Abstract
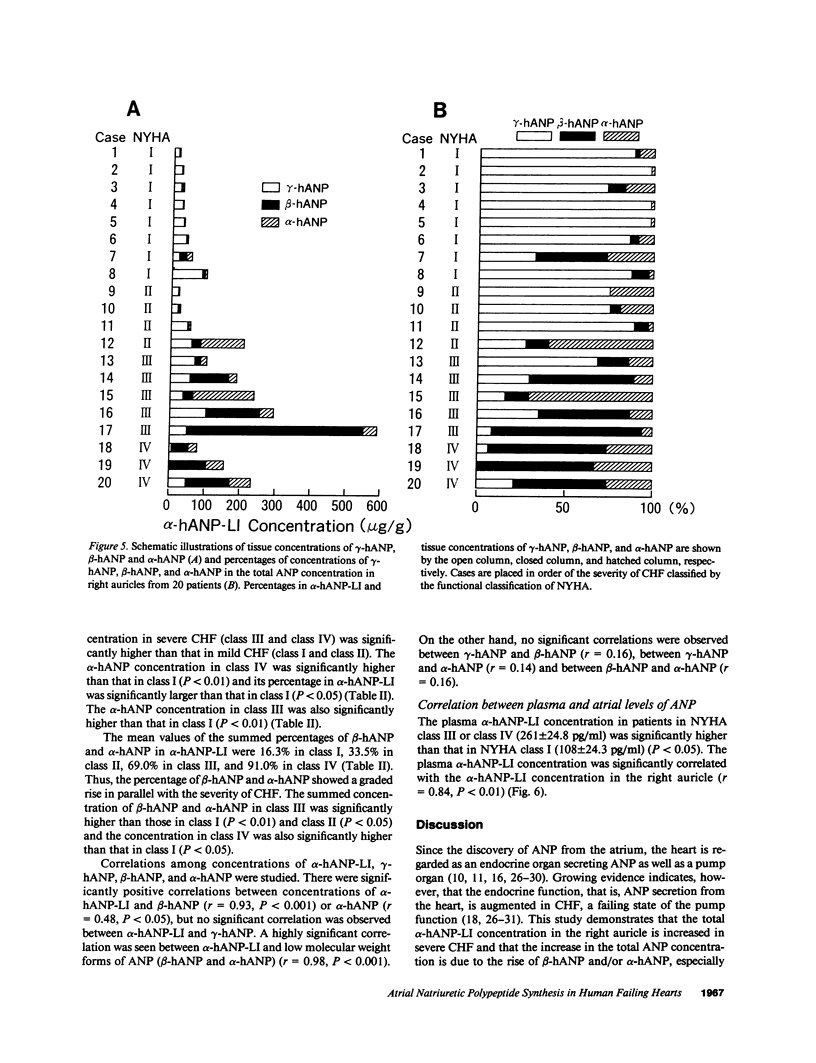
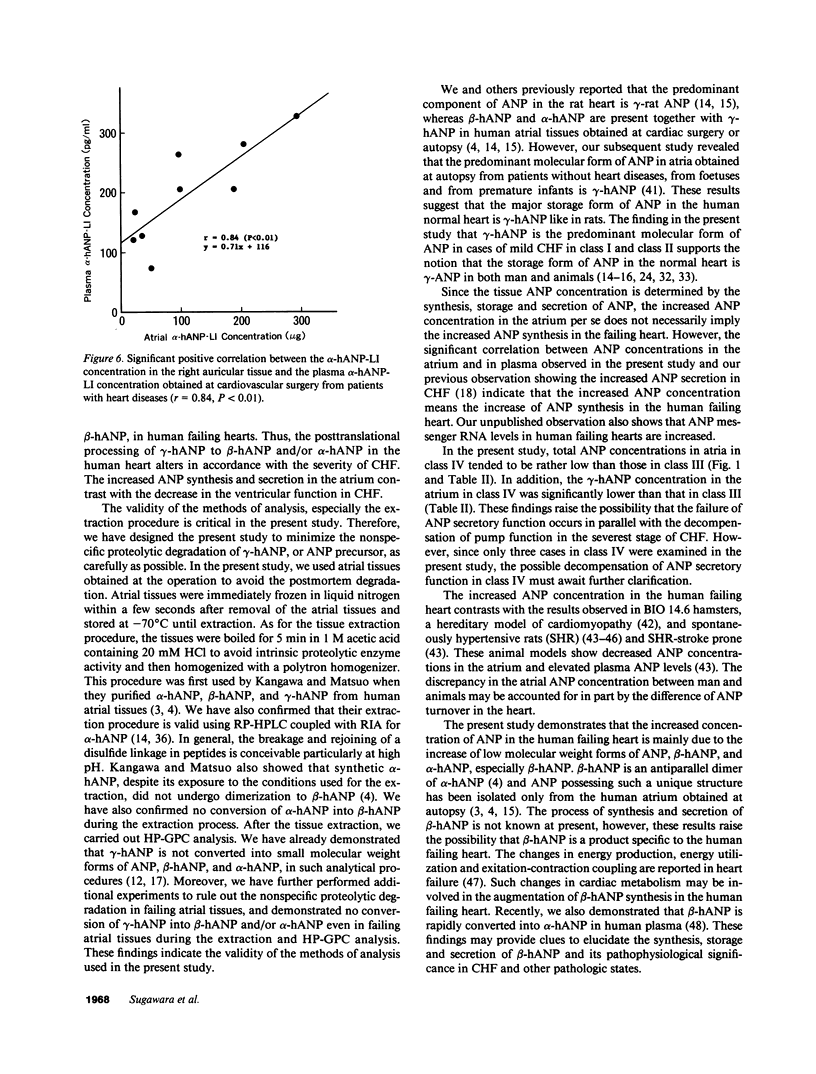
To elucidate the synthesis of atrial natriuretic polypeptide (ANP) in the failing heart, 20 human right auricles obtained at cardiovascular surgery were studied. The concentration of alpha-human ANP-like immunoreactivity (alpha-hANP-LI) in human right auricles ranged from 13.8 to 593.5 micrograms/g, and the tissue alpha-hANP-LI concentration in severe congestive heart failure (CHF) (New York Heart Association [NYHA] functional class III and class IV) (235.4 +/- 57.2 micrograms/g) was much higher than that in mild CHF (NYHA class I and class II) (52.5 +/- 15.6 micrograms/g). Atrial alpha-hANP-LI levels were significantly correlated with plasma concentrations of alpha-hANP-LI in these patients (r = 0.84, P less than 0.01). High performance gel permeation chromatography and reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography coupled with radioimmunoassay for ANP revealed that the alpha-hANP-LI in the human auricle consisted of three major components of ANP, gamma-human ANP (gamma-hANP), beta-human ANP (beta-hANP) and alpha-human ANP (alpha-hANP). Comparing percentages of gamma-hANP, beta-hANP, and alpha-hANP in alpha-hANP-LI in severe CHF with those in mild CHF, the predominant component of alpha-hANP-LI was gamma-hANP in mild CHF, whereas beta-hANP and/or alpha-hANP were prevailing in severe CHF and, especially, beta-hANP was markedly increased in human failing hearts. These results demonstrate that the total ANP concentration in the atrium of the human heart is increased in severe CHF and that the increase of ANP in the human failing heart is mainly due to the increase of small molecular weight forms of ANP, beta-hANP, and alpha-hANP, especially beta-hANP, and indicate that the processing of ANP precursor, or gamma-hANP, in the human failing heart differs from that in the normal heart, suggesting that the failing heart augments synthesis and secretion of ANP as one of its own compensatory responses.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atlas S. A., Kleinert H. D., Camargo M. J., Januszewicz A., Sealey J. E., Laragh J. H., Schilling J. W., Lewicki J. A., Johnson L. K., Maack T. Purification, sequencing and synthesis of natriuretic and vasoactive rat atrial peptide. Nature. 1984 Jun 21;309(5970):717–719. doi: 10.1038/309717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates E. R., Shenker Y., Grekin R. J. The relationship between plasma levels of immunoreactive atrial natriuretic hormone and hemodynamic function in man. Circulation. 1986 Jun;73(6):1155–1161. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.6.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett J. C., Jr, Kao P. C., Hu D. C., Heser D. W., Heublein D., Granger J. P., Opgenorth T. J., Reeder G. S. Atrial natriuretic peptide elevation in congestive heart failure in the human. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1145–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.2935937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin M., Genest J. The heart and the atrial natriuretic factor. Endocr Rev. 1985 Spring;6(2):107–127. doi: 10.1210/edrv-6-2-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chimoskey J. E., Spielman W. S., Brandt M. A., Heidemann S. R. Cardiac atria of BIO 14.6 hamsters are deficient in natriuretic factor. Science. 1984 Feb 24;223(4638):820–822. doi: 10.1126/science.6538050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody R. J., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H., Kubo S. H., Covit A. B., Ryman K. S., Shaknovich A., Pondolfino K., Clark M., Camargo M. J. Atrial natriuretic factor in normal subjects and heart failure patients. Plasma levels and renal, hormonal, and hemodynamic responses to peptide infusion. