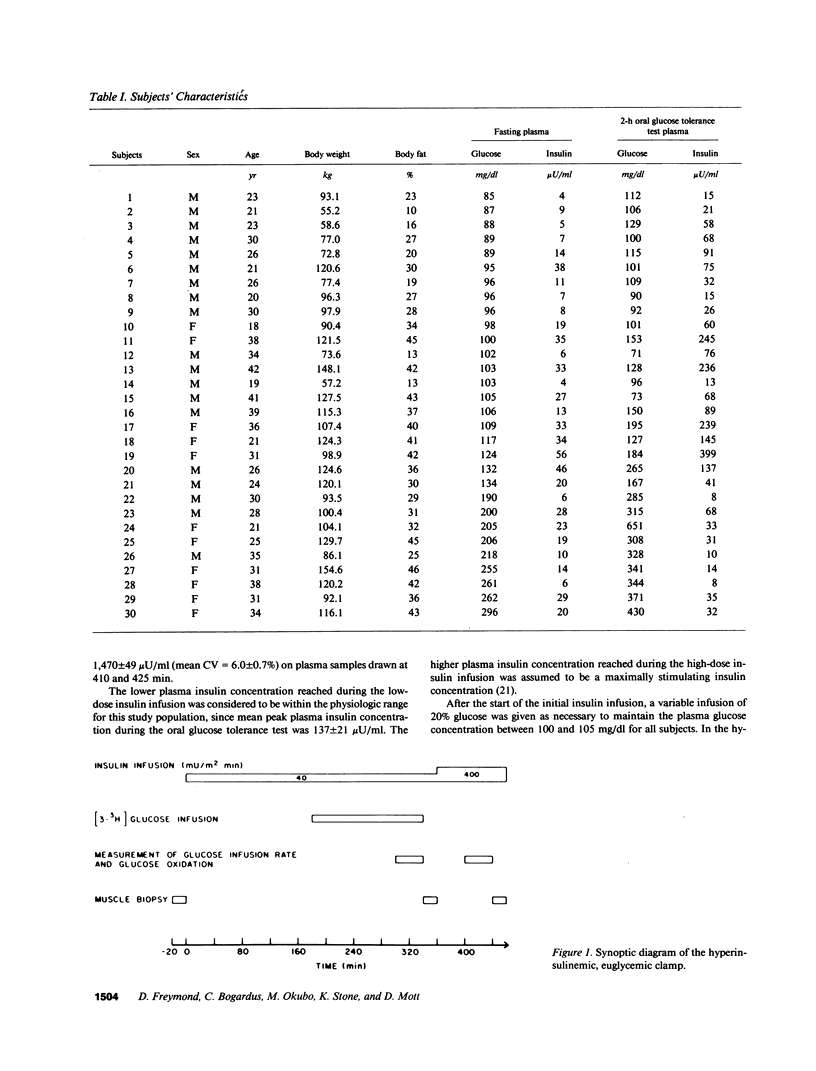
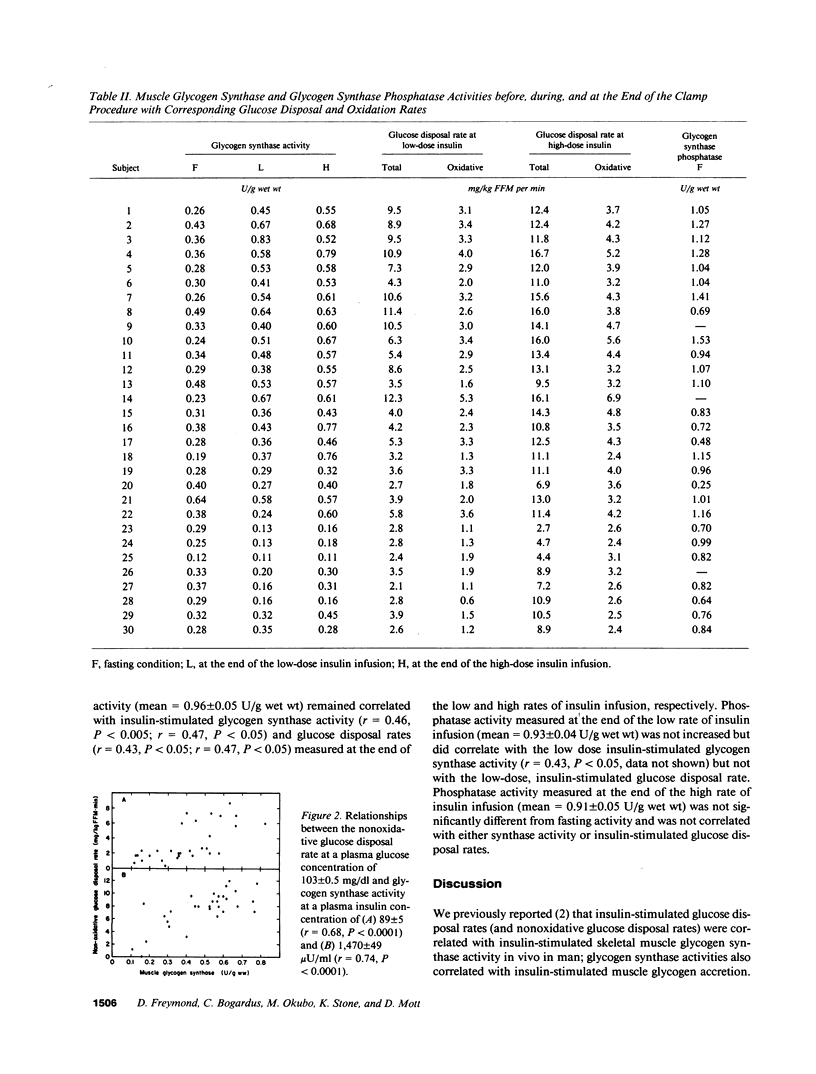
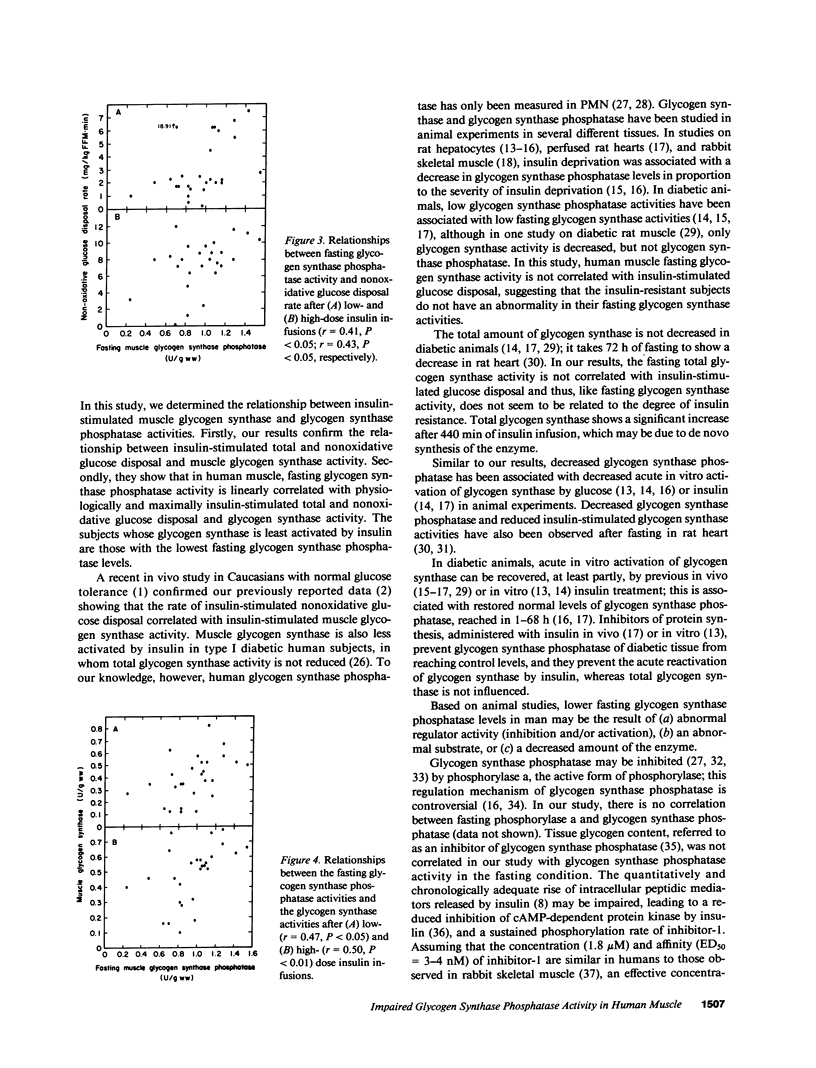
Abstract
Insulin-mediated glycogen synthase activity in skeletal muscle correlates with the rate of insulin-mediated glycogen deposition and is reduced in human subjects with insulin resistance. To assess the role of glycogen synthase phosphatase as a possible mediator of reduced glycogen synthase activity, we studied 30 Southwestern American Indians with a broad range of insulin action in vivo. Percutaneous biopsies of the vastus lateralis muscle were performed before and during a 440-min euglycemic clamp at plasma insulin concentrations of 89 +/- 5 and 1,470 +/- 49 microU/ml (mean +/- SEM); simultaneous glucose oxidation was determined by indirect calorimetry. After insulin stimulation, glycogen synthase activity was correlated with the total and nonoxidative glucose disposal at both low (r = 0.73, P less than 0.0001; r = 0.68, P less than 0.0001) and high (r = 0.75, P less than 0.0001; r = 0.74, P less than 0.0001) plasma insulin concentrations. Fasting muscle glycogen synthase phosphatase activity was correlated with both total and nonoxidative glucose disposal rates at the low (r = 0.48, P less than 0.005; r = 0.41, P less than 0.05) and high (r = 0.47, P less than 0.05; r = 0.43, P less than 0.05) plasma insulin concentrations. In addition, fasting glycogen synthase phosphatase activity was correlated with glycogen synthase activity after low- (r = 0.47, P less than 0.05) and high- (r = 0.50, P less than 0.01) dose insulin stimulations. These data suggest that the decreased insulin-stimulated glucose disposal and reduced glycogen synthase activation observed in insulin resistance could be secondary to a low fasting glycogen synthase phosphatase activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemany S., Cohen P. Phosphorylase a is an allosteric inhibitor of the glycogen and microsomal forms of rat hepatic protein phosphatase-1. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 31;198(2):194–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80404-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best J. D., Judzewitsch R. G., Pfeifer M. A., Beard J. C., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr The effect of chronic sulfonylurea therapy on hepatic glucose production in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1982 Apr;31(4 Pt 1):333–338. