Abstract
Background
HOXA genes cluster plays a fundamental role in embryologic development. Deletion of the entire cluster is known to cause a clinically recognizable syndrome with mild developmental delay, characteristic facies, small feet with unusually short and big halluces, abnormal thumbs, and urogenital malformations. The clinical manifestations may vary with different ranges of deletions of HOXA cluster and flanking regions.
Case presentation
We report a girl with the smallest deletion reported to date involving the entire HOXA cluster at 7p15.2-p14.3. The patient was the third child born to a healthy and non-consanguineous Italian couple. She was born at the 34th week of gestation by caesarean section due to cholestasis of pregnancy. Her birth weight, length, and occipitofrontal circumference were 2,140 g (25-50th centile), 46 cm (50th centile), and 33 cm (75-90th centile), respectively. The Apgar scores were 8 at both the 1st and 5th minutes. The patient presented with typical mild facial anomalies, hand and feet abnormalities, urinary anomalies, and mild speech delay. Unexpectedly, the patient demonstrated complex unusual features of multiple episodes of oxyhemoglobin desaturation, laryngeal stridor and a branchial cyst. Chromosome analysis of the patient revealed an apparently normal karyotype at the 550 band level. Based on array comparative genomic hybridization, a 2.5 Mb interstitial deletion was detected at 7p15.2p14.3 (chr7: 26,333,553-28,859,312), involving the entire HOXA cluster and a small number of other genes as SNX10, SKAP2, EVX1, HIBADH, TAX1BP1, JAZF1, and CREB5.
Conclusions
This report improves our understanding of the genotype-phenotype correlations of HOXA genes cluster deletions via the identification and characterization of the smallest deletion (as well as critical region) reported to date. In particular we discuss the possible implications of preterm and haploinsufficiency in the pathogenesis of the unusual findings, furthermore opening new discussion and interpretation cues.
Keywords: HOXA, Speech delay, Hand-foot-genital syndrome, 7p15 deletion
Background
The homeobox (HOX) genes family consists of 39 genes, which encode transcription factors playing a fundamental role in proper embryologic development. Four HOX genes clusters have been identified on different chromosomal regions in humans, the HOXA on 7p15.3, HOXB on 17q21.3, HOXC on 12q13, and HOXD on 2q31 [1]. All these four clusters are members of highly conserved gene families that are essential for the development of central nervous system (CNS), axial skeleton, limbs, gut, hematopoietic and urogenital tract, and internal and external genitalia. A number of studies stated that HOX genes have partially overlapping expression patterns, and consequently a considerable functional redundancy in the cited tissues [2]. Consequently, full cluster deletion might reveal any HOX cluster-specific function.
Mice lacking all HOXA genes functions suffer from respiratory, cardiac and hematopoietic defects which cause early postnatal death [2]. Individual mutations in some HOXA genes as HOXA1, HOXA2, HOXA11, and HOXA13 are known to cause respectively Athabaskan brainstem dysgenesis syndrome (OMIM #601536), microtia, hearing impairment and cleft palate (OMIM #612290), radioulnar synostosis with amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia (OMIM #605432), and hand-foot-genital syndrome (HFGS, OMIM#140000) or Guttmacher syndrome (GUTTS OMIM #176305) [1].
Only a few studies have reported the heterogeneous chromosomal aberrations of the region 7p15-p14 [3-9]. Genotype-phenotype analyses suggest that deletions involving HOXA13 show HFGS features, which is characterized by small feet with unusually short and big toes and abnormal thumbs, and urogenital malformations. Smaller deletions of this region usually cause clinically recognizable symptoms and signs with mild developmental delay, characteristic facies, and HFGS, but larger deletions may cause more complex phenotypes, leading to difficulties of clinical diagnosis and interpretation [7-9].
Here we report a girl with a deletion of about 2.5 Mb at 7p15.2-p14.3 that contains the entire HOXA cluster. To the best of our knowledge, this is the smallest deletion involving HOXA genes reported to date. Unexpectedly, the patient demonstrated complex unusual features of multiple episodes of oxyhemoglobin desaturation and laryngeal stridor. The aim of this report is to compare this unusual case to previously reported HOXA cluster deletions in order to achieve a closer genotype-phenotype correlation of the only HOXA cluster deletion.
