Abstract
Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the etiologic agent for Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) and primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), malignancies arising primarily in immunocompromised patients particularly AIDS-patients, while which are still lack of effective therapy. Hyaluronan (HA) is a large glucuronic acid and has been found closely related to multiple functions in cancer cells, although its role in viral oncogenesis remains largely unknown. Here we provide first evidence that KSHV de novo infection induces HA production from primary endothelial cells through upregulation of HA synthase gene 1 (Has1) and a multifunctional glycoprotein, CD147. Further data demonstrate that KSHV-induced HA production requires viral latent protein, LANA (in particular functional domain A) and MAPK/ERK signaling activities. In functions, HA production is necessary for KSHV/LANA-induced primary endothelial cell invasion, a hallmark feature for KS development. For clinical relevance, our data indicate that KSHV+ group has higher levels of HA and Has1 activities in their plasma than the KSHV- group of cohort HIV-infected patients. Together, our findings provide innovative insights into the mechanisms of oncogenic virus activation of HA production and its role in virus-associated malignancies pathogenesis, which may help to develop novel therapeutic strategies by targeting HA and related signaling.
Keywords: KSHV, hyaluronan, CD147, LANA
1. Introduction
Hyaluronan (HA) is a very large, linear glycosaminoglycan composed of repeating disaccharides of glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine [1]. In addition to its structural role through interaction with other extracellular matrix (ECM) components, HA binds to several cell surface receptors such as CD44, LYVE-1 and RHAMM that induce the transduction of a range of intracellular signals and contribute to multiple cellular functions such as embryonic development, healing processes and inflammation [2]. HA is overproduced by many types of tumors, and in some cases, HA levels are prognostic for malignant progression [3]. Moreover, HA and related signaling transductions have been involved in many malignant behaviors of cancer cells, including migration/invasion, angiogenesis, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), multidrug resistance, and metastasis [4-6]. Currently, ~20% of human cancers have been attributed to virus infection [7], however, there are limited data describing the role of HA production in viral oncogenesis or how oncogenic viral protein regulate HA level and related signaling transductions.
Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the etiologic agent for Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) and primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), malignancies arising primarily in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or in those receiving organ transplants [8,9]. Furthermore, despite the reduced incidence of KS in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) for HIV infection, KS still remains the most common Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-associated tumor and a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in this setting [10]. Another KSHV-caused malignancy, PEL, comprises transformed B cells harboring KSHV and arises preferentially within the pleural or peritoneal cavities of immune-suppressed patients [9]. PEL is a rapidly progressing malignancy with a median survival time of approximately 6 months, even under the combinational chemotherapy [11]. Our recent study demonstrates that the glycoprotein, CD147, interacts with the lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor-1 (LYVE-1) and the drug transporter, breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP)/ABCG2, to promote multidrug chemoresistance in KSHV+ PEL cells [12]. Moreover, we found higher levels of HA and HA synthase gene (Has1–3) transcripts in chemoresistant PEL cell-lines than in chemosensitive ones. In addition, small HA oligosaccharides (oHA) that interact monovalently with HA receptors, and competitively blocking polyvalent interactions between receptors and endogenous HA, sensitize drug resistant PEL cells to chemotherapeutic agents [12]. In the current study, we investigate the role of HA production in KSHV-infected primary endothelial cells, which represent the major cellular component of KS tumors, and identify the underlying mechanisms whereby oncogenic viral proteins regulate HA production.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Cell culture, reagents and infection protocol
KSHV-infected PEL cells (BCBL-1) was kindly provided by Dr. Dean Kedes (University of Virginia) and maintained in RPMI 1640 medium (Gibco) with supplements as described previously [12]. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were grown in DMEM/F-12 50/50 medium (Cellgro) supplemented with 5% FBS. Selective inhibitors targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK; U0126) and NF-κB (Bay11-7082) were purchased from Sigma. Hyaluronan oligosaccharides (oHA) were prepared as described previously [13]. To obtain KSHV for infection experiments, BCBL-1 cells were incubated with 0.6 mM valproic acid for 6 days, purified virus concentrated from culture supernatants and infectious titers were determined as described previously [14].
2.2. Cell transfection
HUVEC were transfected with control vector pcDNA3.1, pcDNA3.1-LANA (pcLANA) or LANA deletion fragments (pcLANA-A, pcLANA-AB, pcLANA-AC, pcLANA-BC and pcLANA-C) or pcDNA3.1-ERK (pcERK) in 12-well plates for 48 h using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instruction. Transfection efficiency was determined through co-transfection of a lacZ reporter construct and quantified as described previously [14]. For RNA interference assays, Has1 or CD147 ON-TARGET plus SMART pool siRNA (Dharmacon), or negative control siRNA, were delivered using the DharmaFECT transfection reagent according to the manufacturer's instruction.
2.3. Immunofluorescence assays
Cells were incubated in 1:1 methanol-acetone at 20°C for fixation and permeabilization, followed by a blocking reagent (10% normal goat serum, 3% bovine serum albumin, and 1% glycine) for an additional 30 min. Cells were then incubated for 1 h at 25°C with 1:1000 dilution of a rat anti-LANA monoclonal antibody (ABI, for LANA wt) or a mouse anti-V5-Tag monoclonal antibody (Cell Signaling, for LANA deletion fragments) followed by 1:100 dilution of a goat anti-rat or goat anti-mouse secondary antibody conjugated to Texas Red (Invitrogen). For intracellular HA detection, cells were permeabilized for 20 min at room temperature with 0.1% Triton-X-100 in 1% BSA, and incubated overnight at 4 °C with bHABC (biotinylated hyaluronan binding complex, Sigma) (1.25μg/mL) in 1% BSA. To remove the pericellular HA, fixed cells were treated with Streptomyces hyaluronidase (1 turbidity reducing unit/mL, Seikagaku Kogyo) before permeabilization. After washing, the cells were incubated for 1 h with Alexa 488-labeled streptavidin (1:1000) (Invitrogen) for bHABC staining. Cells were counterstained with 0.5 μg/mL 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, Sigma) in 180 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) for nuclear localization. Slides were washed once in 180 mM Tris-HCl for 10 min and prepared for visualization using a Leica TCPS SP5 AOBS confocal microscope.
