Abstract
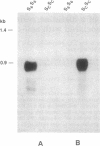
Gametophytic self-incompatibility in the Solanaceae is controlled by a single, multiallelic locus, the S locus. We have recently described an allele of the S locus of Lycopersicon peruvianum that caused this normally self-incompatible plant to become self-compatible. We have now characterized two glycoproteins present in the styles of self-compatible and self-incompatible accessions of L. peruvianum: one is a ribonuclease that cosegregates with a functional self-incompatibility allele (S6 allele); the other cosegregates with the self-compatible allele (Sc allele) but has no ribonuclease activity. The derived amino acid sequences of the cDNAs encoding the S6 and Sc glycoproteins resemble sequences of other ribonucleases encoded by the S locus. The derived sequence for the Sc glycoprotein differs from the others by lacking one of the histidine residues found in all other S-locus ribonucleases. These findings demonstrate the essential role of ribonuclease activity in self-incompatibility and lend further weight to evidence that this histidine residue is involved in the catalytic site of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ai Y. J., Kron E., Kao T. H. S-alleles are retained and expressed in a self-compatible cultivar of Petunia hybrida. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Dec;230(3):353–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00280291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. A., McFadden G. I., Bernatzky R., Atkinson A., Orpin T., Dedman H., Tregear G., Fernley R., Clarke A. E. Sequence variability of three alleles of the self-incompatibility gene of Nicotiana alata. Plant Cell. 1989 May;1(5):483–491. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.5.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessio G., Di Donato A., Parente A., Piccoli R. Seminal RNase: a unique member of the ribonuclease superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):104–106. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90042-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds P. N., Bönig I., Du H., Rödin J., Anderson M. A., Newbigin E., Clarke A. E. S-RNase gene of Nicotiana alata is expressed in developing pollen. Plant Cell. 1993 Dec;5(12):1771–1782. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.12.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett J. W., Strydom D. J., Lobb R. R., Alderman E. M., Bethune J. L., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Isolation and characterization of angiogenin, an angiogenic protein from human carcinoma cells. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5480–5486. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnen W., Batterham M. P., Clarke A. E., Moritz R. L., Simpson R. J. Identification, isolation, and N-terminal sequencing of style glycoproteins associated with self-incompatibility in Nicotiana alata. Plant Cell. 1989 May;1(5):493–499. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann H., Salamini F., Thompson R. D. Sequence variability and gene structure at the self-incompatibility locus of Solanum tuberosum. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 May;226(3):457–466. doi: 10.1007/BF00260659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata Y., Sakiyama F., Hayashi F., Kyogoku Y. Identification of two essential histidine residues of ribonuclease T2 from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 12;187(1):255–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS D. Structure of the incompatibility gene; induced mutation rate. Heredity (Edinb) 1949 Dec;3(3):339–355. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1949.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. S., Huang S., Kao T. S proteins control rejection of incompatible pollen in Petunia inflata. Nature. 1994 Feb 10;367(6463):560–563. doi: 10.1038/367560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matton D. P., Nass N., Clarke A. E., Newbigin E. Self-incompatibility: how plants avoid illegitimate offspring. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):1992–1997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure B. A., Haring V., Ebert P. R., Anderson M. A., Simpson R. J., Sakiyama F., Clarke A. E. Style self-incompatibility gene products of Nicotiana alata are ribonucleases. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):955–957. doi: 10.1038/342955a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murfett J., Atherton T. L., Mou B., Gasser C. S., McClure B. A. S-RNase expressed in transgenic Nicotiana causes S-allele-specific pollen rejection. Nature. 1994 Feb 10;367(6463):563–566. doi: 10.1038/367563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbigin E., Anderson M. A., Clarke A. E. Gametophytic Self-Incompatibility Systems. Plant Cell. 1993 Oct;5(10):1315–1324. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.10.1315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivers B. A., Bernatzky R., Robinson S. J., Jahnen-Dechent W. Molecular diversity at the self-incompatibility locus is a salient feature in natural populations of wild tomato (Lycopersicon peruvianum). Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Apr;238(3):419–427. doi: 10.1007/BF00292001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Unger G., Stark R., Schneider-Scherzer E., Thiel H. J. Identification of a structural glycoprotein of an RNA virus as a ribonuclease. Science. 1993 Aug 27;261(5125):1169–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.8356450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Fox E. A., Riordan J. F. Role of lysines in human angiogenin: chemical modification and site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1726–1732. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Vallee B. L. Site-directed mutagenesis of histidine-13 and histidine-114 of human angiogenin. Alanine derivatives inhibit angiogenin-induced angiogenesis. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7401–7408. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youle R. J., Newton D., Wu Y. N., Gadina M., Rybak S. M. Cytotoxic ribonucleases and chimeras in cancer therapy. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 1993;10(1):1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]