Case presentation
The patient was the third child born to a healthy and non-consanguineous Italian couple. The pregnancy was normal, except for platelet incompatibility between the mother and fetus, treated with periodic intravenous immunoglobulin from the 29th week of gestation. The girl was born at the 34th week of gestation by caesarean section due to cholestasis of pregnancy. Her birth weight, length, and occipitofrontal circumference were 2,140 g (25-50th centile), 46 cm (50th centile), and 33 cm (75-90th centile), respectively. The Apgar scores were 8 at both the 1st and 5th minutes. She received nasal continuous positive airways pressure (NCPAP) ventilation for the first six days due to frequent oxyhemoglobin desaturation, which recurred in the first months especially during feeding, but gradually improved. Bilateral frontal pseudocysts were detected by transfrontal ultrasonography and confirmed by brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). She suffered from bradycardia and sporadic supraventricular extrasystoles, without visible anomalies based on echocardiography examination. Renal ultrasonography detected bilateral bifid pelvis with left vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) of grade III. At night she suffered from laryngeal stridor that gradually improved and disappeared. A fibroscopy of the larynx was performed and excluded any structural defects of the larynx. She also suffered from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) that was improved by Omeprazole and Domperidone, but recurred at three years of age.
A poor growth was evident, while the psychomotor development was normal with the exception of a mild speech delay. The physical examination at 1 year of age showed short stature (<3rd centile, −2.5 SD) and relative macrocephaly (75-90th centile). She exhibited facial dysmorphisms such as frontal bossing, mild hypertelorism, short palpebral fissures, wide nasal bridge, long philtrum, thin lips, micrognathia, uplift of ear lobules, prominent anti-helix, and broad and short neck (Figure 1). She also showed small feet with brachydactyly. Ophthalmological or audiological involvement and genital anomalies were not detected, and complete blood count and chemistry panel were all within the normal range. Hand X-ray showed mild bilateral hypoplasia of the distal phalanges, especially of the first and second fingers (Figure 2). In addition, the parents noted a small cervical mass, which was identified as a branchial cyst by ultrasound examination. A clinical re-evaluation at 3 years of age confirmed the reported findings and the presence of a normal IQ with only an isolated mild speech delay, evaluated with Griffiths Mental Development Scales.
Figure 1.
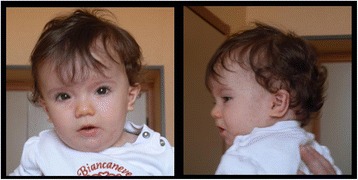
Characteristics of the facial gestalt of the patient: frontal bossing, mild hypertelorism, short palpebral fissures, wide nasal bridge, long philtrum, thin lips, micrognathia, prominent anti-helix, uplift of ear lobules, and broad and short neck.
Figure 2.
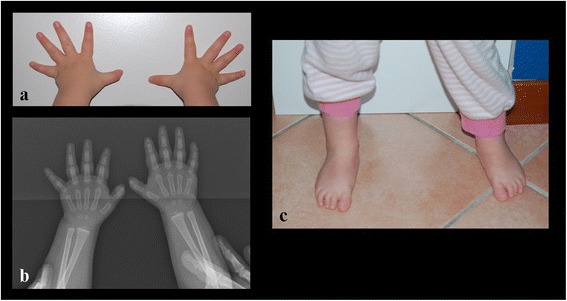
Hands showing tapering fingers and mild bilateral hypoplasia of the distal phalanges of the first and second finger (part a), confirmed by X-ray (part b); small feet with brachydactyly (part c).
