Abstract
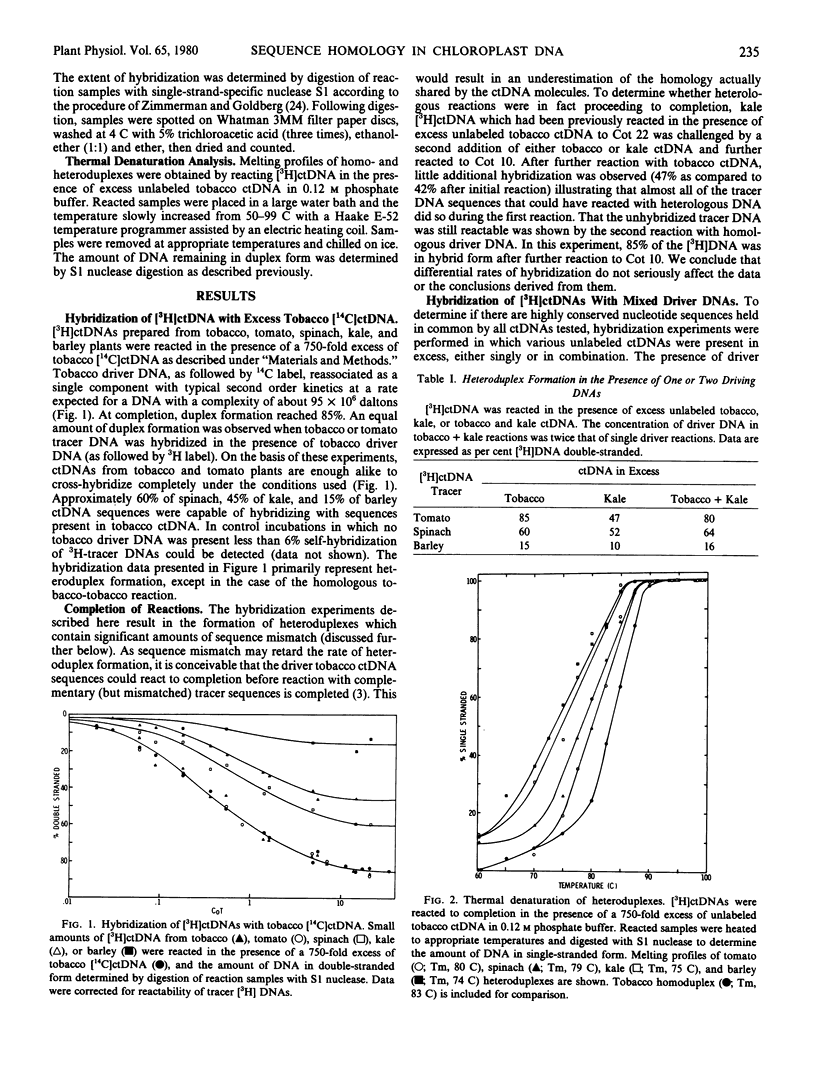
An estimate has been made of the amount of sequence homology present in the chloroplast DNA (ctDNA) of several higher plants by the technique of DNA-DNA hybridization. Approximately 85% of tomato, 60% of spinach, 45% of kale, and 15% of barley ctDNA sequences were found to hybridize with tobacco ctDNA under conditions in which maximum hybridization in homologous reactions reached 85%. All heteroduplexes contained significant amounts of sequence mismatch as indicated by a 3 to 9 C decrease in melting temperature as compared to homoduplex.
The data suggest that considerable sequence homology exists between the ctDNAs of these plants and that some sequences are held in common among all of the species tested.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedbrook J. R., Kolodner R., Bogorad L. Zea mays chloroplast ribosomal RNA genes are part of a 22,000 base pair inverted repeat. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Brenner D. J., Neufeld B. R., Britten R. J. Reduction in the rate of DNA reassociation by sequence divergence. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 5;81(2):123–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley W., Spencer D., Whitfeld P. R. Protein synthesis in isolated spinach chloroplasts: comparison of light-driven and ATP-driven synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Sep;164(1):106–117. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Graham D. E., Neufeld B. R. Analysis of repeating DNA sequences by reassociation. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:363–418. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. H., Wildman S. G. Chloroplast DNA codes for the primary structure of the large subunit of fraction I protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 14;277(3):677–680. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Bedbrook J. R., Bogorad L., Rich A. Maize chloroplast DNA fragment encoding the large subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haff L. A., Bogorad L. Hybridization of maize chloroplast DNA with transfer ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):4105–4109. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk J. T. Chloroplast structure and biogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:161–196. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung S. D., Lee C. I. Evolutionary conservation of chloroplast genes coding for the large subunits of fraction 1 protein. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jul;60(1):89–94. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. Y., Wildman S. G. Evolutionary divergence in the two kinds of subunits of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase isolated from different species of Nicotiana. J Mol Evol. 1974;3(2):103–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01796555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamppa G. K., Bendich A. J. Chloroplast DNA Sequence Homologies among Vascular Plants. Plant Physiol. 1979 Apr;63(4):660–668. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.4.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macgregor H. C., Mizuno S. In situ hybridization of "nick-translated" 3H-ribosomal DNA to chromosomes from salamanders. Chromosoma. 1976 Jan 27;54(1):15–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00331829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozek C. E., Orr W. C., Timberlake W. E. Diversity and abundance of polyadenylated RNA from Achlya ambisexualis. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):716–722. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari K. K., Wildman S. G. Chloroplast DNA from tobacco leaves. Science. 1966 Sep 9;153(3741):1269–1271. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3741.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari K. K., Wildman S. G. Function of chloroplast DNA. I. Hybridization studies involving nuclear and chloroplast DNA with RNA from cytoplasmic (80S) and chloroplast (70S) ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):569–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. R., Tewari K. K. Conservation of 70S ribosomal RNA genes in the chloroplast DNAs of higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3147–3151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walbot V. The dimorphic chloroplasts of the C4 plant Panicum maximum contain identical genomes. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


