Abstract
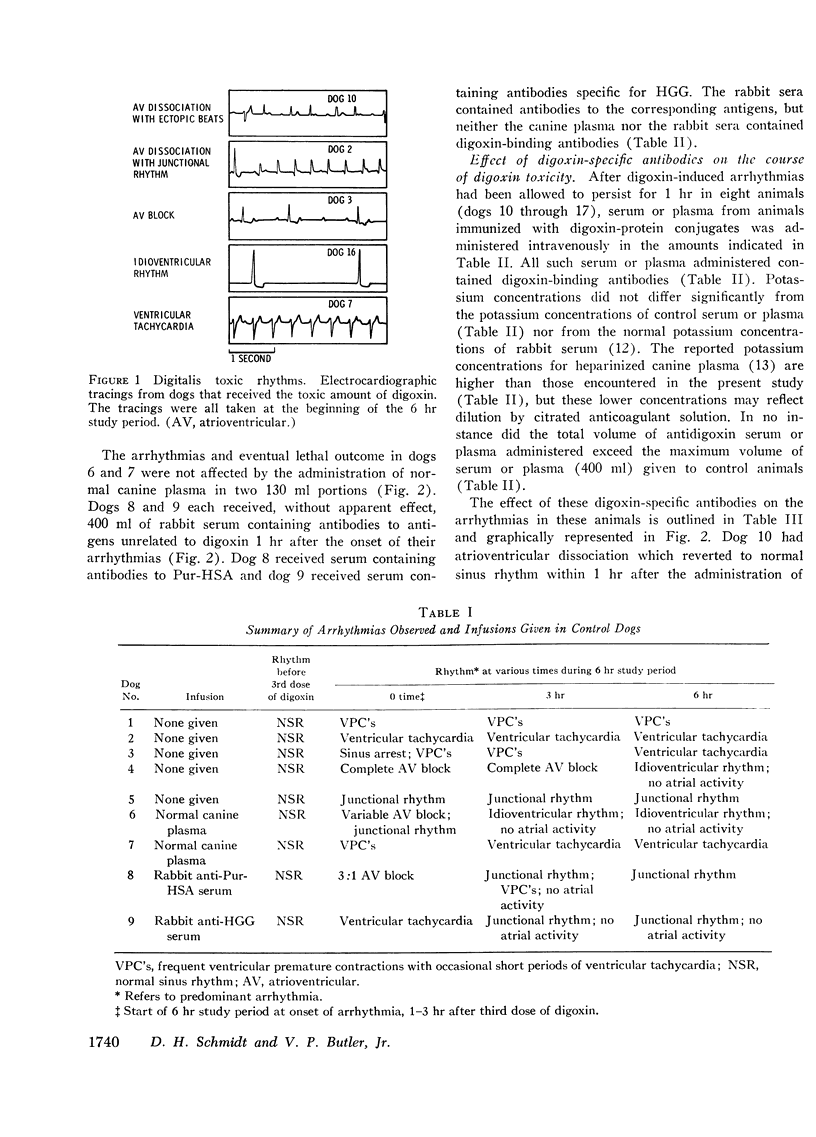
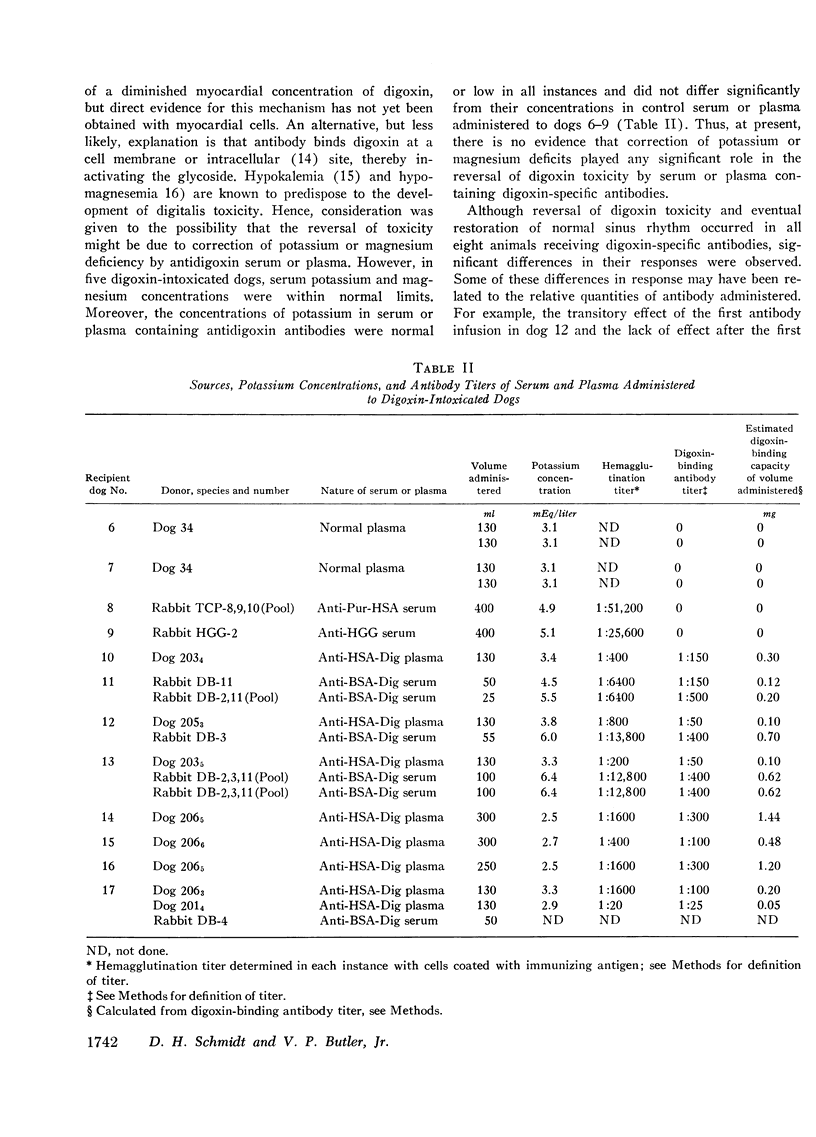
To determine whether digoxin-specific antibodies can reverse established digoxin toxicity in the dog, digoxin intoxication was produced by the intramuscular administration of digoxin, 0.09 mg/kg, on each of 3 consecutive days. All animals developed toxic arrhythmias (atrioventricular block, ventricular premature contractions and/or ventricular tachycardia). In control animals not receiving antidigoxin antibodies, the arrhythmias persisted throughout a 6 hr study period. Seven of the nine control dogs were dead within 24 hr and one moribund animal was sacrificed at that time; the last animal died within 48 hr.
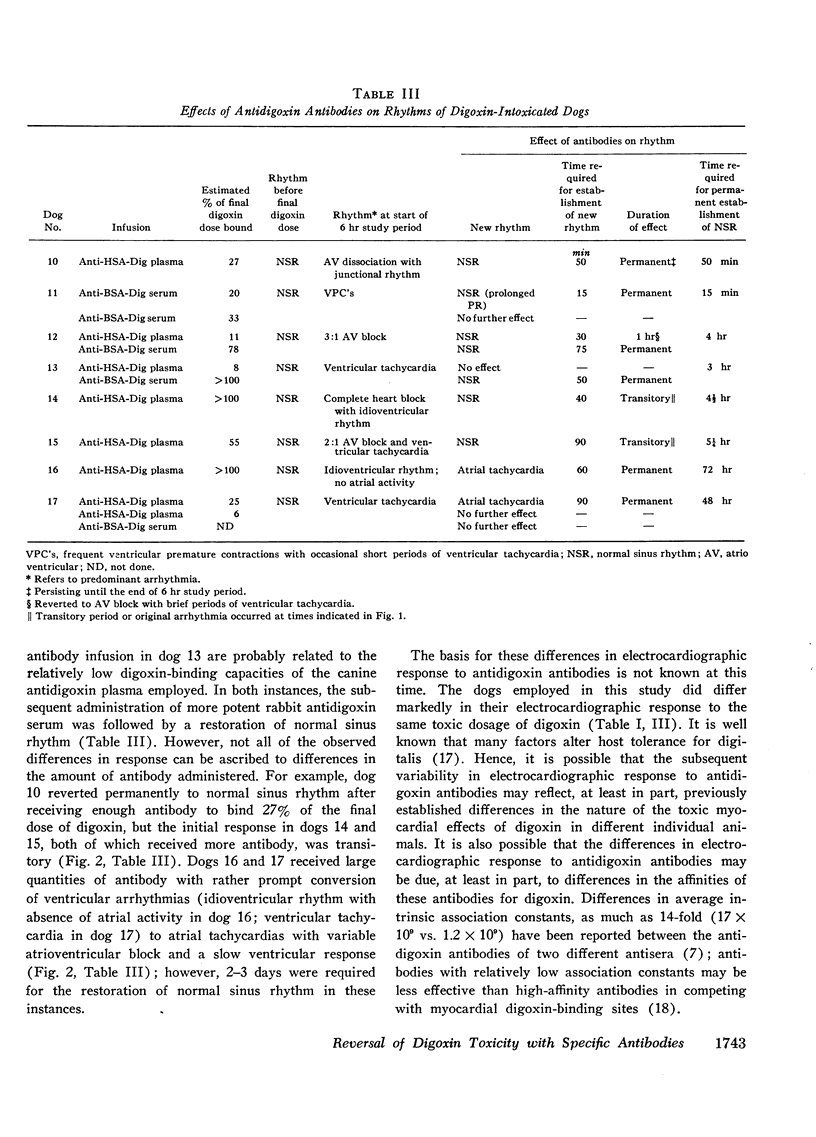
In contrast, in six of eight dogs given digoxin-specific antibodies in canine plasma and/or rabbit serum, the arrhythmias reverted to a sinus mechanism within 30-90 min after the start of the infusion. At the end of a 6 hr period of study, these six dogs were in normal sinus rhythm and all eight were alive and in normal sinus rhythm at the end of 72 hr. This study provides evidence that digoxin-specific antibodies can reverse severe established digoxin toxicity in the dog.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNSTEIN R. E. Potassium and sodium balance in mammalian red cells. Science. 1954 Sep 17;120(3116):459–460. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3116.