Conventional karyotyping of peripheral blood lymphocytes was carried out according to the standard laboratory procedure. Chromosome analysis was performed at 550 banding level, according to the ISCN [10] and the European General Guidelines and Quality Assurance for Cytogenetics [11] and revealed an apparently normal karyotype. Based on a-CGH, a 2.5 Mb interstitial deletion was detected at 7p15.2p14.3 (chr7: 26,333,553-28,859,312), involving the entire HOXA cluster and a small number of other genes as SNX10, SKAP2, EVX1, HIBADH, TAX1BP1, JAZF1, and CREB5 (Figure 3). This deletion was not identified in her parents, indicating the de novo origin of the alteration. Submicroscopic genomic alterations were detected by array comparative genomic hybridization (a-CGH) on genomic DNA from peripheral blood lymphocytes, using Agilent SurePrint G3 human 8x60K kit according to the manufacture’s instruction. Data were analysed using CytoGenomics 2.0.6.0 (Agilent Technologies, Cernusco sul Naviglio, Milan, Italy). Aberrations were considered if at least three adjacent probes were involved. Copy number variations were not reported if they are listed in the Database of Genomic Variants (http://projects.tcag.ca/variation/). This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Milan, Italy, and written informed consent was obtained from patient’s parents.
Figure 3.
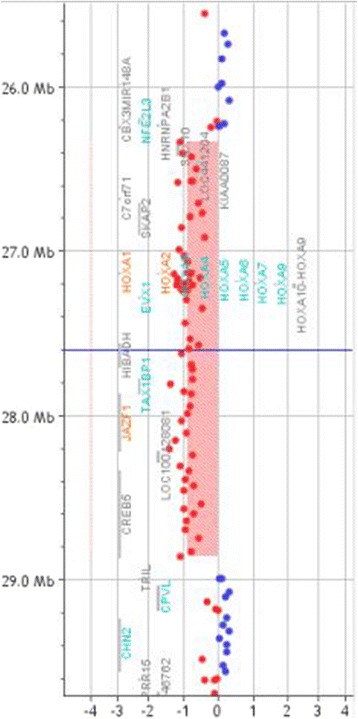
Array CGH results of the patient: a 2.5 Mb deletion at 7p15.2p14.3 involving the HOXA cluster genes. The breakpoints are according to the 37 build (March 2009) of the Human Genome Reference Consortium (GRch37/hg19).
Conclusions
All previously reported deletions involving HOXA13 show HFGS features, namely bilateral and symmetrical limb malformations with incompletely penetrant urogenital defects, and some additional findings in comparison to mutation of the single gene, such as mild dysmorphic facies, developmental delay, feeding difficulties in the first months of life, and mild intellectual disability. These observations are based on clinical findings of seven patients with deletions of about 8.8 ± 3.2 Mb (the deletion described by Kosaki [7], was detected by FISH, so the breakpoints are not available, but it was visible at G-banding chromosome analysis) encompassing the entire HOXA cluster (Figure 4; Table 1) [3-7]. Here we report a girl with a 2.5 Mb deletion at 7p15.2-p14.3, which is the smallest deletion among all previous reports, involving the entire HOXA cluster and seven additional genes.
Figure 4.

Overlapping deletions of the present and of the previous cases. The dotted line means that the exact breakpoints of these patients are unknown (Kasaki [7] and Devriendt [5]). The new smallest region of overlap (26,408,229-28,859,312) is defined by the distal breakpoint of the deletion of Dunø’s patient 2 n and the proximal breakpoint of the aberration of the present case. The breakpoints are according to the 37 build (March 2009) of the Human Genome Reference Consortium (GRch37/hg19).
Table 1.
