Abstract
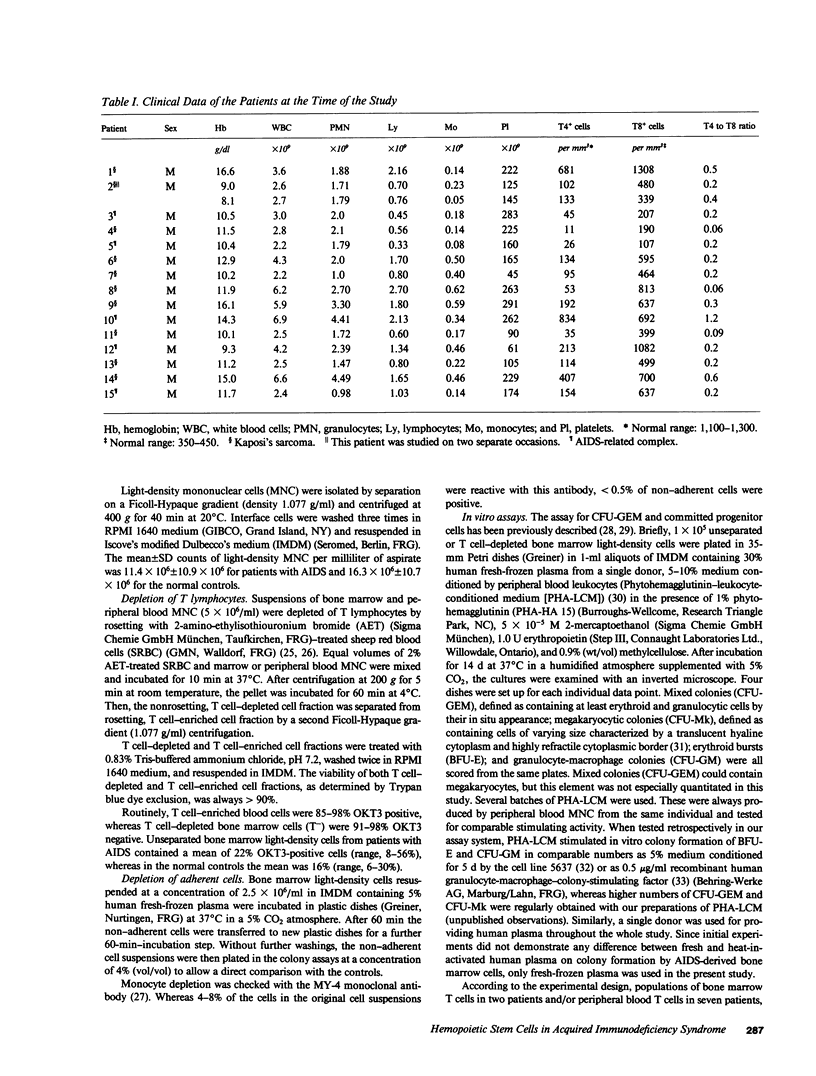
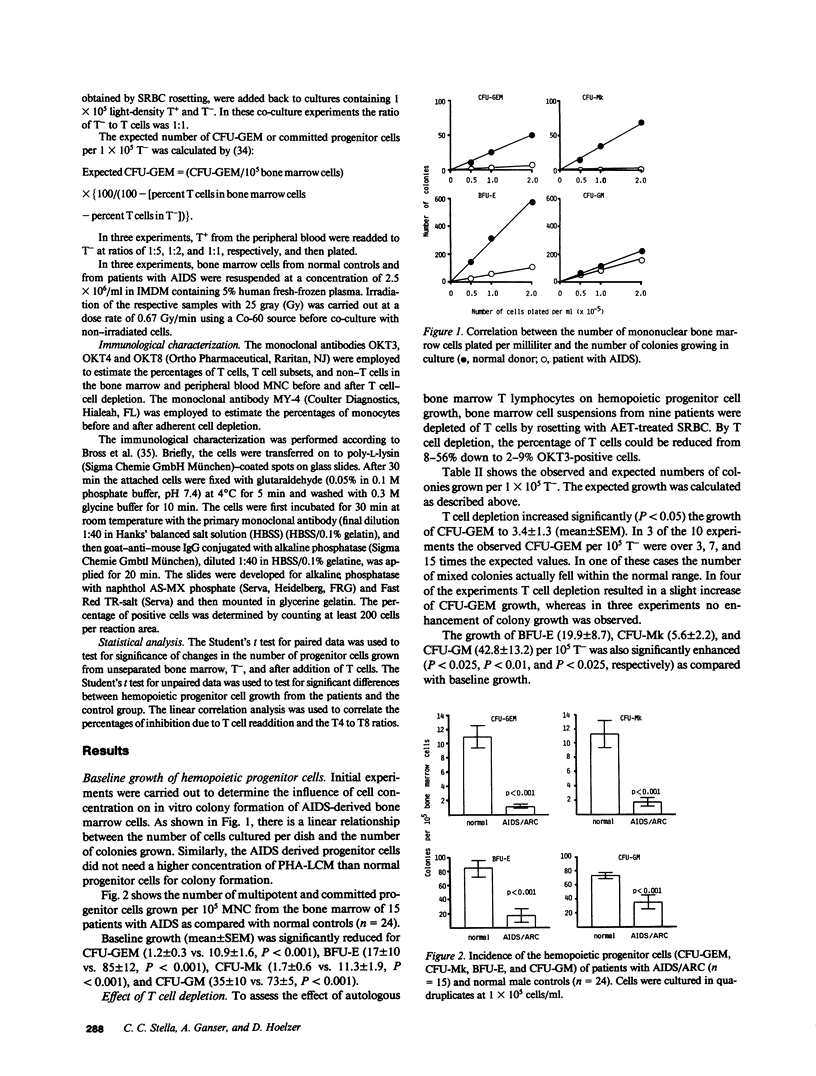
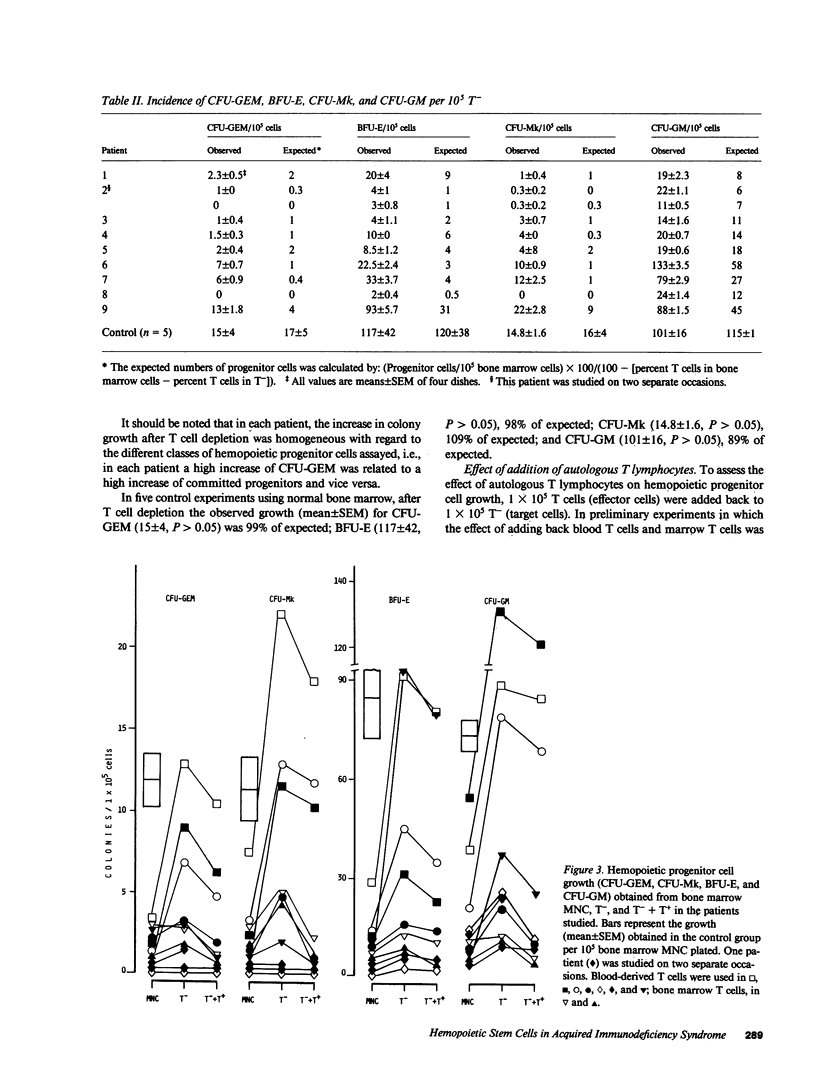
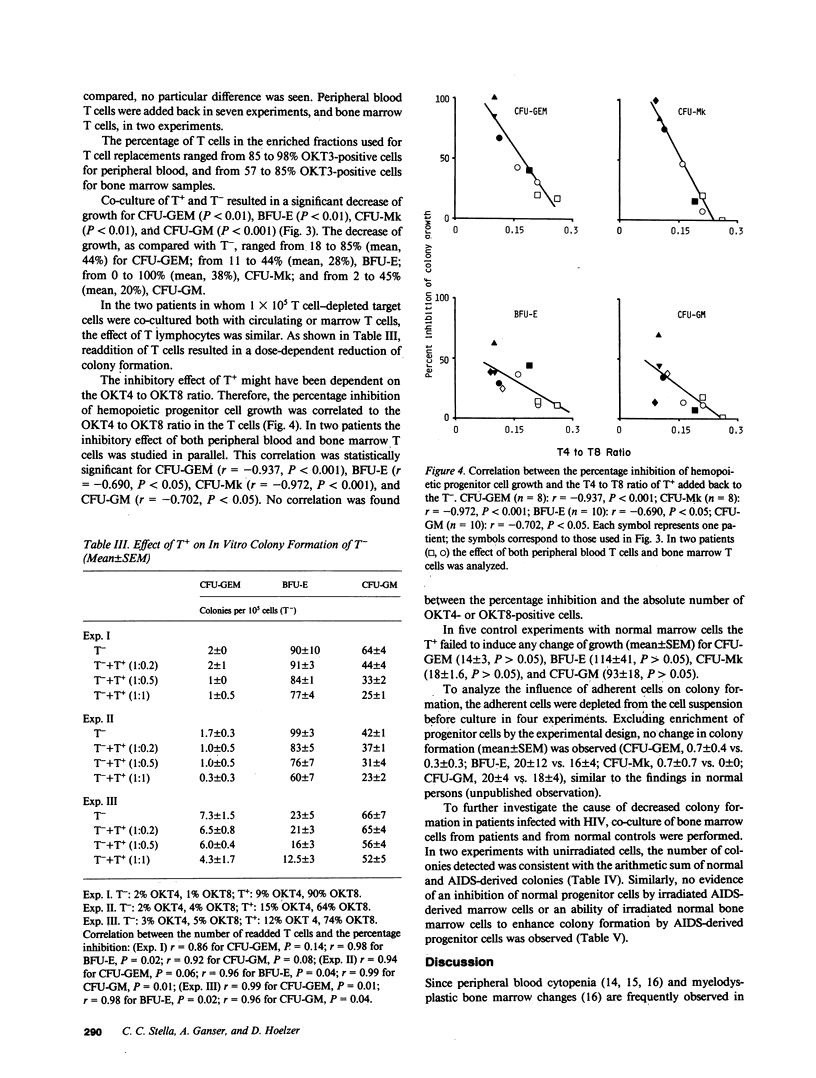
In addition to immunologic derangement, hematological abnormalities have been reported in the majority of patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). In this study 15 patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complex (ARC) were evaluated for the in vitro growth of hemopoietic progenitor cells. In all patients a significant reduction of growth (mean +/- SEM) of colony-forming unit-granulocyte, erythrocyte, macrophage, (megakaryocyte) (CFU-GEM) (1.2 +/- 0.3), burst-forming unit-erythroid (BFU-E) (17 +/- 10), CFU-megakaryocyte (CFU-Mk) (1.7 +/- 0.6), and CFU-granulocyte-macrophage (CFU-GM) (35 +/- 10) was observed in comparison with normal controls. Depletion of T cells from the bone marrow before culture led to a significant increase in colony growth, which indicated an imbalance of the normally modulating T cell subsets. This increase was reversed by readdition of autologous T cells causing a decrease in colony growth to a degree, dependent on the T4 to T8 ratio. A decreased number of hemopoietic progenitor cells and/or a defective modulation of progenitor cell growth, normally carried out by T lymphocyte subsets, might be the cause of the hematological abnormalities in AIDS patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aye M. T., Niho Y., Till J. E., McCulloch E. A. Studies of leukemic cell populations in culture. Blood. 1974 Aug;44(2):205–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bross K. J., Pangalis G. A., Staatz C. G., Blume K. G. Demonstration of cell surface antigens and their antibodies by the peroxidase-antiperoxidase method. Transplantation. 1978 Jun;25(6):331–334. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197806000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell M. A., Anderson D., Cerretti D. P., Price V., McKereghan K., Tushinski R. J., Mochizuki D. Y., Larsen A., Grabstein K., Gillis S. Cloning, sequence, and expression of a human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6250–6254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Golde D. W. Cellular interactions in haematopoiesis. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):177–181. doi: 10.1038/277177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham-Rundles S., Michelis M. A., Masur H. Serum suppression of lymphocyte activation in vitro in acquired immunodeficiency disease. J Clin Immunol. 1983 Apr;3(2):156–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00915487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey J. L., Prince H., Weaver M., Groopman J., Visscher B., Schwartz K., Detels R. Quantitative changes in T helper or T suppressor/cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets that distinguish acquired immune deficiency syndrome from other immune subset disorders. Am J Med. 1984 Jan;76(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90756-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Masur H., Gelmann E. P., Markham P. D., Hahn B. H., Lane H. C. NIH conference. The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: an update. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Jun;102(6):800–813. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-6-800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganser A., Hoelzer D. Effect of intensified chemotherapy on the pluripotent haematopoietic progenitor cells CFU-GEMM in adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1986 Sep;64(1):169–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb07584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler D., Lu L., Bruno E., Yang H. H., Broxmeyer H. E., Hoffman R. The influence of T lymphocyte subsets and humoral factors on colony formation by human bone marrow and blood megakaryocyte progenitor cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2508–2513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller S. A., Muller R., Greenberg M. L., Siegal F. P. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Distinctive features of bone marrow biopsies. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Feb;109(2):138–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S., Groopman J. E., Weinstein W. M., Fahey J. L., Detels R. The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Aug;99(2):208–220. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-2-208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Mayer R. J., Weinstein H. J., Rosenthal D. S., Coral F. S., Beveridge R. P., Schlossman S. F. Surface marker analysis of acute myeloblastic leukemia: identification of differentiation-associated phenotypes. Blood. 