Abstract
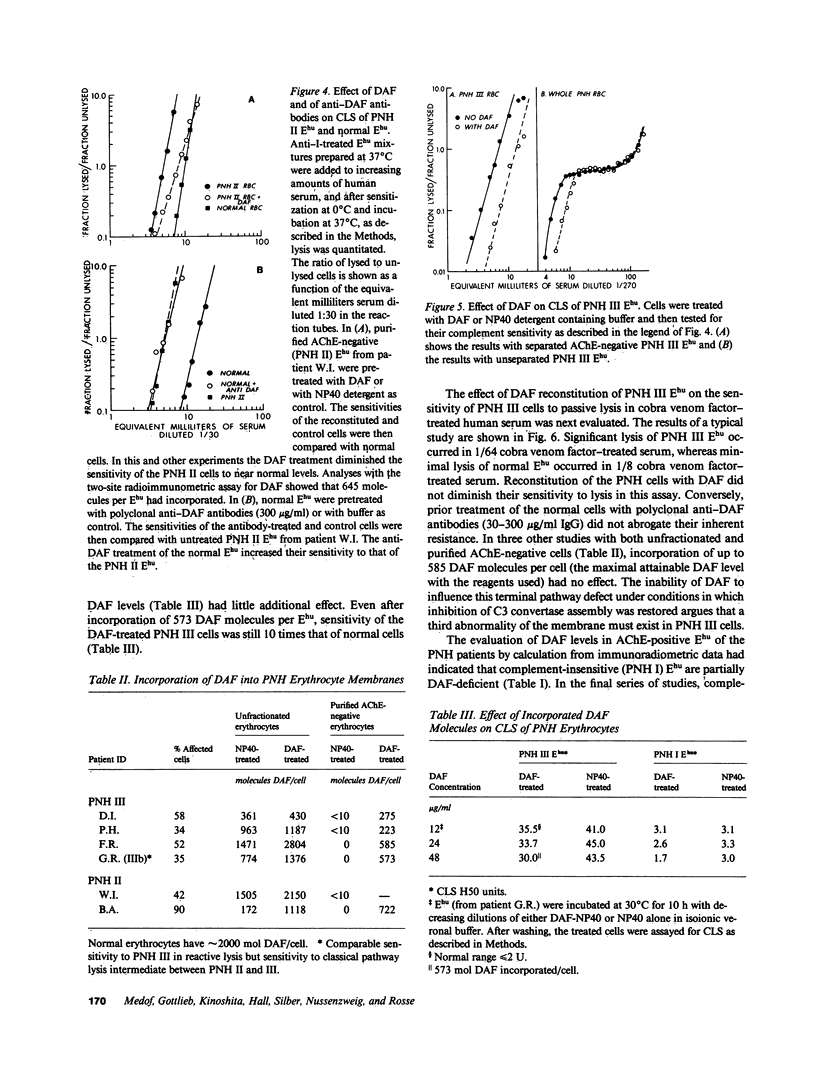
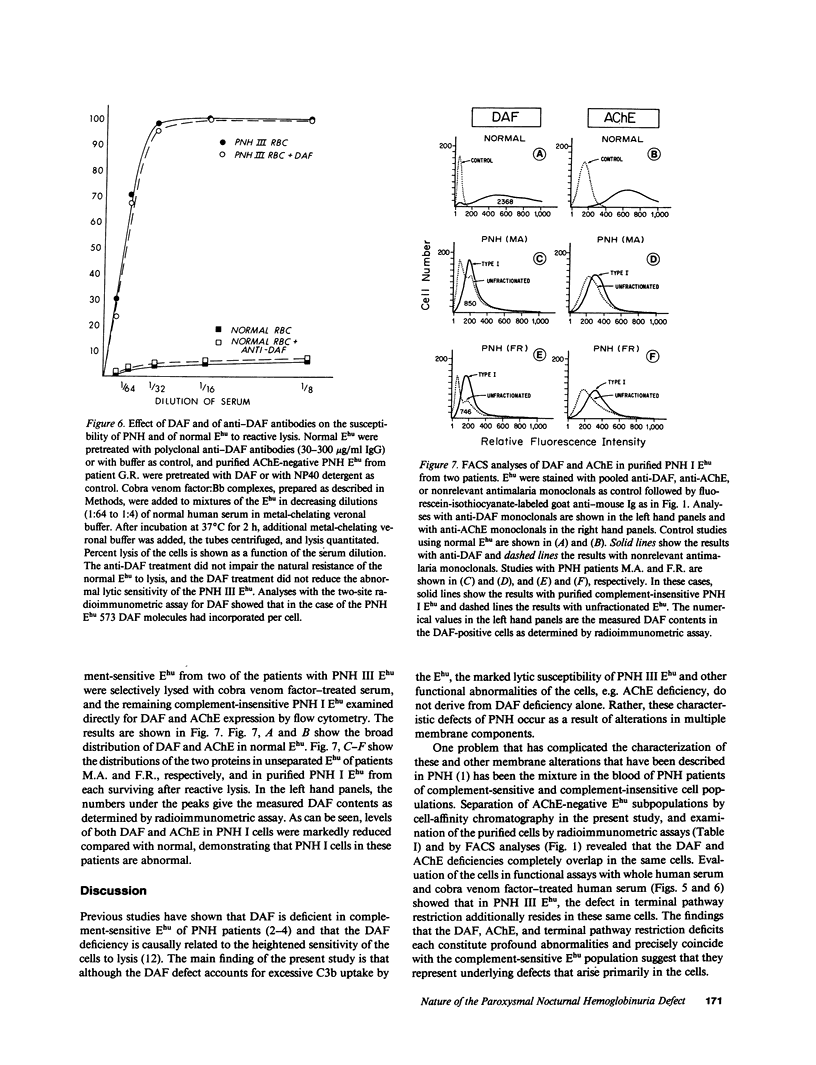
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) erythrocytes exhibit abnormalities in decay accelerating factor (DAF), acetylcholinesterase, and resistance to autologous C5b-9 attack. To investigate the nature of the lesion underlying PNH cells, we examined the relationship of these abnormalities to one another. Analyses of DAF in acetylcholinesterase-negative erythrocytes revealed that these two abnormalities involve functionally independent molecules, coincide precisely in the same cell populations, and are similarly expressed in PNH II and more complement-sensitive PNH III erythrocytes. The DAF and acetylcholinesterase deficiencies contrast with the C3b/C4b receptor (CR1) deficit, which is less profound and similarly distributed in complement-insensitive cell populations. Hemolytic studies showed that defective resistance to autologous C5b-9 attack is mediated by another mechanism. Whereas reconstitution of PNH II erythrocytes with DAF completely corrected their complement sensitivity, DAF reconstitution of PNH III erythrocytes restored their ability to circumvent C3b uptake but had no effect on their heightened susceptibility to reactive lysis. Assays of complement-insensitive (PNH I) erythrocytes surviving after reactive lysis disclosed partial DAF and acetylcholinesterase deficits. These findings indicate that the PNH lesion involves multiple membrane components and that PNH I erythrocytes are also abnormal.
Full text
PDF

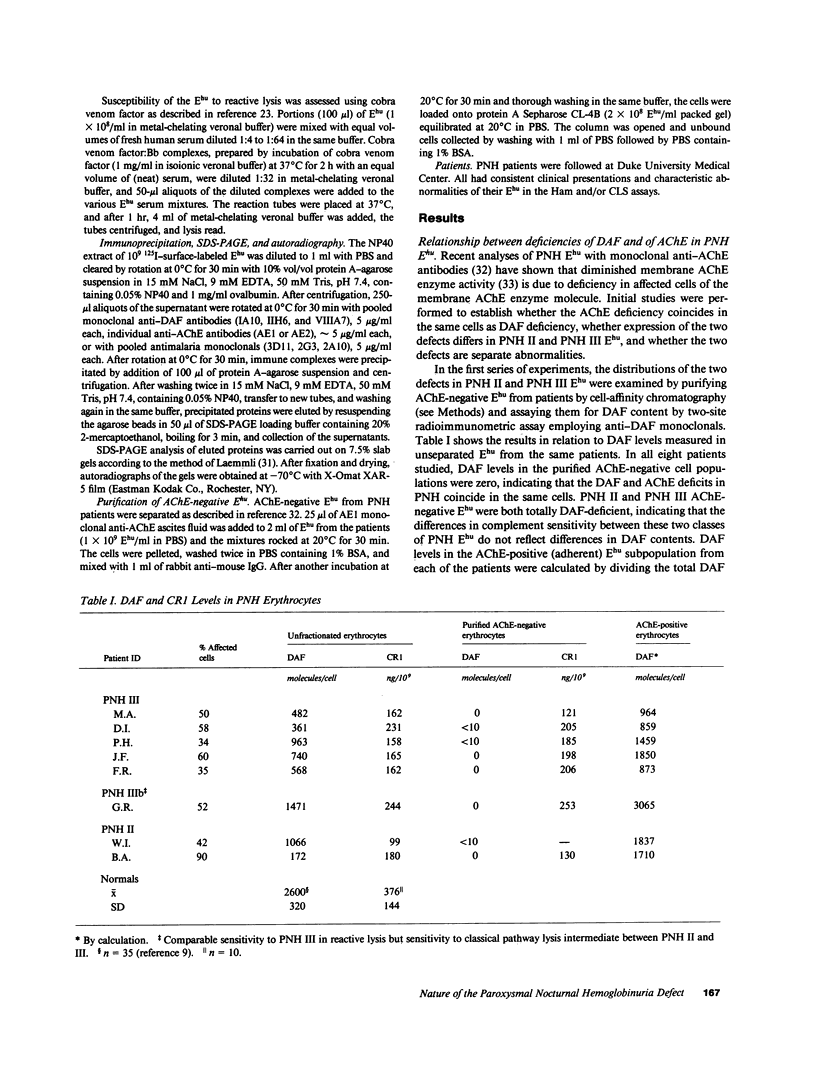
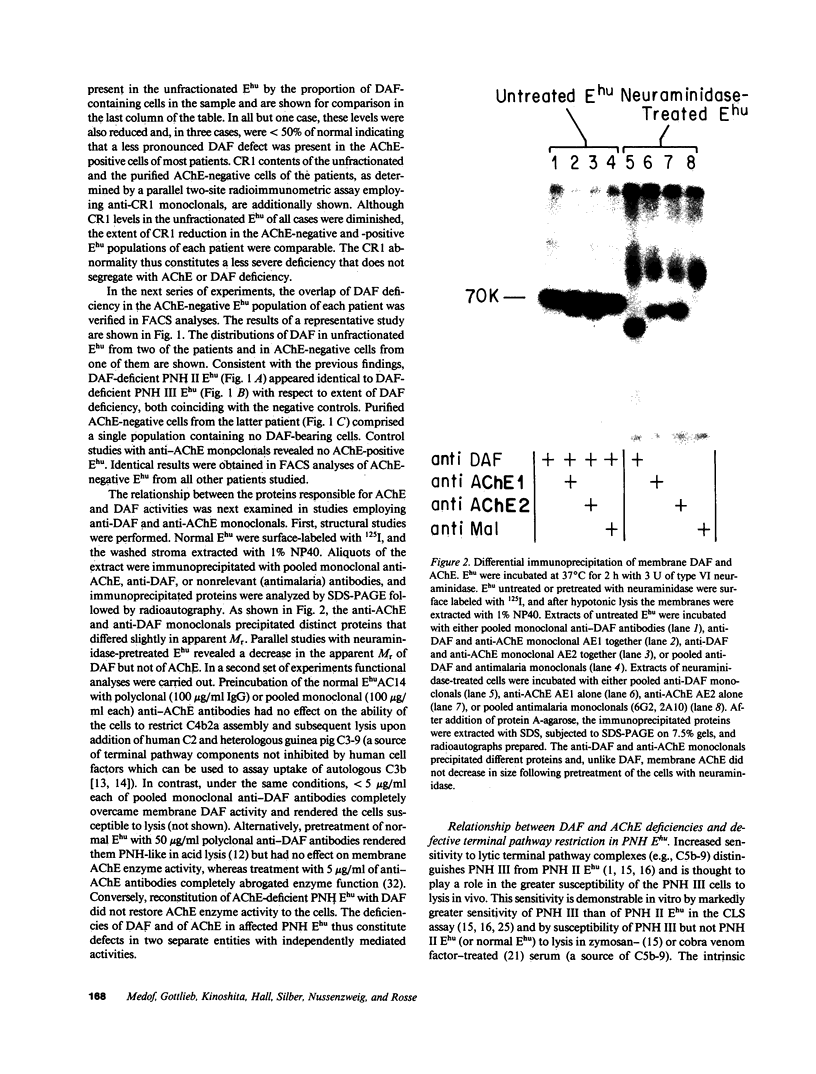
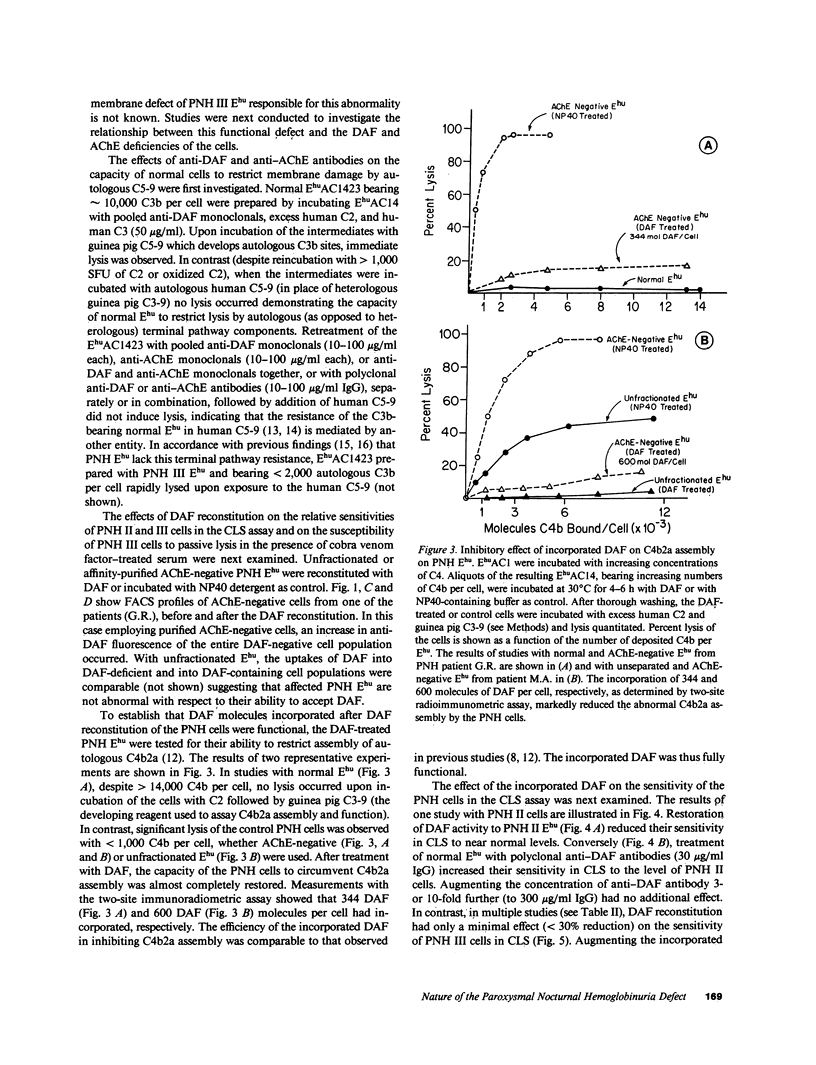



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUDITORE J. V., HARTMANN R. C., FLEXNER J. M., BALCHUM O. J. The erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase enzyme in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Arch Pathol. 1960 May;69:534–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Ramsey J., Hammer C. H., Frank M. M. Surface modulation of classical pathway activation: C2 and C3 convertase formation and regulation on sheep, guinea pig, and human erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow F. L., Hall S. E., Rosse W. F., Telen M. J. Separation of the acetylcholinesterase-deficient red cells in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):893–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The reaction mechanism of human C5 in immune hemolysis. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):775–793. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Low M. G., Nussenzweig V. Release of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) from the cell membrane by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PIPLC). Selective modification of a complement regulatory protein. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1150–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta-Choudhury T. A., Rosenberry T. L. Human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase is an amphipathic protein whose short membrane-binding domain is removed by papain digestion. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5653–5660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykman T. R., Cole J. L., Iida K., Atkinson J. P. Polymorphism of human erythrocyte C3b/C4b receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1698–1702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Engel A. G., Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase of human erythrocytes and neuromuscular junctions: homologies revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1078–1082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Regulation of the amplification C3 convertase of human complement by an inhibitory protein isolated from human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5867–5871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. M. Inhibition of complement by a substance isolated from human erythrocytes. I. Extraction from human erythrocyte stromata. Immunochemistry. 1969 May;6(3):391–403. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann E. M. Inhibition of complement by a substance isolated from human erythrocytes. II. Studies on the site and mechanism of action. Immunochemistry. 1969 May;6(3):405–419. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90297-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu V. W., Nicholson-Weller A. Enhanced complement-mediated lysis of type III paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythrocytes involves increased C9 binding and polymerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5520–5524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu V. W., Shin M. L. Species-restricted target cell lysis by human complement: complement-lysed erythrocytes from heterologous and homologous species differ in their ratio of bound to inserted C9. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2133–2137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänsch G. M., Hammer C. H., Vanguri P., Shin M. L. Homologous species restriction in lysis of erythrocytes by terminal complement proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5118–5121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida K., Mornaghi R., Nussenzweig V. Complement receptor (CR1) deficiency in erythrocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1427–1438. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Medof M. E., Silber R., Nussenzweig V. Distribution of decay-accelerating factor in the peripheral blood of normal individuals and patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):75–92. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Kinoshita T., Nussenzweig V. Inhibition of complement activation on the surface of cells after incorporation of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) into their membranes. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1558–1578. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Kinoshita T., Silber R., Nussenzweig V. Amelioration of lytic abnormalities of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria with decay-accelerating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2980–2984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Roberts W. L., Haas R., Rosenberry T. L. Decay accelerating factor of complement is anchored to cells by a C-terminal glycolipid. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6740–6747. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Rutgers J. L., Knowles D. M., Nussenzweig V. Identification of the complement decay-accelerating factor (DAF) on epithelium and glandular cells and in body fluids. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):848–864. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. G., Frank M. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Young N. S. Decay-accelerating factor is present on paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythroid progenitors and lost during erythropoiesis in vitro. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1182–1192. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. A., Jr, Jensen J., Gigli I., Tamura N. Methods for the separation, purification and measurement of nine components of hemolytic complement in guinea-pig serum. Immunochemistry. 