Abstract
A new bacterial agglutinin was isolated from seeds of the soybean cultivar Clark. Purification was carried out by ammonium sulfate precipitation and ion-exchange chromatography. The agglutinin is a heat-labile glycoprotein most active at pH 4.0. Addition of Ca2+, Mn2+ and Mg2+ did not enhance the agglutinating activity of this glycoprotein. Gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate showed that the agglutinin is composed of two subunits of approximately 50,000 daltons each. In the undissociated state, it agglutinates Xanthomonas phaseoli var. sojensis, the causal agent of bacterial pustule disease of soybean, at concentrations as low as 10 micrograms protein per milliliter but has no hemagglutinating activity. The agglutinin could be distinguished from previously reported soybean lectins on the basis of solubility in ammonium sulfate, lack of hemagglutinating activity, molecular weight, hapten specificity, and immunological determinants.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Bauer W. D. Role of Lectins in Plant-Microorganism Interactions: III. Influence of Rhizosphere/Rhizoplane Culture Conditions on the Soybean Lectin-binding Properties of Rhizobia. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):71–74. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Pueppke S. G., Bauer W. D. Role of lectins in plant-microorganism interactions: I. Binding of soybean lectin to rhizobia. Plant Physiol. 1977 Oct;60(4):486–491. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.4.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Lectins: a possible basis for specificity in the Rhizobium--legume root nodule symbiosis. Science. 1974 Jul 19;185(4147):269–271. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4147.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catsimpoolas N., Meyer E. W. Isolation of soyben hemagglutinin and demonstration of multiple forms by isoelectric focusing. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jun;132(1):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
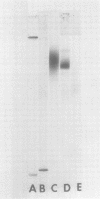
- Fett W. F., Sequeira L. A New Bacterial Agglutinin from Soybean: II. EVIDENCE AGAINST A ROLE IN DETERMINING PATHOGEN SPECIFICITY. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):853–858. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foutain D. W., Yang W. K. Isolectins from soybean (Glycine max). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 27;492(1):176–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Neville D. M., Jr Glycoproteins of cell surfaces. A comparative study of three different cell surfaces of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6339–6346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIENER I. E., PALLANSCH M. J. Purification of a toxic substance from defatted soy bean flour. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;197(1):29–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIENER I. E. The photometric determination of the hemagglutinating activity of soyin and crude soybean extracts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Jan;54(1):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis H., Fridman C., Sharon N., Katchalski E. Multiple hemagglutinins in soybean. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Nov;117(2):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90417-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis H., Sharon N., Katchalski E. Soybean hemagglutinin, a plant glycoprotein. I. Isolation of a glycopeptide. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):684–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis H., Sharon N. The biochemistry of plant lectins (phytohemagglutinins). Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42(0):541–574. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Cacan R., Cacan M., Debray H., Carter W. G., Sharon N. On the presence of two types of subunit in soybean agglutinin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):100–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Lis H., Sharon N. Aggregation and fragmentation of soybean agglutinin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 6;62(1):144–150. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80416-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Siegelman H. W., Lis H., Sharon N. Subunit structure of soybean agglutinin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1219–1224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie G. H., Sawyer W. H., Nichol L. W. The molecular weight and stability of concanavalin A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 15;263(2):283–293. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. II. Prog Allergy. 1962;6:30–154. doi: 10.1159/000313795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge J., Shannon L., Gumpf D. A barley lectin that binds free amino sugars. I. Purification and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 21;451(2):470–483. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusztai A., Watt W. B. Isolectins of Phaseolus vulgaris. A comprehensive study of fractionation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 13;365(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90250-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]