Abstract
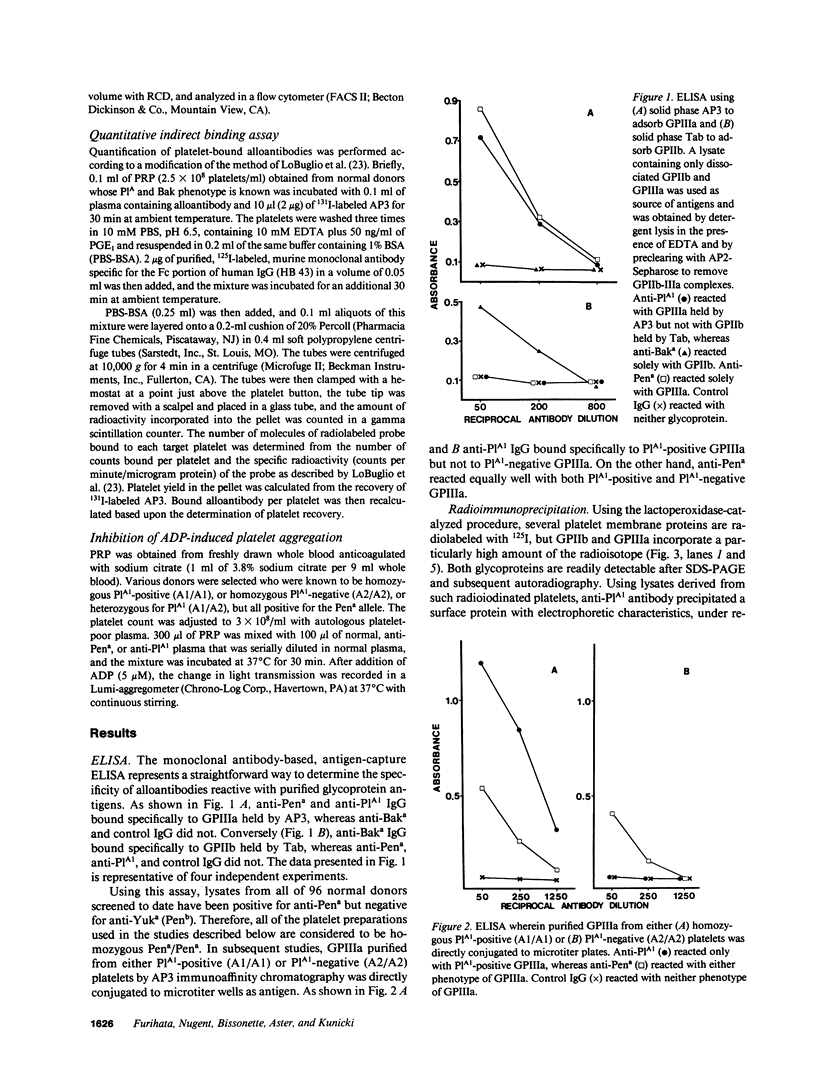
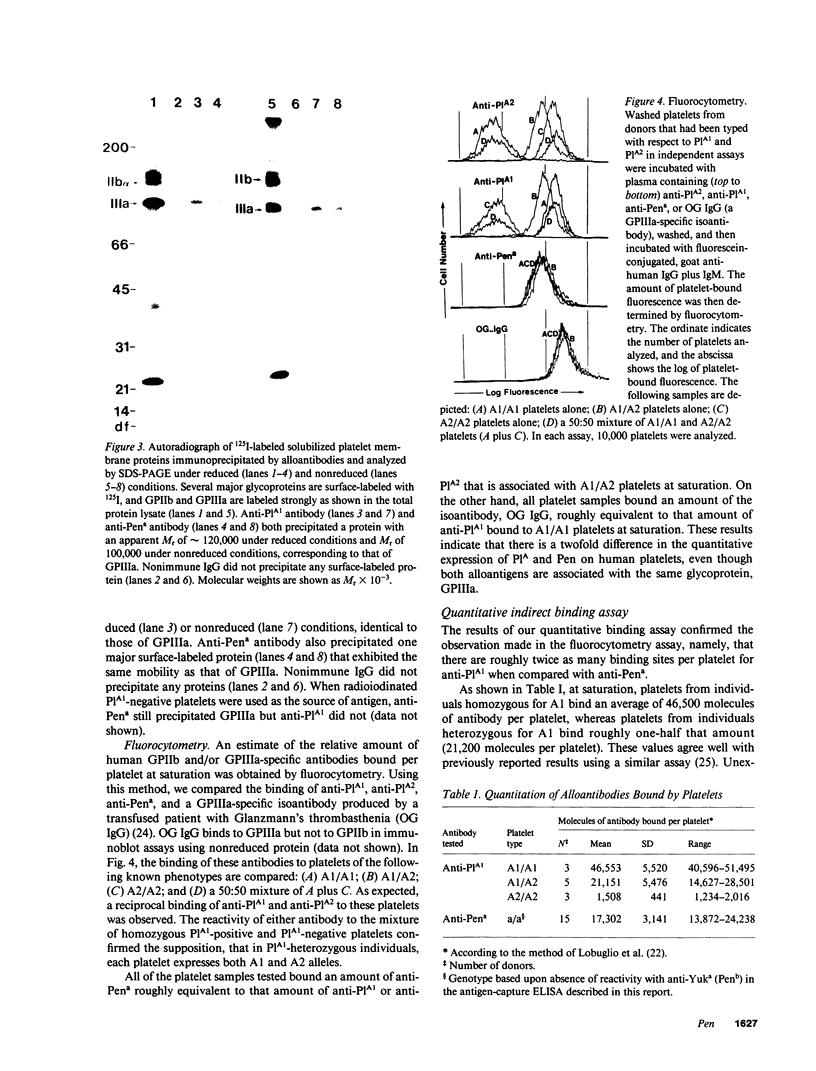
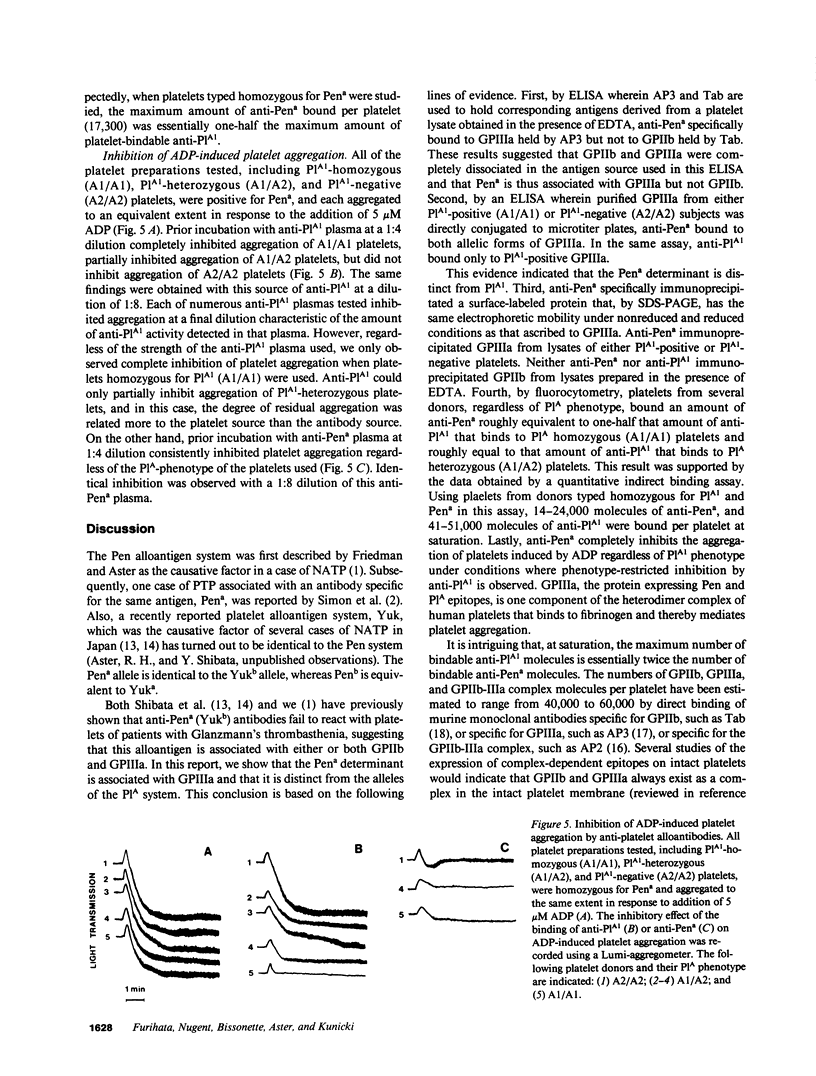
Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenic purpura associated with a new platelet-specific alloantigen Pena has been reported. We now provide direct evidence that the Pena determinant is associated with glycoprotein (GP) IIIa, but that it is distinct from epitopes that define the PlA system. By ELISA wherein monoclonal antibodies specific for GPIIb (Tab) and specific for GPIIIa (AP3) were used to capture and hold antigens from a platelet lysate prepared under conditions that generate free GPIIb and GPIIIa, anti-Pena reacted with GPIIIa held by AP3 but not with GPIIb held by Tab. In an alternative ELISA where purified GPIIIa from both PlA1-positive and PlA1-negative platelets were used individually as antigen, anti-Pena reacted with both allelic forms of GPIIIa. By radioimmuno-precipitation, anti-Pena precipitated a single surface-labeled membrane protein with electrophoretic characteristics in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, under nonreduced or reduced conditions, identical to those of GPIIIa. By fluorocytometry, platelets from several donors, regardless of PlA phenotype, bound an amount of anti-Pena roughly equivalent to one-half that amount of anti-PlA1 bound by PlA1 homozygous (A1/A1) platelets and roughly equal to that amount of anti-PlA1 bound by PlA1 heterozygous (A1/A2) platelets. Using platelets from donors typed homozygous for PlA1 and Pena in a quantitative indirect binding assay, 14-24,000 molecules of anti-Pena and 41-51,000 molecules of anti-PlA1 were bound per platelet at saturation. Anti-Pena completely inhibited ADP-induced aggregation of Pena-positive platelets, regardless of PlA phenotype. These results indicate that the Pena determinant is associated with GPIIIa but distinct from PlA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beardsley D. S., Spiegel J. E., Jacobs M. M., Handin R. I., Lux S. E., 4th Platelet membrane glycoprotein IIIa contains target antigens that bind anti-platelet antibodies in immune thrombocytopenias. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1701–1707. doi: 10.1172/JCI111587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degos L., Dautigny A., Brouet J. C., Colombani M., Ardaillou N., Caen J. P., Colombani J. A molecular defect in thrombasthenic platelets. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):236–240. doi: 10.1172/JCI108074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. M., Aster R. H. Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenic purpura and congenital porencephaly in two siblings associated with a "new" maternal antiplatelet antibody. Blood. 1985 Jun;65(6):1412–1415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N., Nurden A. T., Phillips D. R. Molecular defects in interactions of platelets with the vessel wall. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 25;311(17):1084–1098. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410253111705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N., Thoi L. L., Morgan R. K. Quantitative analysis of platelet membrane glycoproteins: effect of platelet washing procedures and isolation of platelet density subpopulations. Thromb Res. 1981 Jul 1;23(1-2):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Forsyth J., Lightsey A., Chediak J., Plow E. F. Reduced surface expression and binding of fibronectin by thrombin-stimulated thrombasthenic platelets. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):619–624. doi: 10.1172/JCI110808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson M., McFarland J., Aster R. H. Quantitative determination of platelet surface alloantigens using a monoclonal probe. Hum Immunol. 1986 Mar;15(3):251–262. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer N., Boizard B., Didry D., Wautier J. L., Nurden A. T. Immunochemical characterization of the platelet-specific alloantigen Leka: a comparative study with the PlA1 alloantigen. Blood. 1984 Dec;64(6):1212–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J., Aster R. H. Isolation and immunologic characterization of the human platelet alloantigen, P1A1. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jun;16(6):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Toledano S., Tobelem G., Legrand C., Bredoux R., Degos L., Nurden A., Caen J. P. Acquired IgG antibody occurring in a thrombasthenic patient: its effect on human platelet function. Blood. 