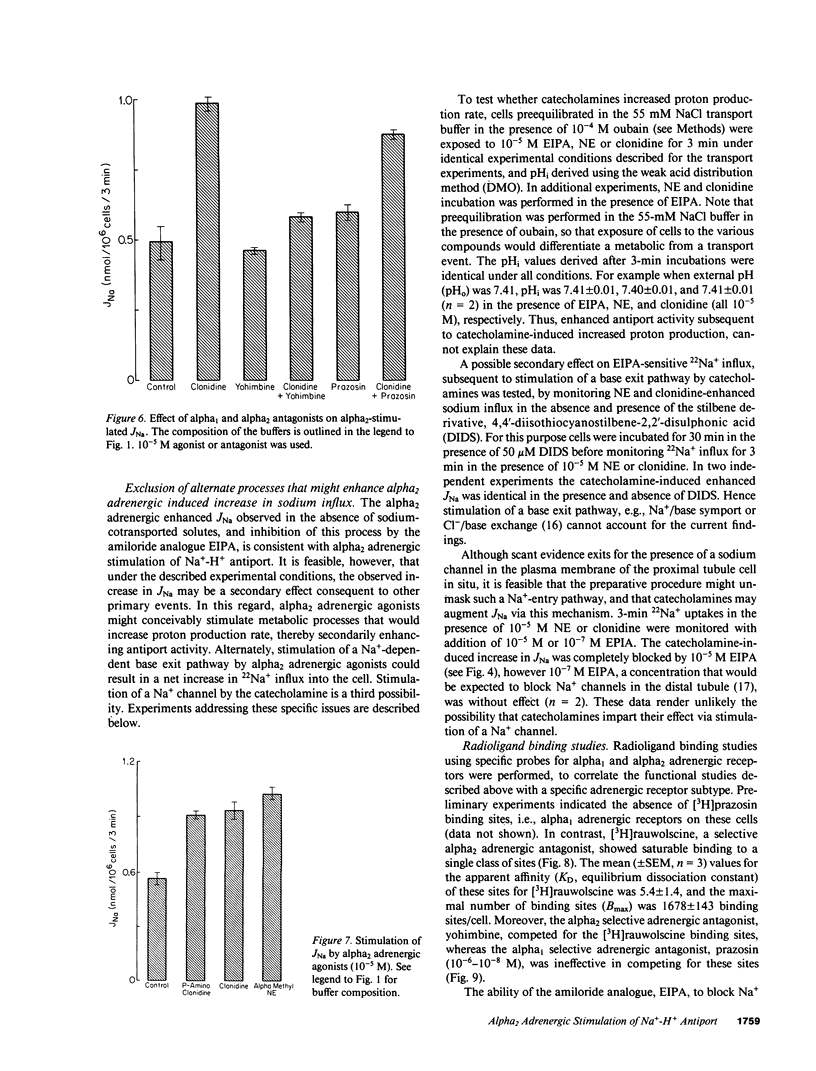
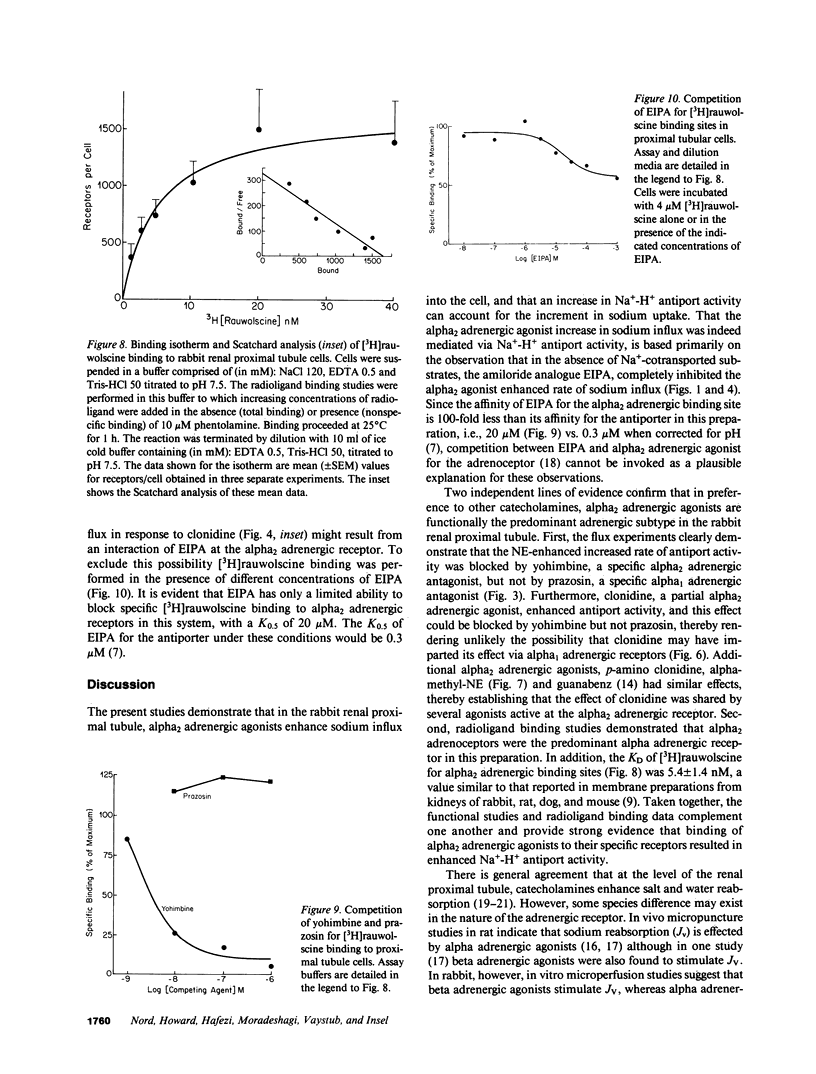
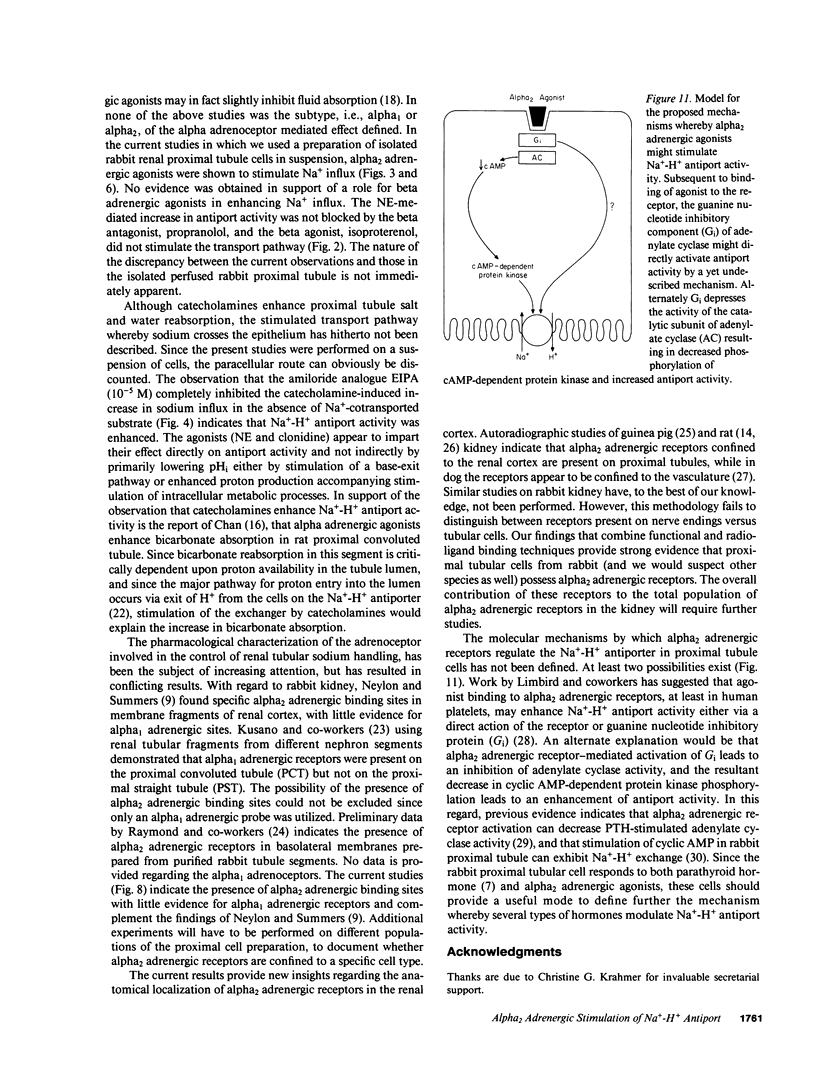
Abstract
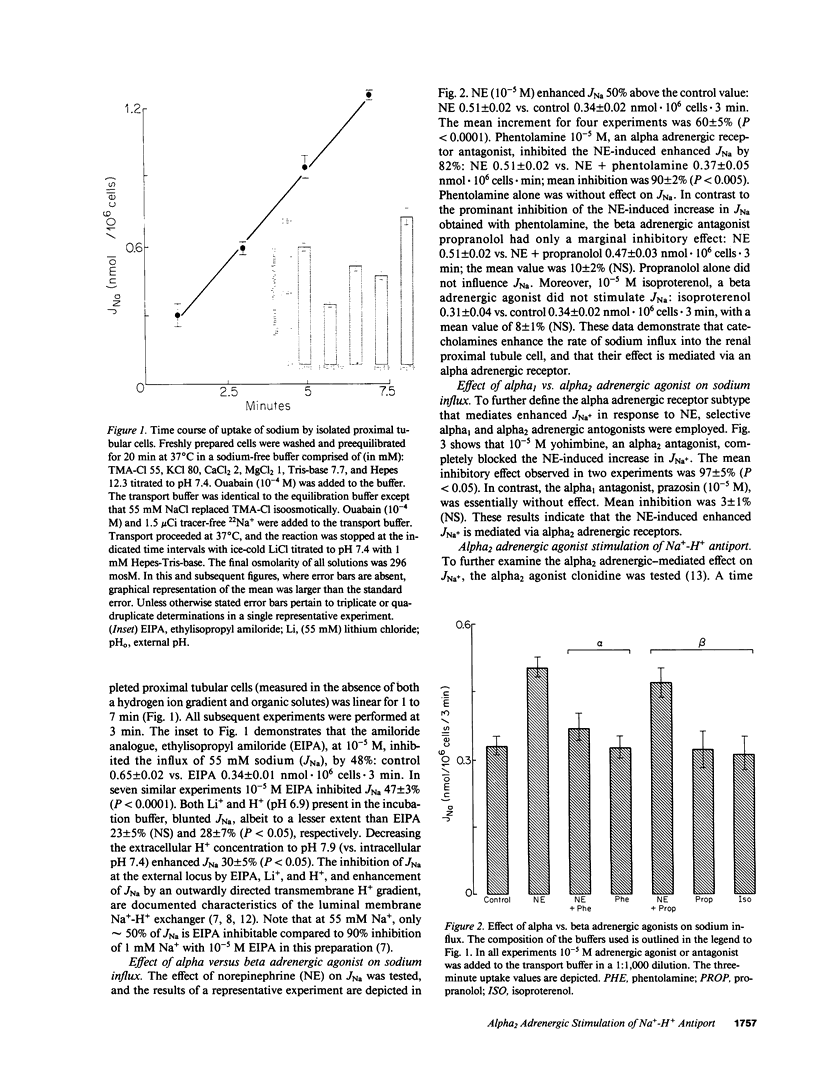
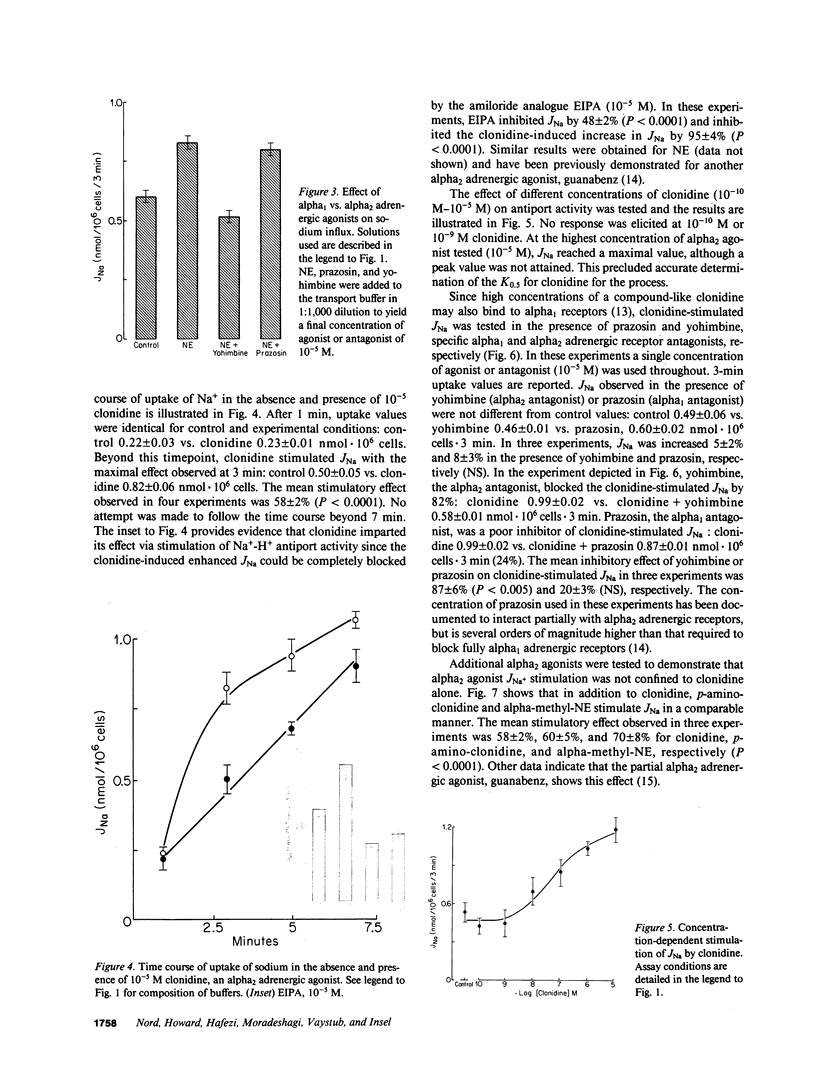
The role of adrenergic agents in augmenting proximal tubular salt and water flux, was studied in a preparation of freshly isolated rabbit renal proximal tubular cells in suspension. Norepinephrine (NE, 10(-5) M) increased sodium influx (JNa) 60 +/- 5% above control value. The alpha adrenergic antagonist, phentolamine (10(-5) M), inhibited the NE-induced enhanced JNa by 90 +/- 2%, while the beta adrenergic antagonist, propranolol, had a minimal inhibitory effect (10 +/- 2%). The alpha adrenergic subtype was further defined. Yohimbine (10(-5) M), an alpha2 adrenergic antagonist but not prazosin (10(-5) M), an alpha1 adrenergic antagonist completely blocked the NE induced increase in JNa. Clonidine, a partial alpha2 adrenergic agonist, increased JNa by 58 +/- 2% comparable to that observed with NE (10(-5) M). Yohimbine, but not prazosin, inhibited the clonidine-induced increase in JNa, confirming that alpha2 adrenergic receptors were involved. Additional alpha2 adrenergic agents, notably p-amino clonidine and alpha-methyl-norepinephrine, imparted a similar increase in JNa. The clonidine-induced increase in JNa could be completely blocked by the amiloride analogue, ethylisopropyl amiloride (EIPA, 10(-5) M). The transport pathway blocked by EIPA was partially inhibited by Li and cis H+, but stimulated by trans H+, consistent with Na+-H+ antiport. Radioligand binding studies using [3H]prazosin (alpha1 adrenergic antagonist) and [3H]rauwolscine (alpha2 adrenergic antagonist) were performed to complement the flux studies. Binding of [3H]prazosin to the cells was