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER V. P., Jr, BEISER S. M., ERLANGER B. F., TANENBAUM S. W., COHEN S., BENDICH A. Purine-specific antibodies which react with deoxvribonucleic acid (DNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Sep 15;48:1597–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.9.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER V. P., Jr, VAUGHAN J. H. HEMAGGLUTINATION BY RHEUMATOID FACTOR OF CELLS COATED WITH ANIMAL GAMMA GLOBULINS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jul;116:585–593. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler V. P., Jr, Chen J. P. Digoxin-specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):71–78. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., BEISER S. M. ANTIBODIES SPECIFIC FOR RIBONUCLEOSIDES AND RIBONUCLEOTIDES AND THEIR REACTION WITH DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:68–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch C., Knoebel S. B. Recognition and therapy of digitalis toxicity. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1970 Jan;13(1):71–96. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(70)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui H., Schwartz A. Mechanism of cardiac glycoside inhibition of the (Na+-K+)-dependent ATPase from cardiac tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 25;151(3):655–663. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Roth J., Macchia V. Binding of hormone to tissue: the first step in polypeptide hormone action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1802–1809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D. H., Butler V. P., Jr Immunological protecion against dixin toxicity. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):866–871. doi: 10.1172/JCI106558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seller R. H., Cangiano J., Kim K. E., Mendelssohn S., Brest A. N., Swartz C. Digitalis toxicity and hypomagnesemia. Am Heart J. 1970 Jan;79(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(70)90394-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Butler V. P., Jr, Haber E. Characterization of antibodies of high affinity and specificity for the digitalis glycoside digoxin. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 20;9(2):331–337. doi: 10.1021/bi00804a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Butler V. P., Jr, Haber E. Determination of therapeutic and toxic serum digoxin concentrations by radioimmunoassay. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 27;281(22):1212–1216. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911272812203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINSOR T. Potassium and digitalis intoxication. Am Heart J. 1960 Jul;60:151–153. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(60)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


