Abstract
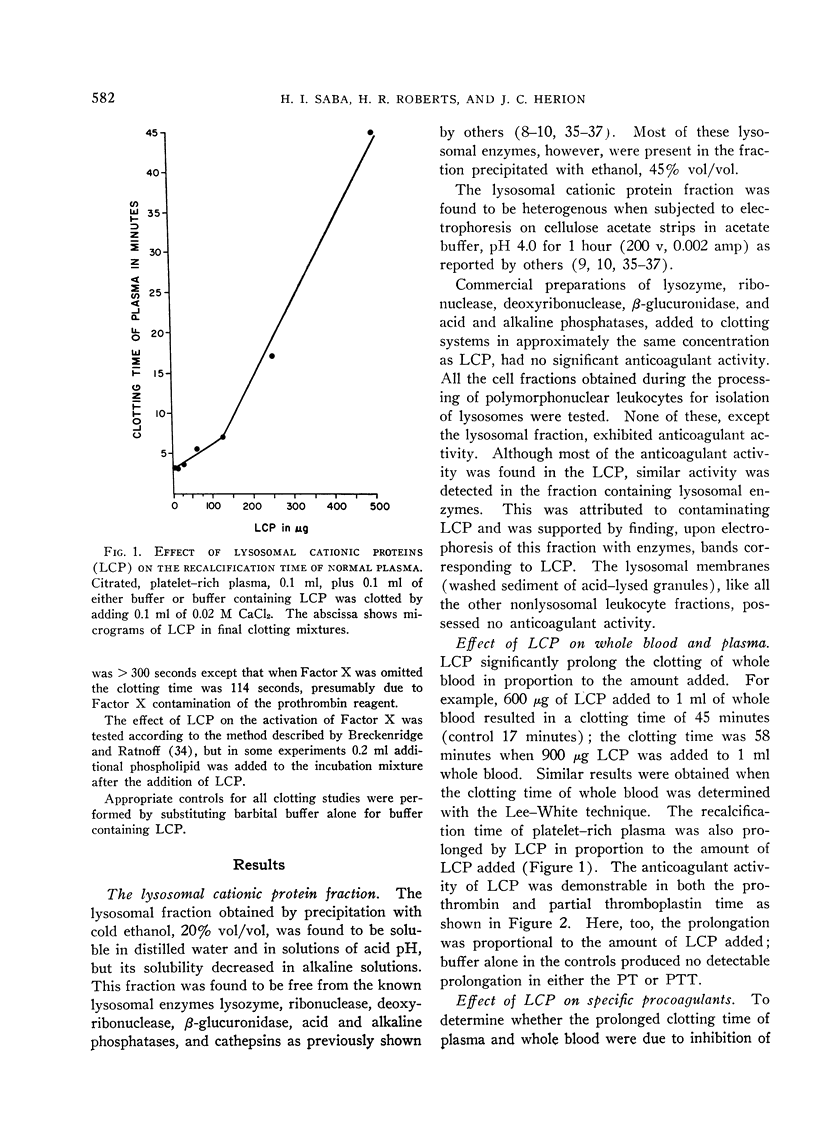
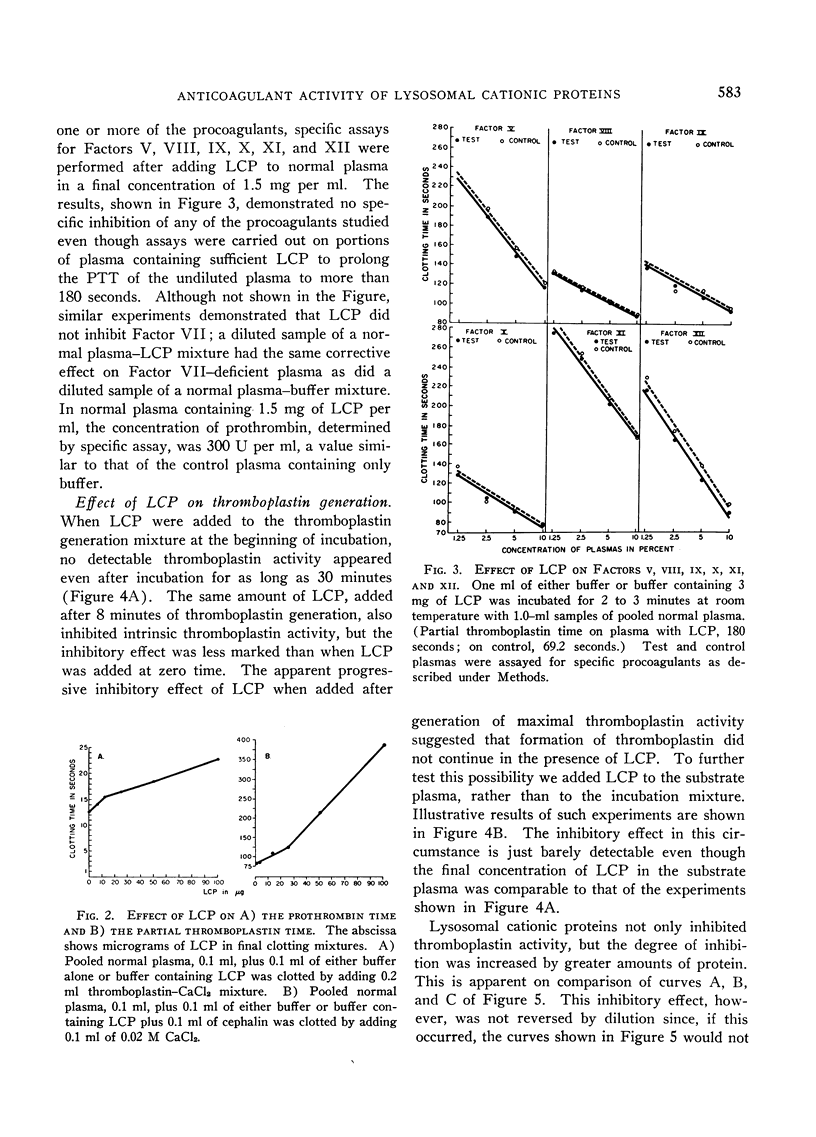
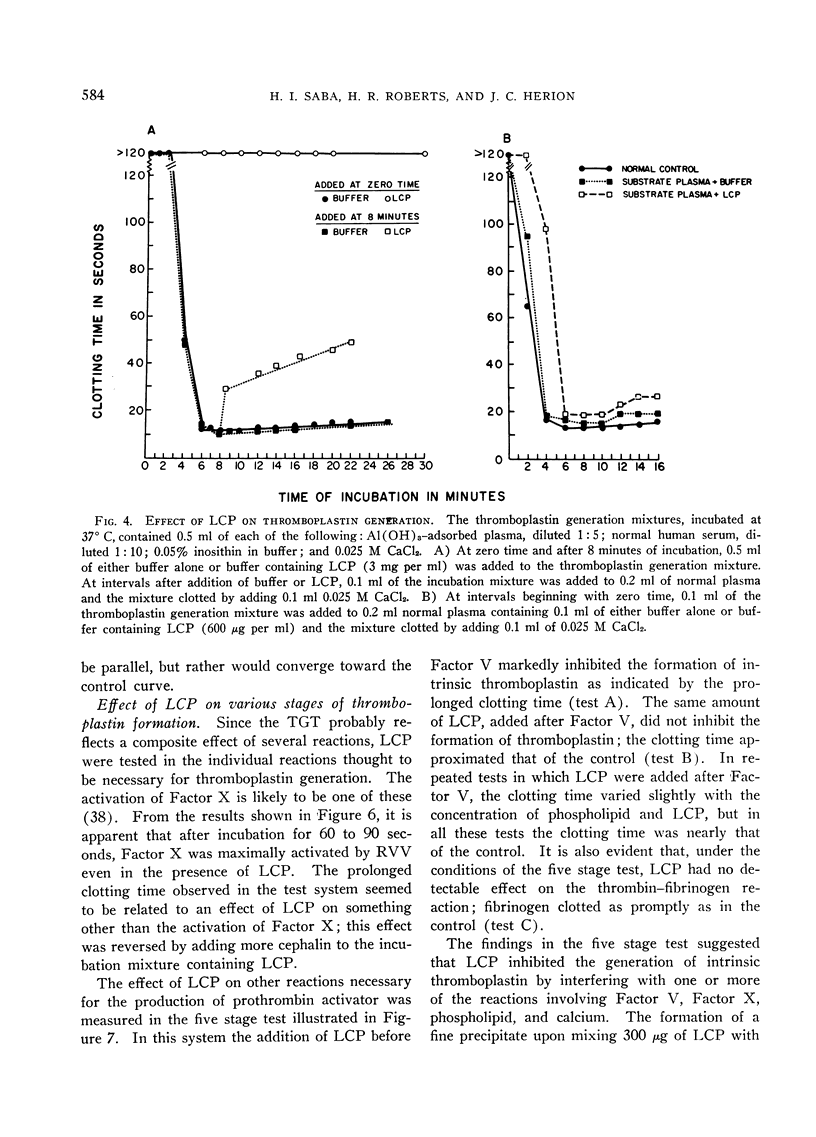
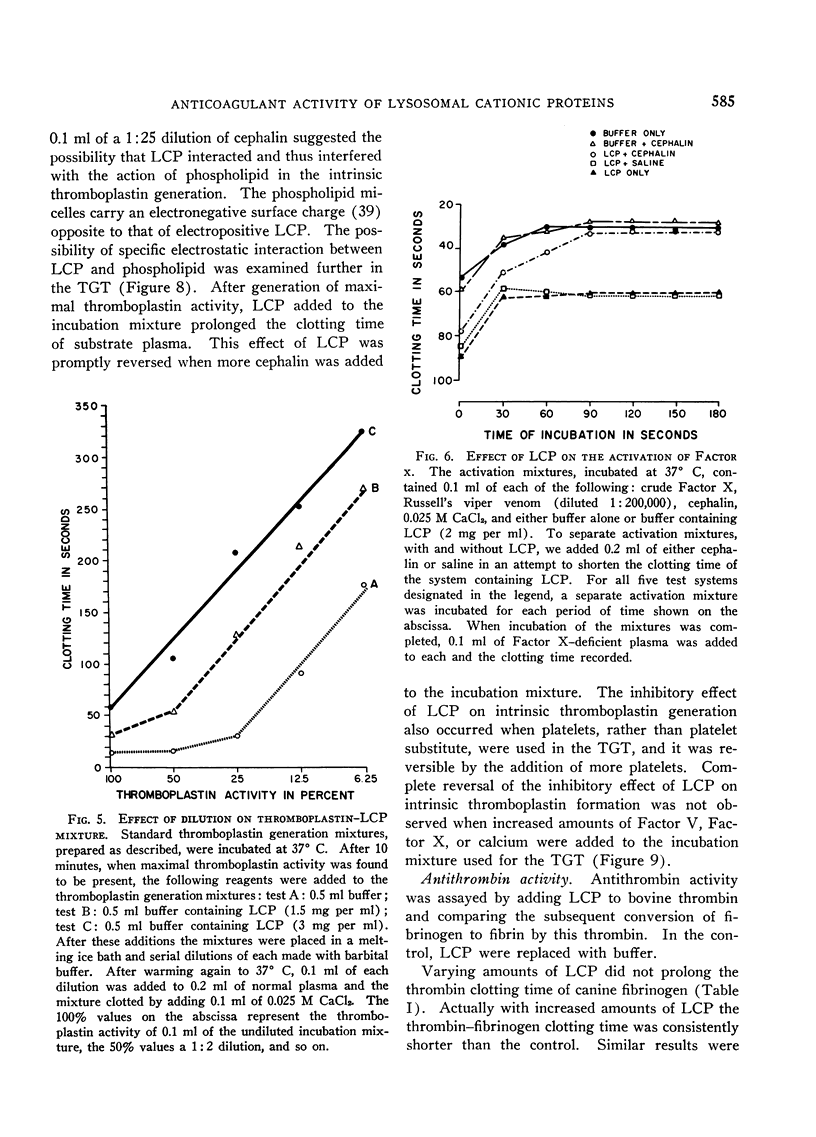
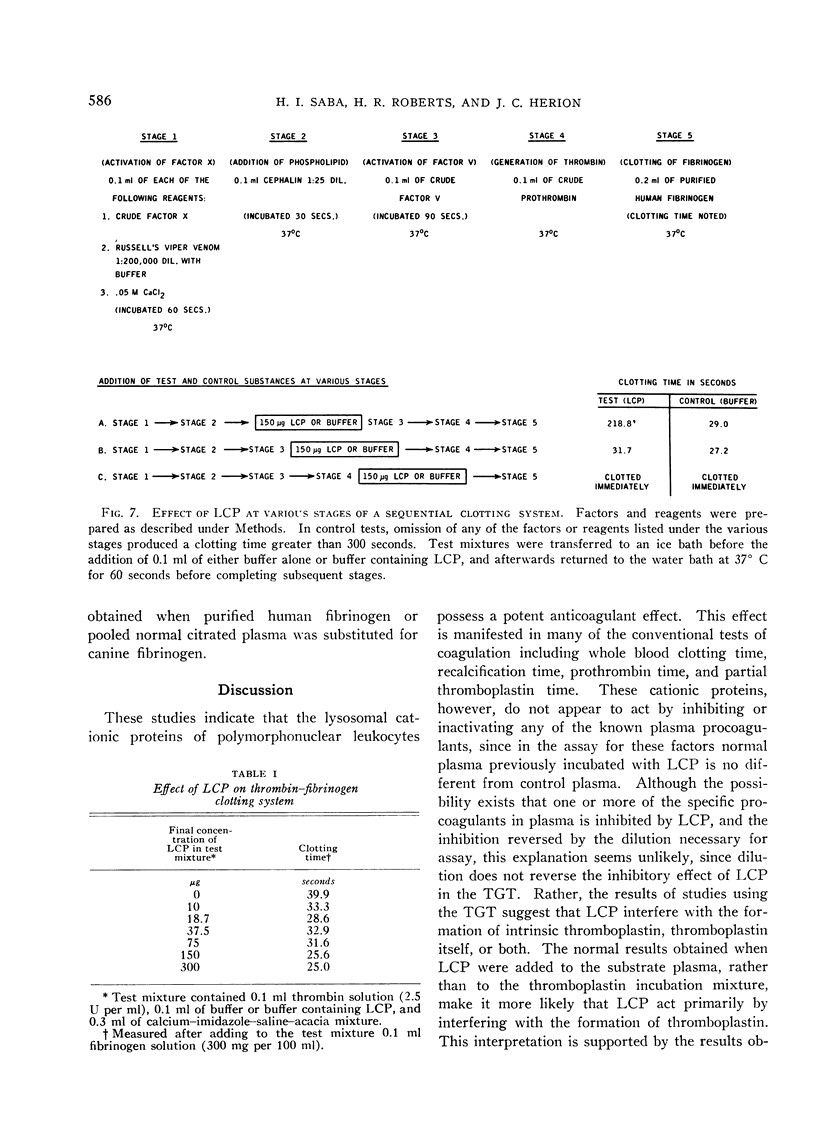
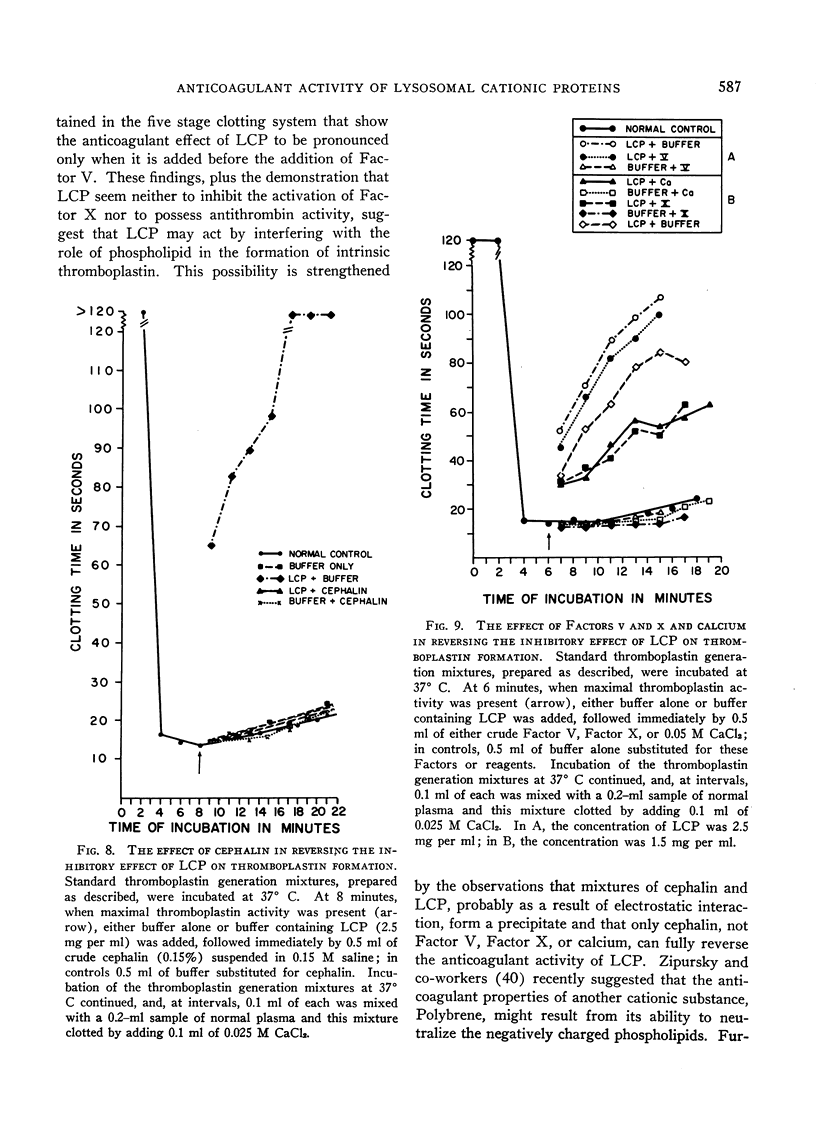
A cationic protein fraction from rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes has been shown to exert a potent anticoagulant effect on human blood in vitro. The anticoagulant activity is detectable in the whole blood clotting time, the recalcification time of platelet-rich plasma, the prothrombin time, the partial thromboplastin time, and the thromboplastin generation test. The lysosomal cationic proteins do not inhibit any of the known specific procoagulants. They appear to inhibit clotting by blocking the formation of intrinsic thromboplastin possibly by interfering with the role of phospholipids in the reaction involving Factors V and X and calcium.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCHER R. K. Studies with eosinophil leucocytes isolated from the blood of the horse. Br J Haematol. 1960 Jul;6:229–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1960.tb06238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM A. D., PETHICA B. A., SEAMAN G. V. The charged groups at the interface of some blood cells. Biochem J. 1958 May;69(1):12–19. doi: 10.1042/bj0690012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARROW E. M., BULLOCK W. R., GRAHAM J. B. A study of the carrier state for plasma thromboplastin component (PTC, Christmas factor) deficiency, utilizing a new assay procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Jun;55:936–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIGGS R., DOUGLAS A. S. The thromboplastin generation test. J Clin Pathol. 1953 Feb;6(1):23–29. doi: 10.1136/jcp.6.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECKENRIDGE R. T., RATNOFF O. D. STUDIES ON THE SITE OF ACTION OF A CIRCULATING ANTICOAGULANT IN DISSEMINATED LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS. EVIDENCE THAT THIS ANTICOAGULANT INHIBITS THE REACTION BETWEEN ACTIVATED STUART FACTOR (FACTOR X) AND PROACCELERIN (FACTOR V). Am J Med. 1963 Dec;35:813–819. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge R. T., Ratnoff O. D. The Role of Proaccelerin in Human Blood Coagulation. Evidence that Proaccelerin Is Converted to a Prothrombin-converting Principle by Activated Stuart Factor: With Notes on the Anticoagulant Action of Soybean Trypsin Inhibitor, Protamine Sulfate, and Hexadimethrine Bromide. J Clin Invest. 1965 Feb;44(2):302–314. doi: 10.1172/JCI105144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., HIRSCH J. G. The isolation and properties of the specific cytoplasmic granules of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:983–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE VRIES A., SCHWAGER A., KATCHALSKI E. The action of some water-soluble poly-alpha-amino-acids on blood clotting. Biochem J. 1951 Jun;49(1):10–17. doi: 10.1042/bj0490010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAM R. C., Jr, EBERT R. H., RATNOFF O. D., MOSES J. M. PATHOGENESIS OF INFLAMMATION. II. IN VIVO OBSERVATIONS OF THE INFLAMMATORY EFFECTS OF ACTIVATED HAGEMAN FACTOR AND BRADYKININ. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:807–818. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub E. S., Spitznagel J. K. The role of lysosomes in hypersensitivity reactions: tissue damage by polymorphonuclear neutrophil lysosomes. J Immunol. 1965 Dec;95(6):1060–1066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOROWITZ H. I., WILCOX W. P., FUJIMOTO M. M. Assay of plasma thromboplastin antecedent (PTA) with artificially depleted normal plasma. Blood. 1963 Jul;22:35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUGIE C., BARROW E. M., GRAHAM J. B. Stuart clotting defect. I. Segregation of an hereditary hemorrhagic state from the heterogeneous group heretofore called stable factor (SPCA, proconvertin, factor VII) deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1957 Mar;36(3):485–496. doi: 10.1172/JCI103446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYUN B. H., DAWSON E. A., BUTCHER J., CUSTER R. P. Studies on soybean phosphatide (inosithin) as a platelet substitute. Stability and effective concentrations in the thromboplastin generation test. Am J Clin Pathol. 1960 Mar;33:209–213. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/33.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herion J. C., Spitznagel J. K., Walker R. I., Zeya H. I. Pyrogenicity of granulocyte lysosomes. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):693–698. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANOFF A., ZWEIFACH B. W. ADHESION AND EMIGRATION OF LEUKOCYTES PRODUCED BY CATIONIC PROTEINS OF LYSOSOMES. Science. 1964 Jun 19;144(3625):1456–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3625.1456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANOFF A., ZWEIFACH B. W. PRODUCTION OF INFLAMMATORY CHANGES IN THE MICROCIRCULATION BY CATIONIC PROTEINS EXTRACTED FROM LYSOSOMES. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:747–764. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPRESLE C., WEBB T. The purification and properties of a proteolytic enzyme, rabbit cathepsin E, and further studies on rabbit cathepsin D. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:455–462. doi: 10.1042/bj0840455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACFARLANE R. G. The coagulant action of Russell's viper venom; the use of antivenom in defining its reaction with a serum factor. Br J Haematol. 1961 Oct;7:496–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1961.tb00358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN H., ROKA L. Beeinflussung der Blutgerinnung durch Leukocyten. Klin Wochenschr. 1951 Aug 1;29(29-30):510–512. doi: 10.1007/BF01483627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Zucker-Franklin D., Safier L. B., Ullman H. L. Studies on human platelet granules and membranes. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):14–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI105318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTMANN A. F., HOLDEN W. D. Protamine sulphate, heparin, and blood coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1949 Nov;28(6 Pt 2):1451–1458. doi: 10.1172/JCI102210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODMAN N. F., Jr, BARROW E. M., GRAHAM J. B. Diagnosis and control of the hemophilioid states with the partial thromboplastin time (PTT) test. Am J Clin Pathol. 1958 Jun;29(6):525–538. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/29.6.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBINI J. R., BECKER R. R., STAHMANN M. A. Effect of synthetic lysine polypeptides on rabbit blood coagulation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Feb;82(2):231–234. doi: 10.3181/00379727-82-20075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts H. R., Scales M. B., Madison J. T., Webster W. P., Penick G. D. A clinical and experimental study of acquired inhibitors to factor 8. Blood. 1965 Dec;26(6):805–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER W. C., HOGEBOOM G. H. Intracellular distribution of enzymes. X. Desoxyribonuclease and ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):155–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUGAR D. The measurement of lysozyme activity and the ultra-violet inactivation of lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952 Mar;8(3):302–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER W. P., ROBERTS H. R., PENICK G. D. HEMOSTASIS IN FACTOR V DEFICIENCY. Am J Med Sci. 1964 Aug;248:194–PASSIM. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196408000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZEYA H. I., SPITZNAGEL J. K. ANTIBACTERIAL AND ENZYMIC BASIC PROTEINS FROM LEUKOCYTE LYSOSOMES: SEPARATION AND IDENTIFICATION. Science. 1963 Nov 22;142(3595):1085–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3595.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIPURSKY A., WODZICKI A. M., RUSSET J. I., ISRAELS E. D., ISRAELS L. G. THE ANTICOAGULANT ACTION OF POLYBRENE. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1965 Mar;43:289–297. doi: 10.1139/y65-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes. I. Resolution of antibacterial and enzymatic activities. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):750–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.750-754.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes. II. Composition, properties, and mechanism of antibacterial action. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):755–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.755-762.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K., Schwab J. H. Antibacterial action of PMN lysosomal cationic proteins resolved by density gradient electrophoresis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jan;121(1):250–253. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


