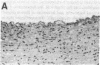
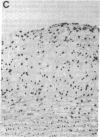
Abstract
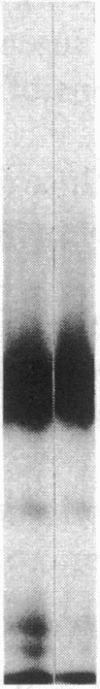
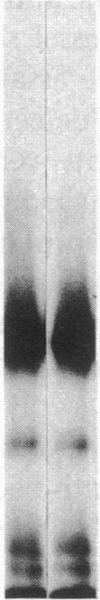
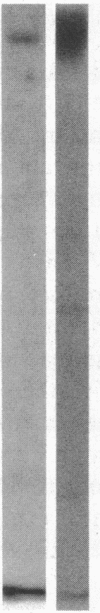
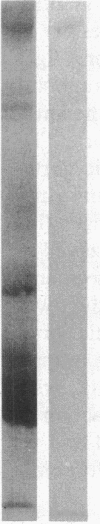
Vascular cell procoagulant activity may be important in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. In previous studies, we described the ability of the atherogenic metabolite homocysteine to activate endothelial cell Factor V, a key coagulation cofactor for thrombin generation. The present study was designed to investigate Factor V activity and Factor Xa-catalyzed prothrombin activation by control and atherosclerotic aorta from normal and hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Factor Xa generated ninefold more thrombin on atherosclerotic aortic segments than on control segments. Atherosclerotic segments activated 125I-prothrombin with Factor Xa in the presence of the thrombin inhibitor dansyl arginine-4-ethylpiperidine amide and cleaved 125I-Factor V. This suggests that increases in vessel-wall Factor V activity and Factor Xa-catalyzed prothrombin activation result from activation of vessel-wall Factor V. 125I-Factor Va peptides generated by atherosclerotic aorta were very similar in molecular weight to those generated by homocysteine-treated cells. When vascular endothelium was mechanically removed by brushing, atherosclerotic vessels still generated four- to fivefold more thrombin than control vessels. These data and results from immunocytochemical studies suggest that Factor V in atherosclerotic vessels is associated with both endothelium and other cells of the lesion. In contrast, Factor V in control vessels is associated primarily with endothelium. The increases in Factor V activity and thrombin formation in the blood vessel wall of hypercholesterolemic rabbits may contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and its complications.
Full text
PDF

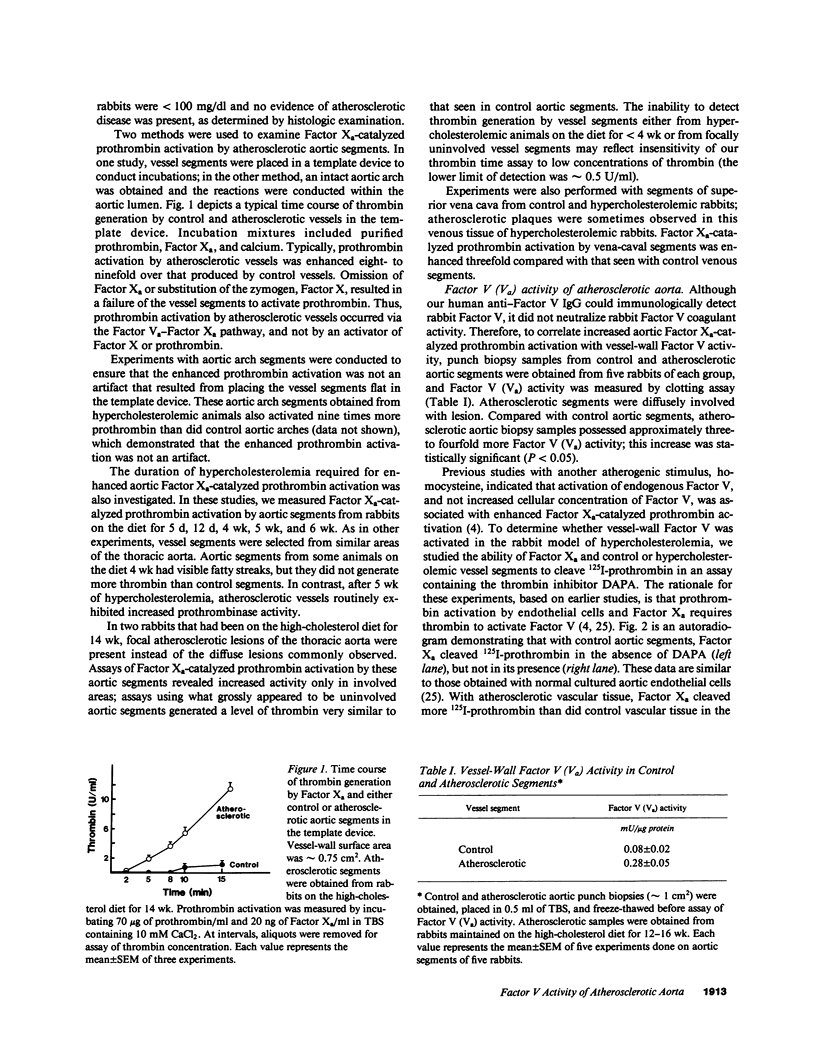
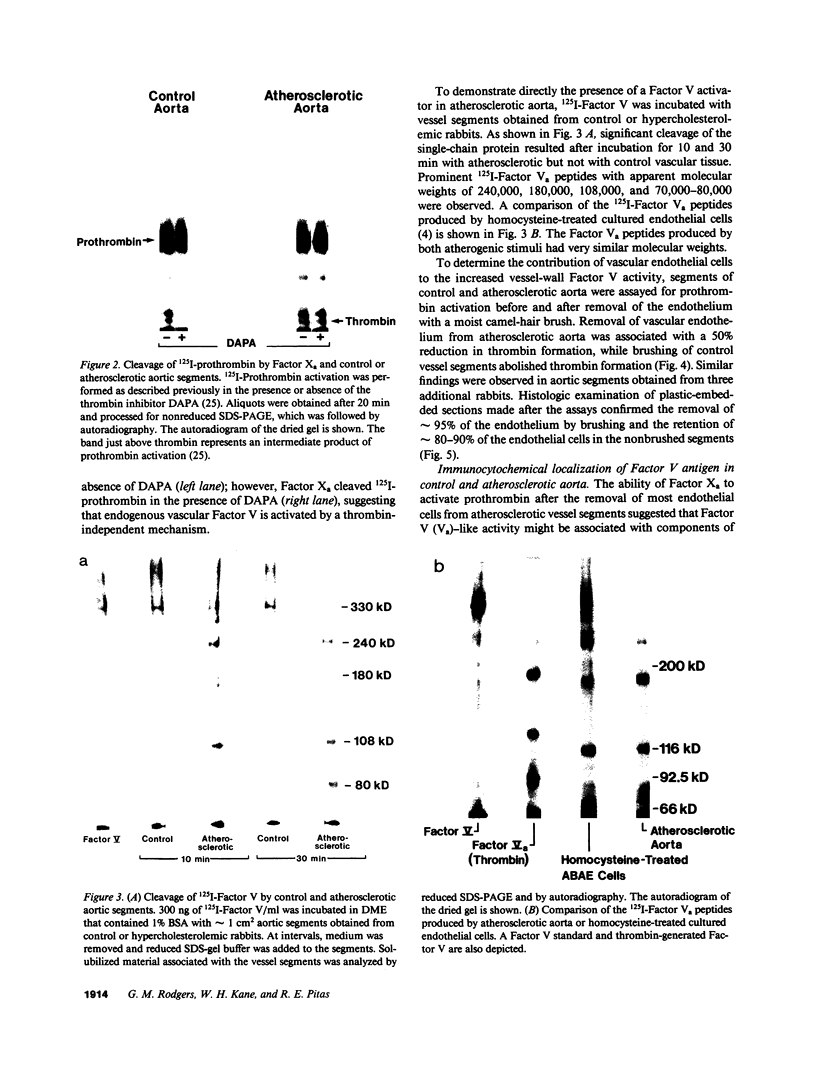
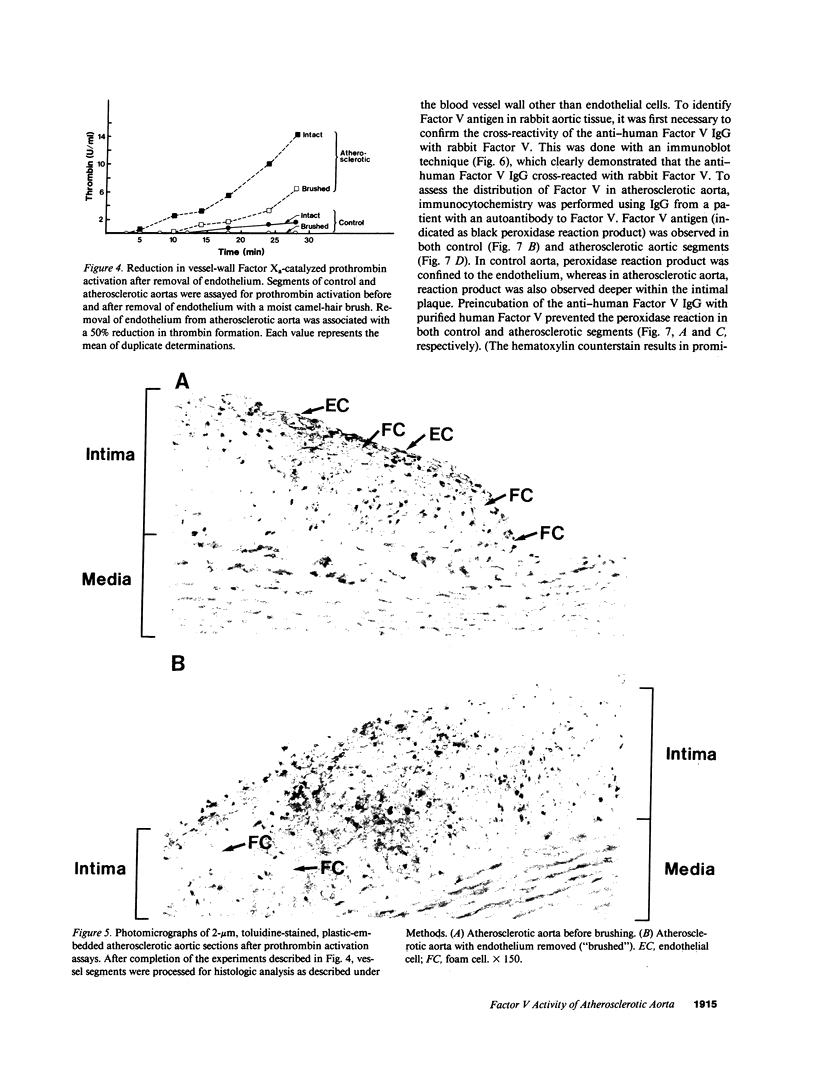

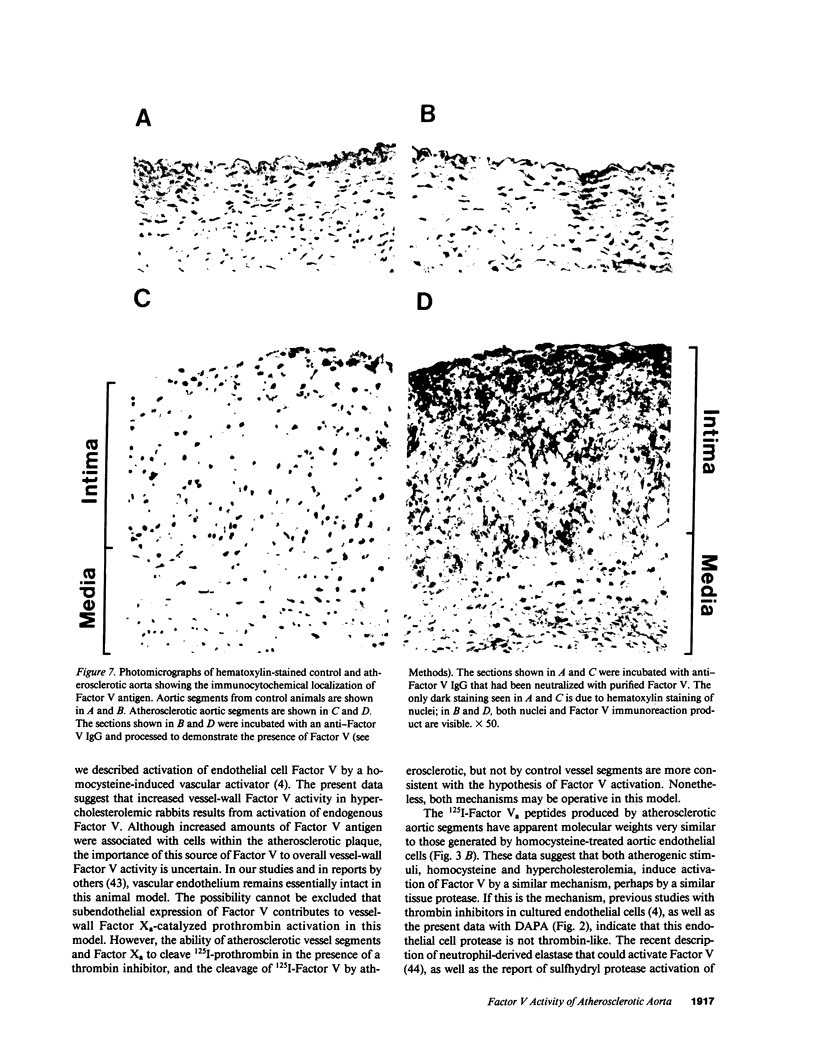


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annamalai A. E., Stewart G. J., Hansel B., Memoli M., Chiu H. C., Manuel D. W., Doshi K., Colman R. W. Expression of factor V on human umbilical vein endothelial cells is modulated by cell injury. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):196–202. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHMANN F., DUCKERT F., KOLLER F. The Stuart-Prower factor assay and its clinical significance. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1958 May 1;2(1-2):24–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker D. P., Van Lenten B. J., Fogelman A. M., Edwards P. A., Kean C., Berliner J. A. LDL, scavenger, and beta-VLDL receptors on aortic endothelial cells. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):248–255. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.3.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit R., Kahn A. J., Mann K. G., Wilner G. D. Identification of a thrombin sequence with growth factor activity on macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):976–980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit R., Kahn A., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Wilner G. D. Chemotactic response of monocytes to thrombin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):282–285. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckstead J. H., Halverson P. S., Ries C. A., Bainton D. F. Enzyme histochemistry and immunohistochemistry on biopsy specimens of pathologic human bone marrow. Blood. 1981 Jun;57(6):1088–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Majeau G. R., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 (IL-1) induces biosynthesis and cell surface expression of procoagulant activity in human vascular endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):618–623. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bini A., Fenoglio J., Jr, Sobel J., Owen J., Fejgl M., Kaplan K. L. Immunochemical characterization of fibrinogen, fibrin I, and fibrin II in human thrombi and atherosclerotic lesions. Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1038–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkerud S., Bondjers G. Endothelial integrity and viability in the aorta of the normal rabbit and rat as evaluated with dye exclusion tests and interference contrast microscopy. Atherosclerosis. 1972 May-Jun;15(3):285–300. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(72)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyles J. K., Pitas R. E., Wilson E., Mahley R. W., Taylor J. M. Apolipoprotein E associated with astrocytic glia of the central nervous system and with nonmyelinating glia of the peripheral nervous system. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1501–1513. doi: 10.1172/JCI112130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Balconi G., Lorenzet R., Pietra A., Locati D., Donati M. B., Semeraro N. Cultured human endothelial cells generate tissue factor in response to endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1893–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI110945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faggiotto A., Ross R., Harker L. Studies of hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate. I. Changes that lead to fatty streak formation. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):323–340. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faggiotto A., Ross R. Studies of hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate. II. Fatty streak conversion to fibrous plaque. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):341–356. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.4.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Fasco M. J. Polyethylene glycol 6,000 enhancement of the clotting of fibrinogen solutions in visual and mechanical assays. Thromb Res. 1974 Jun;4(6):809–817. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guski H., Meyer R., Wassilew G., Wenzelides K., Wilfert K. Characterization of the rabbit heart in cholesterol-induced coronary atherosclerosis. Morphometric studies. Exp Pathol. 1981;19(2):100–111. doi: 10.1016/s0232-1513(81)80040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Bondjers G., Bylock A., Hjalmarsson L. Ultrastructural studies on the localization of IgG in the aortic endothelium and subendothelial intima of atherosclerotic and nonatherosclerotic rabbits. Exp Mol Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(3):302–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(80)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Thompson P. J., Ross R. R., Bowen-Pope D. F. Alpha-thrombin induces release of platelet-derived growth factor-like molecule(s) by cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):1129–1133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen T., Evensen S. A., Carlander B. Injury to human endothelial cells in culture induced by low density lipoproteins. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1979 Jun;39(4):361–368. doi: 10.3109/00365517909106120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingerman-Wojenski C. M., Sedar A. W., Nissenbaum M., Silver M. J., Klurfeld D. M., Kritchevsky D. Early morphological changes in the endothelium of a peripheral artery of rabbits fed an atherogenic diet. Exp Mol Pathol. 1983 Feb;38(1):48–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(83)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokinen M. P., Clarkson T. B., Prichard R. W. Animal models in atherosclerosis research. Exp Mol Pathol. 1985 Feb;42(1):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(85)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Majerus P. W. Purification and characterization of human coagulation factor V. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1002–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS M. L., WARE A. G. A one-stage method for the determination of accelerator globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Dec;84(3):640–643. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laposata M., Dovnarsky D. K., Shin H. S. Thrombin-induced gap formation in confluent endothelial cell monolayers in vitro. Blood. 