2.4. Immunoblotting
Total cell lysates (20μg) were resolved by 10% SDS–PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes, and immunoblotted with antibodies for CD147 (BD), LANA (ABI), phospho-p44/42 ERK (Thr202/Tyr204), t-p44/42 ERK (Cell Signaling) and β-Actin (Sigma) for loading controls. Immunoreactive bands were identified using an enhanced chemiluminescence reaction (Perkin-Elmer), and visualized by autoradiography.
2.5. Transwell invasion assays
Matrigel Invasion Chambers (BD) were hydrated for 4 h at 37°C with culture media. Following hydration, media in the bottom of the well was replaced with fresh media, then 2×104 HUVEC were plated in the top of the chamber. After 24 h, cells were fixed with 4% formaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature and chambers rinsed in PBS prior to staining with 0.2% crystal violet for 10 min. After washing the chambers, cells at the top of the membrane were removed and cells at the bottom of the membrane counted using a phase contrast microscope. Relative invasion was determined for cells in experimental groups as follows: relative invasion = # invading cells in experimental group / # invading cells in control groups.
2.6. ELSA for HA
Concentrations of HA in culture supernatants or plasma from patients were determined using HA ELSA kit (Echelon) according to the manufacturers’ instructions.
2.7. qRT-PCR
Total RNA was isolated from infected or uninfected cells using the RNeasy Mini kit according to the manufacturer's instructions (QIAGEN). cDNA was synthesized from equal total RNA using SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis SuperMix Kit (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's procedures. The primers designed for target genes are displayed in Supplemental Table 1. Amplification experiments were carried out using an iCycler IQ Real-Time PCR Detection System, and cycle threshold (Ct) values were tabulated in duplicate (cDNA) for each gene of interest for each experiment. “No template” (water) controls were also used to ensure minimal background contamination. Using mean Ct values tabulated for different experiments and using Ct values for β-actin as loading controls, fold changes for experimental groups relative to assigned controls were calculated using automated iQ5 2.0 software (Bio-rad).
2.8. Patients and ethics statement
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards for Human Research (IRB, No. 8079) at Louisiana State University Health Science Center – New Orleans (LSUHSC-NO). All subjects were provided written informed consent. In the current study, a total of 28 HIV+ patients with antiretroviral treatment (ART) in our HIV Outpatient (HOP) Clinic are involved. There are 15 females and 13 males, the average age is 48.6 y (range 21-65 y). The average CD4 T cell counts is 539/mL (range 35-1773/mL), and the average HIV viral loads is 5928 copies/mL (range 25-66681 copies/mL).
2.9. Plasma and PBMC preparation
Whole blood was collected in heparin-coated tubes, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated over a Ficoll-Hypaque cushion. Plasma was isolated by centrifugation. The KSHV infection status was determined by using quantitative ELISAs for identifying circulating IgG antibodies to KSHV proteins (LANA and K8.1) as previously described [15,16].
2.10. Statistical Analysis
Significance for differences between experimental and control groups was determined using the two-tailed Student's t-test (Excel 8.0). The linear analyses were determined using SPSS Statistics 20.0.
3. Results
3.1. KSHV de novo infection induces HA production from primary endothelial cells through CD147
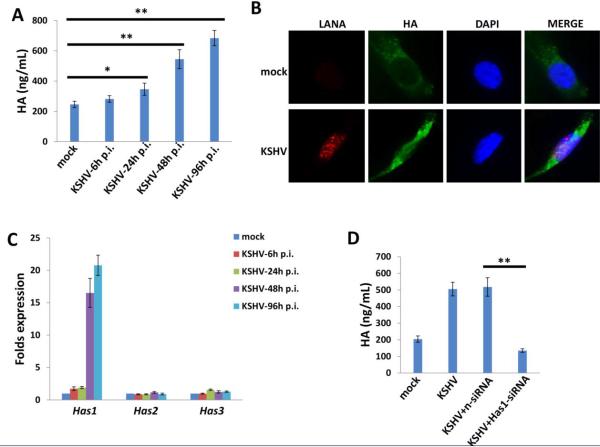
By using an enzyme-linked sorbent assay (ELSA), we found that KSHV de novo infection induced a significant increase in extracellular HA produced by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC); accumulation of extracellular HA continued for at least 96 h post-infection (Fig. 1A). Furthermore, immunofluorescence assay (IFA) data indicated that KSHV de novo infection also induced intracellular HA accumulation within the HUVEC, when compared to uninfected mock cells (Fig. 1B). There are three human HA synthase genes (Has1-3) responsible for HA production [17], and our data indicated that KSHV infection prominently increased Has1 transcripts, while having little or no effect on Has2 or Has3 transcripts (Fig. 1C). To confirm the role of Has1 in KSHV-induced HA production, we directly targeted Has1 by RNAi and showed that it significantly reduced HA production from KSHV-infected HUVEC (Fig. 1D).
