Abstract
Conclusions concerning the physiologic role of pancreatic glucagon in health and its contribution to disorders of carbohydrate metabolism, such as diabetes mellitus, are based entirely on measurements of plasma glucagon by radioimmunoassay. The changes in plasma immunoreactive glucagon can have the metabolic and clinical significance which has been implied, only if the glucagon detected by immunoassay has biological activity. The present study was designed to determine if a relationship between the immunoassayable glucagon and glycogenolytic activity of plasma could be demonstrated.
Plasma specimens obtained from normal and diabetic subjects under widely varying circumstances of alpha cell activity were extracted by a modification of the Kenny technique and the recovery of immunoreactive glucagon was calculated. Glycogenolytic activity of each extract was determined by perfusion in the Mortimore rat liver system, modified so as to detect as little as 1 ng of crystalline glucagon.
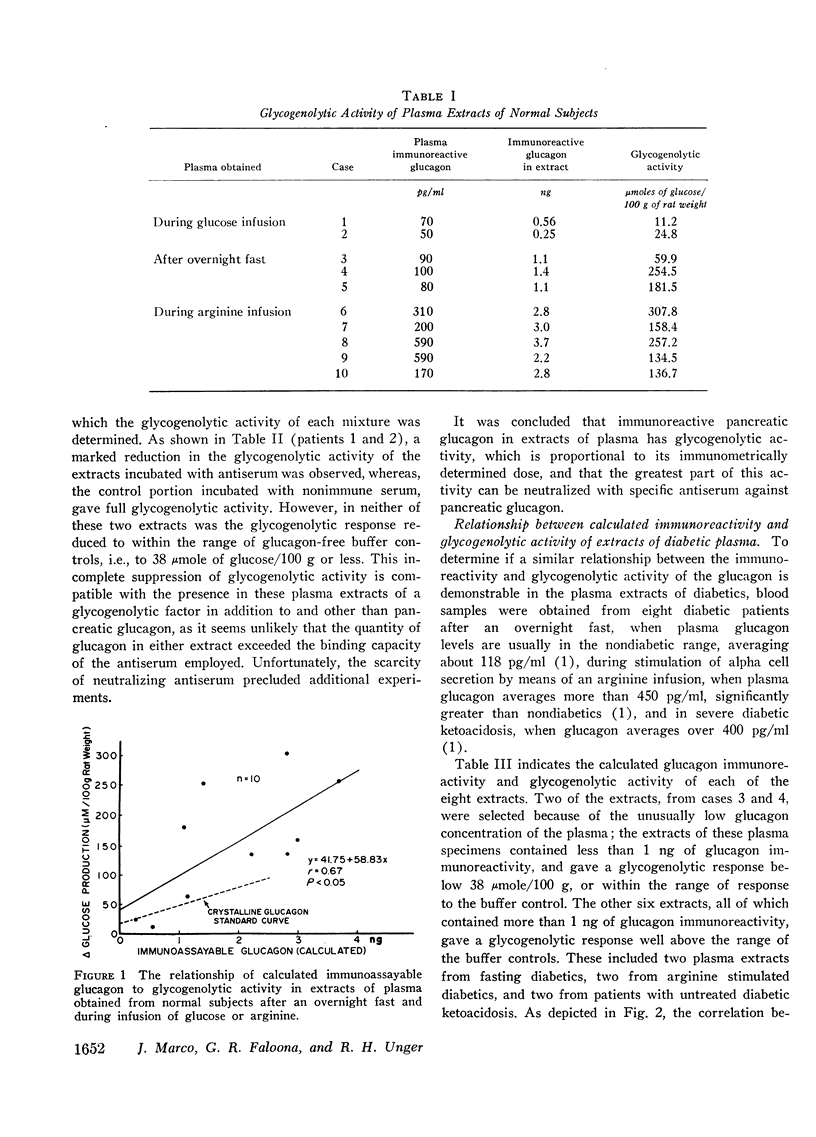
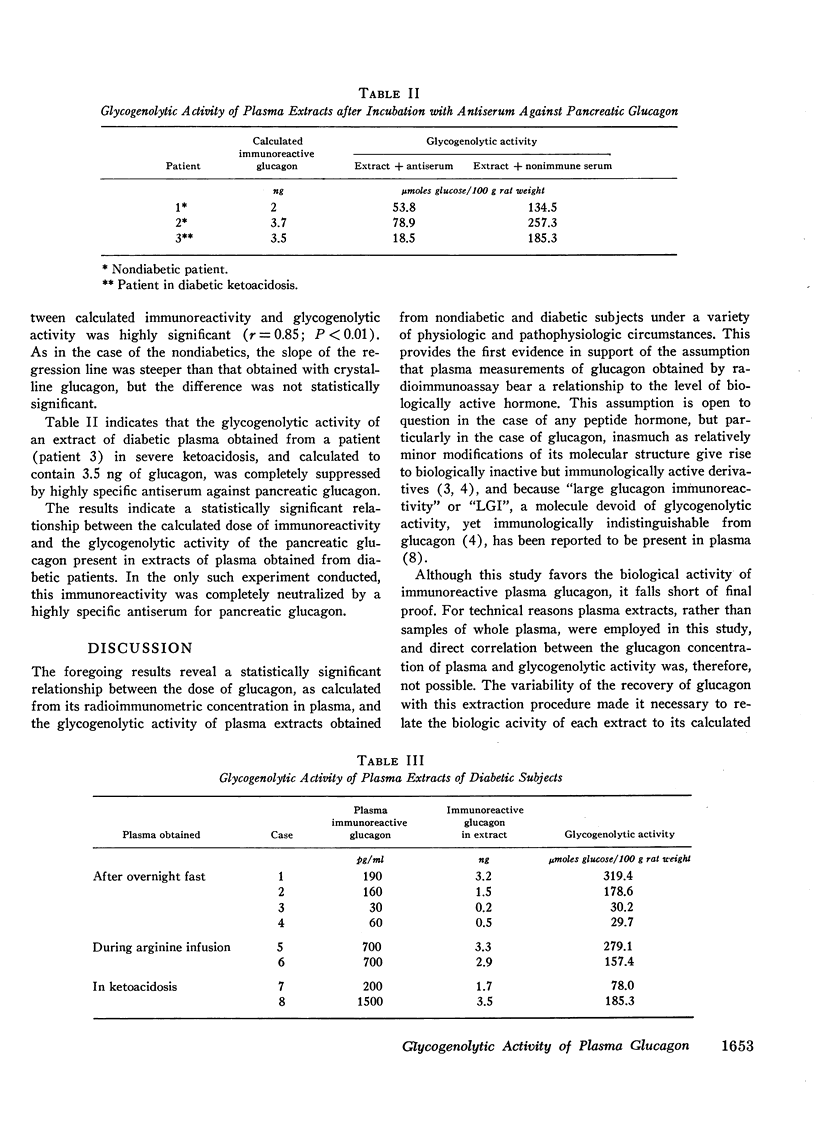
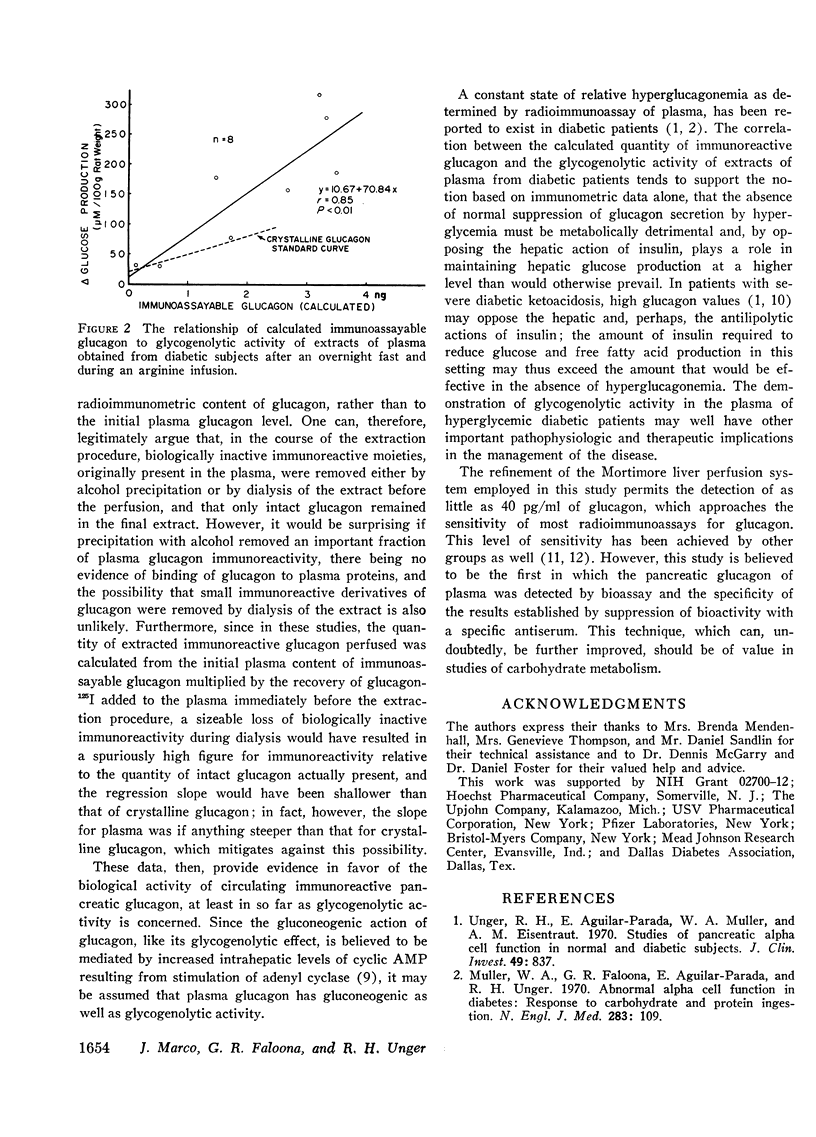
A significant correlation between the calculated quantity of immunoreactive glucagon and the glycogenolytic activity of plasma extracts was observed for both normal and diabetic subjects. Most of the glycogenolytic activity was abolished by incubating the extract with antiglucagon serum.