Genetic and clinical features of the patients included in this study and previous reports
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 | Patient 7 | Patient 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present case 3y, female | Devriendt et al., 1999 [ 5 ] 21y, male | Dunø et al., 2004 [ 6 ] 5y, female | Dunø et al., 2004 [ 6 ] 4y, male | Kosaki et al., 2005 [ 7 ] 1y, male | Jun et al., 2011 [ 3 ] 4y, male | Hosoki et al., 2012 [ 4 ] 13y, male | Fryssira et al., 2011 [ 8 ] 2y, male | |
| Chromosomal deletion | 7p15.2p14.3 | 7p15.3p14.2 | 7p15.3p14.3 | 7p15.2p14.2 | 7p15.2p21 | 7p15.3p15.1 | 7p15.3p15.1 | 7p21.1p14.3 |
| Size (Mb) | 2.5 | 12 | 9,8 | 9 | NA | 5,6 | 6,9 | 13 |
| Inheritance | De novo | De novo | De novo | De novo | De novo | De novo | De novo | De novo |
| Neonatal feeding problem | Yes, due to GERD | Yes, due to velopharingeal insufficiency | NA | NA | NA | Yes, due to dysphagia | Yes | Yes, due to GERD |
| Developmental delay | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Intellectual disability | No | Borderline IQ | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Speech delay | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ear anomalies | Uplift of ear lobules, hyperplastic anti-helix | Low-set, malformed | NA | Short, slightly deformed | Prominent ear crus | Low-set, posterior angulated, mild EAM stenosis | Low-set, posterior rotated | Low-set, Helix hypoplasia, hyperplastic anti-helix and anti-tragus, prominent intertragic notch |
| Palpebral fissures | Short | Upslanted | Upslanted | Dowslanted | NA | Upslanted | No | Short, epicanthic folds, ptosis |
| Other facial anomalies | Frontal bossing, mild hypertelorism, wide nasal bridge, long philtrum, thin lips, micrognathia, short neck | Retrognathia, upturned nostrils, large mouth | Flat nasal bridge, broad nose, anteverted nostrils, broad lips | Broad neck | Depressed supraorbital ridge on the left, maxillary hypoplasia | Flat nasal bridge, frontal bossing | Bifrontal narrowing | Asymmetry, hypertelorism, low nasal bridge, anteverted nostrils, long and smooth philtrum, short neck |
| Small hands and feet | Small feet | NA | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Clinodactyly | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Other fingers anomalies | Hypoplasia of distal phalanges of thumbs and 2nd fingers | Pointed distal phalanx | Short fingers | Short fingers | Hypoplasia of 5th fingers | Limited extension | No | Digital webbing and abnormal hand creases |
| Great toe anomalies | No | Shortened, laterally deviated | Short and broad | NA | No | Hypoplasia | Curved and broad | Relatively long, broad and medially deviated |
| Other toes anomalies | Short toes | Triangular distal phalanx | NA | Short toes, pes planus | No | No | Short | Short |
| Genital anomalies | No | Cryptorchidism, ventral-bowed penis | NA | No | Rectoperineal fistula | Hypospadia | No | Hypospadia, left cryptorchidism and scrotum hypoplasia |
| Urinary anomalies | Bifid pelvis with left VUR | No | No | No | No | No | No | Moderate renal insufficiency |
| Velopharyn-geal anomalies | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Heart malformations | No, only bradycardia and sporadic supraventricular extrasystoles | Patent ductus Botalli | No | No | Patent ductus arteriosus | Patent ductus arteriosus, partial pulmonary venous return | No | Open foramen ovale, aortic insufficiency |
| Other features | Desaturation episodes, GERD, stridor | No | No | Hypermetropia | Anal atresia, cranio-synostosis | Accessory nipples | No | Craniosynostosis, desaturation episodes (abnormal sleep EEG) |
EAM: external acoustic meatus; GERD: gastroesophageal reflux; IQ: intelligence quotient; y: year-old; NA: not available; VUR: vesicoureteral reflux; EEG: electroencephalogram.
Hosoki [4] tried to compare the previous reports and found a small region of overlap (SRO; chr7: 26,374,754-29,360,960) involving nine genes plus the HOXA cluster, and defined it as the critical region. This region almost completely overlaps the alteration of our patient, but exceeds 535 kb containing 2 more genes (CVPL and CHN2). So, we can now redefine and reduce the former critical region.
The girl in the present study showed a number of typical manifestations of HOXA13 deletion, such as speech delay, short stature (below the 3rd centile), VUR, small feet with brachydactyly, bilateral mild hypoplasia of distal phalanges of some fingers of the hands, and some mildly dysmorphic facial features that were highly similar to the case 2 reported by Dunø [6].
In the present study, the psychomotor development of the patient was normal, except for a mild speech delay. It is notable that different degrees of intellectual impairments have been reported to date, that goes from borderline [4,5] or even normal IQ, to severe disability [3].