Figure 1. KSHV de novo infection induces HA production through upregulation of Has1.
(A) Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were infected with purified KSHV (MOI~10) for 2 h, then the extracellular HA production at indicated time-points post-infection (p.i.) was measured and compared with mock cells control by ELSA. (B) Cells were infected as above, and immunofluorescence (IFA) was used to detect endogenous HA production at 48 h p.i. (C) Transcripts representing the 3 HA synthase genes (Has1-3) were quantified by qRT-PCR. (D) Cells were infected with KSHV for 2 h, then transfected with either negative control siRNA (nsiRNA) or Has1-siRNA for 48 h, and the extracellular HA production was measured by ELSA. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for three independent experiments. **=p<0.01.
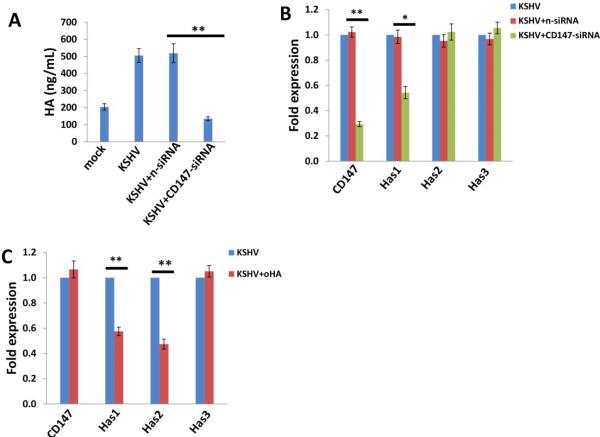
Previous studies have shown that HA production is regulated by a multifunctional glycoprotein, CD147 (emmprin; basigin), in several types of tumor cells [12,18,19]. Our data confirmed that directly targeting CD147 by RNAi significantly reduced HA production from KSHV-infected HUVEC (Fig. 2A). Interestingly, targeting CD147 by RNAi also decreased Has1 transcription but not Has2 and Has3 (Fig. 2B), while knock-down of Has1 by RNAi decreased CD147 transcription but not Has2 and Has3 (Fig. S1), implying a positive feedback for regulation of CD147 and Has1. In comparison, oHA treatment caused reduction of Has1 andHas2 transcription but did not affect CD147 or Has3 (Fig. 2C).
Figure 2. CD147 is involved in KSHV-induced HA production.
(A-B) HUVEC were infected with KSHV for 2 h, then transfected with either negative control siRNA (n-siRNA) or CD147-siRNA for 48 h, and the extracellular HA production was measured by ELSA. Gene expression was quantified by qRT-PCR. (C) Cells were infected with KSHV for 2 h, then treated with or without oHA (150 μg/mL) for 48 h, and gene transcripts were quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for three independent experiments. **=p<0.01.
3.2. HA production is induced by the viral latent protein LANA and requires LANA functional domain A and MAPK/ERK signaling activities
In more than 90% of KSHV-infected host cells, the virus exists at latency stage [20], implying that some viral latent proteins are probably responsible for inducing HA production. Latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA) is one of the only viral proteins consistently expressed in all KS-associated malignancies [21], and its major function is to maintain viral episome in latently-infected cells [22], as well as to modulate expression of a variety of viral and cellular genes [23,24]. To determine the role of LANA in inducing HA production, we ectopically expressed LANA by transfection of HUVEC with a recombinant construct [25] (Fig. 3A), and showed that LANA was sufficient for induction of HA production through upregulation of Has1 transcription (Fig. 3B-C).
Figure 3. KSHV-encoded LANA protein is sufficient to induce HA production from primary endothelial cells.
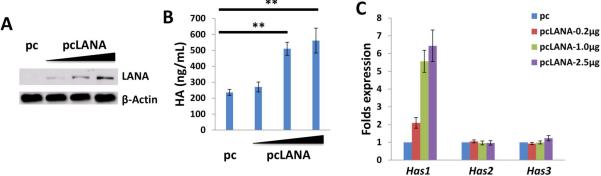
(A-C) HUVEC were transfected with control vector (pc), or vectors encoding LANA (pcLANA) at 0.2, 1.0 or 2.5 μg, respectively, for 48 h, then protein expression, HA production and Has genes transcription were measured by immunoblots, ELSA, qRT-PCR, respectively. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for three independent experiments. **=p<0.01.
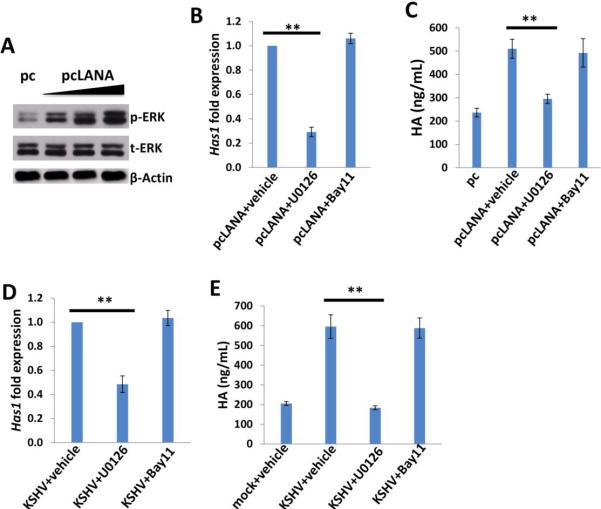
The LANA protein sequence can be divided into three functional domains: a conserved proline- and serine-rich N-terminal region (domain A), a central region composed of several acidic repeats (domain B), and a conserved C-terminal domain containing a proline-rich region and a region rich in charged and hydrophobic amino acids (domain C) [26]. Both N- and C-terminal domains contain a nuclear localization sequence (NLS, Fig. 4A). Further IFA data indicated that the LANA-A fragment containing the N-terminal NLS localized to the nucleus in similar fashion to the full-length control, while the C-terminal NLS within the LANA-BC fragment was non-functional (Fig. 4B), which is in accordance with previous findings [27,28]. By using a variety of LANA deletion fragment and full-length control constructs, we found that the LANA domain A (LANA-A) was sufficient to induce CD147 expression with equivalent efficiency to the full-length control (Fig. 4C).
