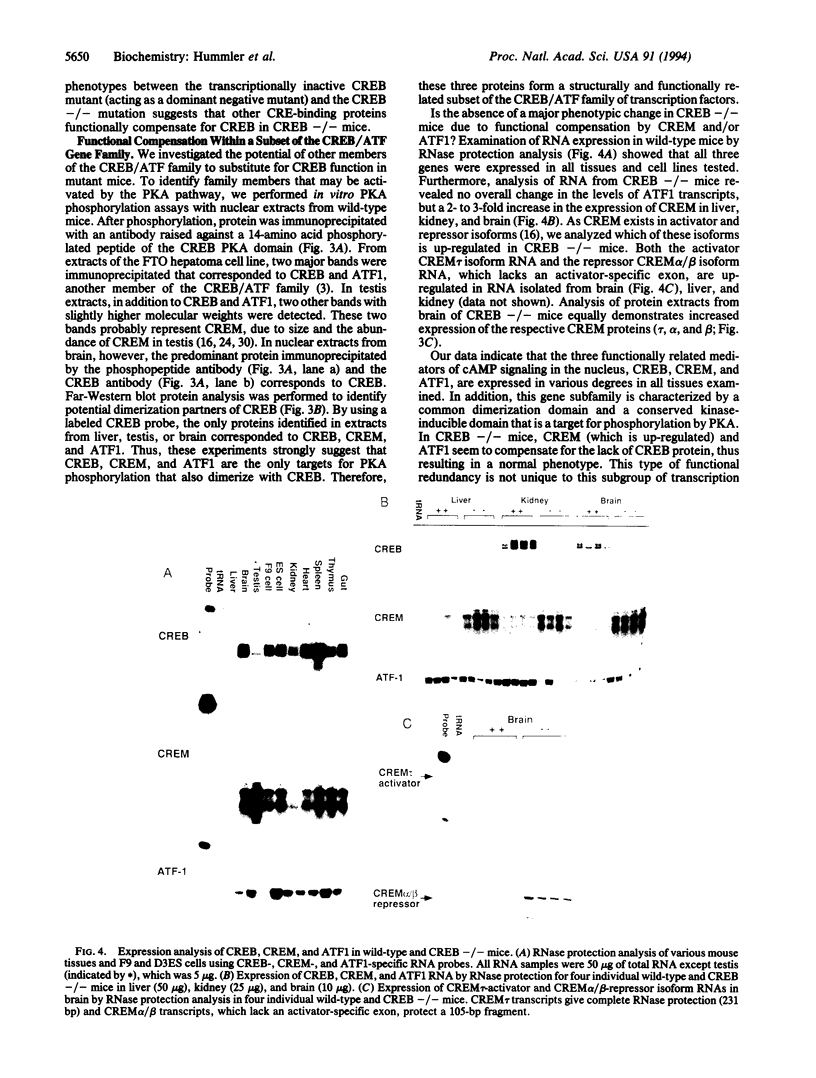
Abstract
The cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) has been implicated as a key regulator in the transcriptional control of many genes. To assess the functional importance of CREB in vivo and its role in development, we used gene targeting to generate mice with a disruption of the CREB gene. Homozygous mutant mice appeared healthy and exhibited no impairment of growth or development. In this report we demonstrate that CREB and two other members of the CREB/ATF family, cAMP response element modulation protein (CREM) and activating transcription factor 1 (ATF1), appear to form a unique subgroup within this extensive class of transcription factors. Examination of CREM mRNA and protein levels in CREB mutant mice demonstrated overexpression of CREM in all tissues examined, but no change in ATF1 levels. These data demonstrate that CREB is not the sole mediator of cAMP-dependent transcriptional regulation and probably acts in concert with a specific subset of cAMP response element-binding proteins to transduce the cAMP signal and, in its absence, these same proteins can compensate for CREB function in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beermann F., Hummler E., Schmid E., Schütz G. Perinatal activation of a tyrosine aminotransferase fusion gene does not occur in albino lethal mice. Mech Dev. 1993 Jul;42(1-2):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90098-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billestrup N., Swanson L. W., Vale W. Growth hormone-releasing factor stimulates proliferation of somatotrophs in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6854–6857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weih F., Nichols M., Schütz G. The tissue-specific extinguisher locus TSE1 encodes a regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90432-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindle P. K., Montminy M. R. The CREB family of transcription activators. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. J., Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Schütz G., Ruppert S. The mouse CREB (cAMP responsive element binding protein) gene: structure, promoter analysis, and chromosomal localization. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):974–982. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90010-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dash P. K., Hochner B., Kandel E. R. Injection of the cAMP-responsive element into the nucleus of Aplysia sensory neurons blocks long-term facilitation. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):718–721. doi: 10.1038/345718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T. C., Eistetter H., Katz M., Schmidt W., Kemler R. The in vitro development of blastocyst-derived embryonic stem cell lines: formation of visceral yolk sac, blood islands and myocardium. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Jun;87:27–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint K. J., Jones N. C. Differential regulation of three members of the ATF/CREB family of DNA-binding proteins. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):2019–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90503-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Mellström B., Benusiglio E., Sassone-Corsi P. Developmental switch of CREM function during spermatogenesis: from antagonist to activator. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):80–84. doi: 10.1038/355080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Sassone-Corsi P. More is better: activators and repressors from the same gene. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90178-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginty D. D., Kornhauser J. M., Thompson M. A., Bading H., Mayo K. E., Takahashi J. S., Greenberg M. E. Regulation of CREB phosphorylation in the suprachiasmatic nucleus by light and a circadian clock. Science. 1993 Apr 9;260(5105):238–241. doi: 10.1126/science.8097062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara M., Alberts A., Brindle P., Meinkoth J., Feramisco J., Deng T., Karin M., Shenolikar S., Montminy M. Transcriptional attenuation following cAMP induction requires PP-1-mediated dephosphorylation of CREB. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90537-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Totty N. F., Jones N. C. Identification and functional characterisation of the cellular activating transcription factor 43 (ATF-43) protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4601–4609. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMeur M., Glanville N., Mandel J. L., Gerlinger P., Palmiter R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene family: hormonal control of X and Y gene transcription and mRNA accumulation. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Q., Yun Y. D., Hoeffler J. P., Habener J. F. Cyclic-AMP-responsive transcriptional activation of CREB-327 involves interdependent phosphorylated subdomains. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4455–4465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Lee K. A., Masson N. Transcriptional regulation by CREB and its relatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Sep 23;1174(3):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90191-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A. Transcriptional regulation by cAMP. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):953–959. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90113-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. R., Chung C. S., Liou M. L., Wu M., Li W. F., Hsueh Y. P., Lai M. Z. Isolation and characterization of nuclear proteins that bind to T cell receptor V beta decamer motif. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1906–1912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson N., Hurst H. C., Lee K. A. Identification of proteins that interact with CREB during differentiation of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 11;21(11):1163–1169. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols M., Weih F., Schmid W., DeVack C., Kowenz-Leutz E., Luckow B., Boshart M., Schütz G. Phosphorylation of CREB affects its binding to high and low affinity sites: implications for cAMP induced gene transcription. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3337–3346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnicki M. A., Braun T., Hinuma S., Jaenisch R. Inactivation of MyoD in mice leads to up-regulation of the myogenic HLH gene Myf-5 and results in apparently normal muscle development. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90508-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert S., Cole T. J., Boshart M., Schmid E., Schütz G. Multiple mRNA isoforms of the transcription activator protein CREB: generation by alternative splicing and specific expression in primary spermatocytes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1503–1512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05195.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacher S., Castellucci V. F., Kandel E. R. cAMP evokes long-term facilitation in Aplysia sensory neurons that requires new protein synthesis. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1667–1669. doi: 10.1126/science.2454509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Thompson M. A., Greenberg M. E. CREB: a Ca(2+)-regulated transcription factor phosphorylated by calmodulin-dependent kinases. Science. 1991 Jun 7;252(5011):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.1646483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struthers R. S., Vale W. W., Arias C., Sawchenko P. E., Montminy M. R. Somatotroph hypoplasia and dwarfism in transgenic mice expressing a non-phosphorylatable CREB mutant. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):622–624. doi: 10.1038/350622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strähle U., Schmidt A., Kelsey G., Stewart A. F., Cole T. J., Schmid W., Schütz G. At least three promoters direct expression of the mouse glucocorticoid receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6731–6735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waeber G., Habener J. F. Nuclear translocation and DNA recognition signals colocalized within the bZIP domain of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate response element-binding protein CREB. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;5(10):1431–1438. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-10-1431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]