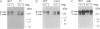Abstract
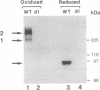
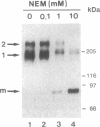
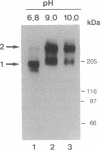
In Drosophila embryos dorsoventral polarity is determined by a concentration gradient of dorsal (dl) protein in the nuclei formed by the differential regulation of nuclear localization of dl protein. cactus (cact) represses the nuclear localization of dl protein. By introducing intermolecular disulfide bonds in homogenates of embryos, we detected three complexes of dl and/or cact proteins. Complex 1 (190 kDa) is a dl protein homodimer (dl2). Complex 2 (270 kDa) consists of one complex 1 and one cact molecule (dl2cact). Complex 3 (200 kDa) is a cact protein complex that does not contain dl protein. In wild-type embryos dl2cact was detected as the major form of dl protein, and dl2 was minor. With this assay virtually no dl monomer is detected. Analysis of the dl protein complexes in ventralized and dorsalized mutant embryos indicates that dl2cact is a cytoplasmic form, whereas dl2 is localized mainly in the nuclei. It seems that a small amount of dl2 is also present in the cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank V., Kourilsky P., Israël A. NF-kappa B and related proteins: Rel/dorsal homologies meet ankyrin-like repeats. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Apr;17(4):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90321-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Disulfide bond formation in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:305–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler R., Bergmann A., Hiromi Y., Nüsslein-Volhard C. cactus, a gene involved in dorsoventral pattern formation of Drosophila, is related to the I kappa B gene family of vertebrates. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):613–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D. Malignant transformation by mutant Rel proteins. Trends Genet. 1991 Oct;7(10):318–322. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90421-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good N. E., Izawa S. Hydrogen ion buffers. Methods Enzymol. 1972;24:53–68. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(72)24054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govind S., Whalen A. M., Steward R. In vivo self-association of the Drosophila rel-protein dorsal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7861–7865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel T., Machleidt T., Alkalay I., Krönke M., Ben-Neriah Y., Baeuerle P. A. Rapid proteolysis of I kappa B-alpha is necessary for activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):182–185. doi: 10.1038/365182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Kraut R., Levine M., Rushlow C. A. The dorsal morphogen is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that interacts with a long-range repression element in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90651-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isoda K., Roth S., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The functional domains of the Drosophila morphogen dorsal: evidence from the analysis of mutants. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):619–630. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Kosman D., Ip Y. T., Levine M. The dorsal morphogen gradient regulates the mesoderm determinant twist in early Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1881–1891. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S. Characterization of the Drosophila cactus locus and analysis of interactions between cactus and dorsal proteins. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):623–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90596-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letsou A., Alexander S., Orth K., Wasserman S. A. Genetic and molecular characterization of tube, a Drosophila gene maternally required for embryonic dorsoventral polarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):810–814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan D. J., Huang J. D., Courey A. J. Functional analysis of the Drosophila twist promoter reveals a dorsal-binding ventral activator region. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1892–1901. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Hiromi Y., Godt D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. cactus, a maternal gene required for proper formation of the dorsoventral morphogen gradient in Drosophila embryos. Development. 1991 Jun;112(2):371–388. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.2.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Stein D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. A gradient of nuclear localization of the dorsal protein determines dorsoventral pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1189–1202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Han K., Manley J. L., Levine M. The graded distribution of the dorsal morphogen is initiated by selective nuclear transport in Drosophila. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1165–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. S., Hudson K. L., Lin T. Y., Anderson K. V. Dominant and recessive mutations define functional domains of Toll, a transmembrane protein required for dorsal-ventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):797–807. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Relocalization of the dorsal protein from the cytoplasm to the nucleus correlates with its function. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1179–1188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90773-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisse C., Perrin-Schmitt F., Stoetzel C., Thisse B. Sequence-specific transactivation of the Drosophila twist gene by the dorsal gene product. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1191–1201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90014-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]