Abstract
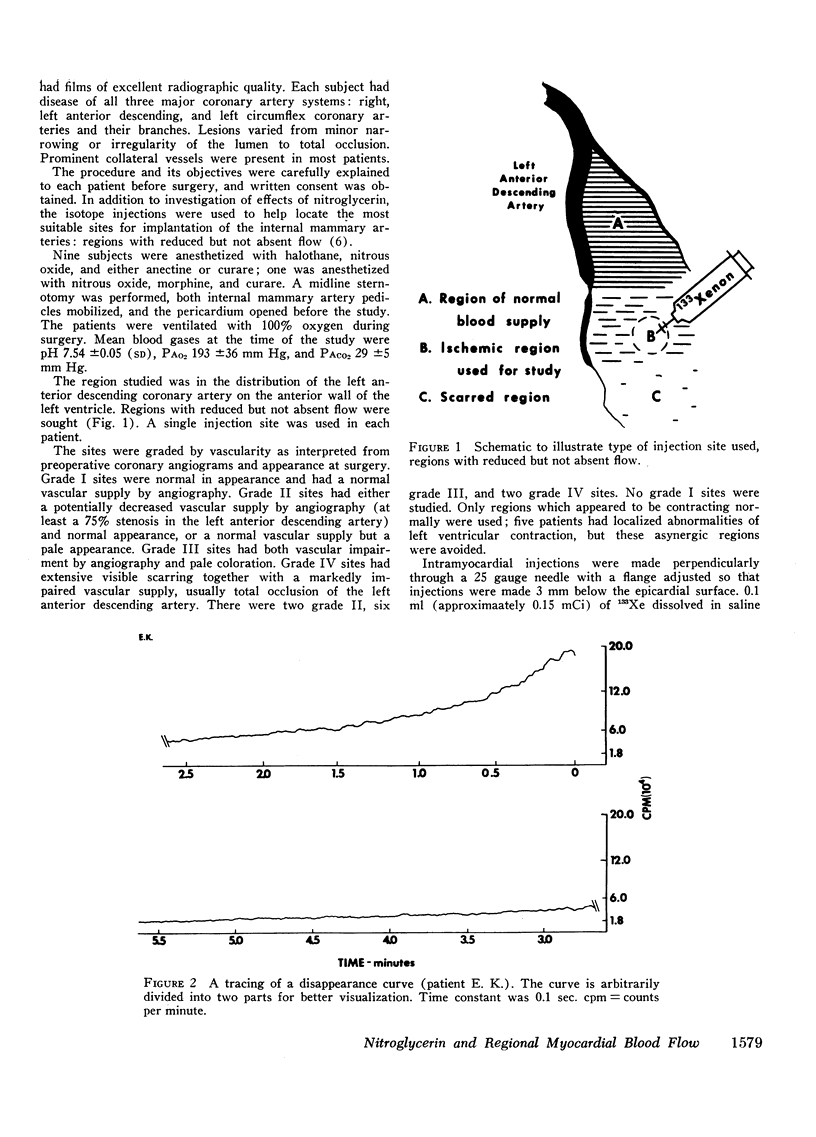
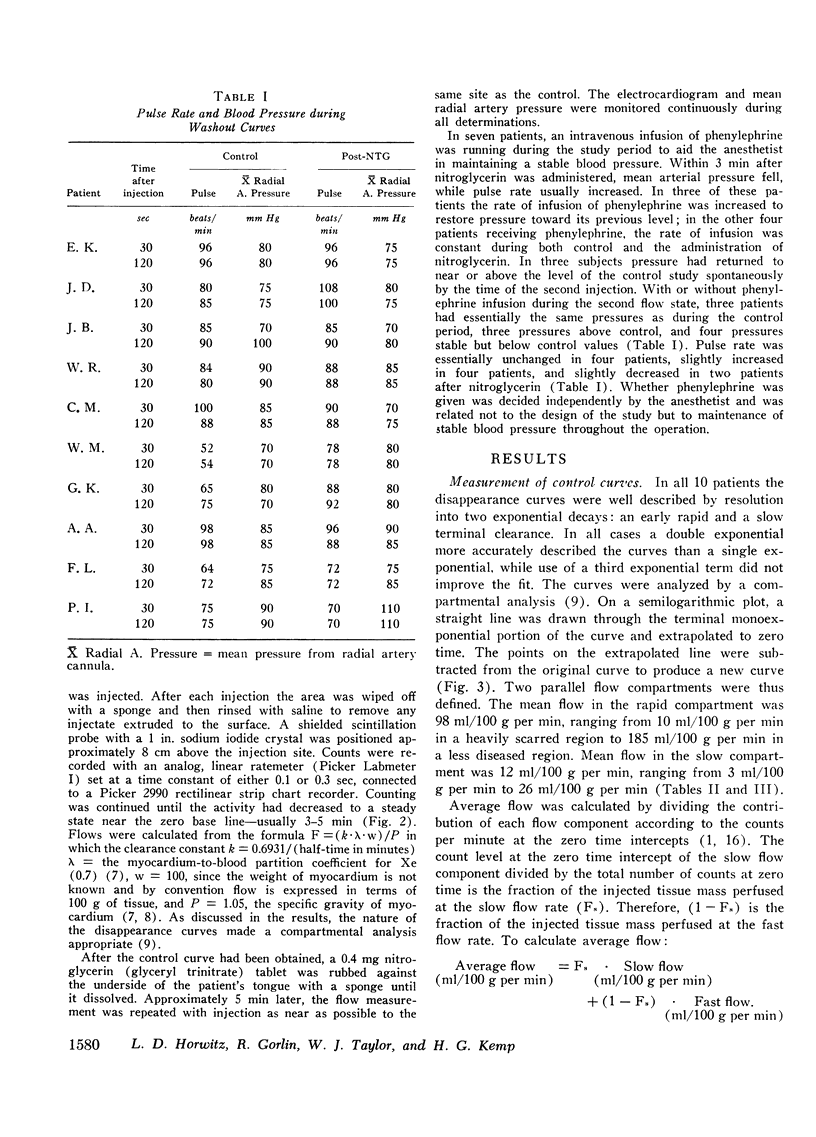
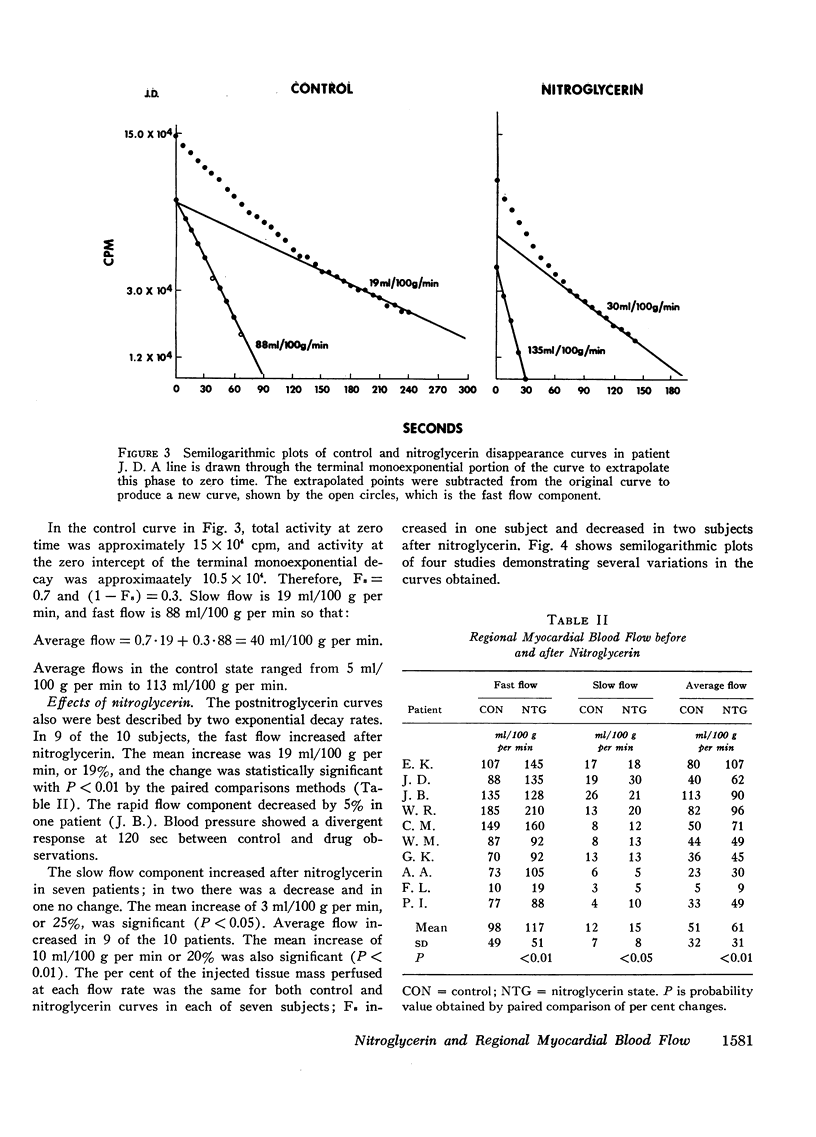
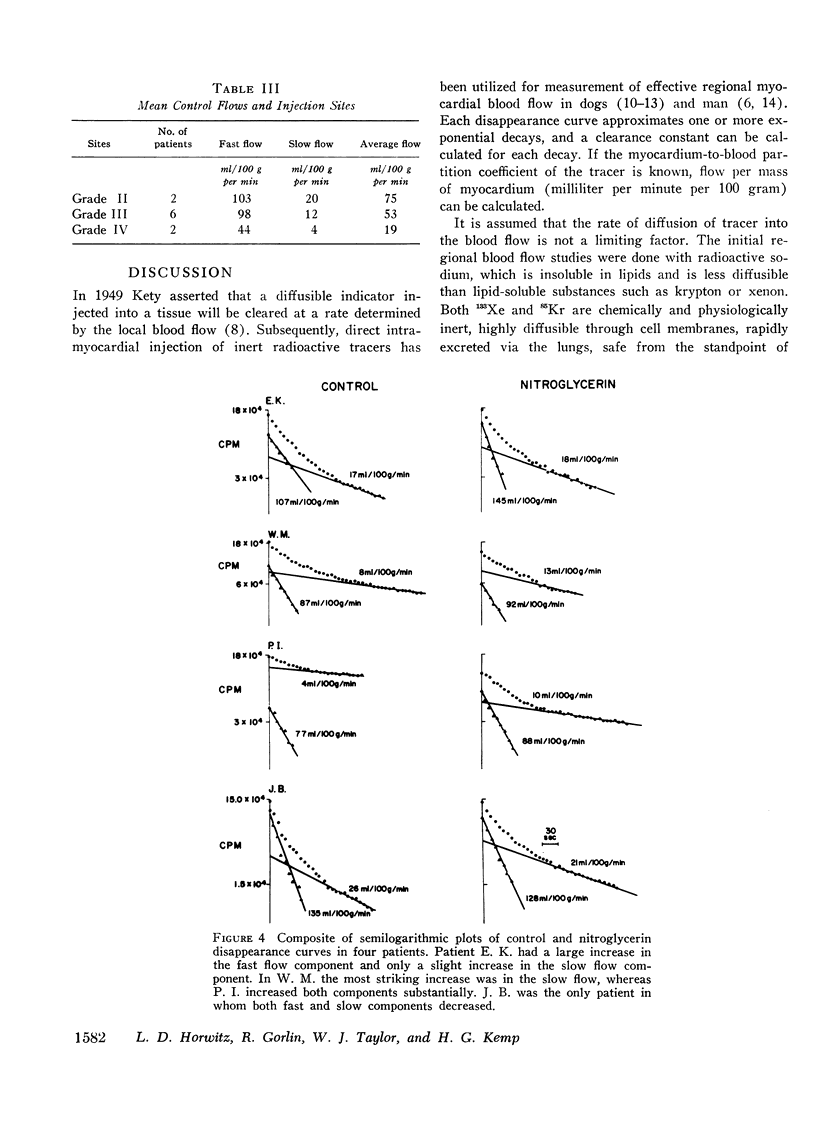
Regional myocardial blood flow before and after sublingual nitroglycerin was measured in 10 patients with coronary artery disease. During thoracotomy, 133Xe was injected directly into the subepicardium in diseased regions of the anterior left ventricular wall, and washout rates were recorded with a scintillation counter. All disappearance curves were closely approximated by two exponential decays analyzed as two parallel flow systems by the compartmental method. The appearance of a double exponential decay pattern in diseased regions suggests that the slow phase was associated with collateral blood flow, although nonhomogeneous myocardium-to-blood partition coefficients for xenon cannot be excluded. Nitroglycerin increased the rapid phase flow in 9 of 10 patients and the slow flow in 7 of 10 patients. Average flow increased in 9 of the 10 patients (P < 0.01). Mean rapid phase flow in the control state was 110 ml/100 g per min and after nitroglycerin increased to 132 ml/100 g per min (P < 0.01); slow phase flow increased from 12 ml/100 g per min to 15 ml/100 g per min (P < 0.05). It is concluded that, under these conditions, nitroglycerin improves perfusion in regions of diseased myocardium in patients with coronary artery disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein L., Friesinger G. C., Lichtlen P. R., Ross R. S. The effect of nitroglycerin on the systemic and coronary circulation in man and dogs: myocardial blood flow measured with xenon. Circulation. 