negligible. In contrast, [3H]rauwolscine showed saturable binding to a single class of sites, with Bmax 1678 +/- 143 binding sites/cell and KD 5.4 +/- 1.4 nM. In summary, in the isolated rabbit renal proximal tubular cell preparation, alpha2 adrenergic receptors are the predominant expression of alpha adreno-receptors, and in the absence of organic Na+-cotransported solutes, alpha2 adrenergic agonists enhance 22Na influx into the cell by stimulating the brush border membrane Na+-H+ exchange pathway.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bello-Reuss E. Effect of catecholamines on fluid reabsorption by the isolated proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1980 May;238(5):F347–F352. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.5.F347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besarab A., Silva P., Landsberg L., Epstein F. H. Effect of catecholamines on tubular function in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jul;233(1):F39–F45. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.1.F39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L. Adrenergic control of bicarbonate absorption in the proximal convoluted tubule of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Nov;388(2):159–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00584122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantrelle B., Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Evidence for coupled sodium/hydrogen exchange in the rat superficial proximal convoluted tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Nov 11;395(3):186–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00584807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. R., Jr, Casper A. G. Effect of renal alpha-adrenergic stimulation on proximal tubular sodium reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1201–1205. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güllner H. G. Regulation of sodium and water excretion by catecholamines. Life Sci. 1983 Feb 28;32(9):921–925. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90920-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse I. F., Johns E. J. The role of alpha-adrenoceptors in the regulation of renal tubular sodium reabsorption and renin secretion in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Mar;84(3):715–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb16154.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Snavely M. D., Healy D. P., Münzel P. A., Potenza C. L., Nord E. P. Radioligand binding and functional assays demonstrate postsynaptic alpha 2-receptors on proximal tubules of rat and rabbit kidney. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985;7 (Suppl 8):S9–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Janicke I., Sorgenfrei D., Keller S. K., Wiederholt M. The regulation of intracellular pH in monkey kidney epithelial cells (BSC-1). Roles of Na+/H+ antiport, Na+-HCO3(-)-(NaCO3-) symport, and Cl-/HCO3- exchange. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12120–12127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. M., Dolson G. M., Hise M. K., Bennett S. C., Weinman E. J. Parathyroid hormone and dibutyryl cAMP inhibit Na+/H+ exchange in renal brush border vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):F212–F218. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.2.F212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Aronson P. S. Properties of the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jun;238(6):F461–F469. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.6.F461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano E., Nakamura R., Asano Y., Imai M. Distribution of alpha-adrenergic receptors in the rabbit nephron. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1984 Mar;142(3):275–282. doi: 10.1620/tjem.142.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. [3H]prazosin and [3H]clonidine binding to alpha-adrenoceptors in membranes prepared from regions of rat kidney. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;33(3):189–191. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky H. J., Insel P. A. [3H]Dihydroergocryptine binding to alpha-adrenergic receptors of human platelets. A reassessment using the selective radioligands [3H]prazosin, [3H]yohimbine, and [3H]rauwolscine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Aug 15;31(16):2591–2597. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90705-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neylon C. B., Summers R. J. [3H]-rauwolscine binding to alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the mammalian kidney: apparent receptor heterogeneity between species. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;85(2):349–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08868.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord E. P., Goldfarb D., Mikhail N., Moradeshagi P., Hafezi A., Vaystub S., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Fine L. G. Characteristics of the Na+-H+ antiporter in the intact renal proximal tubular cell. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 2):F539–F550. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.3.F539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord E. P., Hafezi A., Wright E. M., Fine L. G. Mechanisms of Na+ uptake into renal brush border membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1984 Oct;247(4 Pt 2):F548–F554. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.4.F548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. D., Umemura S., Pettinger W. A. Alpha 2-adrenoceptors and sodium reabsorption in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1984 Oct;247(4 Pt 2):F680–F685. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.4.F680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snavely M. D., Insel P. A. Characterization of alpha-adrenergic receptor subtypes in the rat renal cortex. Differential regulation of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors by guanyl nucleotides and Na. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;22(3):532–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. A., Summers R. J. Light microscopic autoradiography of the distribution of [3H]rauwolscine binding to alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat kidney. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 22;116(3):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner L. C., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Ion transport in cortical collecting tubule; effect of amiloride. Am J Physiol. 1974 Aug;227(2):453–459. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.2.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Sansom S. C., Knight T. F., Senekjian H. O. Alpha and beta adrenergic agonists stimulate water absorption in the rat proximal tubule. J Membr Biol. 1982;69(2):107–111. doi: 10.1007/BF01872270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. alpha 2-Adrenergic receptors are associated with renal proximal tubules. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 31;67(4):493–495. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]