Figure 4. LANA induces HA production requiring functional domain A and CD147.
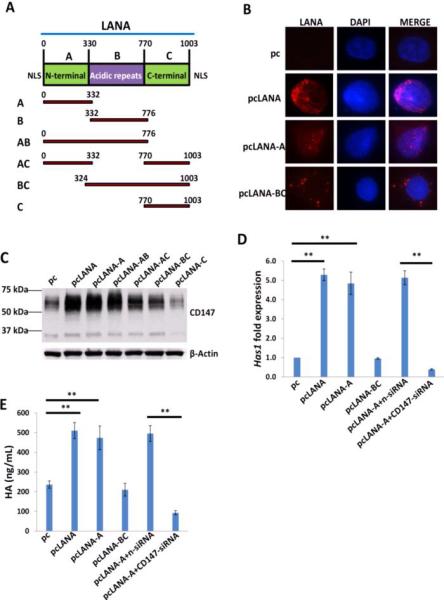
(A) Putative domain structure of LANA based on primary sequence features. The N-terminal region (domain A) is rich in prolines and serines and contains a putative nuclear localization sequences (NLS). The central region of LANA (domain B) is comprised of several repeats and is very acidic. The C-terminal region (domain C) also contains a putative NLS. All fragment variants and their coordinates are depicted below the domain model of LANA. (B) HUVEC were transfected with control vector pc, full-length LANA construct pcLANA, and fragment variants pcLANA-A, pcLANA-BC, respectively, for 48 h. IFA was used to detect their cellular localization, and the nuclear shown by DAPI. (C-E) Cells were transfected with control vector pc, full-length LANA construct and fragment variants, respectively, for 48 h. Immunoblots, qRT-PCR and ELSA were used to detect CD147 expression, Has1 transcription and extracellular HA production, respectively. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for three independent experiments. **=p<0.01.
Our published data have indicated that LANA upregulates CD147 expression, although the underlying mechanisms remain unclear [25]. Here we showed that LANA-A was sufficient to induce has1 transcription and HA production, both of which were blocked by RNAi targeting CD147 (Fig. 4D-E). We have previously shown that the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is involved in KSHV upregulation of CD147 [29]. Here we found that ectopic expression of LANA increased the phosphorylation of MAPK/ERK (Fig. 5A) but did not affect NF-κB p65 phosphorylation (data not shown) in HUVEC. Blocking the activities of MAPK by its specific inhibitor U0126 significantly reduced Has1 transcription and HA production by LANA-transfected cells and KSHV-infected cells, while NF-κB inhibitor Bay11-7082 had no such effects (Fig. 5B-E). Immunoblot analysis indicated that U0126 treatment greatly reduced CD147 expression (Fig. S2A). Moreover, overexpression of ERK by a recombinant vector [14] significantly upregulated Has1 transcripts but slightly increasing CD147 transcripts, while additional silencing of CD147 by RNAi partially reduced Has1 transcripts, implying other mechanisms independent of CD147 are probably involved in MAPK-ERK upregulation of Has1 (Fig. S2B-C).
Figure 5. The MAPK/ERK pathway is involved in LANA-induced HA production from primary endothelial cells.
(A-C) HUVEC were transfected with control vector (pc), or vectors encoding LANA (pcLANA) at 0.2, 1.0 or 2.5 μg, respectively, for 48 h, then some cells were treated with vehicle, MAPK inhibitor U0126 (10 μM), or NF-κB inhibitor Bay11-7085 (10 μM) for 2 h followed by additional 24 h-culture. (D-E) Cells were infected with KSHV for 2 h, then treated with vehicle or signaling inhibitors as above. Protein expression, Has1 gene transcription and HA production were measured as above. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for three independent experiments. **=p<0.01.