1966 Jan;33(1):107–116. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.33.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandi G., Fam W. M., McGregor M. Measurement of coronary flow in local areas of myocardium using xenon 133. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Mar;24(3):446–450. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.24.3.446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CULLEN M. L., REESE H. L. Myocardial circulatory changes measured by clearance of Na24; effect of common duct distension on myocardial circulation. J Appl Physiol. 1952 Dec;5(6):281–284. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1952.5.6.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan C., Duran P. V., Corsini G., Goldschlager N., Bing R. J. The effects of nitroglycerin on myocardial blood flow in man, measured by coincidence counting and bolus injections of 84-rubidium. Am J Cardiol. 1969 Aug;24(2):154–160. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(69)90397-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAM W. M., MCGREGOR M. EFFECT OF CORONARY VASODILATOR DRUGS ON RETROGRADE FLOW IN AREAS OF CHRONIC MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA. Circ Res. 1964 Oct;15:355–364. doi: 10.1161/01.res.15.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINBERG H., GEROLA A., KATZ L. N. Effect of changes in blood CO2 level on coronary flow and myocardial O2 consumption. Am J Physiol. 1960 Aug;199:349–354. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORLIN R., BRACHFELD N., MACLEOD C., BOPP P. Effect of nitroglycerin on the coronary circulation in patients with coronary artery disease or increased left ventricular work. Circulation. 1959 May;19(5):705–718. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.19.5.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLANDER W., MADOFF I. M., CHOBANIAN A. V. Local myocardial blood flow as indicated by the disappearance of Nal-131 from the heart muscle: studies at rest, during exercise, and following nitrite administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Jan;139:53–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddy F. J. Physiology and pharmacology of the coronary circulation and myocardium, particularly in relation to coronary artery disease. Am J Med. 1969 Aug;47(2):274–286. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoedt-Rasmussen K., Sveinsdottir E., Lassen N. A. Regional cerebral blood flow in man determined by intra-arterial injection of radioactive inert gas. Circ Res. 1966 Mar;18(3):237–247. doi: 10.1161/01.res.18.3.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHANSSON B., LINDER E., SEEMAN T. COLLATERAL BLOOD FLOW IN THE MYOCARDIUM OF DOGS MEASURED WITH KRYPTON. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Nov;62:263–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb03973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATTUS A. A., GREGG D. E. Some determinants of coronary collateral blood flow in the open-chest dog. Circ Res. 1959 Jul;7(4):628–642. doi: 10.1161/01.res.7.4.