Abstract
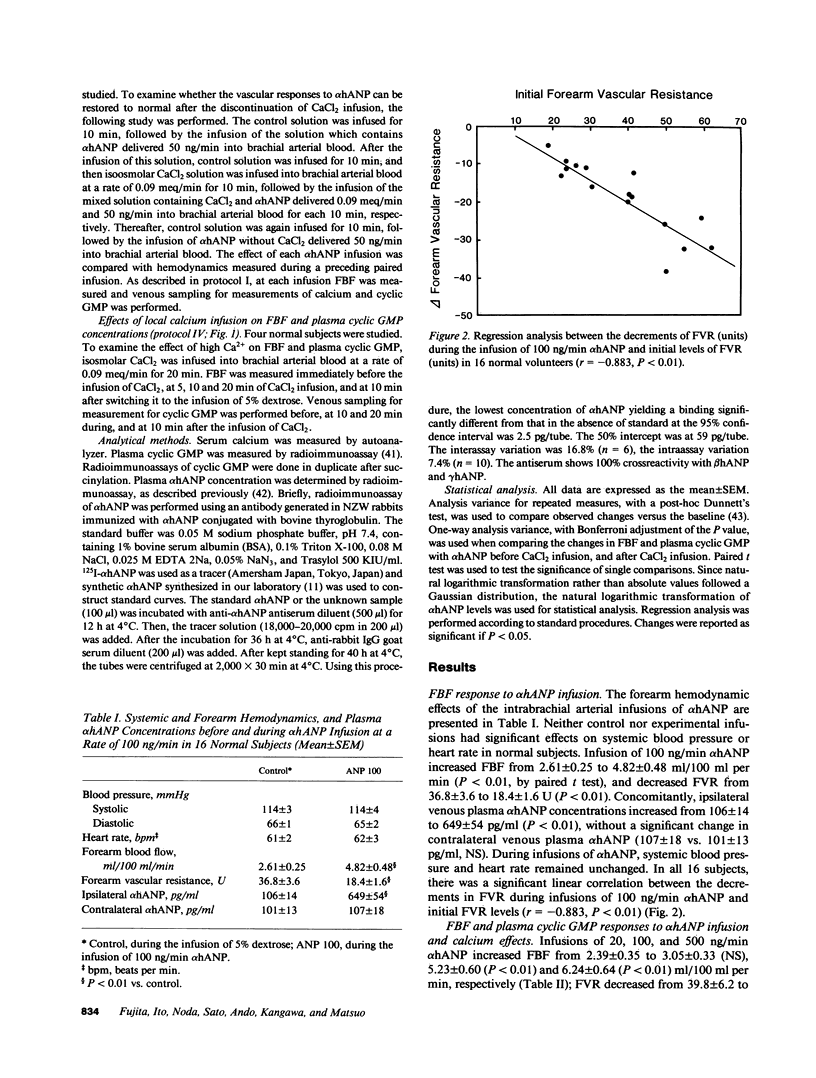
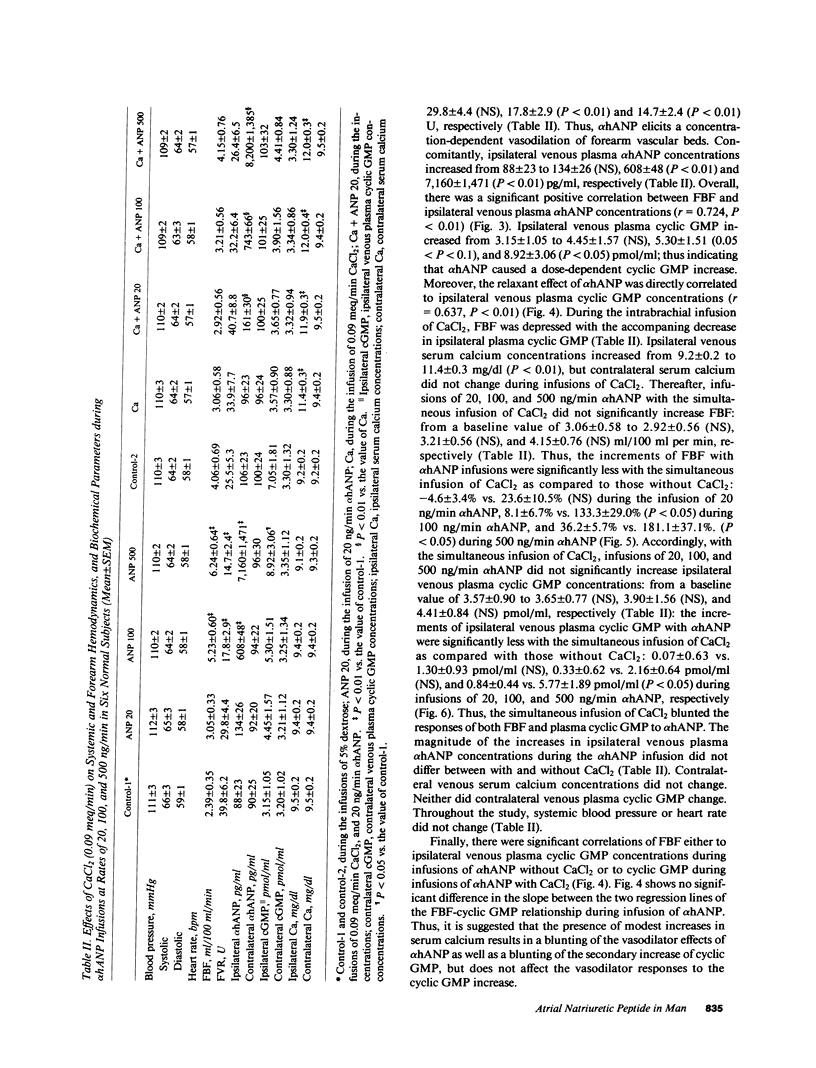
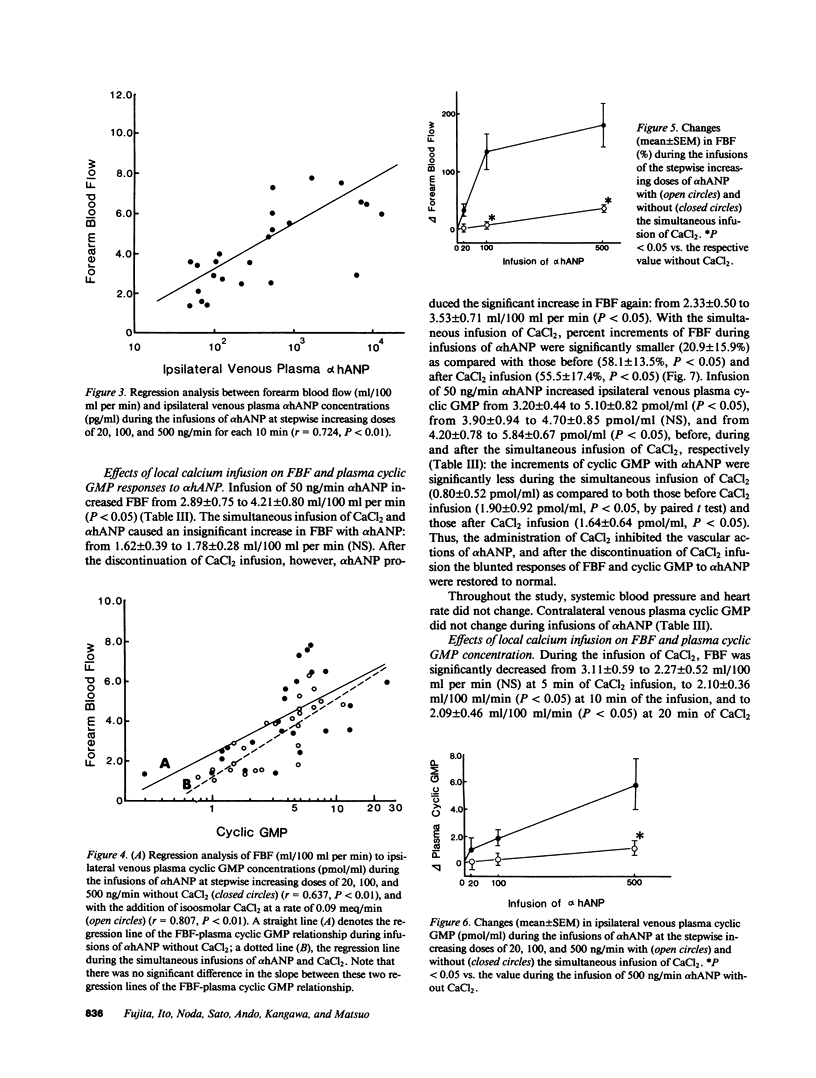
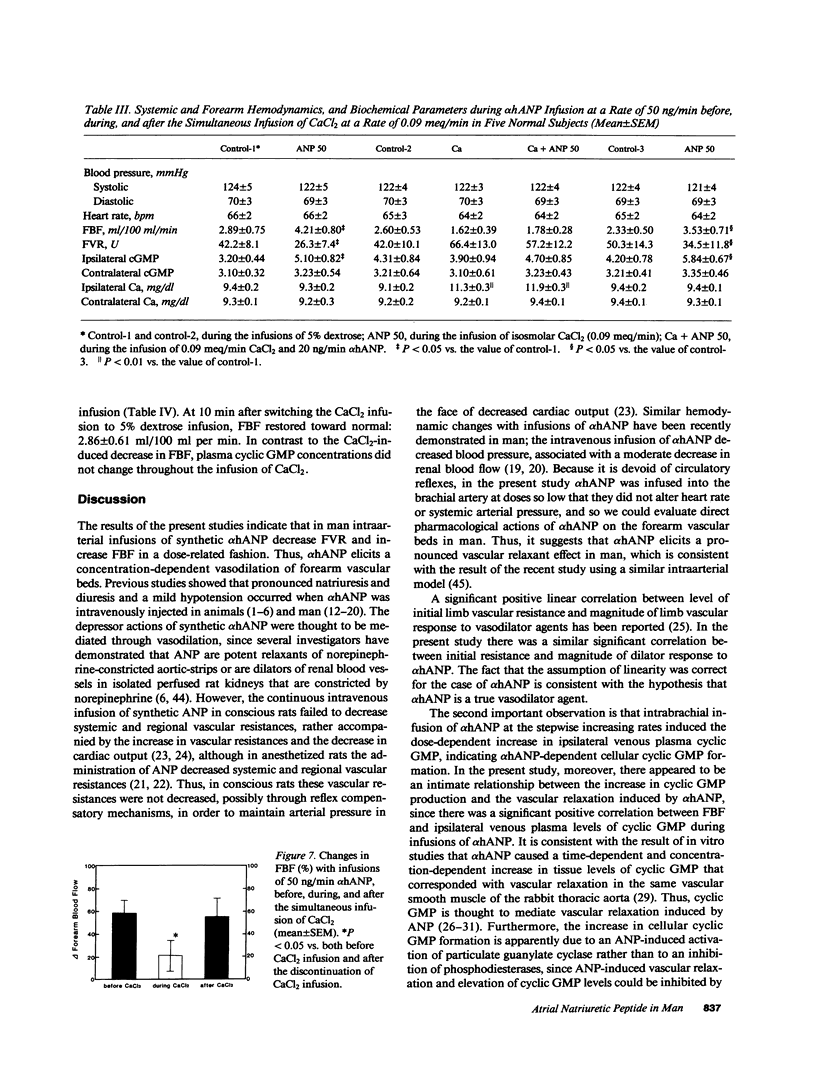
To study vascular actions of synthetic alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide (alpha hANP) in man, forearm blood flow (FBF) was measured by strain-gauge plethysmograph during the continuous infusion of 100 ng/min alpha hANP dissolved in 5% dextrose into the brachial artery in healthy subjects. alpha hANP increased FBF, with the concomitant increase in ipsilateral limb venous plasma concentrations of alpha hANP. Overall, there was a significant linear correlation between the decrements of ipsilateral forearm vascular resistance (FVR) during infusions of alpha hANP and initial FVR levels (r = -0.883, P less than 0.01). Moreover, alpha hANP, at the stepwise increasing doses of 20, 100, and 500 ng/min, increased FBF in a dose-related fashion: alpha hANP elicits a concentration-dependent vasodilation of forearm vascular beds. Concomitantly, infusions of alpha hANP caused a dose-dependent increase in ipsilateral limb venous plasma cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cyclic GMP). Overall, there were direct correlations of FBF either to ipsilateral venous plasma alpha hANP (r = 0.724, P less than 0.01) or to cyclic GMP concentrations (r = 0.637, P less than 0.01). Subsequently, isoosmolar CaCl2 solution was infused into the same brachial artery at a rate of 0.09 meq/min, and then, with a 2.5 +/- 0.2-mg/dl increase in ipsilateral venous serum calcium concentrations the incremental responses of both FBF and plasma cyclic GMP to alpha hANP were severely blunted. There was also a significant positive linear correlation between FBF and venous plasma cyclic GMP during infusions of alpha hANP with the simultaneous administration of CaCl2 (r = 0.807, P less than 0.01). Finally, the addition of CaCl2 infusion did not change the slope of the regression line of the FBF-plasma cyclic GMP relationship during infusions of alpha hANP. Evidence presented suggests that alpha hANP acts directly on the forearm vascular beds in man, eliciting its vascular relaxant effect, possibly by increasing cellular levels of cyclic GMP. Moreover, modest elevations of serum calcium inhibit the alpha hANP-dependent vasodilation, possibly through the suppression of cyclic GMP activation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando K., Fujita T., Ito Y., Noda H., Yamashita K. The role of renal hemodynamics in the antihypertensive effect of captopril. Am Heart J. 1986 Feb;111(2):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(86)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas S. A., Kleinert H. D., Camargo M. J., Januszewicz A., Sealey J. E., Laragh J. H., Schilling J. W., Lewicki J. A., Johnson L. K., Maack T. Purification, sequencing and synthesis of natriuretic and vasoactive rat atrial peptide. Nature. 