Abstract
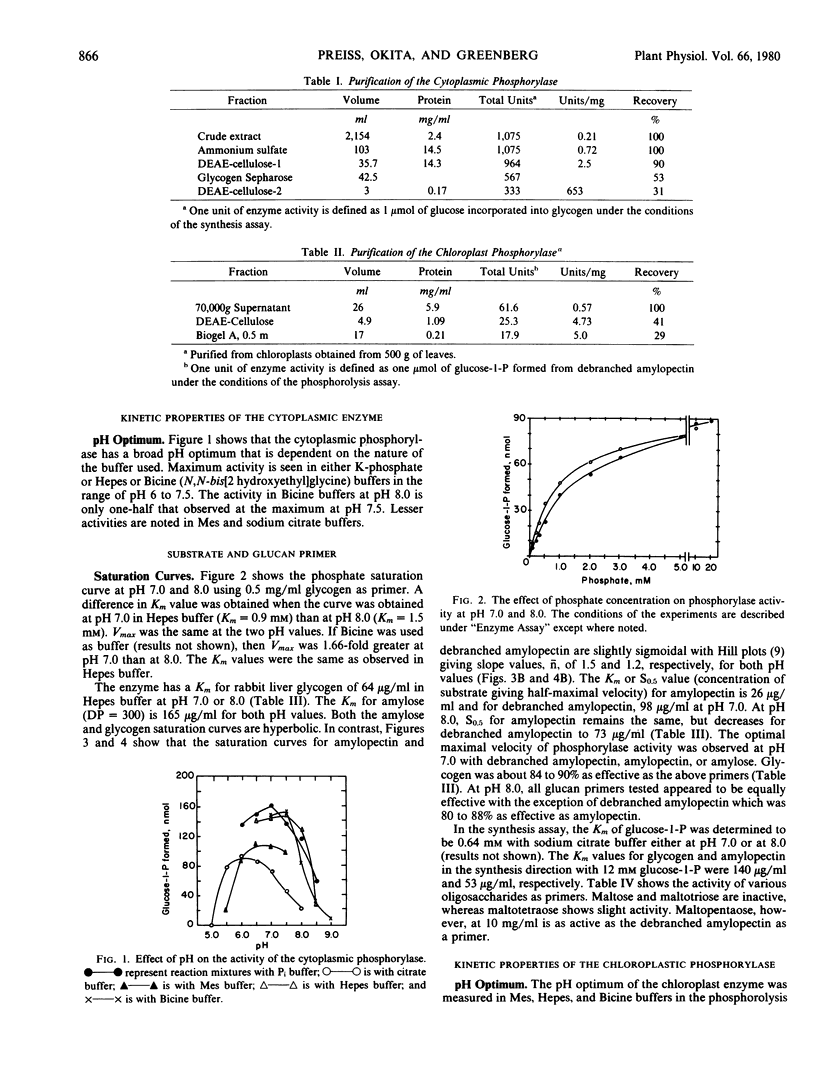
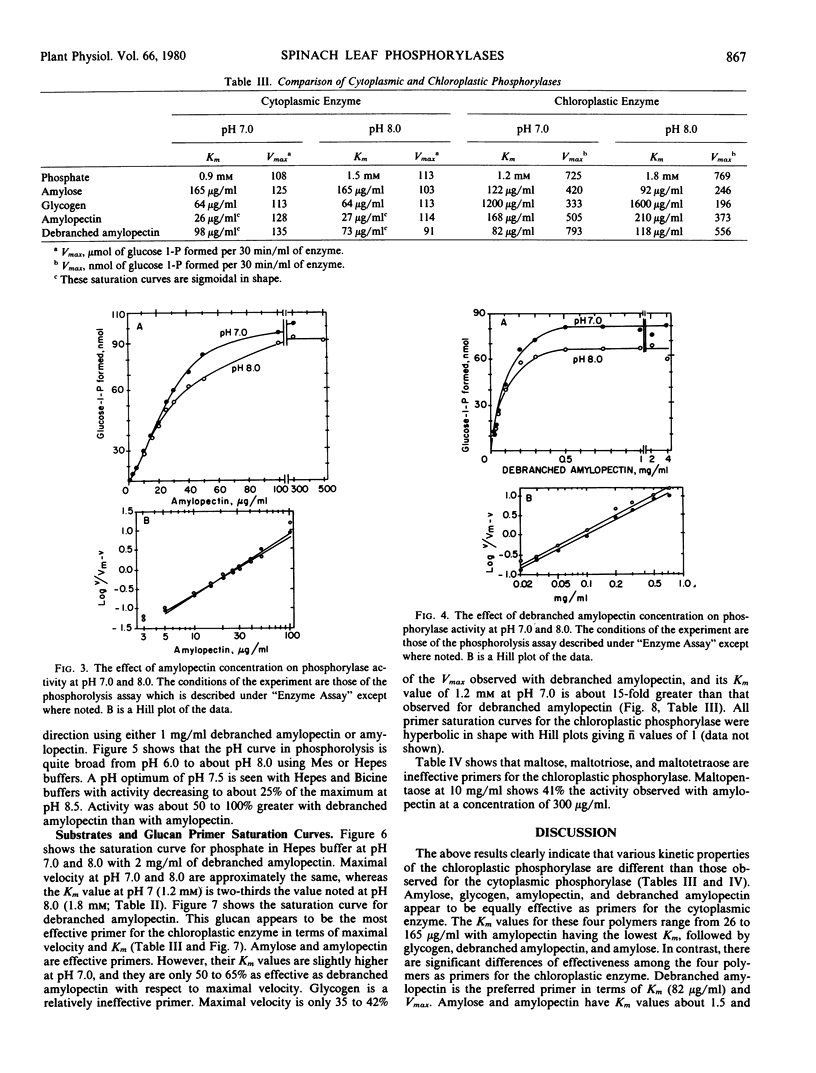
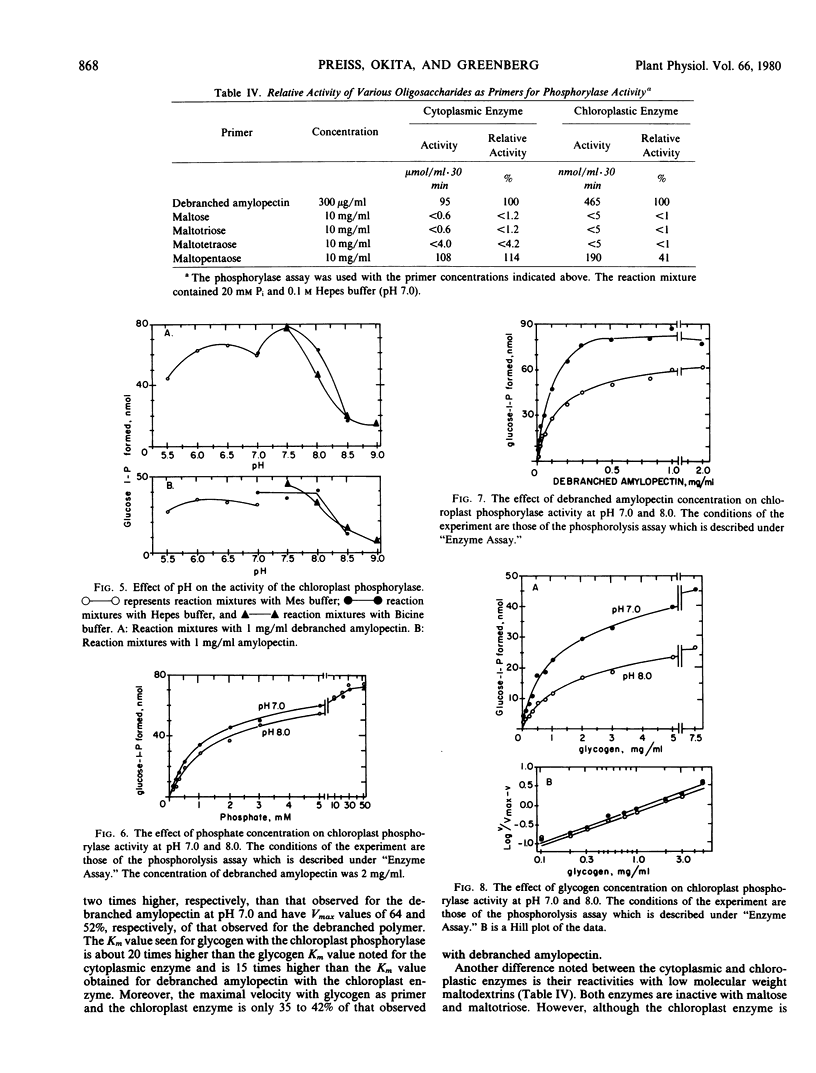
The chloroplastic and the cytoplasmic phosphorylases were purified and their kinetic properties characterized. The cytoplasmic enzyme was purified to homogeneity via affinity chromatography on a glycogen-Sepharose column. Subunit molecular weight studies indicated a value of 92,000, whereas a native molecular weight value of 194,000 was obtained by sucrose density gradient centrifugation. The chloroplast enzyme's native molecular weight was determined to be 203,800. The cytoplasmic enzyme shows the same Vmax for maltopentaose, glycogen, amylopectin, amylose, and debranched amylopectin but is only slightly active toward maltotetraose. The Km for phosphate at pH 7.0 is 0.9 millimolar and for glucose-1-phosphate, 0.64 millimolar. The Km values for phosphorolysis of amylopectin, amylose, glycogen, and debranched amylopectin are 26, 165, 64, and 98 micrograms per milliliter, respectively. In contrast, the relative Vmax values for the chloroplast enzyme at pH 7.0 are debranched amylopectin, 100, amylopectin, 63.7, amylose, 53, glycogen, 42, and maltopentaose, 41. Km values for the above high molecular weight polymers are, respectively, 82, 168, 122 micrograms per milliliter, and 1.2 milligrams per milliliter. The Km value for inorganic phosphate is 1.2 millimolar. The chloroplastic phosphorylase appears to have a lower apparent affinity for glycogen than the cytoplasmic enzyme. The results are discussed with respect to previous findings of multiple