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRK E. S., HONIG C. R. NONUNIFORM DISTRIBUTION OF BLOOD FLOW AND GRADIENTS OF OXYGEN TENSION WITHIN THE HEART. Am J Physiol. 1964 Sep;207:661–668. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.3.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIKOFF W., KASPARIAN H., LEHMAN J. S., SEGAL B. L. EVALUATION OF "CORONARY VASODILATORS" BY CORONARY ARTERIOGRAPHY. Am J Cardiol. 1964 Jan;13:7–9. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(64)90215-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSS R. S., UEDA K., LICHTLEN P. R., REES J. R. MEASUREMENT OF MYOCARDIAL BLOOD FLOW IN ANIMALS AND MAN BY SELECTIVE INJECTION OF RADIOACTIVE INERT GAS INTO THE CORONARY ARTERIES. Circ Res. 1964 Jul;15:28–41. doi: 10.1161/01.res.15.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALISBURY P. F., CROSS C. E., OBLATH R. W., RIEBEN P. A. Local circulation in heart muscle studied with Na24 clearance method. J Appl Physiol. 1962 May;17:475–478. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1962.17.3.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOBOL B. J., WANLASS S. A., JOSEPH E. B., AZARSHAHY I. Alteration of coronary blood flow in the dog by inhalation of 100 per cent oxygen. Circ Res. 1962 Nov;11:797–802. doi: 10.1161/01.res.11.5.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. M., Taylor W. J., Elliott W. C., Gorlin R. Regional myocardial blood flow. J Clin Invest. 1967 Sep;46(9):1402–1412. doi: 10.1172/JCI105632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