1978 Jun;51(6):1065–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoBuglio A. F., Court W. S., Vinocur L., Maglott G., Shaw G. M. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Use of a 125I-labeled antihuman IgG monoclonal antibody to quantify platelet-bound IgG. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 25;309(8):459–463. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308253090804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEver R. P., Bennett E. M., Martin M. N. Identification of two structurally and functionally distinct sites on human platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5269–5275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery R. R., Kunicki T. J., Taves C., Pidard D., Corcoran M. Diagnosis of Bernard-Soulier syndrome and Glanzmann's thrombasthenia with a monoclonal assay on whole blood. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):385–389. doi: 10.1172/JCI110780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Leung L. L. Complex formation of platelet membrane glycoproteins IIb and IIIa with fibrinogen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):263–269. doi: 10.1172/JCI110448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman P. J., Allen R. W., Kahn R. A., Kunicki T. J. Quantitation of membrane glycoprotein IIIa on intact human platelets using the monoclonal antibody, AP-3. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):227–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman P. J., Martin L. S., Knipp M. A., Kahn R. A. Studies on the nature of the human platelet alloantigen, PlA1: localization to a 17,000-dalton polypeptide. Mol Immunol. 1985 Jun;22(6):719–729. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niessner H., Clemetson K. J., Panzer S., Mueller-Eckhardt C., Santoso S., Bettelheim P. Acquired thrombasthenia due to GPIIb/IIIa-specific platelet autoantibodies. Blood. 1986 Aug;68(2):571–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita J. R., Pidard D., Newman P. J., Montgomery R. R., Kunicki T. J. On the association of glycoprotein Ib and actin-binding protein in human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):317–321. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet plasma membrane glycoproteins. Evidence for the presence of nonequivalent disulfide bonds using nonreduced-reduced two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2121–2126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidard D., Montgomery R. R., Bennett J. S., Kunicki T. J. Interaction of AP-2, a monoclonal antibody specific for the human platelet glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex, with intact platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12582–12586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Bader R., de Marco L. Glanzmann thrombasthenia: deficient binding of von Willebrand factor to thrombin-stimulated platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6038–6041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata Y., Matsuda I., Miyaji T., Ichikawa Y. Yuka, a new platelet antigen involved in two cases of neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Vox Sang. 1986;50(3):177–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1986.tb04874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata Y., Miyaji T., Ichikawa Y., Matsuda I. A new platelet antigen system, Yuka/Yukb. Vox Sang. 1986;51(4):334–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1986.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G. C., 2nd, Workman E. F., Jr, Lundblad R. L. Thrombin binding to thrombasthenic platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Jan;91(1):76–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods V. L., Jr, Oh E. H., Mason D., McMillan R. Autoantibodies against the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex in patients with chronic ITP. Blood. 1984 Feb;63(2):368–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen E. F., Leeksma O. C., van Mourik J. A., Engelfriet C. P., von dem Borne A. E. Effect of the binding of anti-Zwa antibodies on platelet function. Vox Sang. 1984;47(4):280–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1984.tb01599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]