It was concluded that the glycogenolytic activity of extractable glucagon is proportional to its immunoreactivity as calculated from its original concentration in plasma. This would tend to support the view that all or most of the immunoreactive glucagon of plasma is biologically active.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assan R., Hautecouverture G., Guillemant S., Dauchy F., Protin P., Derot M. Evolution de paramètres hormonaux (glucagon, cortisol, hormone somatotrope) et énergétiques (glucose, acides gras, glycérol libre) dans dix acido-cétoses diabétiques graves traitées. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1969 Dec;17(23):1095–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Park C. R. Control of gluconeogenesis in liver. II. Effects of glucagon, catecholamines, and adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate on gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 25;243(16):4189–4196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Park C. R. The role of cyclic AMP in the control of liver metabolism. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1968;6:391–407. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(68)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNY A. J. Extractable glucagon of the human pancreas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1955 Sep;15(9):1089–1105. doi: 10.1210/jcem-15-9-1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. A., Faloona G. R., Aguilar-Parada E., Unger R. H. Abnormal alpha-cell function in diabetes. Response to carbohydrate and protein ingestion. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jul 16;283(3):109–115. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197007162830301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigopoulou D., Valverde I., Marco J., Faloona G., Unger R. H. Large glucagon immunoreactivity in extracts of pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1970 Feb 10;245(3):496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokal J. E. Bioassay of glucagon using the isolated perfused rat liver. Endocrinology. 1970 Dec;87(6):1338–1345. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-6-1338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Aguilar-Parada E., Müller W. A., Eisentraut A. M. Studies of pancreatic alpha cell function in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI106297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde I., Rigopoulou D., Marco J., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. Molecular size of extractable glucagon and glucagon-like immunoreactivity (GLI) in plasma. Diabetes. 1970 Sep;19(9):624–629. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.9.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