phosphorylase forms found in plant tissues and to possible regulatory mechanisms for controlling phosphorylase activity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burr B., Nelson O. E. Maize alpha-glucan phosphorylase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):539–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Heppel L. A. Metallo-enzymes released from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock. II. Evidence that 5'-nucleotidase and cyclic phosphodiesterase are zinc metallo-enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2647–2653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunja-Smith Z., Marshall J. J., Mercier C., Smith E. E., Whelan W. J. A revision of the Meyer-Bernfeld model of glycogen and amylopectin. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec 28;12(2):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80573-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldt H. W., Chon C. J., Maronde D. Role of orthophosphate and other factors in the regulation of starch formation in leaves and isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jun;59(6):1146–1155. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.6.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata S., Fukui T. The subunit structure of alpha-glucan phosphorylase from potato. FEBS Lett. 1973 Oct 15;36(2):222–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80373-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C., Gibbs M. Starch degradation in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jun;57(6):933–935. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.6.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C., Preiss J. Amylopectin degradation in pea chloroplast extracts. Plant Physiol. 1978 Feb;61(2):218–220. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita T. W., Greenberg E., Kuhn D. N., Preiss J. Subcellular localization of the starch degradative and biosynthetic enzymes of spinach leaves. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):187–192. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavey D. G., Steup M., Gibbs M. Characterization of starch breakdown in the intact spinach chloroplast. Plant Physiol. 1977 Aug;60(2):305–308. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Bulpin P. V., ap Rees T. Pathway of starch breakdown in photosynthetic tissues of Pisum sativum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 15;544(1):200–214. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. Y., Nelson O. E. Two additional phosphorylases in developing maize seeds. Plant Physiol. 1969 Feb;44(2):159–167. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vretblad P. Immobilization of ligands for biospecific affinity chromatography via their hydroxyl groups. The cyclohexaamylose-beta-amylase system. FEBS Lett. 1974 Oct 1;47(1):86–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werdan K., Heldt H. W., Milovancev M. The role of pH in the regulation of carbon fixation in the chloroplast stroma. Studies on CO2 fixation in the light and dark. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 11;396(2):276–292. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


