Abstract
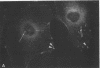
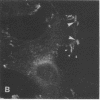
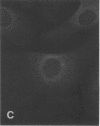
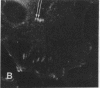
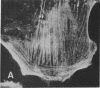
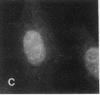
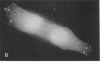
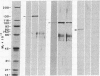
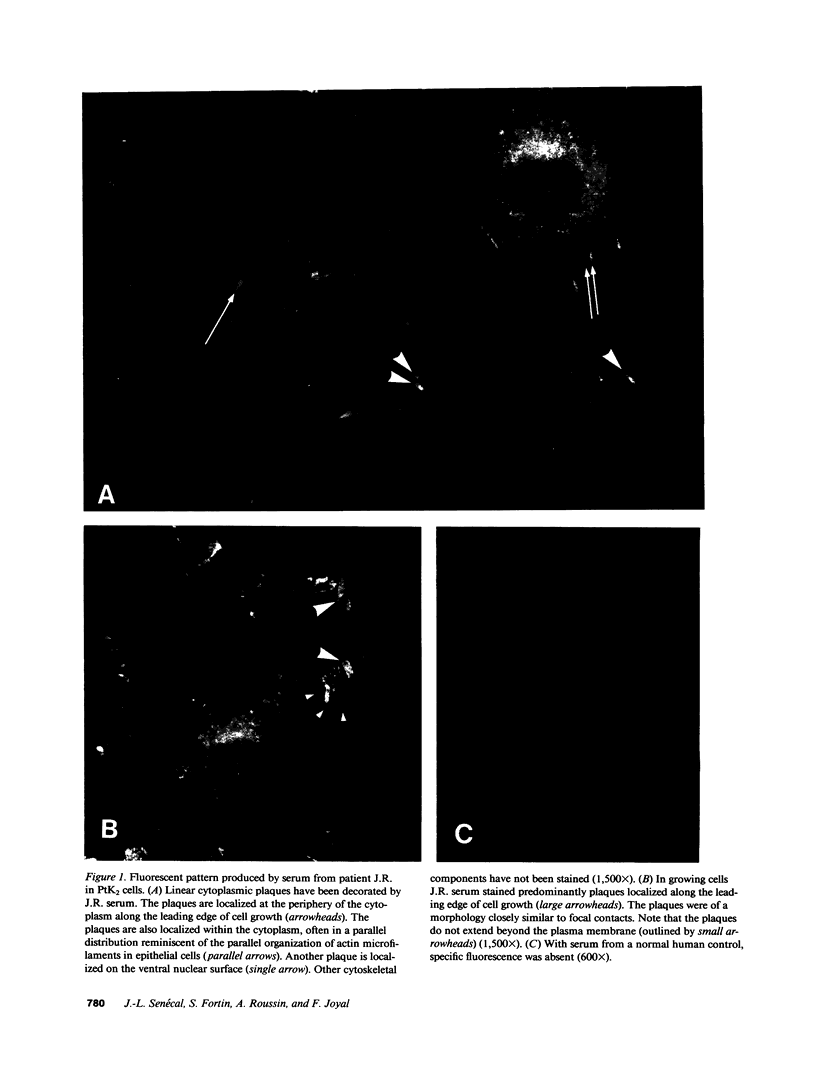
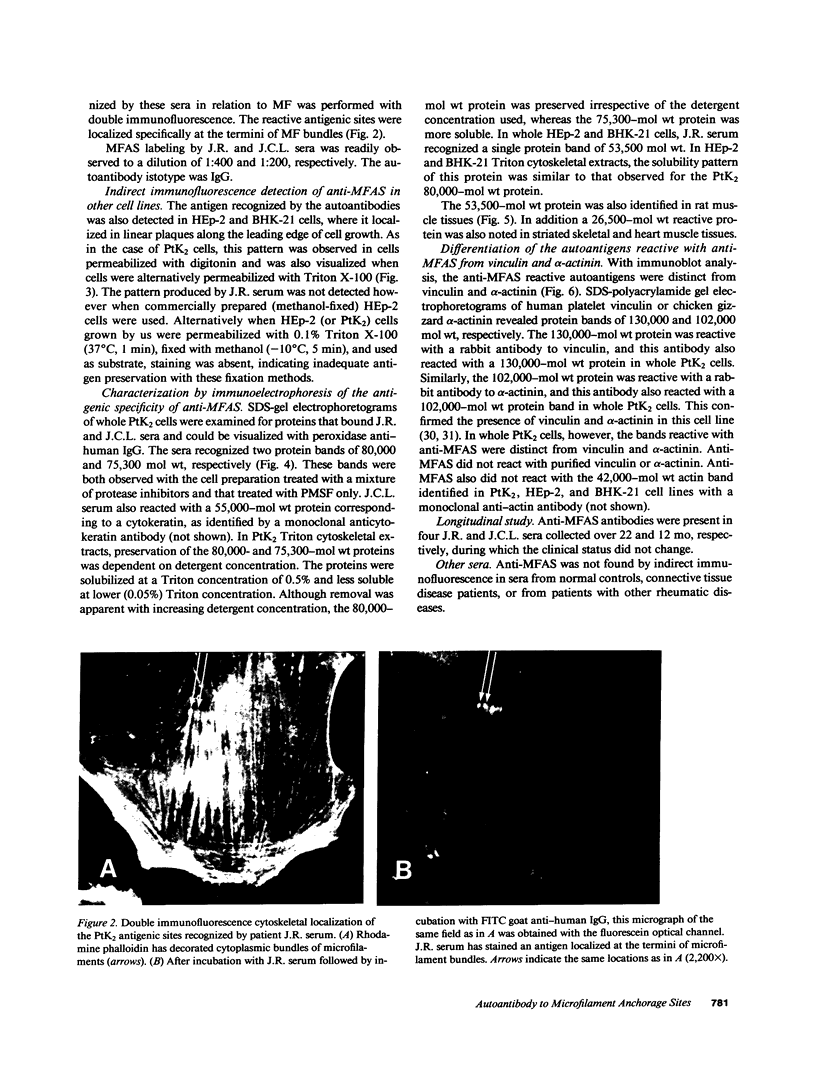
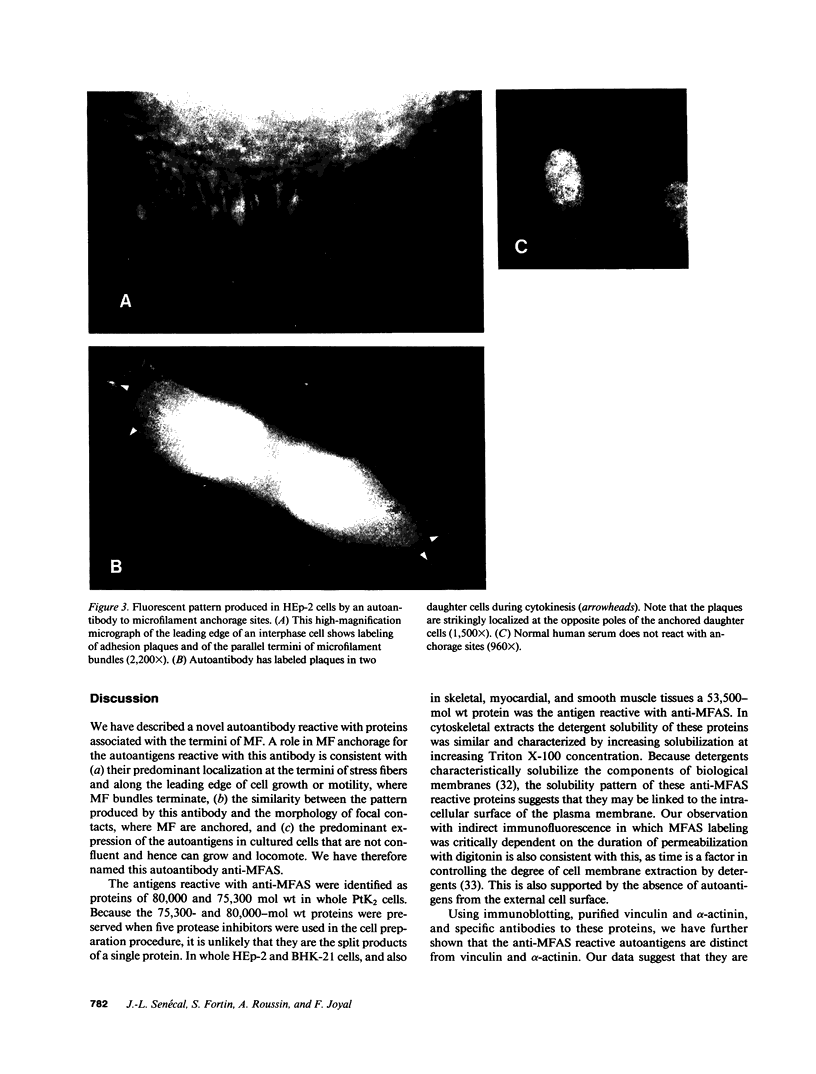
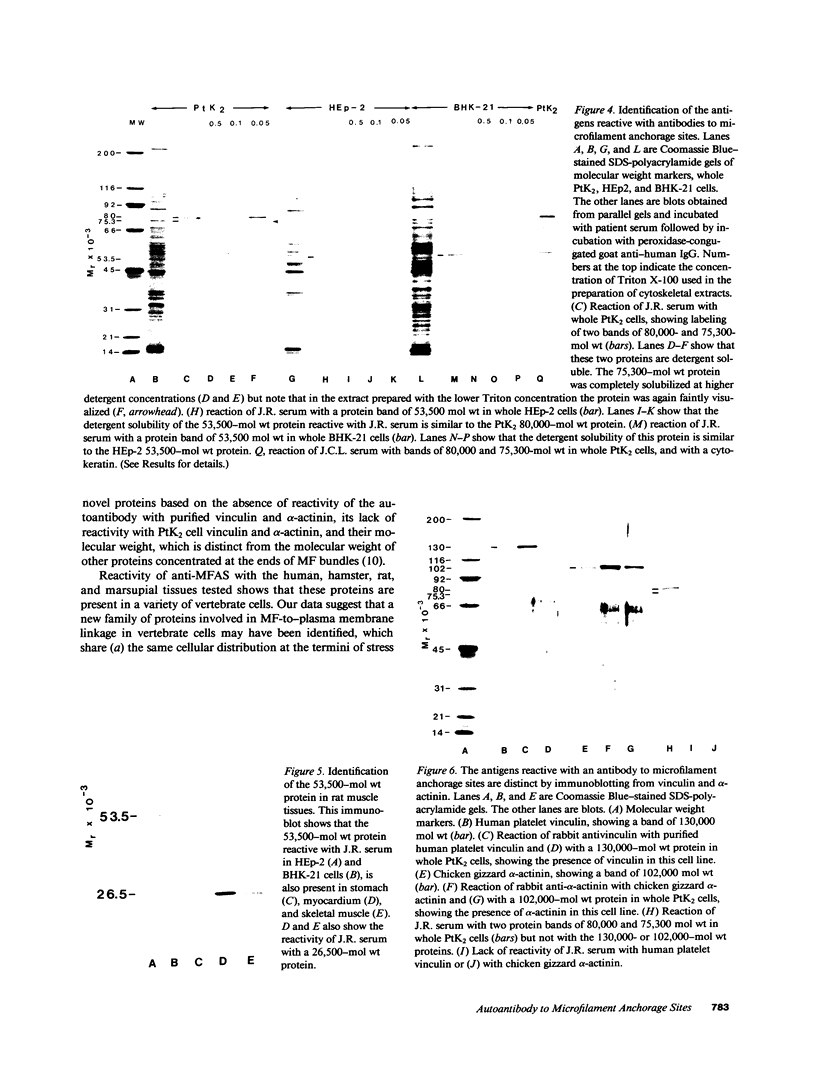
Actin microfilaments are anchored to the plasma membrane at focal contacts. Using an indirect immunofluorescence method, we detected an autoantibody reactive with focal contacts in PtK2, HEp-2, and BHK-21 cells in serum from two patients with early systemic sclerosis. With double immunofluorescence, using the actin-binding drug phalloidin, we localized the plaques decorated by these sera specifically at the termini of microfilament bundles. The reactive antigens were identified by immunoblotting as proteins of 80,000- and 75,300-mol wt in PtK2, and of 53,500-mol wt in HEp-2 and BHK-21 cells. The 53,500-mol wt protein was also identified in rat skeletal, myocardial, and smooth muscle tissues. The detergent solubility of these proteins suggested that they may be linked to the plasma membrane. The autoantigens were immunologically distinct from vinculin and alpha-actinin, two major proteins also known to be concentrated at the ends of microfilament bundles. Our observations suggest that this novel anticytoskeletal autoantibody may identify a novel family of vertebrate cell proteins involved in the linkage of microfilaments to the plasma membrane at focal contacts.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abercrombie M., Heaysman J. E., Pegrum S. M. The locomotion of fibroblasts in culture. IV. Electron microscopy of the leading lamella. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Aug;67(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90420-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibor-Hardy V., Dagenais A., Simard R. In situ localization of the major capsid protein during lytic infection by herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):897–901. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Cohen C. M., Tyler J. Interaction of cytoskeletal proteins on the human erythrocyte membrane. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkley B. R. Microtubule organizing centers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:145–172. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection and localization of a 130K protein in living fibroblasts: a relationship to actin and fibronectin. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):587–595. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Feramisco J. R. Non-muscle alpha actinins are calcium-sensitive actin-binding proteins. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):565–567. doi: 10.1038/294565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., McCullough L. The association of alpha-actinin with the plasma membrane. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(1):53–65. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Halligan N., Cooke C., Rothfield N. The kinetochore is part of the metaphase chromosome scaffold. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):352–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. A 130K protein from chicken gizzard: its localization at the termini of microfilament bundles in cultured chicken cells. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):193–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. Membrane-cytoskeleton interaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 11;737(3-4):305–341. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. Microheterogeneity of avian and mammalian vinculin distinctive subcellular distribution of different isovinculins. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 25;159(4):685–701. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath J. P., Dunn G. A. Cell to substratum contacts of chick fibroblasts and their relation to the microfilament system. A correlated interference-reflexion and high-voltage electron-microscope study. J Cell Sci. 1978 Feb;29:197–212. doi: 10.1242/jcs.29.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams J. S. Rheumatoid sera unravel microtubule organizers. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):604–605. doi: 10.1038/308604b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Actin polymerization and its regulation by proteins from nonmuscle cells. Physiol Rev. 1982 Apr;62(2):672–737. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.2.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Burridge K. Alpha-actinin: immunofluorescent localization of a muscle structural protein in nonmuscle cells. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Weber K. Actin antibody: the specific visualization of actin filaments in non-muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2268–2272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenk R., Penman S. The cytoskeletal framework and poliovirus metabolism. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangeat P., Burridge K. Actin-membrane interaction in fibroblasts: what proteins are involved in this association? J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 2):95s–103s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.95s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miake-Lye R., Kirschner M. W. Induction of early mitotic events in a cell-free system. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi Y., Murata I., Takeuchi A., Kamatani N., Tanimoto K., Yokohari R. Human anticentriole autoantibody in patients with scleroderma and Raynaud's phenomenon. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Dec;29(3):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. M., Senecal J. L., Rothfield N. L. Autoantibodies to the cytoskeleton in human sera. Cell Muscle Motil. 1985;6:55–74. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4723-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn T. G., Ryerse J. S., Bauer N. E., Urhahn J. M., Blair D., Moore T. L. Anticentriole antibody in a patient with progressive systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Jan;29(1):142–146. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D. Actin-binding protein evolution. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):403–403. doi: 10.1038/312403a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D. Cytoplasmic contractile proteins. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):156s–165s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.156s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. W., Sanger J. M., Jockusch B. M. Differences in the stress fibers between fibroblasts and epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;96(4):961–969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.4.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senecal J. L., Rothfield N. F., Oliver J. M. Immunoglobulin M autoantibody to vimentin intermediate filaments. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):716–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI110500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senécal J. L., Oliver J. M., Rothfield N. Anticytoskeletal autoantibodies in the connective tissue diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Aug;28(8):889–898. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Rodnan G. P., Garcia I., Moroi Y., Fritzler M. J., Peebles C. Diversity of antinuclear antibodies in progressive systemic sclerosis. Anti-centromere antibody and its relationship to CREST syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jun;23(6):617–625. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuffanelli D. L., McKeon F., Kleinsmith D. M., Burnham T. K., Kirschner M. Anticentromere and anticentriole antibodies in the scleroderma spectrum. Arch Dermatol. 1983 Jul;119(7):560–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. Intermediate filament associated proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:32–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The molecules of the cell matrix. Sci Am. 1985 Oct;253(4):110–120. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1085-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. Actin-binding proteins--regulators of cell architecture and motility. Nature. 1982 Apr 29;296(5860):811–816. doi: 10.1038/296811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulf E., Deboben A., Bautz F. A., Faulstich H., Wieland T. Fluorescent phallotoxin, a tool for the visualization of cellular actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4498–4502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]