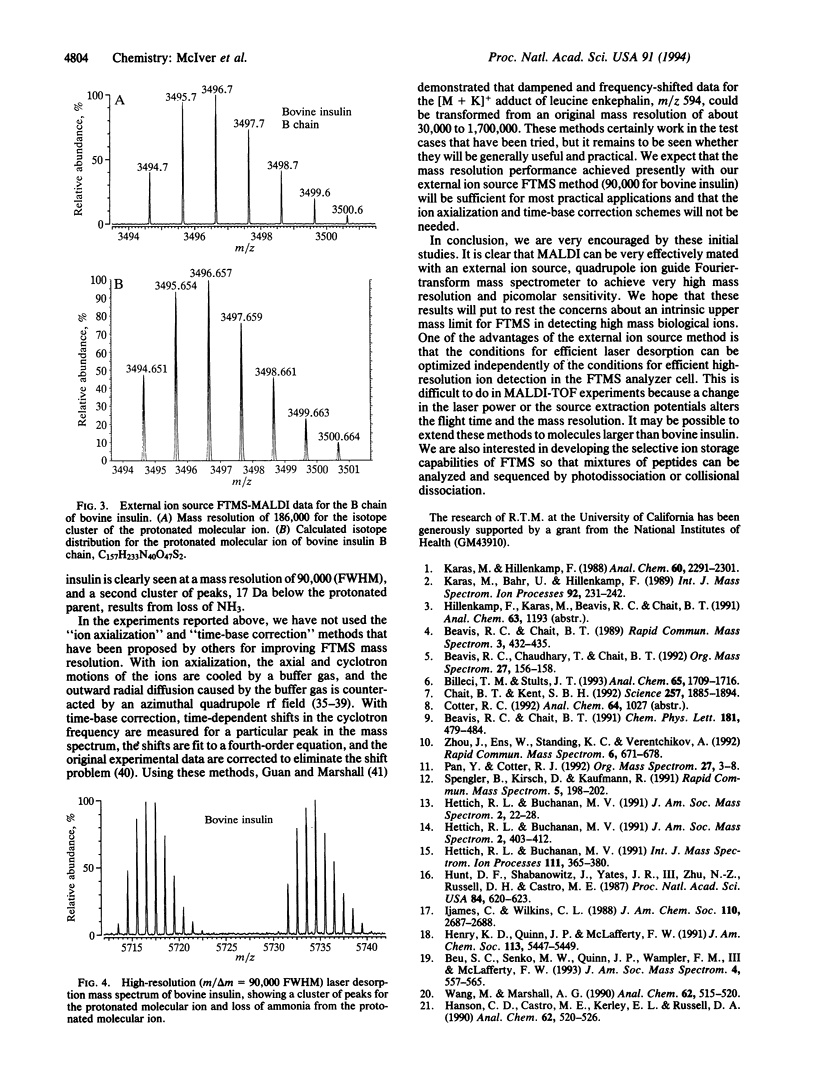
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) has been used with an external ion source Fourier-transform mass spectrometer to obtain the highest mass resolution ever, to our knowledge, demonstrated for laser-produced ions (m/delta m = 1,100,000 for [Arg8]vasopressin, 228,000 for melittin, and 90,000 for bovine insulin). The peaks in the isotope cluster for bovine insulin are fully resolved, and the mass measurement accuracy is an order of magnitude better than can be achieved with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. With the method described here, analyte is applied to a sample probe and mixed with a solution containing a matrix material (2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid) that strongly absorbs ultraviolet light. Upon irradiation with a pulse from an excimer laser (353 nm, 2 mJ), a large number of intact protonated molecular ions are produced. The ions are focused by a 117-cm-long quadrupole ion guide and injected into an ion cyclotron resonance analyzer cell located inside the bore of a 6.5-T superconducting magnet. A pulse of argon buffer gas cools the ions prior to detection. One of the principal advantages of an external ion source Fourier-transform mass spectrometer is that the ion formation and ion detection processes are separated and can be independently optimized.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beavis R. C., Chait B. T. Cinnamic acid derivatives as matrices for ultraviolet laser desorption mass spectrometry of proteins. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1989 Dec;3(12):432–435. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290031207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeci T. M., Stults J. T. Tryptic mapping of recombinant proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1993 Jul 1;65(13):1709–1716. doi: 10.1021/ac00061a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castoro J. A., Wilkins C. L. Ultrahigh resolution matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization of small proteins by Fourier transform mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1993 Oct 1;65(19):2621–2627. doi: 10.1021/ac00067a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro J. A., Köster C., Wilkins C. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization of high-mass molecules by Fourier-transform mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1992 Apr;6(4):239–241. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290060403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chait B. T., Kent S. B. Weighing naked proteins: practical, high-accuracy mass measurement of peptides and proteins. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1885–1894. doi: 10.1126/science.1411504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan S., Marshall A. G. Multiply pulsed collision gas for ion axialization in Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1993 Sep;7(9):857–860. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290070915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. F., Shabanowitz J., Yates J. R., 3rd, Zhu N. Z., Russell D. H., Castro M. E. Tandem quadrupole Fourier-transform mass spectrometry of oligopeptides and small proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):620–623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karas M., Hillenkamp F. Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10,000 daltons. Anal Chem. 1988 Oct 15;60(20):2299–2301. doi: 10.1021/ac00171a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrilla C. B., Wang D. T., Hunter R. L., McIver R. T., Jr Detection of mass 31,830 ions with an external ion source Fourier transform mass spectrometer. Anal Chem. 1990 Apr 15;62(8):878–880. doi: 10.1021/ac00207a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solouki T., Russell D. H. Laser desorption studies of high mass biomolecules in Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5701–5704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speir J. P., Gorman G. S., Pitsenberger C. C., Turner C. A., Wang P. P., Amster I. J. Remeasurement of ions using quadrupolar excitation Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1993 Jul 1;65(13):1746–1752. doi: 10.1021/ac00061a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. D., Marshall A. G. Elimination of z-ejection in Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry by radio frequency electric field shimming. Anal Chem. 1990 Mar 1;62(5):515–520. doi: 10.1021/ac00204a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Ens W., Standing K. G., Verentchikov A. Kinetic energy measurements of molecular ions ejected into an electric field by matrix-assisted laser desorption. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1992 Nov;6(11):671–678. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290061109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