1983 Sep;62(3):549–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G. Membrane-bound enzyme complexes in blood coagulation. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1984;7:1–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr, Majerus P. W. The synthesis of sulfated dextran beads for isolation of human plasma coagulation factors II, IX, and X. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):304–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel D. W., Hessler J. R., Chisolm G. M. Low density lipoprotein cytotoxicity induced by free radical peroxidation of lipid. J Lipid Res. 1983 Aug;24(8):1070–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Thrombin-catalyzed activation of single chain bovine factor V. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1326–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oates A. M., Salem H. H. The regulation of human factor V by a neutrophil protease. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):846–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Cell surface receptor binding of phospholipid . protein complexes containing different ratios of receptor-active and -inactive E apoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5454–5460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Weinstein J. N., Mahley R. W. Acetoacetylated lipoproteins used to distinguish fibroblasts from macrophages in vitro by fluorescence microscopy. Arteriosclerosis. 1981 May-Jun;1(3):177–185. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.1.3.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPAPORT S. I., SCHIFFMAN S., PATCH M. J., AMES S. B. The importance of activation of antihemophilic globulin and proaccelerin by traces of thrombin in the generation of intrinsic prothrombinase activity. Blood. 1963 Feb;21:221–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M., Cong J. Y., Goll D. E., Kane W. H. Activation of coagulation factor V by calcium-dependent proteinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 29;929(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M., Kane W. H. Activation of endogenous factor V by a homocysteine-induced vascular endothelial cell activator. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1909–1916. doi: 10.1172/JCI112519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M., Shuman M. A. Characterization of the interaction between factor Xa and bovine aortic endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Mar 21;844(3):320–329. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M., Shuman M. A. Prothrombin is activated on vascular endothelial cells by factor Xa and calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):7001–7005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.7001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M. Vascular smooth muscle cells synthesize, secrete and express coagulation factor V. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 18;968(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodman N. F., Jagannathan S. N., Jenkins J. J., 3rd, Rodman J. A., Allender P. A. Experimental atherosclerosis: surface ultrastructural studies in the rabbit aorta. Scan Electron Microsc. 1979;(3):835–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Wight T. N., Strandness E., Thiele B. Human atherosclerosis. I. Cell constitution and characteristics of advanced lesions of the superficial femoral artery. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jan;114(1):79–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberger H., McGee M. P. Generation of coagulation factor V activity by cultured rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1880–1890. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau J. L., Parmley W. W., Stevens J., Wikman-Coffelt J., Sievers R., Mahley R. W., Havel R. J. Verapamil suppresses atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1983 Jun;1(6):1453–1460. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(83)80049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinovich O., Montelaro R. C. Reversible staining and peptide mapping of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose after separation by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;156(2):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R., Page I. H. Deposition of modified fibrinogen within the aortic intima. Atherosclerosis. 1972 Nov-Dec;16(3):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(72)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J. Epidemiology of coronary heart disease. Med Clin North Am. 1973 Jan;57(1):5–46. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Stein Y. Bovine aortic endothelial cells display macrophage-like properties towards acetylated 125I-labelled low density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 5;620(3):631–635. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesselinovitch D., Wissler R. W. Comparison of primates and rabbits as animal models in experimental atherosclerosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;82:614–622. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4220-5_131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. N., Reidy M. A., Bowyer D. E. Morphology and cell kinetics of fatty streak lesion formation in the hypercholesterolemic rabbit. Am J Pathol. 1986 Dec;125(3):450–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wissler R. W., Vesselinovitch D. Experimental models of human atherosclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Nov 21;149(2):907–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]