1984 Jun 21;309(5970):717–719. doi: 10.1038/309717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli P., Müller F. B., Linder L., Raine A. E., Resink T. J., Erne P., Kiowski W., Ritz R., Bühler F. R. The vasodilator potency of atrial natriuretic peptide in man. Circulation. 1987 Jan;75(1):221–228. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.75.1.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camargo M. J., Kleinert H. D., Atlas S. A., Sealey J. E., Laragh J. H., Maack T. Ca-dependent hemodynamic and natriuretic effects of atrial extract in isolated rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1984 Apr;246(4 Pt 2):F447–F456. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.4.F447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrisman T. D., Garbers D. L., Parks M. A., Hardman J. G. Characterization of particulate and soluble guanylate cyclases from rat lung. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):374–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody R. J., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H., Kubo S. H., Covit A. B., Ryman K. S., Shaknovich A., Pondolfino K., Clark M., Camargo M. J. Atrial natriuretic factor in normal subjects and heart failure patients. Plasma levels and renal, hormonal, and hemodynamic responses to peptide infusion. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1362–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI112723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie M. G., Geller D. M., Cole B. R., Boylan J. G., YuSheng W., Holmberg S. W., Needleman P. Bioactive cardiac substances: potent vasorelaxant activity in mammalian atria. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):71–73. doi: 10.1126/science.6857267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B., GRIMBY G., THULESIUS O. Adaptive structural changes of the vascular walls in hypertension and their relation to the control of the peripheral resistance. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Dec 15;44(3-4):255–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn T. G., de Bold M. L., de Bold A. J. The amino acid sequence of an atrial peptide with potent diuretic and natriuretic properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):859–865. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91675-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Ando K., Noda H., Sato Y., Yamashita N., Yamashita K. Hemodynamic and endocrine changes associated with captopril in diuretic-resistant hypertensive patients. Am J Med. 1982 Sep;73(3):341–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Cantin M., Thibault G., Ong H., Genest J. Relationship of specific granules to the natriuretic and diuretic activity of rat atria. Experientia. 