Interestingly, our patient exhibited a number of additional features, such as bradycardia and sporadic supraventricular extrasystoles in absence of heart malformations, GERD, oxyhemoglobin desaturation during feeding, and laryngeal stridor. These manifestations, together with frontal pseudocysts, may be related to preterm delivery. Respiratory distress caused by oxyhemoglobin desaturation [12], especially during feeding, as well as GERD, bradycardia [13], and frontal pseudocysts, are indeed well documented in preterms [14]. However, interestingly, one of the HOXA genes, HOXA5, is known to be essential for organogenesis and function of respiratory tracts [15]. Moreover in homozygous newborn mutant mice, abnormal morphogenesis of respiratory tracts and tracheal occlusion have been observed, which led to respiratory distress immediately after birth [15].
Loss of HOXA3 function in mouse results in larynx anomalies that are similar to the phenotypes caused by HOXA5 mutations. Homozygous defects of HOXA3 actually seem to cause lethal cardiovascular dysfunctions, loss and malformations of throat cartilages and jaw bones, disorganization of the throat musculature, absent thymus and parathyroids, and thyroid hypoplasia [16,17], while heterozygous defects are associated to ectopic thymus and/or parathyroids [18] so haploinsufficiency of this gene has been suggested [5] as the cause of these anomalies. The presence of a cervical branchial cyst in our patient, never pointed out in the previous reported cases, is intriguing too, given the cited role of HOXA3 in the differentiation of neck tissues.
The previously reported cases of velopharyngeal insufficiency and dysphagia [3,5], and the manifestations of our patient may be related to the haploinsufficiency of HOXA3 and/or HOXA5 as already stated by Devriendt [5]; alternatively in our case, they may be explained by the additive effects of haploinsufficiency and mild prematurity.
Concerning the other genes involved in our deletion, only JAZF1 and SNX10 were designated as morbid genes, according to the OMIM database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/). JAZF1 is known as participant in the fusion gene resulting from recurrent t(7;17) (p15;q21) translocation in endometrial stromal sarcoma [19], while homozygous mutations in SNX10 cause autosomal recessive Osteopetrosis [20].
It is notable that in 2004 Lehoczky et al. [21] demonstrated that EVX1, HIBADH, TAX1BP, JAZF1 and CREB5 show embryonic distal limb and genital bud expression, but at this time it is not known whether they have a role in their development.
In conclusion, this report improves our understanding of the genotype-phenotype correlations of HOXA genes cluster deletions via the identification and characterization of the smallest deletion (as well as critical region) reported to date, furthermore opening new discussion and interpretation cues on the unusual findings outlined.
Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s parents for publication of this Case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor of this journal.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patient and her parents for allowing us to publish this case report.
Abbreviations
- a-CGH
array comparative genomic hybridization
- CNS
Central nervous system
- GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- GUTTS
Guttmacher syndrome
- HFGS
Hand-foot-genital syndrome
- HOX
Homeobox
- MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NCPAP
Nasal continuous positive airways pressure
- SRO
Small region of overlap
- VUR
Vesicoureteral reflux
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
LP, DM, and FM drafted the manuscript. MB, RS and SG performed the analysis and interpretation of data. SE revised the manuscript and made substantial scientific contributions. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Contributor Information
Lidia Pezzani, Email: lidia.pezzani@unimi.it.
Donatella Milani, Email: donatella.milani@policlinico.mi.it.
Francesca Manzoni, Email: fmp.manzoni@gmail.com.
Marco Baccarin, Email: marco.baccarin@policlinico.mi.it.
Rosamaria Silipigni, Email: rosamaria.silipigni@unimi.it.
Silvana Guerneri, Email: s.guerneri@policlinico.mi.it.
Susanna Esposito, Email: susanna.esposito@unimi.it.
