Full text
PDF


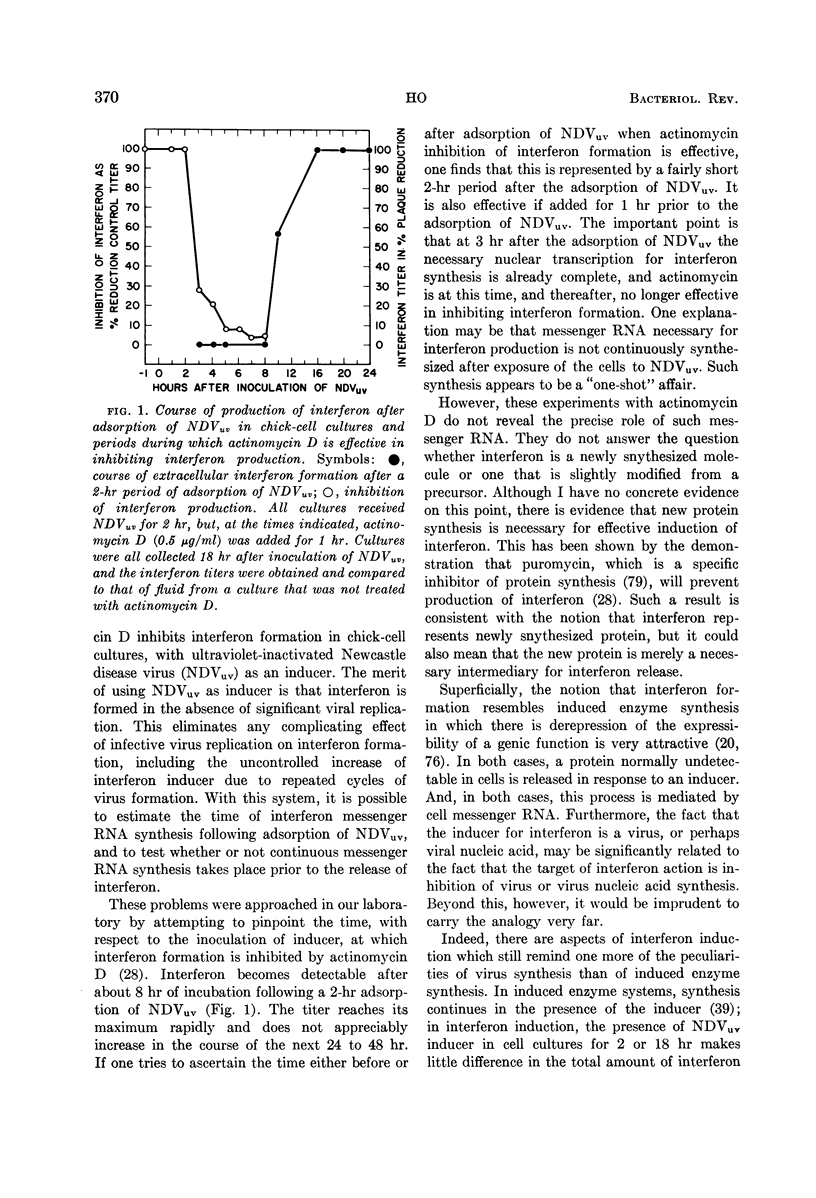

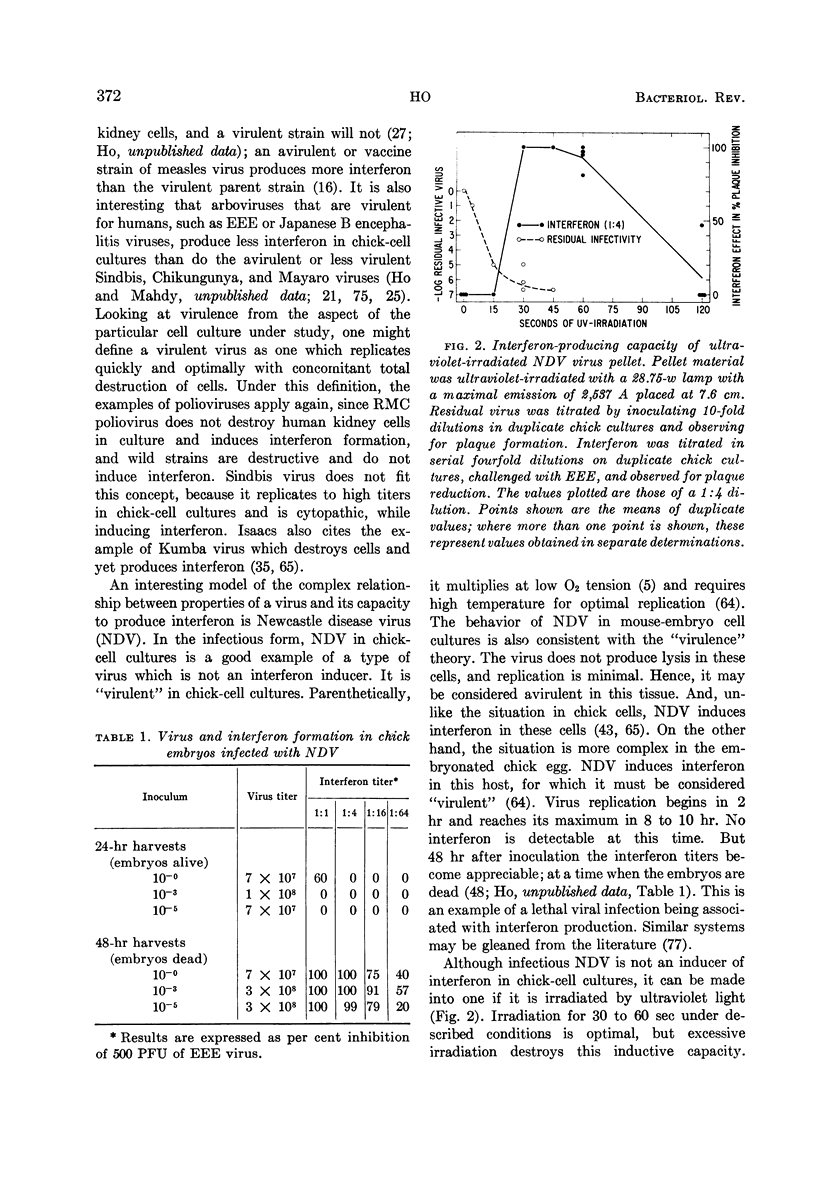

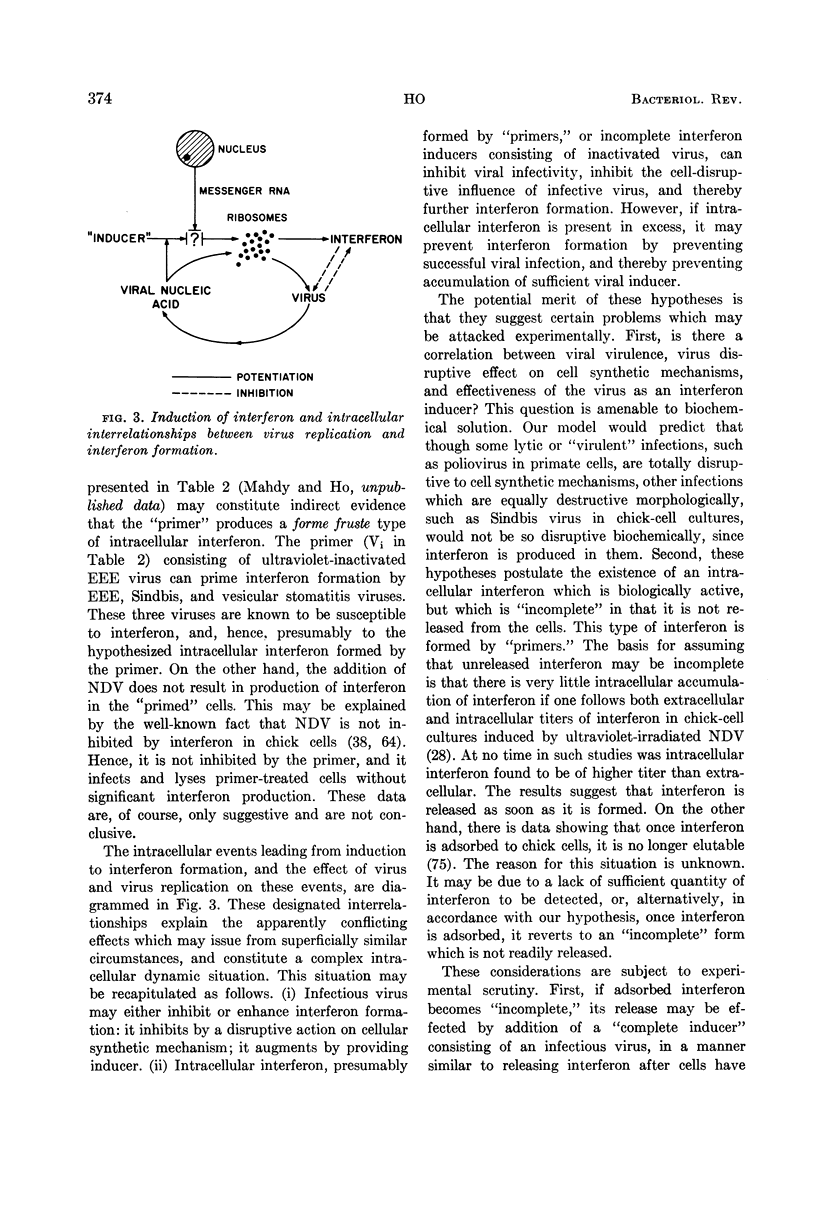
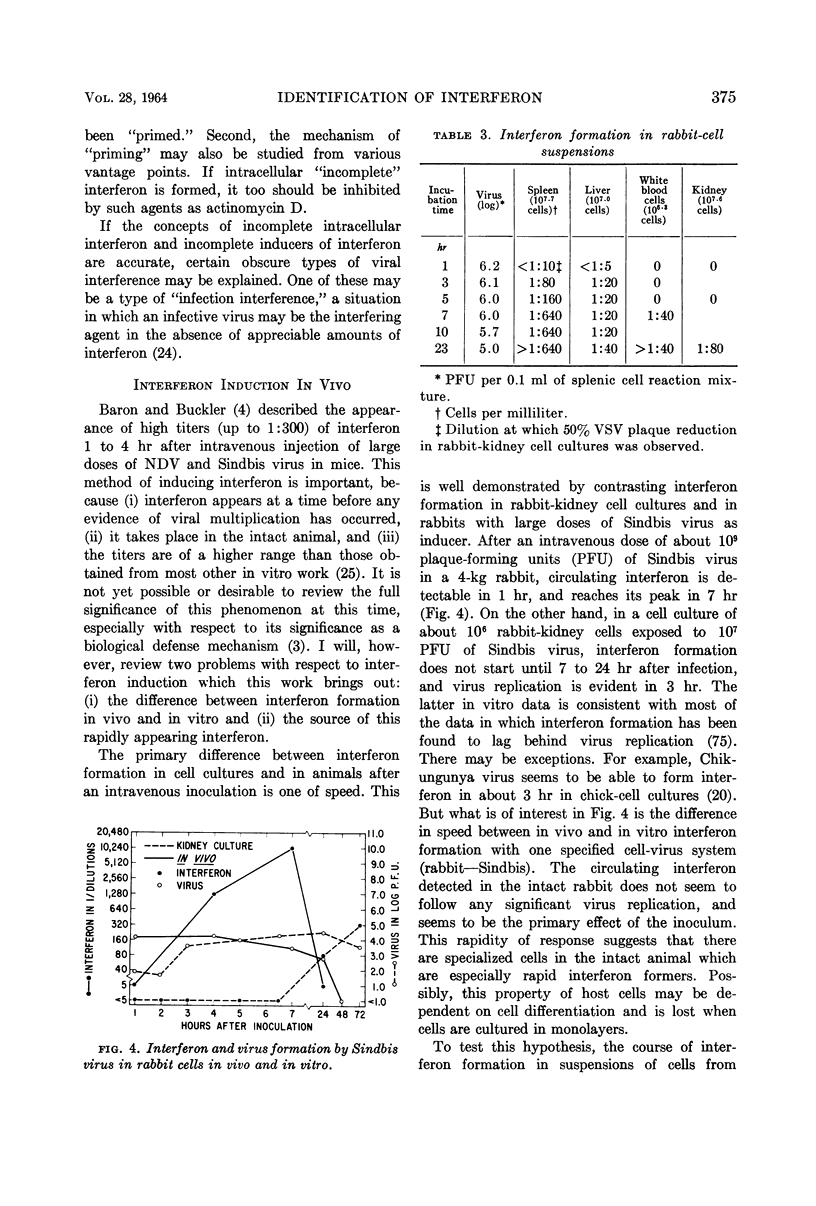






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R. D. Specificity of Interferon. Br Med J. 1961 Jun 17;1(5241):1728–1730. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5241.1728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTIMORE D., FRANKLIN R. M. The effect of Mengovirus infection on the activity of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of L-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1383–1390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARON S., BUCKLER C. E. CIRCULATING INTERFERON IN MICE AFTER INTRAVENOUS INJECTION OF VIRUS. Science. 1963 Sep 13;141(3585):1061–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3585.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARON S. MECHANISM OF RECOVERY FROM VIRAL INFECTION. Adv Virus Res. 1963;10:39–64. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60696-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARON S., PORTERFIELD J. S., ISAACS A. The influence of oxygenation of virus growth I. Effect on plaque formation by different viruses. Virology. 1961 Aug;14:444–449. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90336-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURKE D. C., ISAACS A. Some factors affecting the production of interferon. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Oct;39(5):452–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANY C. An interferon-like inhibitor of viral multiplication from malignant cells (the viral autoinhibition phenomenon). Virology. 1961 Apr;13:485–492. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCITO C., DE MAEYER E., DE SOMER P. The action of interferon on the synthesis of RNA in fibroblasts infected with RNA-virus. Life Sci. 1962 Dec;1:753–758. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(62)90144-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCITO C., DE MAEYER E., DE SONER P. Synthesis of messenger RNA in neoplastic cells treated in vitro with interferon. Life Sci. 1962 Dec;1:759–764. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(62)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., AUSTEN K. F. Contribution of serum and cellular factors in host defense reactions. II. Cellular factors in host resistance. N Engl J Med. 1963 May 9;268:1056–concl. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196305092681906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE MAEYER E., ENDERS J. F. An interferon appearing in cell cultures infected with measles virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jul;107:573–578. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE SOMER P., PRINZIE A., DENYS P., Jr, SCHONNE E. Mechanism of action of interferon. I. Relationship with viral ribonucleic acid. Virology. 1962 Jan;16:63–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90202-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMAEYER E., DEMAEYER-GUIGNARD J. INHIBITION BY 20-METHYLCHOLANTHRENE OF INTERFERON PRODUCTION IN RAT CELLS. Virology. 1963 Jul;20:536–539. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENDERS J. F. A consideration of the mechanisms of resistance to viral infection based on recent studies of the agents of measles and poliomyelitis. Trans Stud Coll Physicians Phila. 1960 Oct;28:68–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIFFORD G. E. STUDIES ON THE SPECIFICITY OF INTERFERON. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:437–443. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASGOW L. A., HABEL K. The role of interferon in vaccinia virus infection of mouse embryo tissue culture. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:503–512. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSSBERG S. E., HOLLAND J. J. Interferon and viral ribonucleic acid. Effect on virus-susceptible and insusceptible cells. J Immunol. 1962 Jun;88:708–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLER E. ENHANCEMENT OF CHIKUNGUNYA VIRUS REPLICATION AND INHIBITION OF INTERFERON PRODUCTION BY ACTINOMYCIN D. Virology. 1963 Dec;21:652–656. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDERSON J. R., TAYLOR R. M. Studies on mechanisms of arthropod-borne virus interference in tissue culture. Virology. 1961 Apr;13:477–484. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLEMAN M. R. INTERFERON IN PROSPECT AND PERSPECTIVE. J Cell Physiol. 1963 Dec;62:337–353. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030620314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. Depression of host-controlled RNA synthesis in human cells during poliovirus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan 15;49:23–28. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. ENTEROVIRUS ENTRANCE INTO SPECIFIC HOST CELLS, AND SUBSEQUENT ALTERATIONS OF CELL PROTEIN AND NUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Mar;28:2–13. doi: 10.1128/br.28.1.2-13.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. Receptor affinities as major determinants of enterovirus tissue tropisms in humans. Virology. 1961 Nov;15:312–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M., BREINIG M. K. Conditions for the production of an interferon appearing in chick cell cultures infected with Sindbis virus. J Immunol. 1962 Aug;89:177–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M., ENDERS J. F. Further studies on an inhibitor of viral activity appearing in infected cell cultures and its role in chronic viral infections. Virology. 1959 Nov;9:446–477. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M. Inhibition of the infectivity of poliovirus ribonucleic acid by an interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jul;107:639–644. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M. Interferons. N Engl J Med. 1962 Jun 21;266:1313–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196206212662506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M. Role of infection in viralinterference. I. Inhibition of lethal infections in chick embryos preinfected with influenza viruses. Arch Intern Med. 1962 Nov;110:653–659. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1962.03620230099014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ J., FURTH J. J., MALAMY M., ALEXANDER M. The role of deoxyribonucleic acid in ribonucleic acid synthesis. III. The inhibition of the enzymatic synthesis of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid by actinomycin D and proflavin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1222–1230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A. FOREIGN NUCLEIC ACIDS. Sci Am. 1963 Oct;209:46–50. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1063-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A. INTERFERON. Adv Virus Res. 1963;10:1–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A., PORTERFIELD J. S., BARON S. The influence of oxygenation on virus growth. II. Effect on the antiviral action of interferon. Virology. 1961 Aug;14:450–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A., WESTWOOD M. A. Inhibition by interferon of the growth of vaccinia virus in the rabbit skin. Lancet. 1959 Sep 12;2(7098):324–325. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91361-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENSEN K. E., NEAL A. L., OWENS R. E., WARREN J. INTERFERON RESPONSES OF CHICK EMBRYO FIBROBLASTS TO NUCLEIC ACIDS AND RELATED COMPOUNDS. Nature. 1963 Nov 2;200:433–434. doi: 10.1038/200433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILBOURNE E. D., SMART K. M., POKORNY B. A. Inhibition by cortisone of the synthesis and action of interferon. Nature. 1961 May 13;190:650–651. doi: 10.1038/190650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M., JORDAN W. S., Jr In vitro absorption of poliovirus by noncultured tissues. Effect of species, age and malignancy. Am J Hyg. 1961 May;73:245–257. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPSON G. P., TYTELL A. A., NEMES M. M., HILLEMAN M. R. Purification and characterization of chick embryo interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Feb;112:468–478. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S. Some characteristics of an interferon derived from embryonated eggs infected with Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1962 Aug;17:593–595. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90161-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. B., SNELLBAKER L. F., BARON S. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF INTERFERON. Virology. 1963 Sep;21:48–55. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90303-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDENMANN J., BURKE D. C., ISAACS A. Studies on the production, mode of action and properties of interferon. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Oct;38(5):551–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDENMANN J. [Interferon and inverse interference]. Z Haut Geschlechtskr. 1960;28:287–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHDY M. S., HO M. POTENTIATING EFFECT OF FRACTIONS OF EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALOMYELITIS VIRUS ON INTERFERON PRODUCTION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 May;116:174–177. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERIGAN T. C. PURIFIED INTERFERONS: PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND SPECIES SPECIFICITY. Science. 1964 Aug 21;145(3634):811–813. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3634.811-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIMS C. A. ASPECTS OF THE PATHOGENESIS OF VIRUS DISEASES. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Mar;28:30–71. doi: 10.1128/br.28.1.30-71.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUMPER R. W., YAMASHIROYA H. M., ALFRED L. J. Cytopathic protective factor: its production by normal uninfected serum-free cell cultures. Nature. 1961 Dec 16;192:1101–1102. doi: 10.1038/1921101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICH E., FRANKLIN R. M., SHATKIN A. J., TATUMEL Action of actinomycin D on animal cells and viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1238–1245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTEM Z., COX R. A., ISAACS A. Inhibition of virus multiplication by foreign nucleic acid. Nature. 1963 Feb 9;197:564–566. doi: 10.1038/197564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUIZ-GOMEZ J., ISAACS A. Interferon production by different viruses. Virology. 1963 Jan;19:8–12. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUIZ-GOMEZ J., ISAACS A. Optimal temperature for growth and sensitivity to interferon among different viruses. Virology. 1963 Jan;19:1–7. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSILINSKY YAYA, LEVASHEV V. S. INHIBIBITORS OF VIRAL ACTIVITY FROM UNINFECTED CULTURES OF STABLE CELL LINES. IV. STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE CONTAMINATION OF CELL CULTURES WITH PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS (PPLO) AND OCCURRENCE OF INHIBITORS. Acta Virol. 