1983 Sep;62(3):557–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser G. J., Bino T., Rosenberg H., Zakuth V., Geller E., Spirer Z. Interleukin-2 production and response to exogenous interleukin-2 in a patient with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Apr;56(1):14–17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth C., Morris-Jones P. H., Testa N. G. Long-term bone-marrow damage in children treated for ALL: evidence from in vitro colony assays (GM-CFC and CFUF). Br J Cancer. 1982 Dec;46(6):918–923. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heagy W., Kelley V. E., Strom T. B., Mayer K., Shapiro H. M., Mandel R., Finberg R. Decreased expression of human class II antigens on monocytes from patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Increased expression with interferon-gamma. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2089–2096. doi: 10.1172/JCI111633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoelzer D., Ganser A., Heimpel H. "Atypical" leukemias: preleukemia, smoldering leukemia and hypoplastic leukemia. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1984;93:69–101. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-82249-0_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. E., Clark C. An improved rosetting assay for detection of human T lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Jul;5(2):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Burstein S. A., Thorning D., Powell J. S., Harker L. A., Fialkow P. J., Adamson J. W. Human megakaryocytic progenitors (CFU-M) assayed in methylcellulose: physical characteristics and requirements for growth. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Jan;118(1):87–96. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Masur H., Edgar L. C., Whalen G., Rook A. H., Fauci A. S. Abnormalities of B-cell activation and immunoregulation in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 25;309(8):453–458. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308253090803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurence J., Gottlieb A. B., Kunkel H. G. Soluble suppressor factors in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome and its prodrome. Elaboration in vitro by T lymphocyte-adherent cell interactions. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):2072–2081. doi: 10.1172/JCI111172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt L., Kipps T. J., Engleman E. G., Greenberg P. L. Human bone marrow and peripheral blood T lymphocyte depletion: efficacy and effects of both T cells and monocytes on growth of hematopoietic progenitors. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):663–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Champlin R., Fitchen J. H., Gale R. P. Abnormalities of myeloid progenitor cells after "successful" bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):234–241. doi: 10.1172/JCI111679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan K. F. T-cell-mediated suppression of hematopoiesis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 31;312(5):306–307. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501313120509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner H. A., Jamal N., Izaguirre C. The growth of large megakaryocyte colonies from human bone marrow. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1982;1:45–51. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden M. D., Buick R. N., McCulloch E. A. Separation of blast cell and T-lymphocyte progenitors in the blood of patients with acute myeloblastic leukemia. Blood. 1979 Jul;54(1):186–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Masur H., Roberts R. B. Impaired production of lymphokines and immune (gamma) interferon in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 5;310(14):883–889. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404053101404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne B. M., Guarda L. A., Butler J. J. Bone marrow biopsies in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1984 Nov;15(11):1048–1053. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. F., Morens D. M., Stewart J. A., Kaminski R. M., Spira T. J., Feorino P. M., Larsen S. A., Francis D. P., Wilson M., Kaufman L. National case-control study of Kaposi's sarcoma and Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in homosexual men: Part 2. Laboratory results. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Aug;99(2):151–158. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-2-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. R., Picker L. J. Myelodysplasia in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Aug;84(2):144–152. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/84.2.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P. Immune function and dysfunction in AIDS. Semin Oncol. 1984 Mar;11(1):29–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak J. L., Bender B. S., Quinn T. C. Hematologic abnormalities in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1984 Aug;77(2):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90695-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak J. L., Selonick S. E., Quinn T. C. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome and pancytopenia. JAMA. 1983 Dec 9;250(22):3084–3087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricker R. B., Abrams D. I., Corash L., Shuman M. A. Target platelet antigen in homosexual men with immune thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 28;313(22):1375–1380. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198511283132202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torok-Storb B., Hansen J. A. Modulation of in vitro BFU-E growth by normal Ia-positive T cells is restricted by HLA-DR. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):473–474. doi: 10.1038/298473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welte K., Platzer E., Lu L., Gabrilove J. L., Levi E., Mertelsmann R., Moore M. A. Purification and biochemical characterization of human pluripotent hematopoietic colony-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1526–1530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Human T-lymphotropic retroviruses. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):395–403. doi: 10.1038/317395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoumbos N. C., Gascon P., Djeu J. Y., Young N. S. Interferon is a mediator of hematopoietic suppression in aplastic anemia in vitro and possibly in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):188–192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoumbos N. C., Gascón P., Djeu J. Y., Trost S. R., Young N. S. Circulating activated suppressor T lymphocytes in aplastic anemia. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 31;312(5):257–265. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501313120501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