1982 Sep 15;38(9):1071–1073. doi: 10.1007/BF01955373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Thibault G., Cantin M., Genest J. Effect of a purified atrial natriuretic factor on rat and rabbit vascular strips and vascular beds. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 2):R34–R39. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.247.1.R34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerzer R., Witzgall H., Tremblay J., Gutkowska J., Hamet P. Rapid increase in plasma and urinary cyclic GMP after bolus injection of atrial natriuretic factor in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Dec;61(6):1217–1219. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-6-1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass M., Kopin I. J., Goldstein D. S., Zukowska-Grojec Z. Differential inhibition of alpha adrenoceptor-mediated pressor responses by rat atrial natriuretic peptide in the pithed rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Oct;235(1):122–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamet P., Tremblay J., Pang S. C., Garcia R., Thibault G., Gutkowska J., Cantin M., Genest J. Effect of native and synthetic atrial natriuretic factor on cyclic GMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):515–527. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90260-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Ishii M., Sugimoto T., Matsuoka H., Sugimoto T., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. The effects of human atrial 28-amino acid peptide on systemic and renal hemodynamics in anesthetized rats. Circ Res. 1985 Oct;57(4):634–639. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.4.634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Tomita M., Takada S., Yoshimi H. Vascular receptor binding activities and cyclic GMP responses by synthetic human and rat atrial natriuretic peptides (ANP) and receptor down-regulation by ANP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):538–546. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honma M., Satoh T., Takezawa J., Ui M. An ultrasensitive method for the simultaneous determination of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in small-volume samples from blood and tissue. Biochem Med. 1977 Dec;18(3):257–273. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(77)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz L., McGuffee L. J., Smith P. M., Little S. A. Specific inhibition of calcium channels by calcium ions in smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Feb;220(2):382–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Purification and complete amino acid sequence of alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide (alpha-hANP). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 13;118(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeler R. Atrial natriuretic factor has a direct, prostaglandin-independent action on kidneys. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Aug;60(8):1078–1082. doi: 10.1139/y82-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Murad F. Evidence for two different forms of guanylate cyclase in rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6910–6916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Misu Y. Release of noradrenaline by splenic nerve stimulation and its dependence on calcium. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(2):219–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuribayashi T., Nakazato M., Tanaka M., Nagamine M., Kurihara T., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Renal effects of human alpha-atrial natriuretic polypeptide. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 30;312(22):1456–1457. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505303122213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappe R. W., Smits J. F., Todt J. A., Debets J. J., Wendt R. L. Failure of atriopeptin II to cause arterial vasodilation in the conscious rat. Circ Res. 1985 Apr;56(4):606–612. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.4.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misono K. S., Fukumi H., Grammer R. T., Inagami T. Rat atrial natriuretic factor: complete amino acid sequence and disulfide linkage essential for biological activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Mar 15;119(2):524–529. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata A., Kangawa K., Toshimori T., Hatoh T., Matsuo H. Molecular forms of atrial natriuretic polypeptides in mammalian tissues and plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 31;129(1):248–255. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91429-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murad F. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate as a mediator of vasodilation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI112536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlstein E. H., Berkowitz B. A. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate mediates vascular relaxation induced by atrial natriuretic factor. Hypertension. 1985 Mar-Apr;7(2):306–310. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.2.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeck H. W., Daugherty R. M., Jr, Haddy F. J. Continuous infusion indicator dilution measurement of limb blood flow and vascular response to magnesium sulfate in normotensive and hypotensive men. J Clin Invest. 1969 Oct;48(10):1944–1957. doi: 10.1172/JCI106161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSEN M. J., EDELMAN I. S. CALCIUM INHIBITION OF THE ACTION OF VASOPRESSIN ON THE URINARY BLADDER OF THE TOAD. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:583–594. doi: 10.1172/JCI104943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegram B. L., Kardon M. B., Trippodo N. C., Cole F. E., MacPhee A. A. Atrial extract: hemodynamics in Wistar-Kyoto and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 Aug;249(2 Pt 2):H265–H271. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.249.2.H265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Goodman D. B. Relationships between calcium and cyclic nucleotides in cell activation. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jul;57(3):421–509. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.3.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards A. M., Nicholls M. G., Espiner E. A., Ikram H., Yandle T. G., Joyce S. L., Cullens M. M. Effects of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide in essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1985 Sep-Oct;7(5):812–817. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards A. M., Nicholls M. G., Ikram H., Webster M. W., Yandle T. G., Espiner E. A. Renal, haemodynamic, and hormonal effects of human alpha atrial natriuretic peptide in healthy volunteers. Lancet. 1985 Mar 9;1(8428):545–549. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91207-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk D. B., Johnson L. K., Schwartz K., Sista H., Scarborough R. M., Lewicki J. A. Distinct atrial natriuretic factor receptor sites on cultured bovine aortic smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 15;127(2):433–442. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seymour A. A., Blaine E. H., Mazack E. K., Smith S. G., Stabilito I. I., Haley A. B., Napier M. A., Whinnery M. A., Nutt R. F. Renal and systemic effects of synthetic atrial natriuretic factor. Life Sci. 1985 Jan 7;36(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90283-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaichi K., Uchida S., Kurokawa K. High Ca2+ inhibits AVP-dependent cAMP production in thick ascending limbs of Henle. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 2):F770–F776. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.5.F770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikkanen I., Fyhrquist F., Metsärinne K., Leidenius R. Plasma atrial natriuretic peptide in cardiac disease and during infusion in healthy volunteers. Lancet. 1985 Jul 13;2(8446):66–69. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay J., Gerzer R., Vinay P., Pang S. C., Béliveau R., Hamet P. The increase of cGMP by atrial natriuretic factor correlates with the distribution of particulate guanylate cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 11;181(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITNEY R. J. The measurement of volume changes in human limbs. J Physiol. 