Abstract
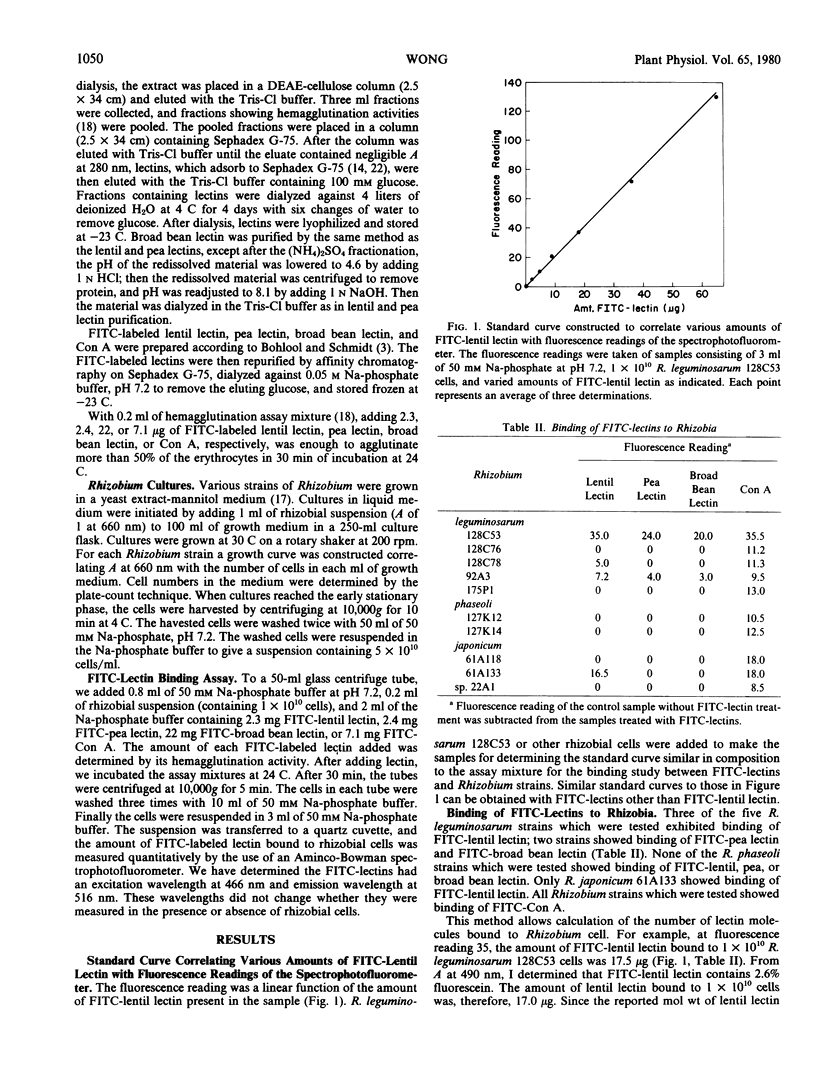
A quantitative method was developed to measure the binding of fluorescent-labeled lentil (Lens esculenta Moench), pea (Pisum sativum L.), broad bean (Vicia faba L.), and jackbean (Canavalia ensiformis L., DC.) lectins to various Rhizobium strains. Lentil lectin bound to three of the five Rhizobium leguminosarum strains tested. The number of lentil lectin molecules bound per R. leguminosarum 128C53 cell was 2.1 × 104. Lentil lectin also bound to R. japonicum 61A133. Pea and broad bean lectins bound to only two of the five strains of R. leguminosarum, whereas concanavalin A (jackbean lectin) bound to all strains of R. leguminosarum, R. phaseoli, R. japonicum, and R. sp. tested. Since these four lectins have similar sugarbinding properties but different physical properties, the variation in bindings of these lectins to various Rhizobium strains indicates that binding of lectin to Rhizobium is determined not only by the sugar specificity of the lectin but also by its physical characteristics.
