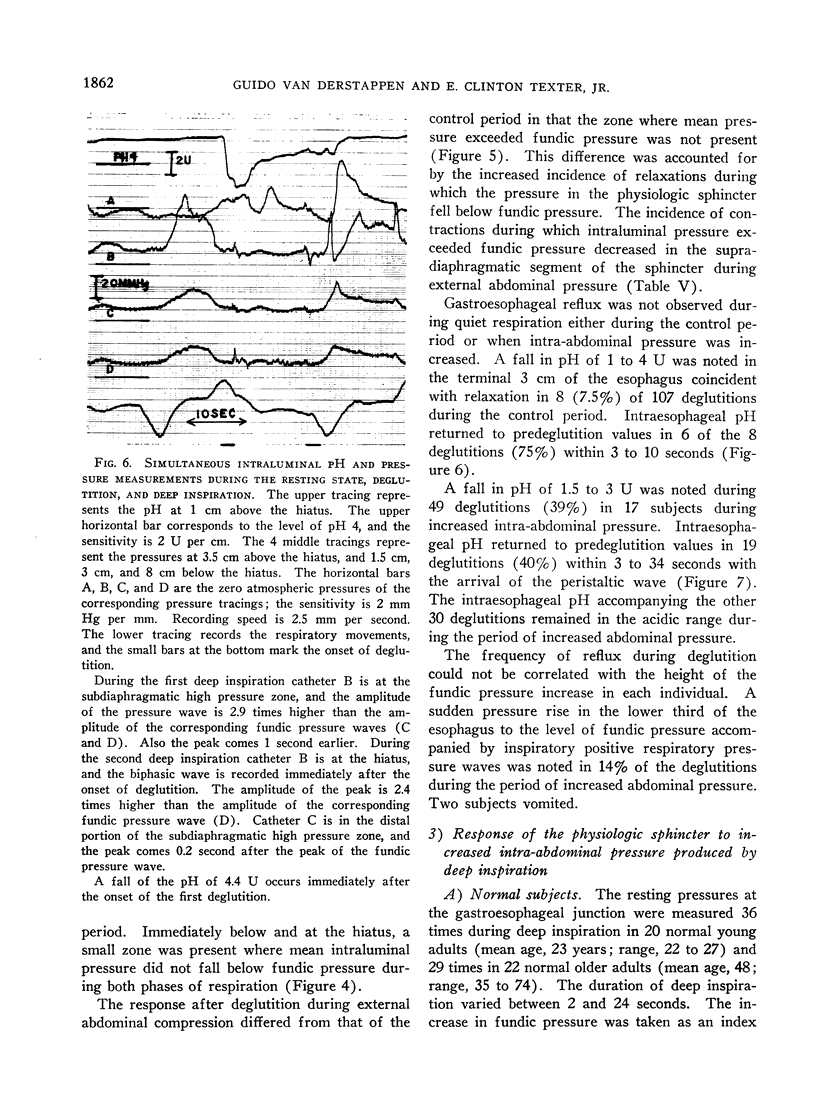
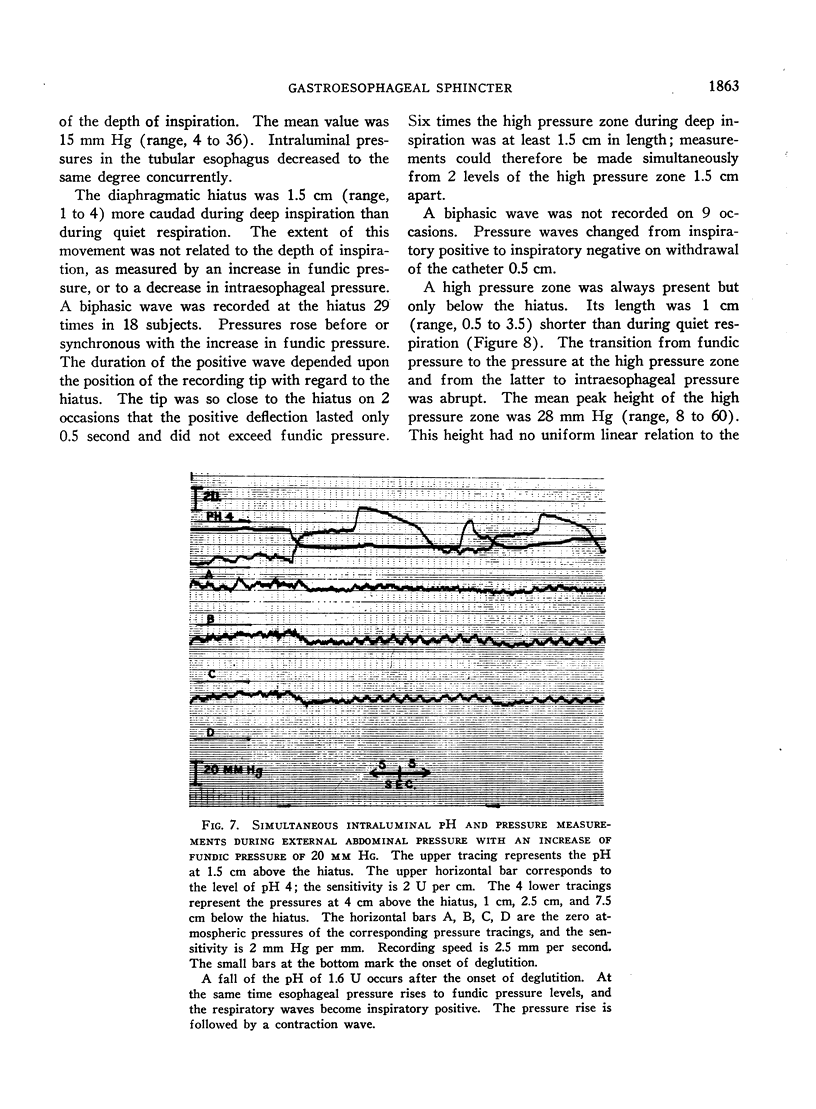
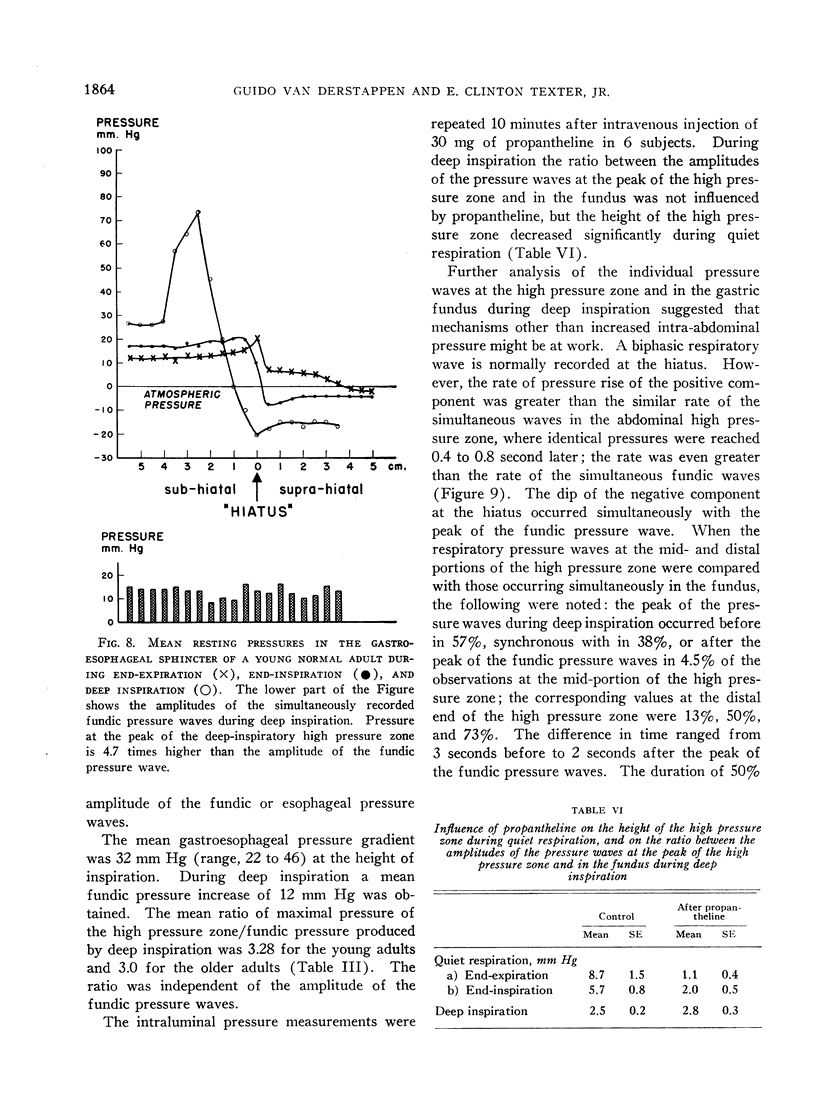
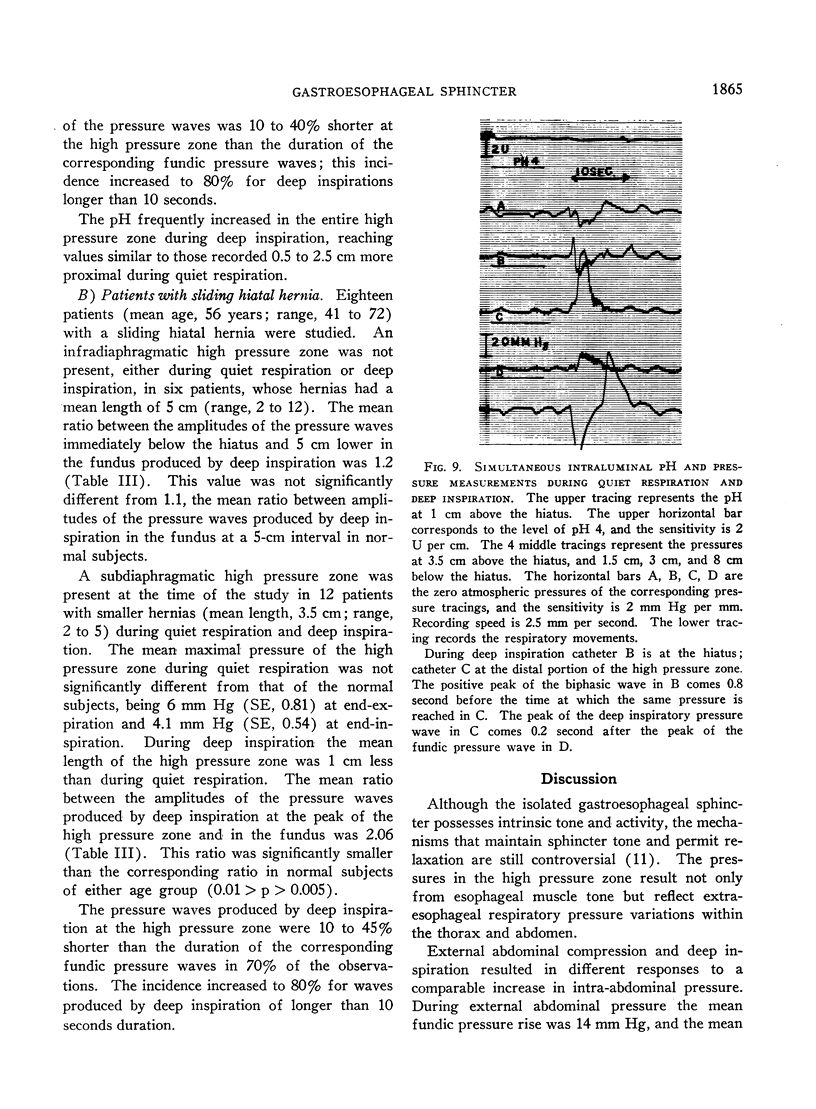
Full text
PDF

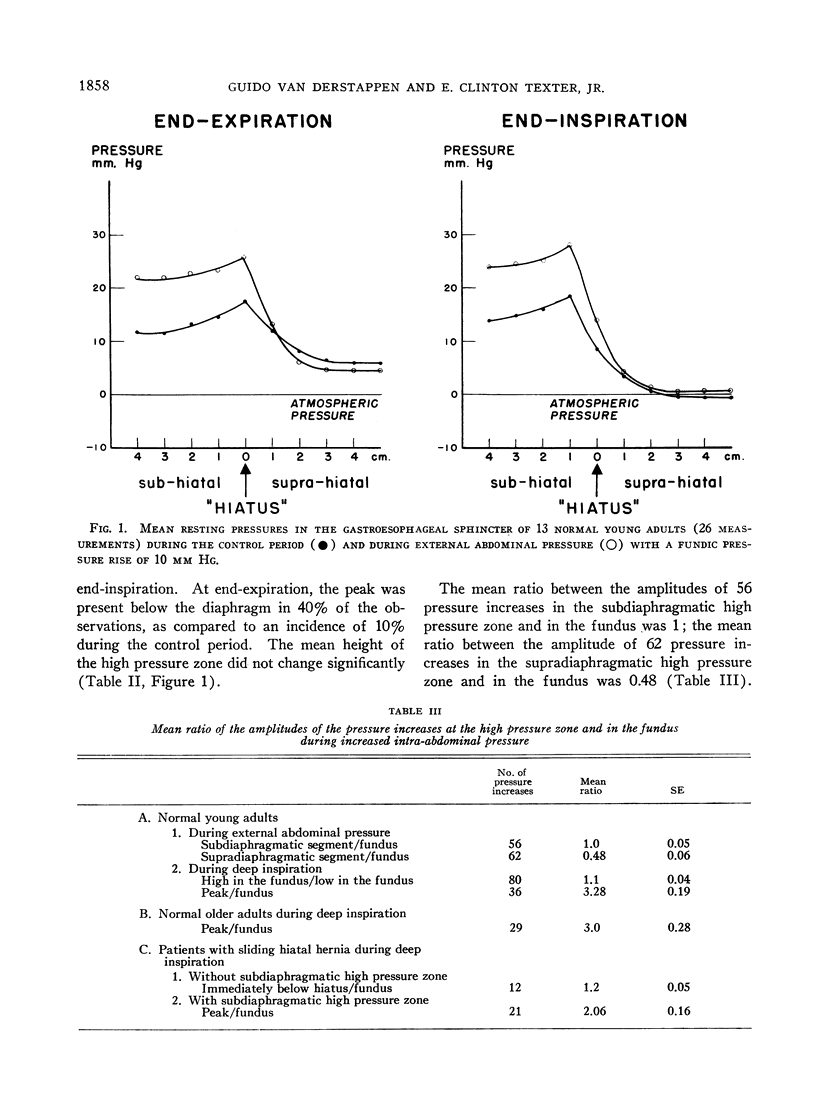
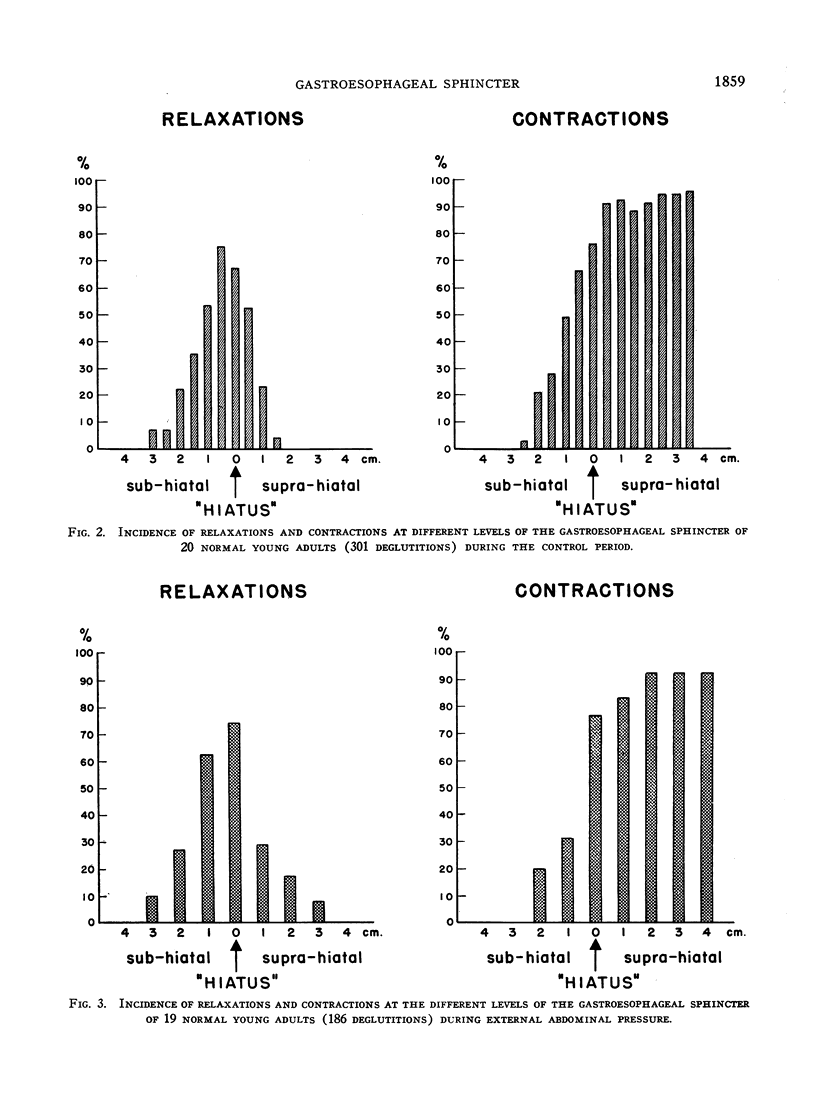
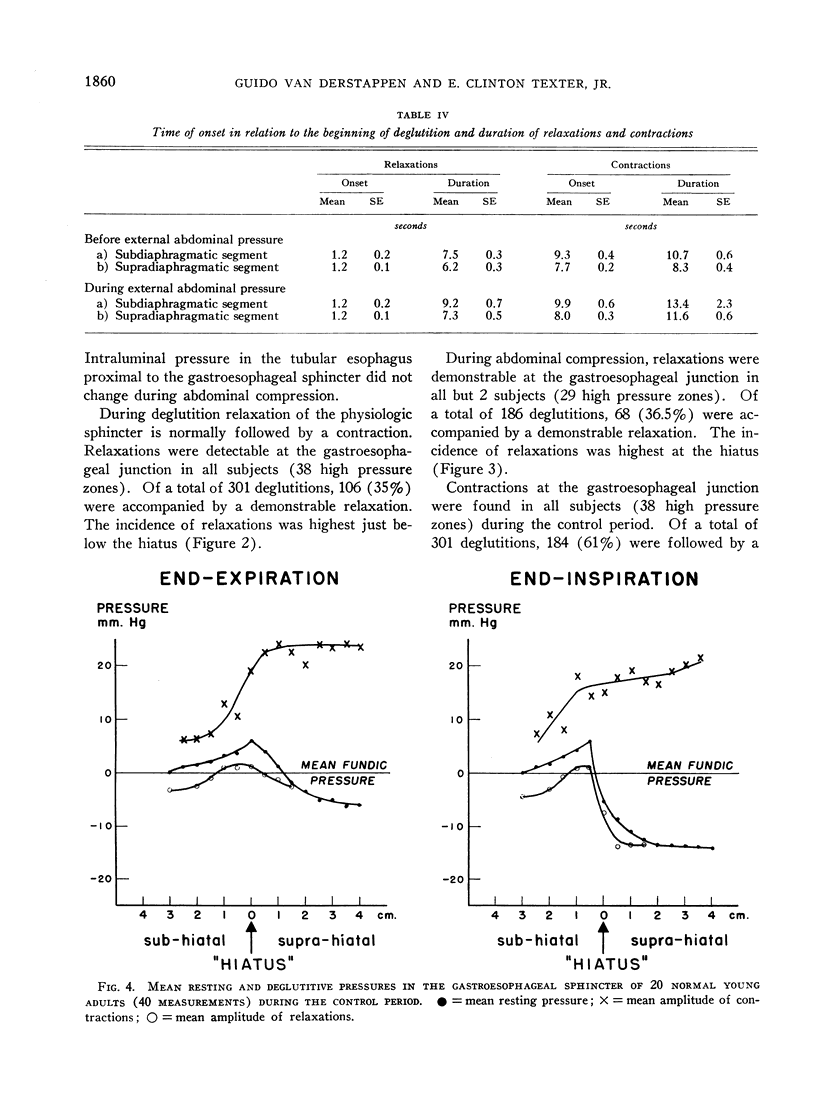
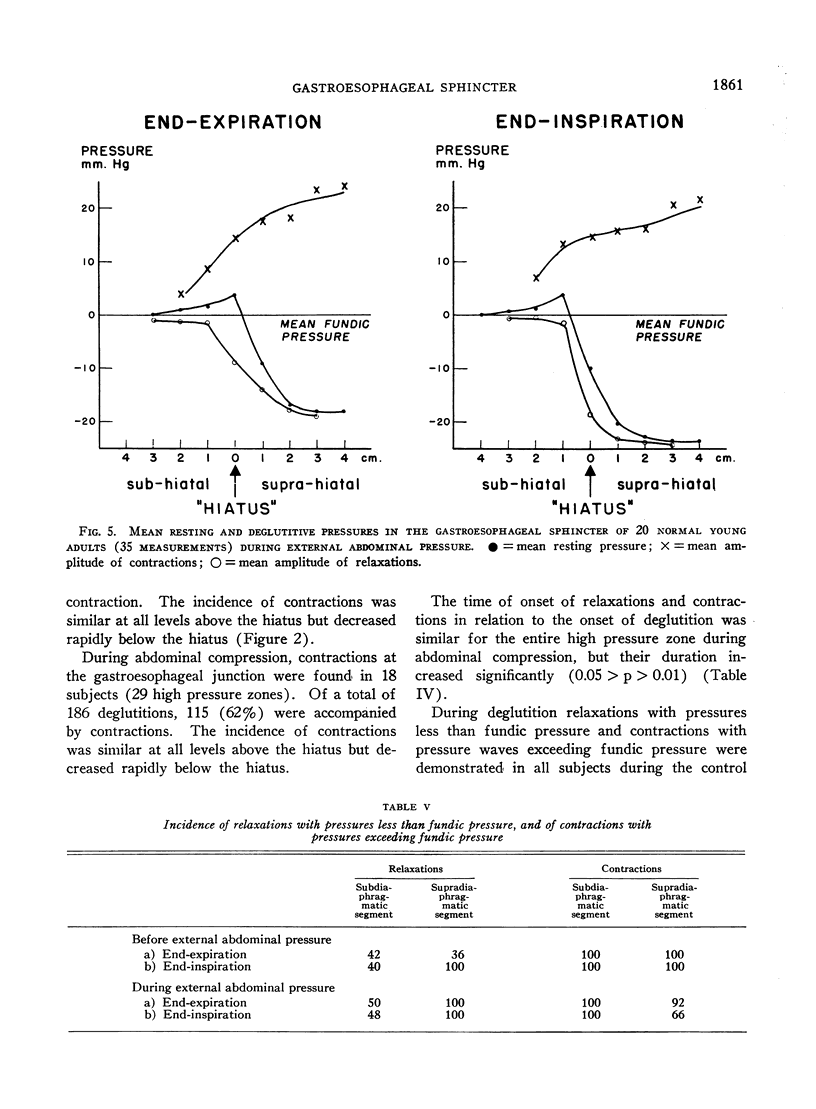



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINSON M., EDWARDS D. A., HONOUR A. J., ROWLANDS E. N. The oesophago-gastric sphincter in hiatus hernia. Lancet. 1957 Dec 7;273(7006):1138–1142. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CODE C. F., FYKE F. E., Jr, SCHLEGEL J. F. The gastroesophageal sphincter in healthy human beings. Gastroenterologia. 1956;86(3):135–150. doi: 10.1159/000200544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CODE C. F., SCHLEGEL J. F., KELLEY M. L., Jr, OLSEN A. M., ELLIS F. H., Jr Hypertensive gastroesophageal sphincter. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1960 Jul 6;35:391–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN B. R., WOLF B. S. Roentgen localization of the physiologically determined esophageal hiatus. Gastroenterology. 1962 Jul;43:43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREAMER B., HARRISON G. K., PIERCE J. W. Further observations on the gastro-oesophageal junction. Thorax. 1959 Jun;14:132–137. doi: 10.1136/thx.14.2.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGELFINGER F. J. Esophageal motility. Physiol Rev. 1958 Oct;38(4):533–584. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.4.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEY M. L., Jr, WILBUR D. L., 3rd, SCHLEGEL J. F., CODE C. F. Deglutitive responses in the gastroesophageal sphincter of healthy human beings. J Appl Physiol. 1960 May;15:483–488. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.3.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLAURIN C. THE INTRINSIC SPHINCTER IN THE PREVENTION OF GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX. Lancet. 1963 Oct 19;2(7312):801–805. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90499-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONGES H. Considérations sur le rôle du diaphragme dans la physiologie de la continence gastro-oesophagienne et sur la projection radiologique de l'hiatus oesophagien. Gastroenterologia. 1956;86(3):232–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGLER R., SPIRO H. M. Segmental response of the inferior esophageal sphincter to elevated intragastric pressure. Gastroenterology. 1961 Mar;40:405–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROVELSTAD R. A., OWEN C. A., Jr, MAGATH T. B. Factors influencing the continuous recording of in situ pH of gastric and duodenal contents. Gastroenterology. 1952 Apr;20(4):609–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEXTER E. C., Jr, VAN DERSTAPPEN G., CHEJFEC G., CHVOJKA V. E., VIDINLI M., BARBORKA C. J., BUNDESEN W. E. Criteria for the diagnosis of hiatal hernia. Arch Intern Med. 1962 Dec;110:827–836. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1962.03620240009004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANTRAPPEN G., TEXTER E. C., Jr, BARBORKA C. J., VANDEN-BROUCKE J. The closing mechanism at the gastroesophageal junction. Am J Med. 1960 Apr;28:564–577. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLF B. S., COHEN B. R. Radiologic localization of the esophageal hiatus as determined by intraluminal pressure measurements. Radiology. 1961 Jun;76:903–910. doi: 10.1148/76.6.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLF B. S. The esophagogastric closing mechanism: role of the abdominal esophagus. J Mt Sinai Hosp N Y. 1960 Jul-Aug;27:404–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