1963 Nov;7:549–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSILINSKY Ia Ia. INHIBITORS OF VIRAL ACTIVITY FROM UNINFECTED CULTURES OF STABLE CELL LINES. III. INTERACTION OF INHIBITORS WITH TRYPSINIZED MONKEY KIDNEY CELLS. Acta Virol. 1963 Nov;7:542–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSILINSKY Y. Y. INHIBITORS OF VIRAL ACTIVITY FROM UNINFECTED CULTURES OF STABLE CELL LINES.II. PROPERTIES OF INHIBITORS. Acta Virol. 1963 Sep;7:437–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYRRELL D. A. Interferon produced by cultures of calf kidney cells. Nature. 1959 Aug 8;184(Suppl 7):452–453. doi: 10.1038/184452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER R. R. Biological studies of interferon. I. Suppression of cellular infection with eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus. Virology. 1961 Mar;13:323–337. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER R. R. Biological studies of interferon. II. Temporal relationships of virus and interferon production by cells infected with Eastern equine encephalomyelitis and influenza viruses. Virology. 1963 Feb;19:215–224. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER R. R., LEVY A. H. Interferon as a chemical intermediary in viral interference. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 21;88:1308–1318. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER R. R. THE INTERFERONS: CELLULAR INHIBITORS OF VIRAL INFECTION. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1963;17:285–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.17.100163.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNGNER J. S., STINEBRING W. R. INTERFERON REDUCTION IN CHICKENS INJECTED WITH BRUCELLA ABORTUS. Science. 1964 May 22;144(3621):1022–1023. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3621.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarmolinsky M. B., Haba G. L. INHIBITION BY PUROMYCIN OF AMINO ACID INCORPORATION INTO PROTEIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Dec;45(12):1721–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.12.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