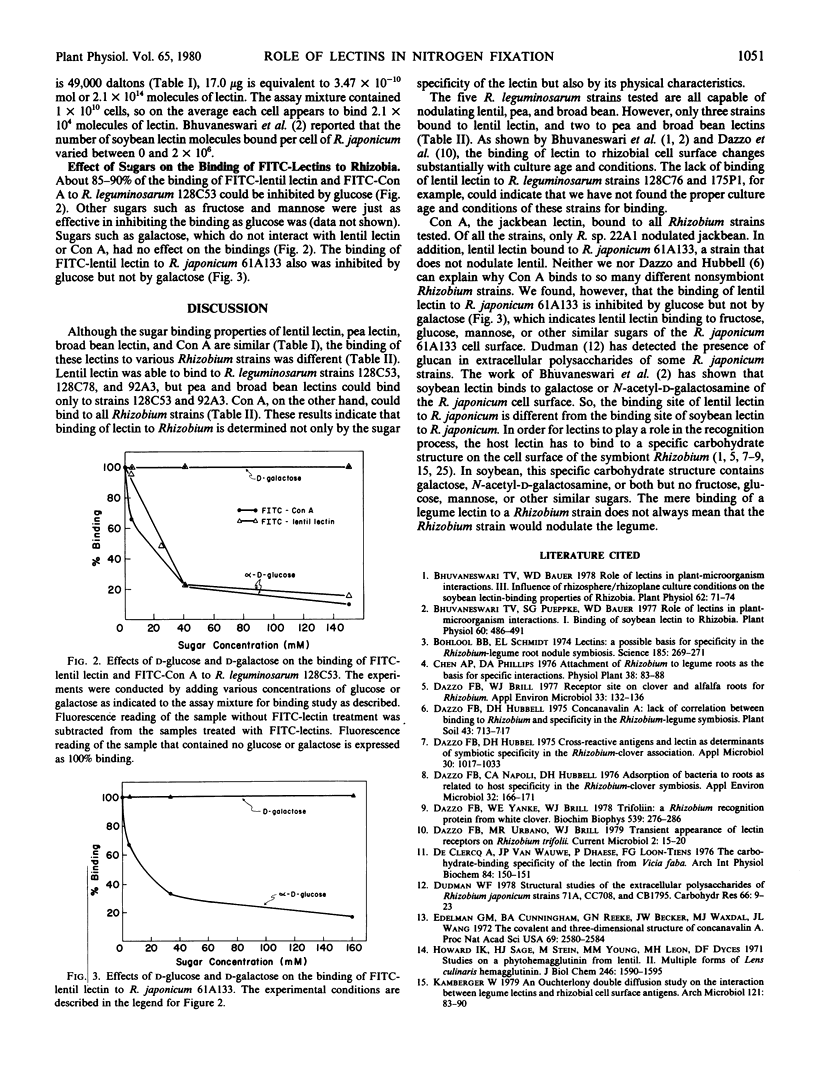
The binding of lentil lectin and concanavalin A to R. leguminosarum 128C53 could be inhibited by glucose, fructose, and mannose. However, even at 150 millimolar glucose, about 15% of the binding remained. The binding of lentil lectin to R. japonicum 61A133 could be inhibited by glucose but not by galactose. It is concluded that the binding site of lentil lectin to R. japonicum is different from the binding site of soybean lectin to R. japonicum.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Bauer W. D. Role of Lectins in Plant-Microorganism Interactions: III. Influence of Rhizosphere/Rhizoplane Culture Conditions on the Soybean Lectin-binding Properties of Rhizobia. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):71–74. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Pueppke S. G., Bauer W. D. Role of lectins in plant-microorganism interactions: I. Binding of soybean lectin to rhizobia. Plant Physiol. 1977 Oct;60(4):486–491. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.4.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Lectins: a possible basis for specificity in the Rhizobium--legume root nodule symbiosis. Science. 1974 Jul 19;185(4147):269–271. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4147.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Brill W. J. Receptor site on clover and alfalfa roots for Rhizobium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):132–136. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.132-136.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Hubbell D. H. Cross-reactive antigens and lectin as determinants of symbiotic specificity in the Rhizobium-clover association. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):1017–1033. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.1017-1033.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Napoli C. A., Hubbell D. H. Adsorption of bacteria to roots as related to host specificity in the Rhizobium-clover symbiosis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.166-171.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Yanke W. E., Brill W. J. Trifolin: a Rhizobium recognition protein from white clover. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 20;539(3):276–286. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq A., Van Wauwe J. P., Dhaese P., Loontiens F. G. Proceedings: The carbohydrate-binding specificity of the lectin from Vicia faba. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1976 Feb;84(1):150–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A., Reeke G. N., Jr, Becker J. W., Waxdal M. J., Wang J. L. The covalent and three-dimensional structure of concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2580–2584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard I. K., Sage H. J., Stein M. D., Young N. M., Leon M. A., Dyckes D. F. Studies on a phytohemagglutinin from the lentil. II. Multiple forms of Lens culinaris hemagglutinin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1590–1595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manhart J. R., Wong P. P. Nitrate reductase activities of rhizobia and the correlation between nitrate reduction and nitrogen fixation. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Oct;25(10):1169–1174. doi: 10.1139/m79-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto I., Osawa T. Purification and characterization of an anti-H(O) phytohemagglutinin of Ulex europeus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 11;194(1):180–189. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planqué K., Kijne J. W. Binding of pea lectins to a glycan type polysaccharide in the cell walls of Rhizobium leguminosarum. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):64–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So L. L., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. XX. On the number of combining sites on concanavalin A, the phytohemagglutinin of the jack bean. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 15;165(3):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein M. D., Howard I. K., Sage H. J. Studies on a phytohemagglutinin from the lentil. IV. Direct binding studies of Lens culinaris hand myoglobin derivatives. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Sep;146(1):353–355. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(71)80074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S. Isolation and chemical characterization of a mitogenic lectin from Pisum sativum. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):6004–6012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. L., Becker J. W., Reeke G. N., Jr, Edelman G. M. Favin, a crystalline lectin from Vicia faba. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert J. S., Albersheim P. Host-symbiont interactions. I. The lectins of legumes interact with the o-antigen-containing lipopolysaccharides of their symbiont Rhizobia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


