Abstract
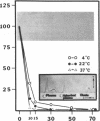
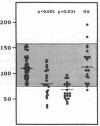
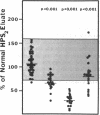
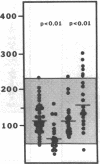
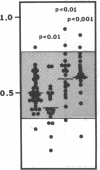
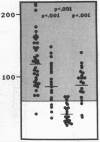
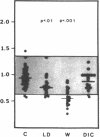
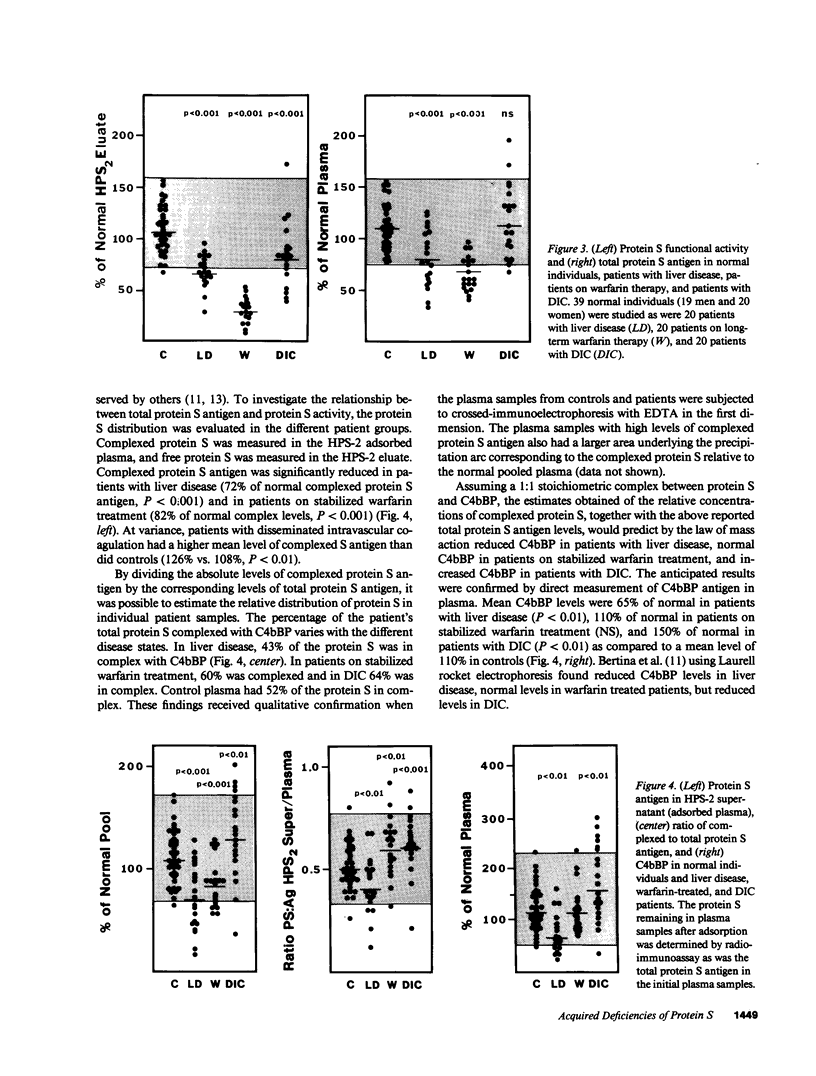
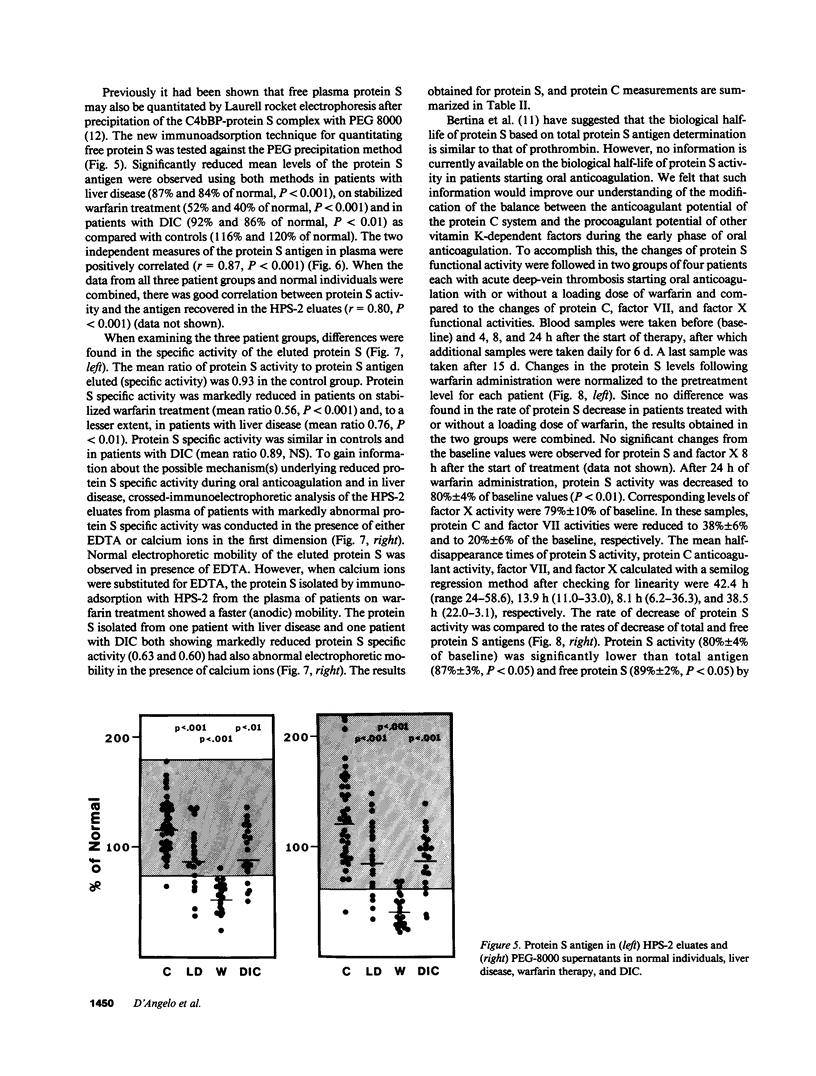
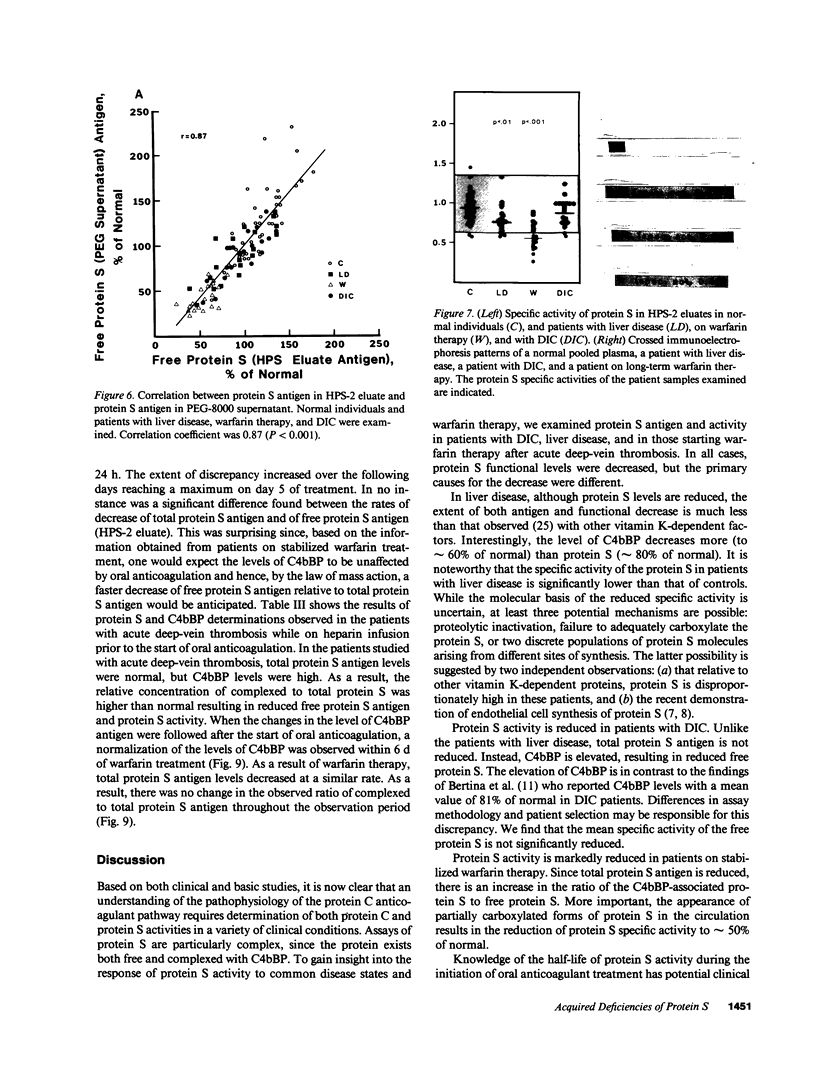
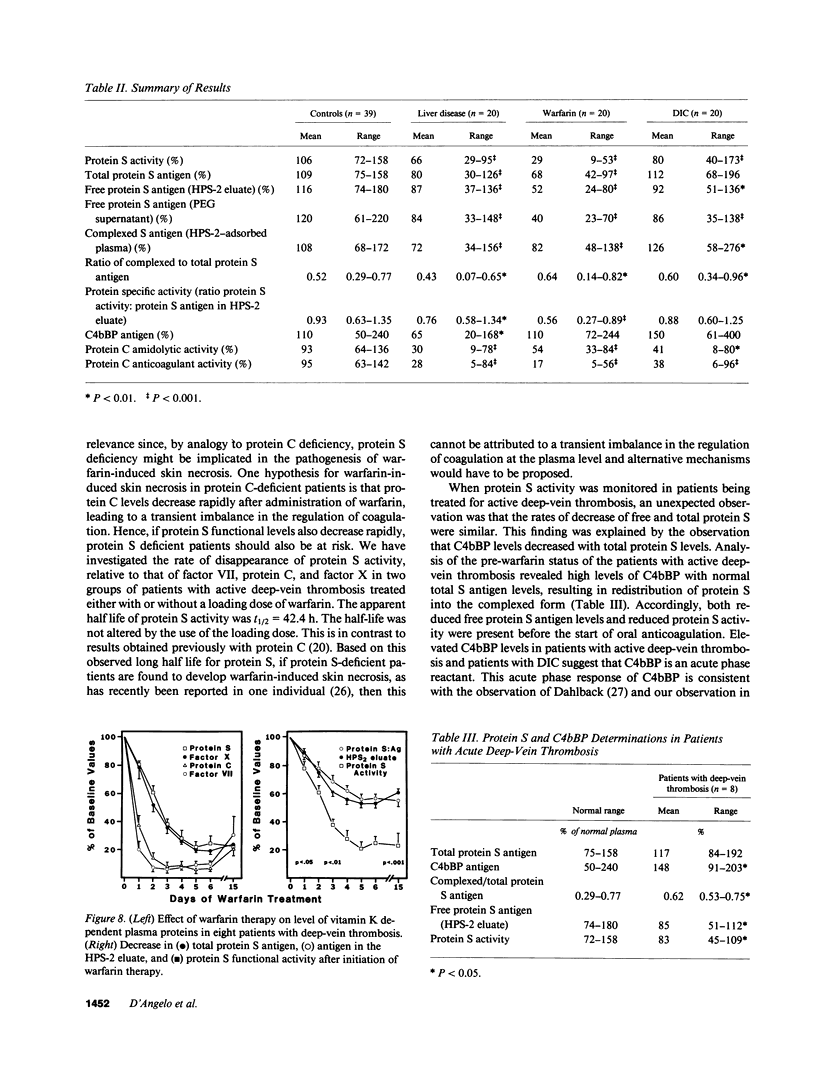
Protein S is a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein which serves as the cofactor for activated protein C. Protein S circulates in both an active, free form and in an inactive complex with C4b-binding protein. To elucidate the role of protein S in disease states and during oral anticoagulation, we developed a functional assay for protein S that permits evaluation of the distribution of protein S between free and bound forms and permits determination of the specific activity of the free protein S. In liver disease, free protein S antigen is moderately reduced and the free protein S has significantly reduced specific activity. In disseminated intravascular coagulation, reduced protein S activity occurs due to a redistribution of protein S to the inactive bound form. During warfarin anticoagulation, reduction of free protein S antigen and the appearance of forms with abnormal electrophoretic mobility significantly decrease protein S activity. After the initiation of warfarin, the apparent half-life of protein S is 42.5 h. In patients with thromboembolic disease, transient protein S deficiency occurs due to redistribution to the complexed form. Caution should be exercised in diagnosing protein S deficiency in such patients by use of functional assays.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertina R. M., van Wijngaarden A., Reinalda-Poot J., Poort S. R., Bom V. J. Determination of plasma protein S--the protein cofactor of activated protein C. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Apr 22;53(2):268–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biland L., Duckert F., Prisender S., Nyman D. Quantitative estimation of coagulation factors in liver disease. The diagnostic and prognostic value of factor XIII, factor V and plasminogen. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Jun 30;39(3):646–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerger L. M., Morris P. C., Thurnau G. R., Esmon C. T., Comp P. C. Oral contraceptives and gender affect protein S status. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):692–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Doray D., Patton D., Esmon C. T. An abnormal plasma distribution of protein S occurs in functional protein S deficiency. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):504–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Esmon C. T. Recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with a partial deficiency of protein S. N Engl J Med. 1984 Dec 13;311(24):1525–1528. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198412133112401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Nixon R. R., Cooper M. R., Esmon C. T. Familial protein S deficiency is associated with recurrent thrombosis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2082–2088. doi: 10.1172/JCI111632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Thurnau G. R., Welsh J., Esmon C. T. Functional and immunologic protein S levels are decreased during pregnancy. Blood. 1986 Oct;68(4):881–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Inhibition of protein Ca cofactor function of human and bovine protein S by C4b-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12022–12027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Purification of human C4b-binding protein and formation of its complex with vitamin K-dependent protein S. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):847–856. doi: 10.1042/bj2090847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fair D. S., Marlar R. A. Biosynthesis and secretion of factor VII, protein C, protein S, and the Protein C inhibitor from a human hepatoma cell line. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):64–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fair D. S., Revak D. J. Quantitation of human protein S in the plasma of normal and warfarin-treated individuals by radioimmunoassay. Thromb Res. 1984 Dec 15;36(6):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Fujita T., Nussenzweig V. Modulation of the classical pathway C3 convertase by plasma proteins C4 binding protein and C3b inactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6596–6600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris K. W., Esmon C. T. Protein S is required for bovine platelets to support activated protein C binding and activity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2007–2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Majerus D. W., Majerus P. W. Patients with congenital factor V deficiency have decreased factor Xa binding sites on their platelets. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):824–831. doi: 10.1172/JCI109194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T., Jackson C. M. The conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. I. Characterization of the reaction products formed during the activation of bovine prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):594–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz H. P., Fischer M., Hopmeier P., Batard M. A., Griffin J. H. Plasma protein S deficiency in familial thrombotic disease. Blood. 1984 Dec;64(6):1297–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz H. P., Heeb M. J., Wencel-Drake J. D., Griffin J. H. Identification and quantitation of protein S in human platelets. Blood. 1985 Dec;66(6):1452–1455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogen W. F., Esmon C. T., Cox A. C. Comparison of coagulation factor Xa and des-(1-44)factor Xa in the assembly of prothrombinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2306–2310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. M., Nawroth P. P., Harris K., Esmon C. T. Cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells promote activated protein C-protein S-mediated inactivation of factor Va. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):713–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D., Brett J., Harris K., Nawroth P. Participation of endothelial cells in the protein C-protein S anticoagulant pathway: the synthesis and release of protein S. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1971–1978. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Identification of a new protein involved in the regulation of the anticoagulant activity of activated protein C. Protein S-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10941–10944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of activated protein C by a new protein. A possible function for bovine protein S. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5521–5524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of activated protein C by protein S. The role of phospholipid in factor Va inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11128–11131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Fouw N. J., Haverkate F., Bertina R. M., Koopman J., van Wijngaarden A., van Hinsbergh V. W. The cofactor role of protein S in the acceleration of whole blood clot lysis by activated protein C in vitro. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):1189–1192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]