3.3. Targeting HA production represses KSHV/LANA-induced endothelial cell invasiveness
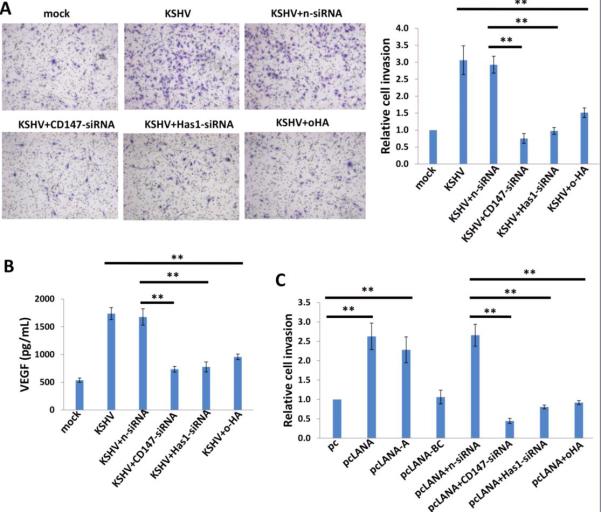
Acquisition of a migratory or invasive phenotype represents one hallmark of KSHV-infected endothelial cells, with implications for both viral dissemination and angiogenesis within KS lesions [30]. Here we found that either targeting CD147 or Has1 by RNAi or inhibiting HA-receptor interactions by oHA treatment significantly blocked KSHV-induced endothelial cell invasiveness, as measured by the transwell assays (Fig. 6A). Further analysis indicated that RNAi against CD147 or Has1 or oHA treatment also reduced VEGF, a major pro-migratory and proangiogenic factor production for endothelial cells (Fig. 6B). These results suggest that the effects of HA and CD147 on invasiveness are potentially mediated by VEGF. We further found that LANA-A induced endothelial cell invasiveness with a similar efficiency as the full-length LANA, and that the effect of LANA on invasiveness was significantly blocked by targeting CD147 or Has1 with RNAi or by inhibiting HA-receptor interactions via oHA treatment (Fig. 6C). Interestingly, we found that silencing of Has1 also partially reduced the transcripts of VEGF receptor 1 and 2 (VEGFR1 and VEGFR2), while silencing of CD147 mainly reduced the transcripts of VEGFR2 (Fig. S3). Taken together, our data indicate that HA production is required for KSHV- or viral protein-induced invasiveness of primary endothelial cells.
Figure 6. Targeting HA production represses KSHV/LANA-induced endothelial cell invasiveness.
(A) HUVEC were infected with KSHV for 2 h, then transfected with either negative control siRNA (n-siRNA) or Has1-siRNA, CD147-siRNA, or treated with oHA (150 μg/mL) for 48 h, and cell invasion were assessed using the transwell assays and calculations detailed in the Methods. (B) VEGF concentrations within culture supernatant were quantified by ELISA. (C) Cells were transfected with control vector pc, full-length LANA construct pcLANA, and fragment variants, respectively, for 48 h. Some cells were then transfected with either negative control siRNA (n-siRNA) or Has1-siRNA, CD147-siRNA, or treated with oHA (150 μg/mL) for additional 48 h. Cell invasion were assessed as above. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for three independent experiments. **=p<0.01.
3.4. Upregulation of HA production and Has1 in KSHV+ HIV-infected patients
To explore the clinical relevance of HA production within KSHV+ HIV-infected patients, we tested plasma HA levels by ELSA in a small collection of our cohort HIV-infected patients; KSHV infection status in these patients was determined as described in the Methods. We found that the KSHV+ group (n=16) had higher HA concentrations in their plasma than those from the KSHV- group (n=12) of HIV-infected patients (Fig. 7A). Further analysis of a subset of these same patients indicated that the KSHV+ group had higher Has1-3 transcripts within their peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) than those from the KSHV- group (Fig. 7B). Only the difference in Has1 level was highly statistically significant, whereas Has2 level was moderately significant and Has3 level had no significance. Moreover, in the KSHV+ group, only the Has1 level was highly linearly correlated with HA concentration whereas Has2 and Has3 levels had moderate or no linear correlation, respectively (Fig. 7C). In contrast, there was no linear correlation between HA concentrations and HIV viral loads or CD4 counts from these patients (Fig. S4), implying that HA production was potentially induced by KSHV co-infection.
Figure 7. Upregulation of HA production and Has1 in KSHV+ HIV-infected patients.
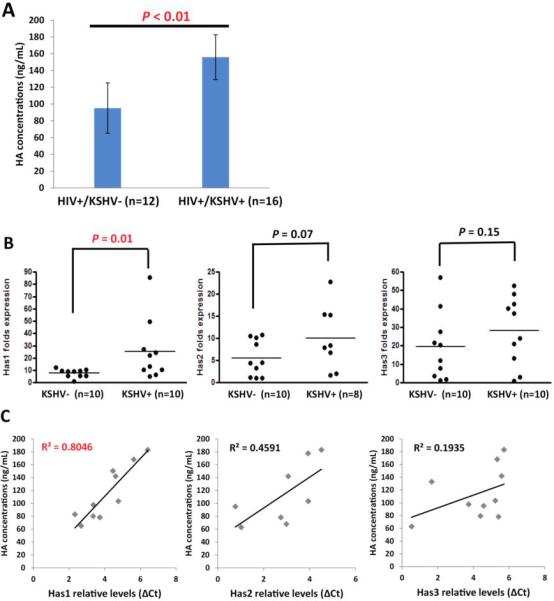
(A) The HA concentrations within plasma from HIV-infected patients were quantified using ELSA. KSHV infection status was identified as described in the Methods. (B) The transcriptional levels of Has1-3 within PBMCs from the same patients were quantified by qRT-PCR. (C) The linear analysis of correlation between HA concentrations and Has1-3 transcriptional levels were performed by SPSS.
4. Discussion
As mentioned above, HA binds with a number of cellular receptors, leading directly or indirectly to activation of downstream signaling pathways [2]. Although the current study does not address the levels of HA receptors on KSHV-infected primary endothelial cells, we have observed upregulation of HA receptors including CD44 and LYVE-1 by either KSHV de novo infection or ectopic expression of LANA (Fig. S5). Interestingly, LYVE-1 has been found highly expressed by KSHV-infected cells and within KSHV-associated tumors [31,32], although its role in HA-mediated signaling and functions remains largely unknown. Another major HA receptor, CD44, is also a well-known cancer stem cell (CSC) marker for many tumors [33], while its functions in KSHV pathogenesis and tumorigenesis still remains unclear. Therefore, future work is required to understand the contribution to KSHV pathogenesis by regulation of these HA receptors.