1953 Jul;121(1):1–27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakitani K., Oshima T., Loewy A. D., Holmberg S. W., Cole B. R., Adams S. P., Fok K. F., Currie M. G., Needleman P. Comparative vascular pharmacology of the atriopeptins. Circ Res. 1985 Apr;56(4):621–627. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.4.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldhäusl W., Vierhapper H., Nowotny P. Prolonged administration of human atrial natriuretic peptide in healthy men: evanescent effects on diuresis and natriuresis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 May;62(5):956–959. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-5-956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Atrial natriuretic factor selectively activates particulate guanylate cyclase and elevates cyclic GMP in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14332–14334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb R. C., Bohr D. F. Mechanism of membrane stabilization by calcium in vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):C227–C232. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1978.235.5.C227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidmann P., Hasler L., Gnädinger M. P., Lang R. E., Uehlinger D. E., Shaw S., Rascher W., Reubi F. C. Blood levels and renal effects of atrial natriuretic peptide in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):734–742. doi: 10.1172/JCI112368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. N., Baird C. E., Hardman Y. J., Wu J. G. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activities of pig coronary arteries. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 19;384(2):430–442. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. F., Caterson I. D., Turtle J. R. Control of insulin receptor affinity by a Ca2+-sensitive binding site. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 24;797(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90378-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Faison E. P., Nutt R. F. Vasodilator profile of synthetic atrial natriuretic factor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jun 15;102(1):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90353-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Faison E. P., Waldman S. A., Schwartz K., Murad F., Rapoport R. M. Atrial natriuretic factor elicits an endothelium-independent relaxation and activates particulate guanylate cyclase in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7661–7664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J., Borenstein H. B., Veress A. T., Sonnenberg H. A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous injection of atrial myocardial extract in rats. Life Sci. 1981 Jan 5;28(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


