Abstract
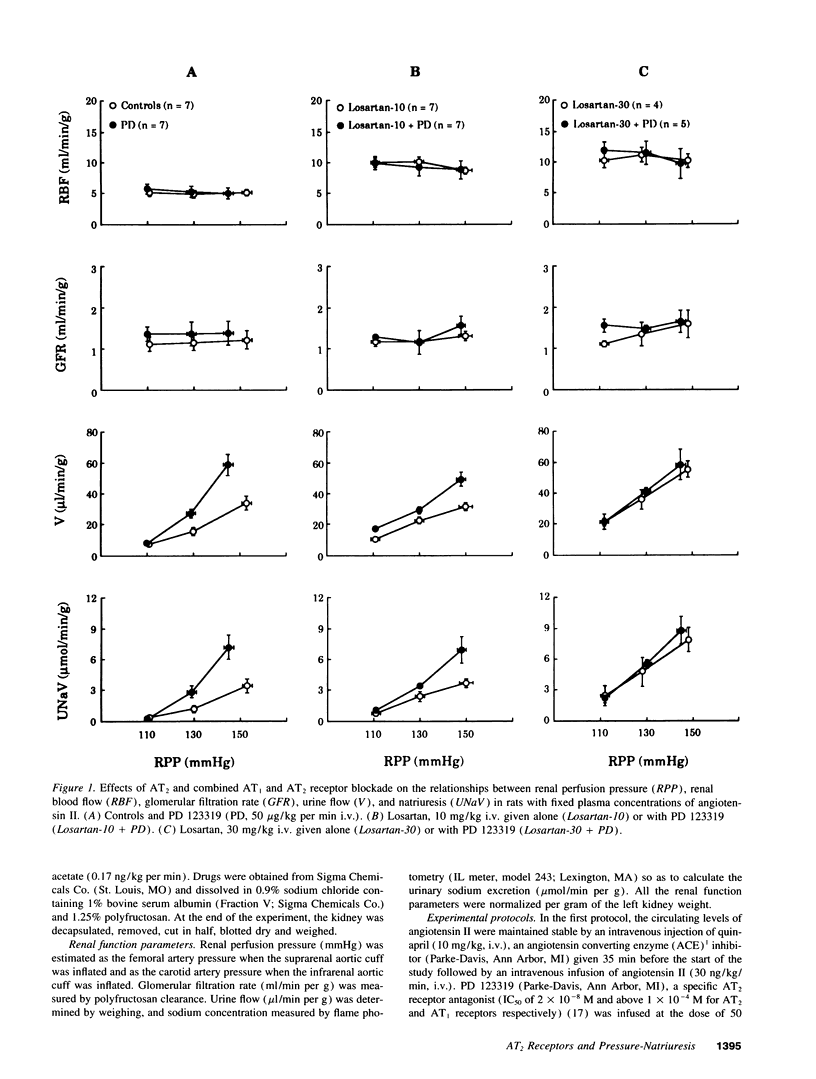
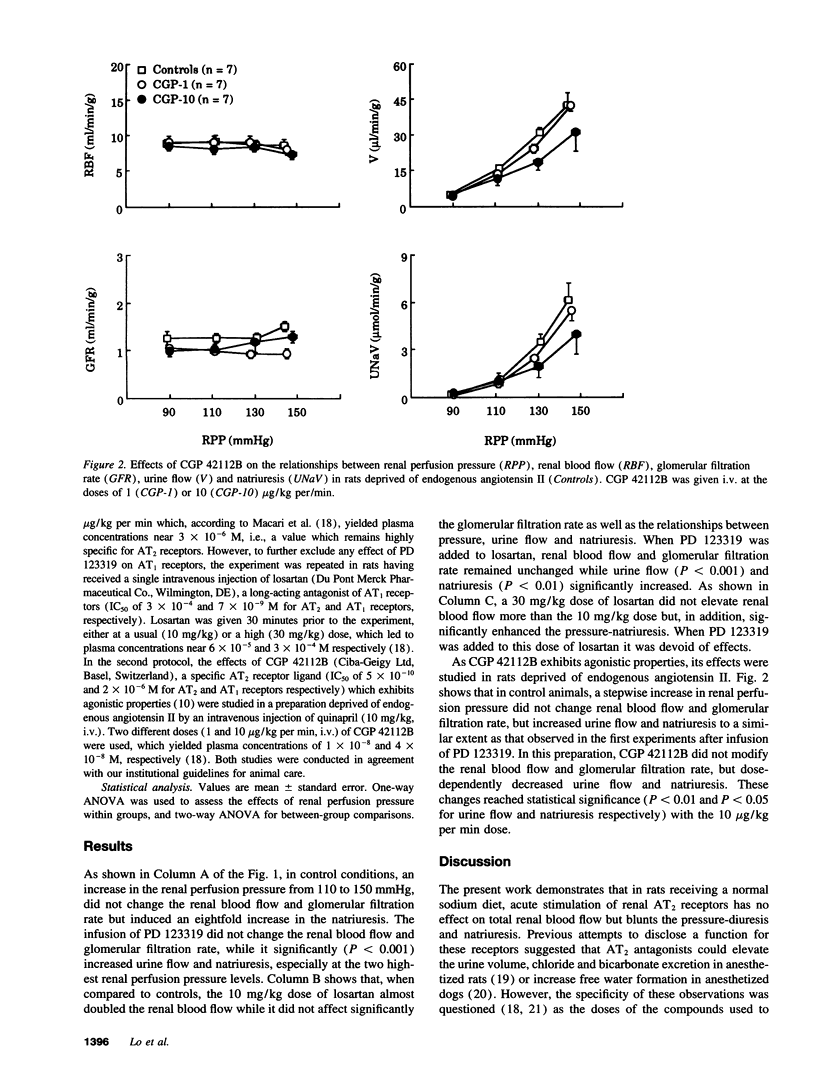
Angiotensin II recognizes two receptor subtypes, AT1 and AT2, both of them having been recently cloned. Although AT2 receptors represent 5-10% of angiotensin II receptors in the kidneys of adult rats, their function remains unknown. In the present work, we examined the possible contribution of AT2 receptors to the regulation of pressure-natriuresis in anesthetized rats infused either with the specific AT2 antagonist PD 123319, or with CGP 42112B, an AT2 ligand with agonistic properties. The effects of PD 123319 were examined in a preparation with stable levels of angiotensin II, and in which AT1 receptors were blocked by the specific antagonist losartan. The effects of CGP 42112B were studied in rats deprived of endogenous angiotensin II. AT2 receptor blockade with PD 123319 did not change the renal blood flow while it increased the diuresis and natriuresis. These effects persisted even after full AT1 receptor blockade with losarfan. CGP 42112B did not modify the renal blood flow, but dose-dependently decreased urine flow and natriuresis. These results show that, contrary to AT1 receptors, renal AT2 receptors have no effect on total renal blood flow, but blunt the pressure-natriuresis, thus demonstrating that this receptor subtype is involved in a function of importance for body fluid and blood pressure regulation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brasch H., Sieroslawski L., Dominiak P. Angiotensin II increases norepinephrine release from atria by acting on angiotensin subtype 1 receptors. Hypertension. 1993 Nov;22(5):699–704. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.22.5.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumpus F. M., Catt K. J., Chiu A. T., DeGasparo M., Goodfriend T., Husain A., Peach M. J., Taylor D. G., Jr, Timmermans P. B. Nomenclature for angiotensin receptors. A report of the Nomenclature Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension. 1991 May;17(5):720–721. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.5.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark K. L., Robertson M. J., Drew G. M. Role of angiotensin AT1 and AT2 receptors in mediating the renal effects of angiotensin II in the anaesthetized dog. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 May;109(1):148–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13545.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan M. G., Liu F. Y., Wong P. C., Timmermans P. B. Comparison of inhibitory potency by nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists PD123177 and DuP 753 on proximal nephron and renal transport. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Nov;259(2):687–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley D. T., Panek R. L., Major T. C., Lu G. H., Bruns R. F., Klinkefus B. A., Hodges J. C., Weishaar R. E. Subclasses of angiotensin II binding sites and their functional significance. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;38(3):370–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenoy F. J., Roman R. J. Effect of volume expansion on papillary blood flow and sodium excretion. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 2):F813–F822. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.6.F813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyton A. C. Long-term arterial pressure control: an analysis from animal experiments and computer and graphic models. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 2):R865–R877. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.259.5.R865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jover B., Saladini D., Nafrialdi N., Dupont M., Mimran A. Effect of losartan and enalapril on renal adaptation sodium restriction in rat. Am J Physiol. 1994 Aug;267(2 Pt 2):F281–F288. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.267.2.F281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kambayashi Y., Bardhan S., Takahashi K., Tsuzuki S., Inui H., Hamakubo T., Inagami T. Molecular cloning of a novel angiotensin II receptor isoform involved in phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24543–24546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser J. A., Bjork F. A., Hodges J. C., Taylor D. G., Jr Renal hemodynamic and excretory responses to PD 123319 and losartan, nonpeptide AT1 and AT2 subtype-specific angiotensin II ligands. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Sep;262(3):1154–1160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline R. L., Liu F. Modification of pressure natriuresis by long-term losartan in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1994 Oct;24(4):467–473. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.24.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu S., Mattson D. L., Cowley A. W., Jr Renal medullary captopril delivery lowers blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1994 Mar;23(3):337–345. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.23.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macari D., Bottari S., Whitebread S., De Gasparo M., Levens N. Renal actions of the selective angiotensin AT2 receptor ligands CGP 42112B and PD 123319 in the sodium-depleted rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov 2;249(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90665-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson D. L., Raff H., Roman R. J. Influence of angiotensin II on pressure natriuresis and renal hemodynamics in volume-expanded rats. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 2):R1200–R1209. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1991.260.6.R1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukoyama M., Nakajima M., Horiuchi M., Sasamura H., Pratt R. E., Dzau V. J. Expression cloning of type 2 angiotensin II receptor reveals a unique class of seven-transmembrane receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24539–24542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. J., Alexander R. W., Griendling K. K., Runge M. S., Bernstein K. E. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the vascular type-1 angiotensin II receptor. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):233–236. doi: 10.1038/351233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navar L. G., Rosivall L. Contribution of the renin-angiotensin system to the control of intrarenal hemodynamics. Kidney Int. 1984 Jun;25(6):857–868. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman R. J., Cowley A. W., Jr Characterization of a new model for the study of pressure-natriuresis in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):F190–F198. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.2.F190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Yamano Y., Bardhan S., Iwai N., Murray J. J., Hasegawa M., Matsuda Y., Inagami T. Cloning and expression of a complementary DNA encoding a bovine adrenal angiotensin II type-1 receptor. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):230–233. doi: 10.1038/351230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. C., Hart S. D., Zaspel A. M., Chiu A. T., Ardecky R. J., Smith R. D., Timmermans P. B. Functional studies of nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor subtype-specific ligands: DuP 753 (AII-1) and PD123177 (AII-2). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):584–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie M. H., Liu F. Y., Wong P. C., Timmermans P. B., Cogan M. G. Proximal nephron and renal effects of DuP 753, a nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Kidney Int. 1990 Sep;38(3):473–479. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo J., Song K., Harris P. J., Mendelsohn F. A. In vitro autoradiography reveals predominantly AT1 angiotensin II receptors in rat kidney. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1992 Sep-Oct;15(5):231–239. doi: 10.1159/000173458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Mark J., Kline R. L. Altered pressure natriuresis in chronic angiotensin II hypertension in rats. Am J Physiol. 1994 Mar;266(3 Pt 2):R739–R748. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1994.266.3.R739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


