Full text
PDF

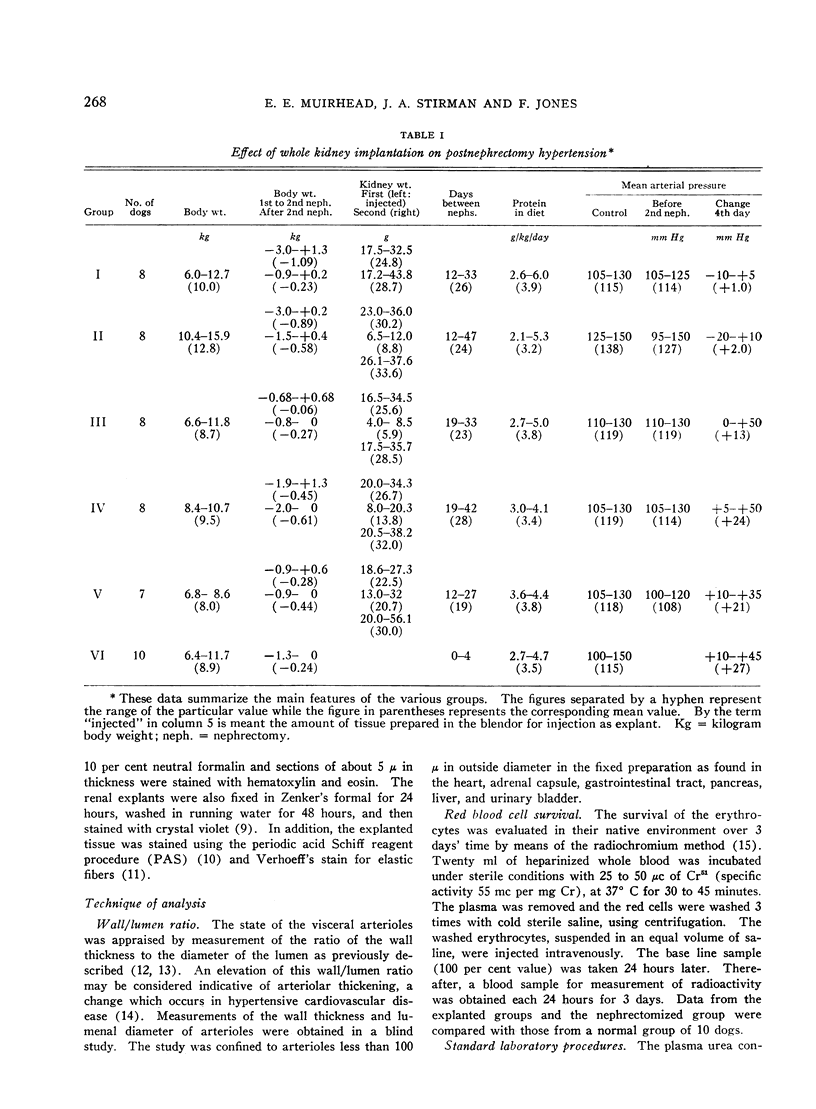
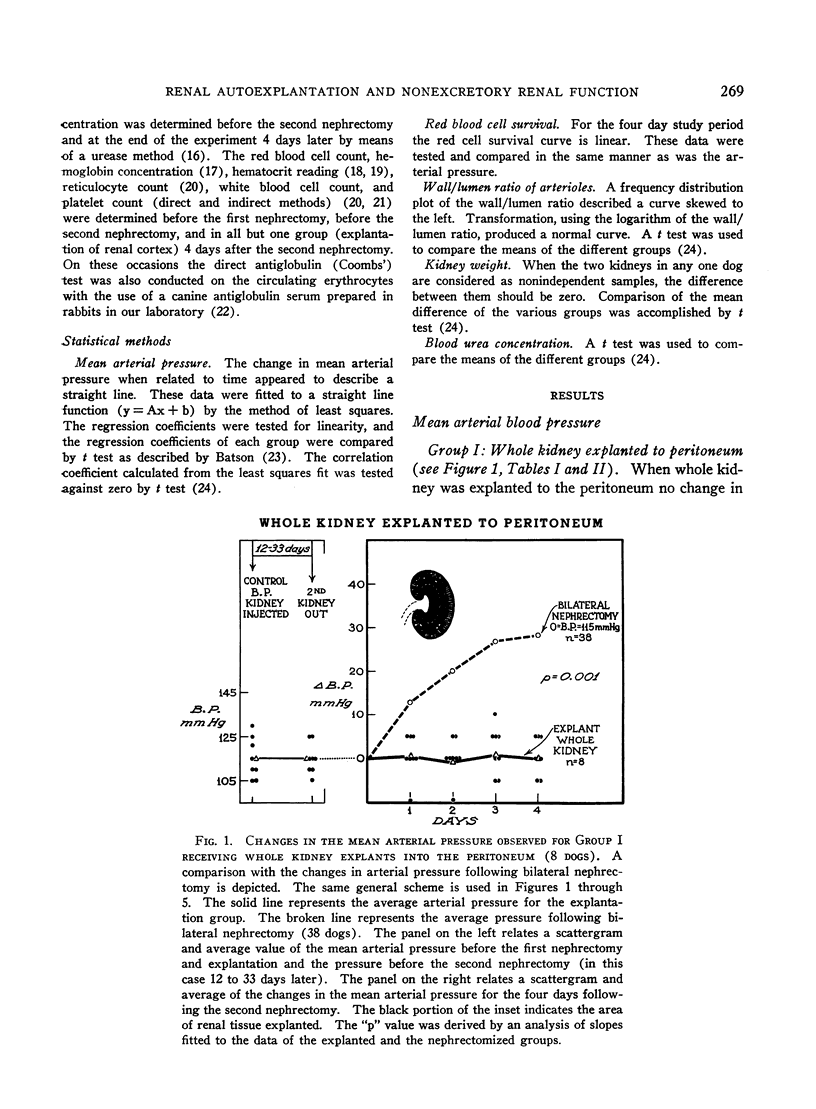
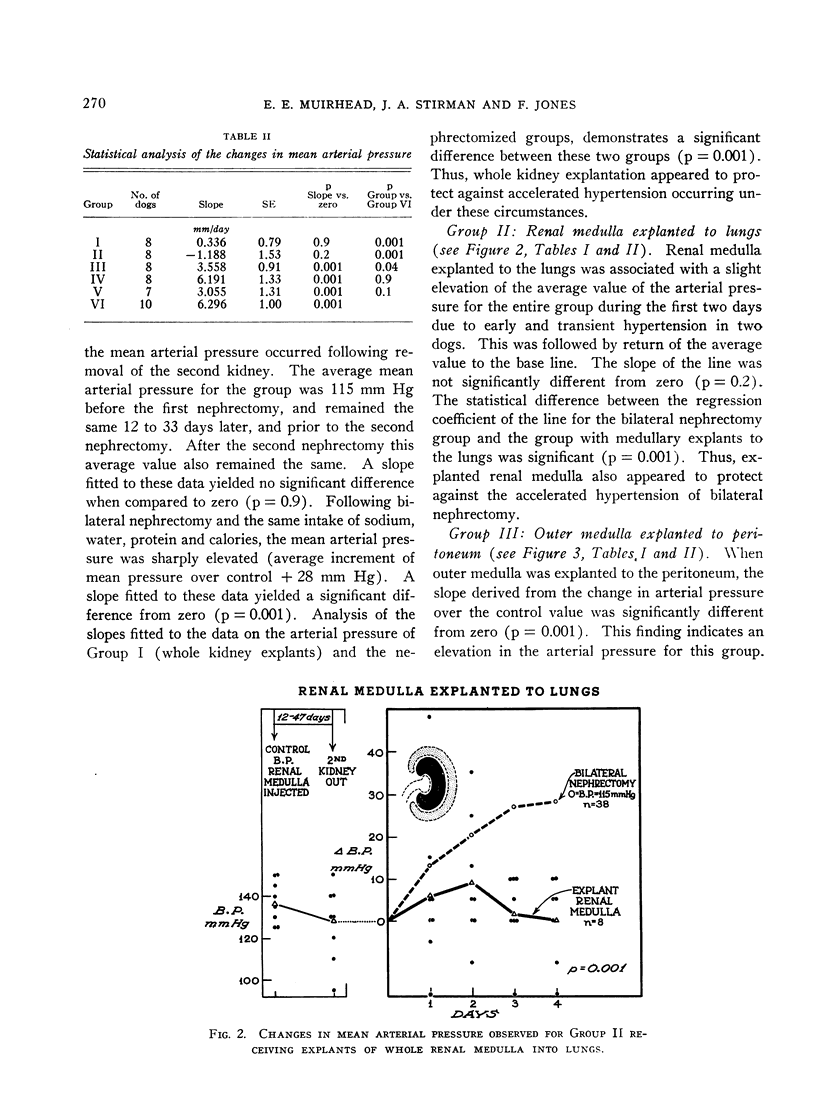
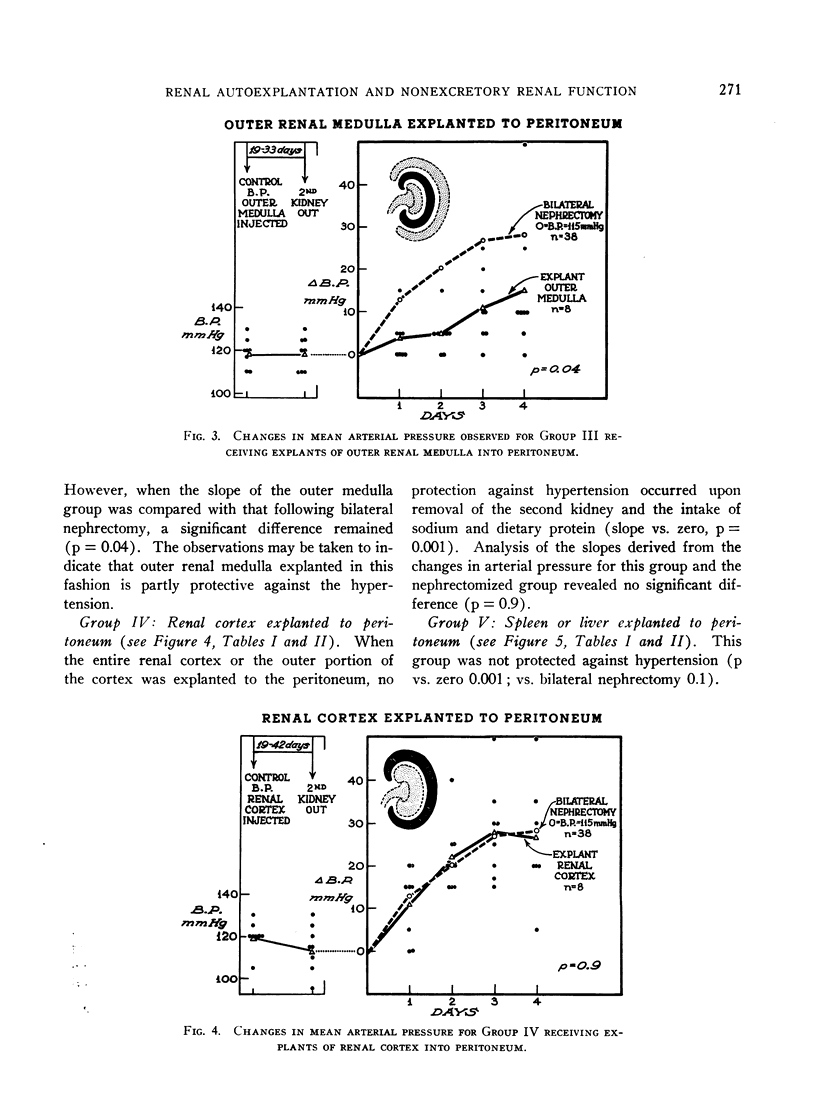
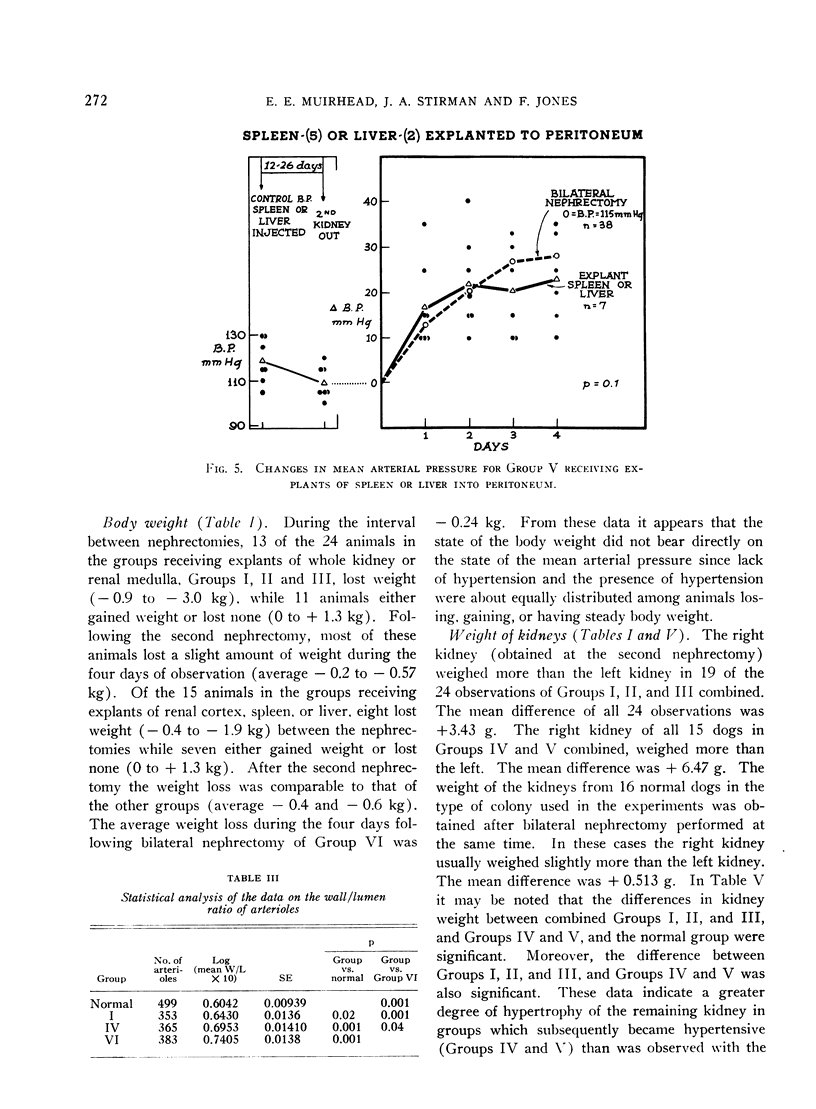
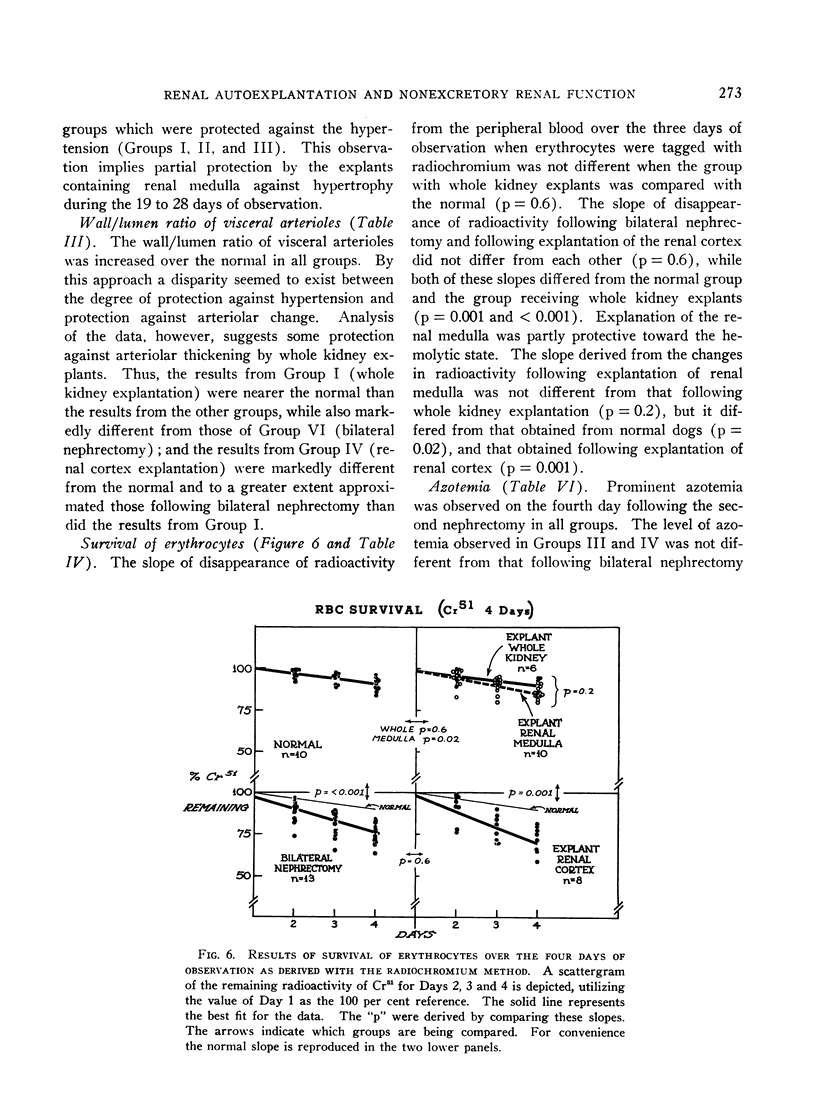

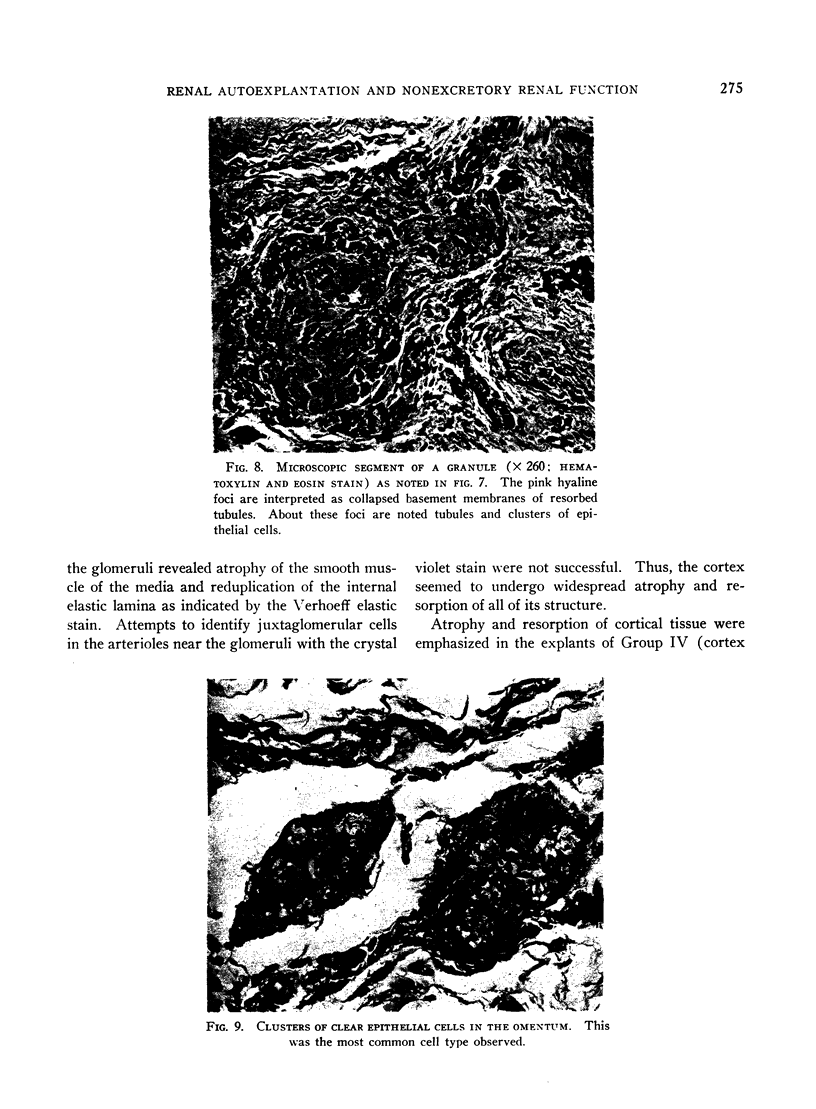


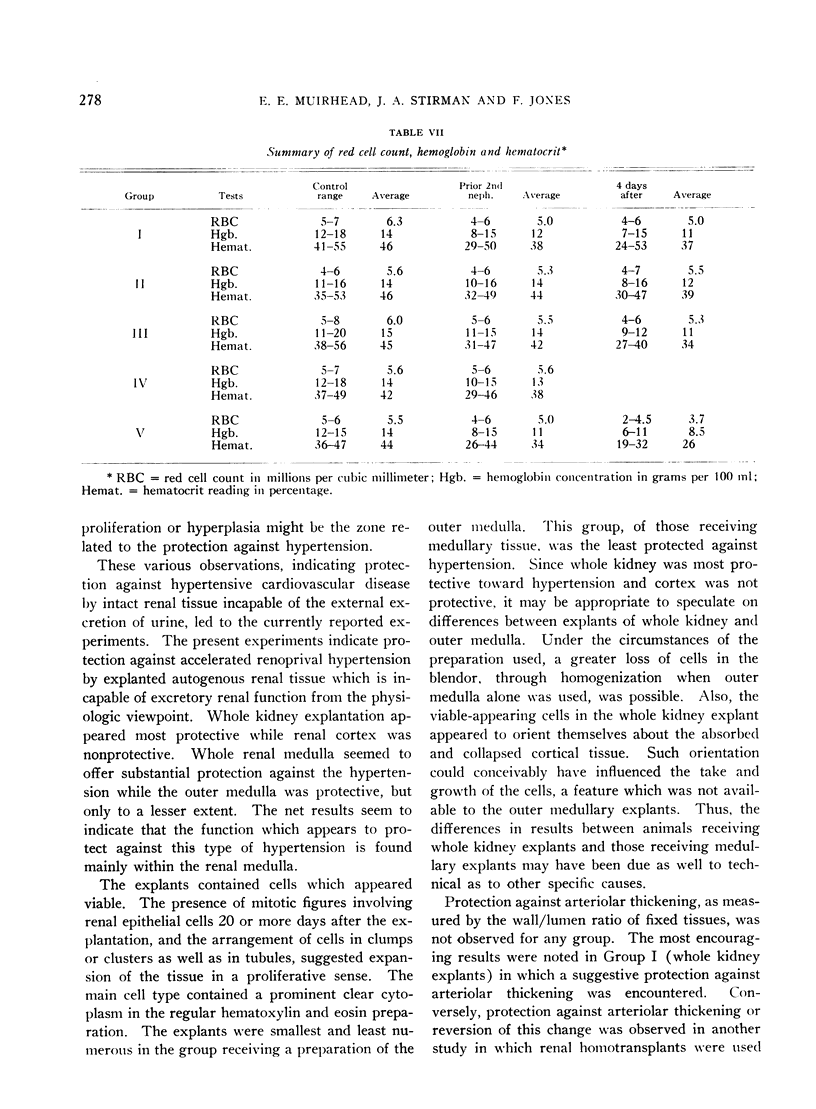



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAPLIN H., Jr, MOLLISON P. L. Correction for plasma trapped in the red cell column of the hematocrit. Blood. 1952 Dec;7(12):1227–1238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOYER M. A. Role of the kidney in experimental hypertension. Br Med Bull. 1957 Jan;13(1):29–32. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROLLMAN A., TURNER L. B., LEVITCH M., HILL D. Hemodynamics of bilaterally nephrectomized dog subjected to intermittent peritoneal lavage. Am J Physiol. 1951 Apr 1;165(1):167–172. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.165.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUCK C. R. Effect of hydration and dehydration on hypertension in the chronic bilaterally nephrectomized dog. Am J Physiol. 1954 Feb;176(2):183–189. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.176.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES F., LESCH W., MUIRHEAD E. E., STIRMAN J. A. The reduction of postnephrectomy hypertension by renal homotransplant. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1956 Dec;103(6):673–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOLFF W. J., PAGE I. H. Blood pressure reducing function of the kidney; reduction of renoprival hypertension by kidney perfusion. Am J Physiol. 1954 Jul;178(1):75–81. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.178.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOLFF W. J., PAGE I. H., CORCORAN A. C. Pathogenesis of renoprival cardiovascular disease in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1954 Aug;178(2):237–245. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.178.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOLFF W. J., PAGE I. H. Influence of protein and other factors of postnephrectomy hypertension in rats sustained with an improved method of peritoneal lavage. Am J Physiol. 1954 Jul;178(1):69–74. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.178.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONARDS J. R., HEISLER C. R. Artificial kidney. IV. Maintenance of life in bilaterally nephrectomized dogs and its relation to malignant hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1951 Nov;167(2):553–558. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.167.2.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERRILL J. P., MURRAY J. E., HARRISON J. H., GUILD W. R. Successful homotransplantation of the human kidney between identical twins. J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Jan 28;160(4):277–282. doi: 10.1001/jama.1956.02960390027008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIRHEAD E. E. Experimental hypertension following bilateral nephrectomy; the influence of protein and sodium on its pathogenesis. South Med J. 1954 Feb;47(2):110–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIRHEAD E. E., GROVES M., BRYAN S. Positive direct Coombs test induced by phenylhydrazine. J Clin Invest. 1954 Dec;33(12):1700–1711. doi: 10.1172/JCI103050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIRHEAD E. E., JONES F., GRAHAM P. Hypertension following bilateral nephrectomy of the dog; the influence of dietary protein on its pathogenesis with emphasis on its development in the absence of extracellular fluid expansion. Circ Res. 1953 Sep;1(5):439–453. doi: 10.1161/01.res.1.5.