References
- 1.Quinonez SC, Innis JW. Human HOX gene disorders. Mol Genet Metab. 2014;111:4–15. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Di-Poï N, Koch U, Radtke F, Duboule D. Additive and global functions of HoxA cluster genes in mesoderm derivatives. Dev Biol. 2010;341:488–498. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jun KR, Seo EJ, Lee JO, Yoo HW, Park IS, Yoon HK. Molecular cytogenetic and clinical characterization of a patient with a 5.6-Mb deletion in 7p15 including HOXA cluster. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155:642–647. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hosoki K, Ohta T, Fujita K, Nishigaki S, Shiomi M, Niikawa N, et al. Hand-foot-genital syndrome with a 7p15 deletion: clinically recognizable syndrome. Pediatr Int. 2012;54:22–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200X.2011.03550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Devriendt K, Jaeken J, Matthijs G, Van Esch H, Debeer P, Gewillig M, et al. Haploinsufficiency of the HOXA gene cluster, in a patient with hand-foot-genital syndrome, velopharyngeal insufficiency, and persistent patent Ductus botalli. Am J Hum Genet. 1999;65:249–251. doi: 10.1086/302452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dunø M, Hove H, Kirchhoff M, Devriendt K, Schwartz M. Mapping genomic deletions down to the base: a quantitative copy number scanning approach used to characterise and clone the breakpoints of a recurrent 7p14.2p15.3 deletion. Hum Genet. 2004;115:459–467. doi: 10.1007/s00439-004-1174-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kosaki R, Higuchi M, Mitsui N, Matsushima K, Ohashi H, Kosaki K. Deletion involving the TWIST locus and the HOXA cluster: a contiguous gene syndrome on 7p? Congenit Anom. 2005;45:35–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-4520.2005.00059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fryssira H, Makrythanasis P, Kattamis A, Stokidis K, Menten B, Kosaki K, et al. Severe Developmental Delay in a Patient with 7p21.1–p14.3 Microdeletion Spanning the TWIST Gene and the HOXA Gene Cluster. Mol Syndromol. 2011;2:45–49. doi: 10.1159/000334313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hoover-Fong JE, Cai J, Cargile CB, Thomas GH, Patel A, Griffin CA, et al. Facial dysgenesis: a novel facial syndrome with chromosome 7 deletion p 15.1–21.1. Am J Med Genet A. 2003;117:47–56. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.10046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shaffer LG, McGowan-Jordan J, Schmid M. ISCN (2013): An International system for human cytogenetic nomenclature. Basel: S. Karger; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hastings RJ, Cavani S, Bricarelli FD, Patsalis PC, Kristoffersson U, ECA PWG Co-ordinators Cytogenetic guidelines and quality assurance: a common European framework for quality assessment for constitutional and acquired cytogenetic investigations. Eur J Hum Genet. 2007;15:525–527. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hammerman C, Kaplan M. Oxygen saturation during and after feeding in healthy term infants. Biol Neonate. 1995;67:94–99. doi: 10.1159/000244149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Abu Jawdeh EG, Martin RJ. Neonatal apnea and gastroesophageal reflux (GER): is there a problem? Early Hum Dev. 2013;89:14–16. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3782(13)70005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pal BR, Preston PR, Morgan ME, Rushton DI, Durbin GM. Frontal horn thin walled cysts in preterm neonates are benign. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal. 2001;85:187–93. doi: 10.1136/fn.85.3.F187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Aubin J, Lemieux M, Tremblay M, Bérard J, Jeannotte L. Early postnatal lethality in Hoxa-5 mutant mice is attributable to respiratory tract defects. Dev Biol. 1997;192:432–445. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1997.8746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chisaka O, Capecchi MR. Regionally restricted developmental defects resulting from targeted disruption of the mouse homeobox gene hox-1.5. Nature. 1991;350:473–479. doi: 10.1038/350473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Manley NR, Capecchi MR. The role of Hoxa-3 in mouse thymus and thyroid development. Development. 1995;121:1989–2003. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.7.1989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chojnowski JL, Masuda K, Trau HA, Thomas K, Capecchi M, Manley NR. Multiple roles for HOXA3 in regulating thymus and parathyroid differentiation and morphogenesis in mouse. Development. 2014;19:3697–3708. doi: 10.1242/dev.110833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Koontz JI, Soreng AL, Nucci M, Kuo FC, Pauwels P, van Den Berghe H, et al. Frequent fusion of the JAZF1 and JJAZ1 genes in endometrial stromal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:6348–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.101132598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pangrazio A, Fasth A, Sbardellati A, Orchard PJ, Kasow KA, Raza J, et al. SNX10 mutations define a subgroup of human autosomal recessive osteopetrosis with variable clinical severity. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28:1041–1049. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lehoczky JA, Williams ME, Innis JW. Conserved expression domains for genes upstream and within the HoxA and HoxD clusters suggests a long-range enhancer existed before cluster duplication. Evol Dev. 2004;6:423–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2004.04050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