Here we have shown that HA and related signaling pathways are involved in KSHV-infected cell invasiveness. Previous studies suggest that they may also regulate other functions within these cells, such as multidrug resistance and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transformation (EndMT). We and others have found that, in response to interaction with HA, HA receptors interact with many signaling and transporter proteins such as ErbB2, EGFR, BCRP, P-glycoprotein, monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) to mediate cancer cells multidrug resistance [12,13,34-36]. EndMT is an important pathophysiologic correlate for cancer progression, and two recent studies demonstrate that EndMT is induced by KSHV infection and contributes to viral tumorigenesis [37,38]. Interestingly, HA has been found as a critical regulator of EndMT during cardiac valve formation [39,40].
We found a higher level of HA production and Has genes transcripts in KSHV+ than KSHV- groups of HIV-infected patients. Moreover, no linear correlation was observed between HA concentrations and HIV viral loads or CD4 counts from the same patients, indicating the importance of KSHV co-infection for regulation of HA production. However, due to the small number of samples analyzed here, the final conclusion still requires analyses of additional samples from HIV-infected patients. Therefore, we are now working with clinicians within LSUHSC HIV Outpatient (HOP) Clinic to collect more plasma and PBMC samples from HIV-infected patients to continue this analysis.
Published data have reported a higher level of plasma HA within HIV/HCV co-infected patients, and patients with liver fibrosis and/or cirrhosis [41,42]. Therefore, we cannot exclude the possibility of other pathogen co-infection or pathological conditions contributing to upregulation of HA levels in our cohort HIV-infected patients. These factors should be resolved by further investigation in future.
Supplementary Material
Figure S1. Silencing of Has1 by RNAi from KSHV-infected primary endothelial cells. HUVEC were infected with KSHV for 2 h, then transfected with either negative control siRNA (n-siRNA) or Has1-siRNA for 48 h, and gene transcripts were quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for three independent experiments. **=p<0.01.
Figure S2. MAPK-ERK pathway was involved in KSHV/LANA-induced HA production. (A) HUVEC were transfected with control vector (pc), or vectors encoding LANA (pcLANA) for 48 h, then treated with vehicle, MAPK inhibitor U0126 (10 μM) for 2 h followed by additional 24 h-culture. After that, protein expression was measured by immunoblots. (B-C) Cells were transfected with control vector (pc), or vectors encoding MAPK-ERK (pcERK) for 24 h, then transfected with either negative control siRNA (n-siRNA) or CD147-siRNA for additional 48 h. Gene transcription and expression were measured by qRT-PCR and immunoblots. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for three independent experiments. **=p<0.01.
Figure S3. Targeting Has1 or CD147 reduces VEGF receptor gene expression. HUVEC were infected with KSHV for 2 h, then transfected with either negative control siRNA (n-siRNA), CD147-siRNA or Has1-siRNA for 48 h, and gene transcripts were quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for three independent experiments. **=p<0.01.
Figure S4. There is no linear correlation between HA concentrations and HIV viral loads/CD4 counts from patients. (A-B) The linear analysis of correlation between HA concentrations and HIV viral loads/CD4 counts from the same HIV-infected patients were performed by SPSS.
Figure S5. Upregulation of HA receptors by KSHV/LANA. (A) HUVEC were transfected with control vector (pc), or vectors encoding LANA (pcLANA) for 48 h. (B) Cells were infected with KSHV for 2 h then followed by additional 24-h incubation. Protein expression was measured by immunoblots.
Highlights.
-
1)
KSHV de novo infection induces HA production from primary endothelial cells through upregulation of HA synthase gene 1 (Has1) and a multifunctional glycoprotein, CD147.
-
2)
KSHV-induced HA production requires viral latent protein, LANA (in particular functional domain A) and MAPK/ERK signaling activities.
-
3)
HA production is necessary for KSHV/LANA-induced primary endothelial cell invasion, a hallmark feature for KS development.
-
4)
KSHV+ group has higher levels of HA and Has1 activities in their plasma than the KSHV- group of cohort HIV-infected patients.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Rolf Renne at Shands Cancer Center, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL for providing LANA overexpression and deletion mutant constructs, and Dr. Momka Bratoeva at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC for preparing the oHA. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01-CA142362 to CP, R01-CA082867 to BPT and P20-RR021970-06 to ZQ), the Ladies Leukemia League Grant (2014-2015) to ZQ, the National Natural Science Foundation (81101791, 81272191, 81472547 to ZQ; 81400164 to LD) and the Foundation for Innovative Research Groups of the NNSF of China (81221001 to YC).