1966 Mar;3(2):111–135. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., Burge J., Fearon D. T., Weller P. F., Austen K. F. Isolation of a human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein with decay-accelerating activity for C3 convertases of the complement system. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):184–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., March J. P., Rosen C. E., Spicer D. B., Austen K. F. Surface membrane expression by human blood leukocytes and platelets of decay-accelerating factor, a regulatory protein of the complement system. Blood. 1985 May;65(5):1237–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., March J. P., Rosenfeld S. I., Austen K. F. Affected erythrocytes of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria are deficient in the complement regulatory protein, decay accelerating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., Spicer D. B., Austen K. F. Deficiency of the complement regulatory protein, "decay-accelerating factor," on membranes of granulocytes, monocytes, and platelets in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 1985 Apr 25;312(17):1091–1097. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198504253121704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman C. H., Rosenfeld S. I., Jenkins D. E., Jr, Thiem P. A., Leddy J. P. Complement lysis of human erythrocytes. Differeing susceptibility of two types of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells to C5b-9. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):428–433. doi: 10.1172/JCI109479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Deficiency of an erythrocyte membrane protein with complement regulatory activity in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5430–5434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Trombold J. S., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: deficiency in factor H-like functions of the abnormal erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1971–1980. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. J., Baker P. J., Rosse W. F. Comparison of binding characteristics of factors B and H to C3b on normal and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2484–2489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. J., Soldato C. M., Telen M. J. Increased efficiency of binding of nascent C3b to the erythrocytes of chronic cold agglutinin disease. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):1050–1062. doi: 10.1172/JCI111472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. N., Wilson J. G., Wong W., Jenkins D. E., Jr, Fearon D. T., Austen K. F., Nicholson-Weller A. Normal function of CR1 on affected erythrocytes of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):512–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L., Scoggin D. M. Structure of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Characterization of intersubunit disulfide bonding and detergent interaction. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5643–5652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Jenkins D. E., Jr, Leddy J. P. Enhanced reactive lysis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythrocytes by C5b-9 does not involve increased C7 binding or cell-bound C3b. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):506–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Dacie J. V. Immune lysis of normal human and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) red blood cells. I. The sensitivity of PNH red cells to lysis by complement and specific antibody. J Clin Invest. 1966 May;45(5):736–748. doi: 10.1172/JCI105388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Parker C. J. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Clin Haematol. 1985 Feb;14(1):105–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F. Variations in the red cells in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Br J Haematol. 1973 Mar;24(3):327–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman J., Devine D. V., Rosse W. F. Structural and functional differences between decay-accelerating factor and red cell acetylcholinesterase. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):680–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida N., Nussenzweig R. S., Potocnjak P., Nussenzweig V., Aikawa M. Hybridoma produces protective antibodies directed against the sporozoite stage of malaria parasite. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):71–73. doi: 10.1126/science.6985745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Wood L. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Isolation of a human erythrocyte membrane protein capable of inhibiting expression of homologous complement transmembrane channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6975–6979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]