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1362–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI112723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crozier I. G., Nicholls M. G., Ikram H., Espiner E. A., Gomez H. J., Warner N. J. Haemodynamic effects of atrial peptide infusion in heart failure. Lancet. 1986 Nov 29;2(8518):1242–1245. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92675-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie M. G., Geller D. M., Cole B. R., Siegel N. R., Fok K. F., Adams S. P., Eubanks S. R., Galluppi G. R., Needleman P. Purification and sequence analysis of bioactive atrial peptides (atriopeptins). Science. 1984 Jan 6;223(4631):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.6419347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskay R., Zukowska-Grojec Z., Haass M., Dave J. R., Zamir N. Circulating atrial natriuretic peptides in conscious rats: regulation of release by multiple factors. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):636–639. doi: 10.1126/science.2938258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn T. G., de Bold M. L., de Bold A. J. The amino acid sequence of an atrial peptide with potent diuretic and natriuretic properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):859–865. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91675-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkowska J., Bourassa M., Roy D., Thibault G., Garcia R., Cantin M., Genest J. Immunoreactive atrial natriuretic factor (IR-ANF) in human plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1350–1357. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada T., Takayanagi R., Inagami T. Changes in the content of atrial natriuretic factor with the progression of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):759–765. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90969-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui K., Saito H., Matsukawa Y., Nakao K., Morii N., Imura H., Shimokura M., Kiso Y., Hori R. Specific binding activities and cyclic GMP responses by atrial natriuretic polypeptide in kidney epithelial cell line (LLC-PK1). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 15;132(1):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Nakao K., Shiono S., Mukoyama M., Morii N., Sugawara A., Yamada T., Saito Y., Arai H., Kambayashi Y. Conversion of beta-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide into alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide in human plasma in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 13;143(2):560–569. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91390-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kambayashi Y., Kawabata T., Hara S., Yamauchi A., Ueda A., Kono M., Doteuchi M., Nakamura M., Inouye K. Synthesis and biological properties of two dimeric forms of human alpha-atrial natriuretic peptide. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Fukuda A., Matsuo H. Structural identification of beta- and gamma-human atrial natriuretic polypeptides. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):397–400. doi: 10.1038/313397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Purification and complete amino acid sequence of alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide (alpha-hANP). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 13;118(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Tawaragi Y., Oikawa S., Mizuno A., Sakuragawa Y., Nakazato H., Fukuda A., Minamino N., Matsuo H. Identification of rat gamma atrial natriuretic polypeptide and characterization of the cDNA encoding its precursor. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):152–155. doi: 10.1038/312152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi K., Nakao K., Hayashi K., Morii N., Sugawara A., Sakamoto M., Imura H., Mikawa H. Ontogeny of atrial natriuretic polypeptide in the human heart. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1987 Jun;115(2):211–217. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1150211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. E., Thölken H., Ganten D., Luft F. C., Ruskoaho H., Unger T. Atrial natriuretic factor--a circulating hormone stimulated by volume loading. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):264–266. doi: 10.1038/314264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misono K. S., Fukumi H., Grammer R. T., Inagami T. Rat atrial natriuretic factor: complete amino acid sequence and disulfide linkage essential for biological activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Mar 15;119(2):524–529. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata A., Kangawa K., Toshimori T., Hatoh T., Matsuo H. Molecular forms of atrial natriuretic polypeptides in mammalian tissues and plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 31;129(1):248–255. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91429-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morii N., Nakao K., Kihara M., Sugawara A., Sakamoto M., Yamori Y., Imura H. Decreased content in left atrium and increased plasma concentration of atrial natriuretic polypeptide in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and SHR stroke-prone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 26;135(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90944-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morii N., Nakao K., Sugawara A., Sakamoto M., Suda M., Shimokura M., Kiso Y., Kihara M., Yamori Y., Imura H. Occurrence of atrial natriuretic polypeptide in brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 15;127(2):413–419. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80176-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Morii N., Itoh H., Yamada T., Shiono S., Sugawara A., Saito Y., Mukoyama M., Arai H., Sakamoto M. Atrial natriuretic polypeptide in brain--implication of central cardiovascular control. Klin Wochenschr. 1987;65 (Suppl 8):103–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Morii N., Itoh H., Yamada T., Shiono S., Sugawara A., Saito Y., Mukoyama M., Arai H., Sakamoto M. Atrial natriuretic polypeptide in the brain: implication of central cardiovascular control. J Hypertens Suppl. 1986 Dec;4(6):S492–S496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Sugawara A., Morii N., Sakamoto M., Suda M., Soneda J., Ban T., Kihara M., Yamori Y., Shimokura M. Radioimmunoassay for alpha-human and rat atrial natriuretic polypeptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 14;124(3):815–821. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Sugawara A., Shiono S., Saito Y., Morii N., Yamada T., Itoh H., Mukoyama M., Arai H., Sakamoto M. Secretory form of atrial natriuretic polypeptide as cardiac hormone in humans and rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;65(8):1756–1761. doi: 10.1139/y87-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Adams S. P., Cole B. R., Currie M. G., Geller D. M., Michener M. L., Saper C. B., Schwartz D., Standaert D. G. Atriopeptins as cardiac hormones. Hypertension. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):469–482. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.4.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeheffer R. J., Tanaka I., Imada T., Hollister A. S., Robertson D., Inagami T. Atrial pressure and secretion of atrial natriuretic factor into the human central circulation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1986 Jul;8(1):18–26. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(86)80086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Nakao K., Morii N., Sugawara A., Shiono S., Yamada T., Itoh H., Sakamoto M., Kurahashi K., Fujiwara M. Bay K 8644, a voltage-sensitive calcium channel agonist, facilitates secretion of atrial natriuretic polypeptide from isolated perfused rat hearts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1170–1176. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80405-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Nakao K., Nishimura K., Sugawara A., Okumura K., Obata K., Sonoda R., Ban T., Yasue H., Imura H. Clinical application of atrial natriuretic polypeptide in patients with congestive heart failure: beneficial effects on left ventricular function. Circulation. 1987 Jul;76(1):115–124. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.76.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D., Geller D. M., Manning P. T., Siegel N. R., Fok K. F., Smith C. E., Needleman P. Ser-Leu-Arg-Arg-atriopeptin III: the major circulating form of atrial peptide. Science. 1985 Jul 26;229(4711):397–400. doi: 10.1126/science.3160114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Lazure C., Chrétien M., Thibault G., Garcia R., Cantin M., Genest J., Nutt R. F., Brady S. F., Lyle T. A. Amino acid sequence of homologous rat atrial peptides: natriuretic activity of native and synthetic forms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2640–2644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenker Y., Sider R. S., Ostafin E. A., Grekin R. J. Plasma levels of immunoreactive atrial natriuretic factor in healthy subjects and in patients with edema. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1684–1687. doi: 10.1172/JCI112154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiono S., Nakao K., Morii N., Yamada T., Itoh H., Sakamoto M., Sugawara A., Saito Y., Katsuura G., Imura H. Nature of atrial natriuretic polypeptide in rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 28;135(3):728–734. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90989-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara A., Nakao K., Morii N., Sakamoto M., Suda M., Shimokura M., Kiso Y., Kihara M., Yamori Y., Nishimura K. Alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide is released from the heart and circulates in the body. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 14;129(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibault G., Garcia R., Gutkowska J., Bilodeau J., Lazure C., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Genest J., Cantin M. The propeptide Asn1-Tyr126 is the storage form of rat atrial natriuretic factor. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):265–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2410265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibault G., Lazure C., Schiffrin E. L., Gutkowska J., Chartier L., Garcia R., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Genest J., Cantin M. Identification of a biologically active circulating form of rat atrial natriuretic factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 15;130(3):981–986. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91711-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikkanen I., Fyhrquist F., Metsärinne K., Leidenius R. Plasma atrial natriuretic peptide in cardiac disease and during infusion in healthy volunteers. Lancet. 1985 Jul 13;2(8446):66–69. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaji T., Ishibashi M., Takaku F. Atrial natriuretic factor in human blood. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1705–1709. doi: 10.1172/JCI112159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J., Borenstein H. B., Veress A. T., Sonnenberg H. A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous injection of atrial myocardial extract in rats. Life Sci. 1981 Jan 5;28(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


