Abstract
A technique of centrifuging pea epicotyl sections which extracts water-soluble cell wall polysaccharides with less than 1.5% cytoplasmic contamination as revealed by malate dehydrogenase activity determinations was developed. Tests for protein, hexose, pentose, and malate dehydrogenase indicate that significant damage to the cells occurs above 3,000g. Below this force, there is little damage, as evidenced by the similar growth rates of centrifuged and noncentrifuged sections. Centrifugation at 1,000g extracts polysaccharides containing rhamnose, fucose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, galactose, and glucose. An increase in xylose and glucose, presumably xyloglucan, is induced by treating sections with indoleacetic acid. Much of the alcohol-insoluble, water-soluble polysaccharide within the wall is extractable by centrifugation, since nearly as much arabinose and xylose are extractable by centrifugation as by homogenization. The utility of this method for the study of cell wall metabolism is discussed.
Full text
PDF

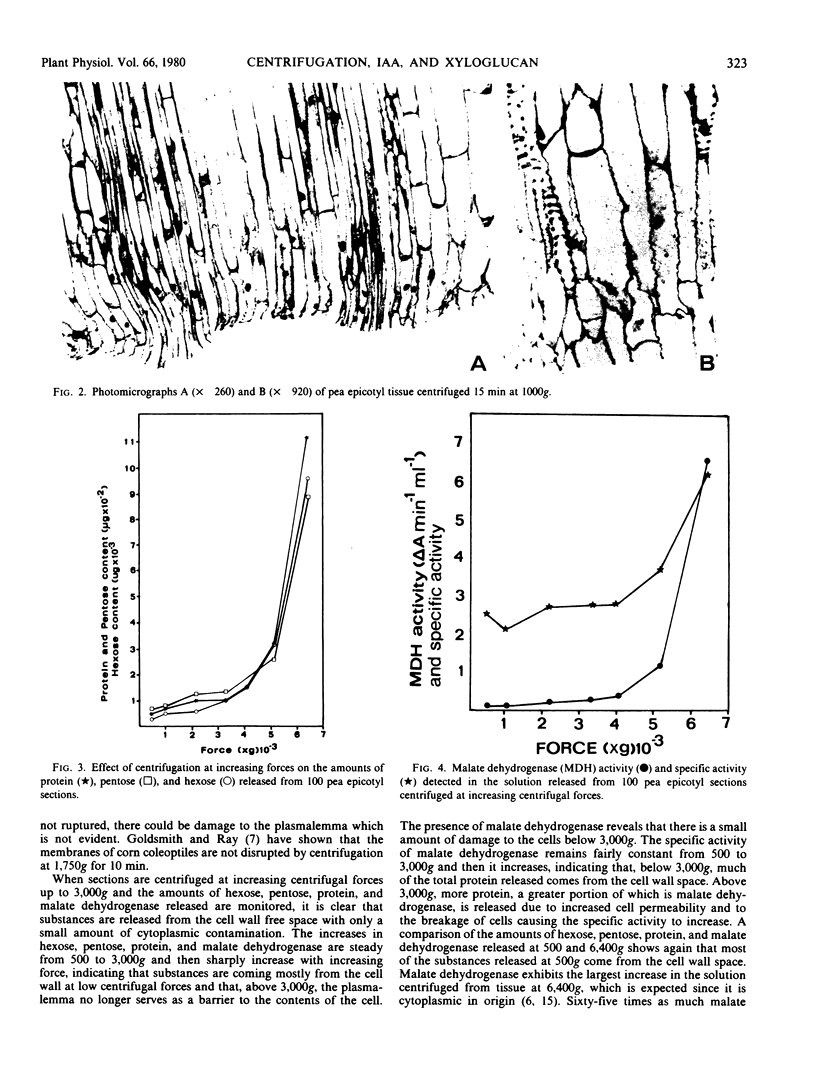

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer W. D., Talmadge K. W., Keegstra K., Albersheim P. The Structure of Plant Cell Walls: II. The Hemicellulose of the Walls of Suspension-cultured Sycamore Cells. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):174–187. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari T. E. Extraction and partial characterization of cellulases from expanding pea epicotyls. Plant Physiol. 1974 Oct;54(4):487–493. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.4.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labavitch J. M., Ray P. M. Relationship between Promotion of Xyloglucan Metabolism and Induction of Elongation by Indoleacetic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1974 Oct;54(4):499–502. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.4.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labavitch J. M., Ray P. M. Turnover of cell wall polysaccharides in elongating pea stem segments. Plant Physiol. 1974 May;53(5):669–673. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.5.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford H. A., Bravinder-Bree S. Peroxidase isozymes of first internodes of sorghum: tissue and intracellular localization and multiple peaks of activity isolated by gel filtration chromatography. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jun;49(6):950–956. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.6.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung K. H., Northcote D. H. Some enzymes present in the walls of mesophyll cells of tobacco leaves. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;151(1):141–144. doi: 10.1042/bj1510141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]