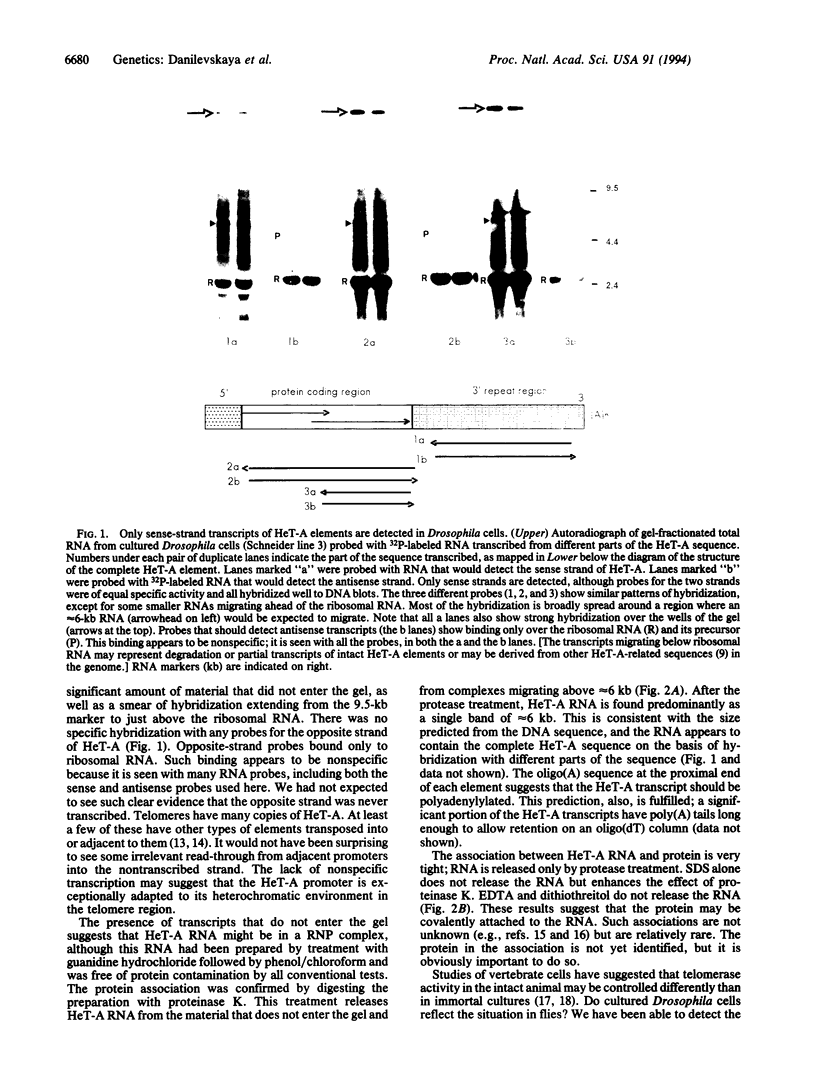
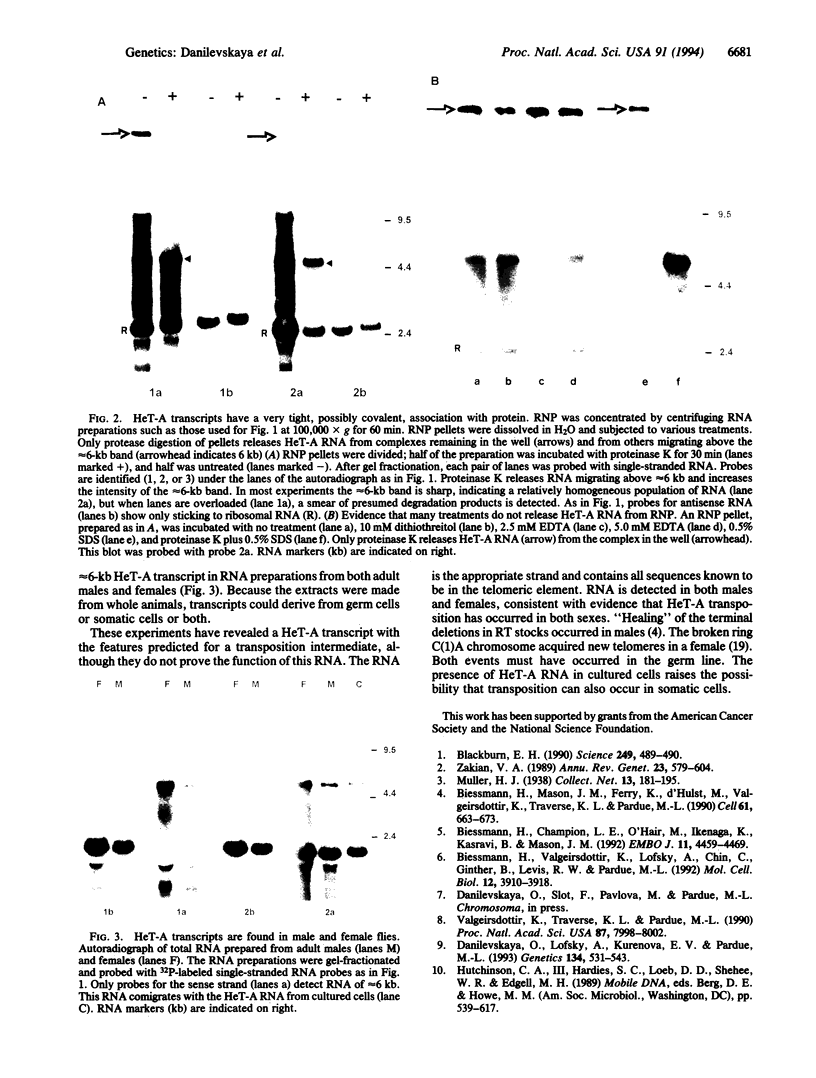
Abstract
Telomeres from Drosophila appear to be very different from those of other organisms. A transposable element, HeT-A, plays a major role in forming telomeres and may be the sole structural element, since telomerase-generated repeats are not found. The structure of the HeT-A element, deduced from cloned fragments of DNA, suggests that transposition of the element is mediated by a polyadenylylated RNA intermediate. We now report analyses of HeT-A transcripts. The major RNA is of the appropriate size and strandedness to serve as a transposition intermediate. This RNA is found in cultured cells and in intact flies and is unusual in that it is associated with protein after treatments that apparently remove all protein from other RNAs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biessmann H., Champion L. E., O'Hair M., Ikenaga K., Kasravi B., Mason J. M. Frequent transpositions of Drosophila melanogaster HeT-A transposable elements to receding chromosome ends. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4459–4469. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Mason J. M., Ferry K., d'Hulst M., Valgeirsdottir K., Traverse K. L., Pardue M. L. Addition of telomere-associated HeT DNA sequences "heals" broken chromosome ends in Drosophila. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90478-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Valgeirsdottir K., Lofsky A., Chin C., Ginther B., Levis R. W., Pardue M. L. HeT-A, a transposable element specifically involved in "healing" broken chromosome ends in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3910–3918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomeres and their synthesis. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):489–490. doi: 10.1126/science.2200120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danilevskaya O., Lofsky A., Kurenova E. V., Pardue M. L. The Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster contains a distinctive subclass of Het-A-related repeats. Genetics. 1993 Jun;134(2):531–543. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Futcher A. B., Greider C. W. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):458–460. doi: 10.1038/345458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Dempster M., Dunlop M. G., Thompson A. M., Green D. K., Allshire R. C. Telomere reduction in human colorectal carcinoma and with ageing. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):866–868. doi: 10.1038/346866a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan N. C., Traverse K. L., Sullivan D. E., Pardue M. L. The nucleus-limited Hsr-omega-n transcript is a polyadenylated RNA with a regulated intranuclear turnover. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(1):21–30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen G. H., Spradling A. C. Analysis of subtelomeric heterochromatin in the Drosophila minichromosome Dp1187 by single P element insertional mutagenesis. Genetics. 1992 Nov;132(3):737–753. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R. W., Ganesan R., Houtchens K., Tolar L. A., Sheen F. M. Transposons in place of telomeric repeats at a Drosophila telomere. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90318-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., Uhlenbeck O. C. Nucleoside and nucleotide inactivation of R17 coat protein: evidence for a transient covalent RNA-protein bond. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):4239–4244. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santi D. V., Hardy L. W. Catalytic mechanism and inhibition of tRNA (uracil-5-)methyltransferase: evidence for covalent catalysis. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 29;26(26):8599–8606. doi: 10.1021/bi00400a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traverse K. L., Pardue M. L. A spontaneously opened ring chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster has acquired He-T DNA sequences at both new telomeres. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8116–8120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valgeirsdóttir K., Traverse K. L., Pardue M. L. HeT DNA: a family of mosaic repeated sequences specific for heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7998–8002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]