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIRHEAD E. E., JONES F., GRAHAM P. Hypertension in bilaterally nephrectomized dogs in absence of exogenous sodium excess; maintenance of fluid balance during peritoneal irrigation. AMA Arch Pathol. 1953 Sep;56(3):286–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIRHEAD E. E., JONES F., STIRMAN J. A., LESCH W. Experimental uremia; excessive quantities of plasma protein and nitrogen removed in the outflow fluid during peritoneal irrigation of bilaterally nephrectomized dogs. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1953 Aug;97(2):189–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIRHEAD E. E., JONES F., STIRMAN J. A., LESCH W. Hemolytic anemia of the dog following bilateral nephrectomy. Am J Physiol. 1953 May;173(2):371–378. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.173.2.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIRHEAD E. E., JONES F., STIRMAN J. A. Potentiation of renoprival hypertension by alanine, pyruvate and lactate. Am J Physiol. 1957 Dec;191(3):537–541. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.191.3.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIRHEAD E. E., STIRMAN J. A., JONES F. Further observations on the potentiation of postnephrectomy hypertension of the dog by dietary protein. Circ Res. 1959 Jan;7(1):68–78. doi: 10.1161/01.res.7.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORBISON J. L., CHRISTIAN C. L., PETERS E. Studies on experimental hypertension and cardiovascular disease. I. A method for the rapid production of malignant hypertension in bilaterally nephrectomized dogs. AMA Arch Pathol. 1952 Aug;54(2):185–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND D. A., McCALL M. S., GROVES M. T., MUIRHEAD E. E. The survival of human erythrocytes estimated by means of cells tagged with radioactive chromium; a study of the normal state. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 May;43(5):717–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER L. B., GROLLMAN A. Role of adrenal in pathogenesis of experimental renal hypertension as determined by a study of the bilaterally adrenalectomized nephrectomized dog. Am J Physiol. 1951 Nov;167(2):462–472. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.167.2.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON W. A new staining method for demonstrating the granules of the juxtaglomerular complex. Anat Rec. 1952 Mar;112(3):497–507. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091120303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]