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Conflicts of Interest Statement:
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Tammi MI, Day AJ, Turley EA. Hyaluronan and homeostasis: a balancing act. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:4581–4584. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R100037200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Turley EA, Noble PW, Bourguignon LY. Signaling properties of hyaluronan receptors. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:4589–4592. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R100038200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tammi RH, Kultti A, Kosma VM, Pirinen R, Auvinen P, Tammi MI. Hyaluronan in human tumors: pathobiological and prognostic messages from cell-associated and stromal hyaluronan. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008;18:288–295. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Toole BP. Hyaluronan: from extracellular glue to pericellular cue. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:528–539. doi: 10.1038/nrc1391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Toole BP, Slomiany MG. Hyaluronan, CD44 and Emmprin: partners in cancer cell chemoresistance. Drug Resist Updat. 2008;11:110–121. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2008.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Grass GD, Dai L, Qin Z, Parsons C, Toole BP. CD147: regulator of hyaluronan signaling in invasiveness and chemoresistance. Adv Cancer Res. 2014;123:351–373. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800092-2.00013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mesri EA, Feitelson MA, Munger K. Human viral oncogenesis: a cancer hallmarks analysis. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;15:266–282. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.02.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, Lee F, Culpepper J, Knowles DM, Moore PS. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science. 1994;266:1865–1869. doi: 10.1126/science.7997879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW, Knowles DM. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1186–1191. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199505043321802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Engels EA, Biggar RJ, Hall HI, Cross H, Crutchfield A, Finch JL, Grigg R, Hylton T, Pawlish KS, McNeel TS, Goedert JJ. Cancer risk in people infected with human immunodeficiency virus in the United States. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:187–194. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chen YB, Rahemtullah A, Hochberg E. Primary effusion lymphoma. Oncologist. 2007;12:569–576. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.12-5-569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Qin Z, Dai L, Bratoeva M, Slomiany MG, Toole BP, Parsons C. Cooperative roles for emmprin and LYVE-1 in the regulation of chemoresistance for primary effusion lymphoma. Leukemia. 2011;25:1598–1609. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Slomiany MG, Dai L, Tolliver LB, Grass GD, Zeng Y, Toole BP. Inhibition of Functional Hyaluronan-CD44 Interactions in CD133-positive Primary Human Ovarian Carcinoma Cells by Small Hyaluronan Oligosaccharides. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:7593–7601. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Qin Z, Dai L, Defee M, Findlay VJ, Watson DK, Toole BP, Cameron J, Peruzzi F, Kirkwood K, Parsons C. Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Suppression of DUSP1 Facilitates Cellular Pathogenesis following De Novo Infection. J Virol. 2013;87:621–635. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01441-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mbisa GL, Miley W, Gamache CJ, Gillette WK, Esposito D, Hopkins R, Busch MP, Schreiber GB, Little RF, Yarchoan R, Ortiz-Conde BA, Labo N, Whitby D. Detection of antibodies to Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus: a new approach using K8.1 ELISA and a newly developed recombinant LANA ELISA. J Immunol Methods. 2010;356:39–46. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2010.02.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Benavente Y, Mbisa G, Labo N, Casabonne D, Becker N, Maynadie M, Foretova L, Cocco PL, Nieters A, Staines A, Bofetta P, Brennan P, Whitby D, de Sanjose S. Antibodies against lytic and latent Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus antigens and lymphoma in the European EpiLymph case-control study. Br J Cancer. 2011;105:1768–1771. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Weigel PH, DeAngelis PL. Hyaluronan synthases: a decade-plus of novel glycosyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:36777–36781. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R700036200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Marieb EA, Zoltan-Jones A, Li R, Misra S, Ghatak S, Cao J, Zucker S, Toole BP. Emmprin promotes anchorage-independent growth in human mammary carcinoma cells by stimulating hyaluronan production. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1229–1232. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-2832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Grass GD, Tolliver LB, Bratoeva M, Toole BP. CD147, CD44, and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathway cooperate to regulate breast epithelial cell invasiveness. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:26089–26104. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.497685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ye F, Lei X, Gao SJ. Mechanisms of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency and Reactivation. Adv Virol. 2011;2011 doi: 10.1155/2011/193860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dupin N, Fisher C, Kellam P, Ariad S, Tulliez M, Franck N, van Marck E, Salmon D, Gorin I, Escande JP, Weiss RA, Alitalo K, Boshoff C. Distribution of human herpesvirus-8 latently infected cells in Kaposi's sarcoma, multicentric Castleman's disease, and primary effusion lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:4546–4551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.8.4546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ballestas ME, Chatis PA, Kaye KM. Efficient persistence of extrachromosomal KSHV DNA mediated by latency-associated nuclear antigen. Science. 1999;284:641–644. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5414.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Krithivas A, Young DB, Liao G, Greene D, Hayward SD. Human herpesvirus 8 LANA interacts with proteins of the mSin3 corepressor complex and negatively regulates Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in dually infected PEL cells. J Virol. 2000;74:9637–9645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.20.9637-9645.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Renne R, Barry C, Dittmer D, Compitello N, Brown PO, Ganem D. Modulation of cellular and viral gene expression by the latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. J Virol. 2001;75:458–468. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.1.458-468.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Qin Z, Dai L, Slomiany MG, Toole BP, Parsons C. Direct activation of emmprin and associated pathogenesis by an oncogenic herpesvirus. Cancer Res. 2010;70:3884–3889. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Garber AC, Shu MA, Hu J, Renne R. DNA binding and modulation of gene expression by the latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. J Virol. 2001;75:7882–7892. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.17.7882-7892.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schwam DR, Luciano RL, Mahajan SS, Wong L, Wilson AC. Carboxy terminus of human herpesvirus 8 latency-associated nuclear antigen mediates dimerization, transcriptional repression, and targeting to nuclear bodies. J Virol. 2000;74:8532–8540. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.18.8532-8540.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cloutier N, Flamand L. Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen inhibits interferon (IFN) beta expression by competing with IFN regulatory factor-3 for binding to IFNB promoter. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:7208–7221. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.018838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dai L, Bratoeva M, Toole BP, Qin Z, Parsons C. KSHV activation of VEGF secretion and invasion for endothelial cells is mediated through viral upregulation of emmprin-induced signal transduction. Int J Cancer. 2012;131:834–843. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Qian LW, Xie J, Ye F, Gao SJ. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection promotes invasion of primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells by inducing matrix metalloproteinases. J Virol. 2007;81:7001–7010. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00016-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Carroll PA, Brazeau E, Lagunoff M. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection of blood endothelial cells induces lymphatic differentiation. Virology. 2004;328:7–18. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2004.07.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pyakurel P, Pak F, Mwakigonja AR, Kaaya E, Heiden T, Biberfeld P. Lymphatic and vascular origin of Kaposi's sarcoma spindle cells during tumor development. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:1262–1267. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zoller M. CD44: can a cancer-initiating cell profit from an abundantly expressed molecule? Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:254–267. doi: 10.1038/nrc3023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Misra S, Ghatak S, Toole BP. Regulation of MDR1 expression and drug resistance by a positive feedback loop involving hyaluronan, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and ErbB2. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:20310–20315. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500737200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Miletti-Gonzalez KE, Chen S, Muthukumaran N, Saglimbeni GN, Wu X, Yang J, Apolito K, Shih WJ, Hait WN, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L. The CD44 receptor interacts with P-glycoprotein to promote cell migration and invasion in cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:6660–6667. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Slomiany MG, Grass GD, Robertson AD, Yang XY, Maria BL, Beeson C, Toole BP. Hyaluronan, CD44, and emmprin regulate lactate efflux and membrane localization of monocarboxylate transporters in human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2009;69:1293–1301. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gasperini P, Espigol-Frigole G, McCormick PJ, Salvucci O, Maric D, Uldrick TS, Polizzotto MN, Yarchoan R, Tosato G. Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus promotes endothelial-to mesenchymal transition through Notch-dependent signaling. Cancer Res. 2012;72:1157–1169. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cheng F, Pekkonen P, Laurinavicius S, Sugiyama N, Henderson S, Gunther T, Rantanen V, Kaivanto E, Aavikko M, Sarek G, Hautaniemi S, Biberfeld P, Aaltonen L, Grundhoff A, Boshoff C, Alitalo K, Lehti K, Ojala PM. KSHV-initiated notch activation leads to membrane-type-1 matrix metalloproteinase-dependent lymphatic endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell Host Microbe. 2011;10:577–590. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Camenisch TD, Spicer AP, Brehm-Gibson T, Biesterfeldt J, Augustine ML, Calabro A, Jr., Kubalak S, Klewer SE, McDonald JA. Disruption of hyaluronan synthase-2 abrogates normal cardiac morphogenesis and hyaluronan-mediated transformation of epithelium to mesenchyme. J Clin Invest. 2000;106:349–360. doi: 10.1172/JCI10272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Camenisch TD, Schroeder JA, Bradley J, Klewer SE, McDonald JA. Heart-valve mesenchyme formation is dependent on hyaluronan-augmented activation of ErbB2-ErbB3 receptors. Nat Med. 2002;8:850–855. doi: 10.1038/nm742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Grint D, Peters L, Rockstroh JK, de Wit S, Mitsura VM, Knysz B, Pedersen C, Kirk O, Lundgren JD, Mocroft A, Euro S.i.E. Increased incidence of antiretroviral drug discontinuation among patients with viremic hepatitis C virus coinfection and high hyaluronic acid, a marker of liver fibrosis. AIDS. 2014;28:577–587. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Halfon P, Bourliere M, Penaranda G, Deydier R, Renou C, Botta-Fridlund D, Tran A, Portal I, Allemand I, Rosenthal-Allieri A, Ouzan D. Accuracy of hyaluronic acid level for predicting liver fibrosis stages in patients with hepatitis C virus. Comp Hepatol. 2005;4:6. doi: 10.1186/1476-5926-4-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Silencing of Has1 by RNAi from KSHV-infected primary endothelial cells. HUVEC were infected with KSHV for 2 h, then transfected with either negative control siRNA (n-siRNA) or Has1-siRNA for 48 h, and gene transcripts were quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for three independent experiments. **=p<0.01.
Figure S2. MAPK-ERK pathway was involved in KSHV/LANA-induced HA production. (A) HUVEC were transfected with control vector (pc), or vectors encoding LANA (pcLANA) for 48 h, then treated with vehicle, MAPK inhibitor U0126 (10 μM) for 2 h followed by additional 24 h-culture. After that, protein expression was measured by immunoblots. (B-C) Cells were transfected with control vector (pc), or vectors encoding MAPK-ERK (pcERK) for 24 h, then transfected with either negative control siRNA (n-siRNA) or CD147-siRNA for additional 48 h. Gene transcription and expression were measured by qRT-PCR and immunoblots. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for three independent experiments. **=p<0.01.
Figure S3. Targeting Has1 or CD147 reduces VEGF receptor gene expression. HUVEC were infected with KSHV for 2 h, then transfected with either negative control siRNA (n-siRNA), CD147-siRNA or Has1-siRNA for 48 h, and gene transcripts were quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for three independent experiments. **=p<0.01.
Figure S4. There is no linear correlation between HA concentrations and HIV viral loads/CD4 counts from patients. (A-B) The linear analysis of correlation between HA concentrations and HIV viral loads/CD4 counts from the same HIV-infected patients were performed by SPSS.
Figure S5. Upregulation of HA receptors by KSHV/LANA. (A) HUVEC were transfected with control vector (pc), or vectors encoding LANA (pcLANA) for 48 h. (B) Cells were infected with KSHV for 2 h then followed by additional 24-h incubation. Protein expression was measured by immunoblots.