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus C., Lillioja S., Stone K., Mott D. Correlation between muscle glycogen synthase activity and in vivo insulin action in man. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1185–1190. doi: 10.1172/JCI111304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen M., Stalmans W. The hepatic defect in glycogen synthesis in chronic diabetes involves the G-component of synthase phosphatase. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 15;217(2):427–434. doi: 10.1042/bj2170427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Eichner R. D., Thompson B., Mayer S. Dephosphorylation and activation of exogenous glycogen synthase by adipose-tissue phosphatase. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):221–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1880221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. Y., Huang L. C. Effects of insulin treatment on the activities of phosphoprotein phosphatase and its inhibitors. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1980 Nov;95(3):427–432. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0950427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Protein phosphorylation and the control of glycogen metabolism in skeletal muscle. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Jul 5;302(1108):13–25. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1983.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes J. G., Jefferson L. S., Cohen P. The hormonal control of glycogen metabolism: dephosphorylation of protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 in vivo in response to insulin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Mar 24;112(1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon M. C., Nuttall F. Q. Effect of prolonged starvation on glycogen synthase and glycogen synthase phosphatase activity in rat heart. J Nutr. 1984 Nov;114(11):2147–2154. doi: 10.1093/jn/114.11.2147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon M. C., Tan A. W., Nuttall F. Q. Effect of starvation and insulin treatment on glycogen synthase D and synthase D phosphatase activity in rat heart. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Jan 20;34(1):31–34. doi: 10.1007/BF02354849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboe D. P., Nuttall F. Q. The role of ATP and glucose 6-phosphate in the regulation of glycogen synthetase D phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 21;48(4):898–906. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90693-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboe D. P., Nuttall F. Q. The synergistic action of caffeine or adenosine on glucose stimulation of liver glycogen synthase phosphatase activity. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 21;170(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81345-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. E., Curnow R. T. Impaired glycogen synthase activating system in human diabetic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Diabetes. 1980 Mar;29(3):217–220. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.3.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk W. K., Jarett L. Intracellular mediators of insulin action. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1985;1(3):229–259. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. Protein phosphatases: properties and role in cellular regulation. Science. 1983 Jul 22;221(4608):331–338. doi: 10.1126/science.6306765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatra B. S. Properties of a phosphoprotein phosphatase from skeletal muscle and its regulation in diabetes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1984 Oct;177(1):33–41. doi: 10.3181/00379727-177-41908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuniecki P. R., Kochan R. G., Schlender K. K., Reimann E. M. Glycogen synthase in diabetic rat skeletal muscle: activation by insulin. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Oct 29;48(3):129–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00421224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruszynska Y. T., Petranyi G., Home P. D., Taylor R., Alberti K. G. Muscle enzyme activity and insulin sensitivity in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1986 Oct;29(10):699–675. doi: 10.1007/BF00870279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LELOIR L. F., OLAVARRIA J. M., GOLDEMBERG S. H., CARMINATTI H. Biosynthesis of glycogen from uridine diphosphate glucose. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Apr;81(2):508–520. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J. Mediators of postreceptor action of insulin. Am J Med. 1983 Jan 17;74(1A):38–51. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90653-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillioja S., Mott D. M., Zawadzki J. K., Young A. A., Abbott W. G., Bogardus C. Glucose storage is a major determinant of in vivo "insulin resistance" in subjects with normal glucose tolerance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 May;62(5):922–927. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-5-922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandarino L. J., Wright K. S., Verity L. S., Nichols J., Bell J. M., Kolterman O. G., Beck-Nielsen H. Effects of insulin infusion on human skeletal muscle pyruvate dehydrogenase, phosphofructokinase, and glycogen synthase. Evidence for their role in oxidative and nonoxidative glucose metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):655–663. doi: 10.1172/JCI113118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. N., Selawry H. P., Curnow R. T. Regulation of hepatic glycogen metabolism: effects of diabetes, insulin infusion, and pancreatic islet transplantation. Metabolism. 1985 Jan;34(1):62–68. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. B., Jr A dual role for insulin in the regulation of cardiac glycogen synthase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5389–5394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. B., Jr, Garnache A. K., Cruz J., McPherson R. K., Wolleben C. Regulation of glycogen metabolism in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Restoration of acute effects of insulin and glucose in cells from diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):785–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. B., Jr, Garnache A. K., Cruz J., Wolleben C. Regulation of glycogen metabolism in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Restoration of acute effects of glucose in cells from diabetic rats involves protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4000–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. B., Jr, Garnache A., Vicalvi J. J., Jr Hormonal regulation of hepatic glycogen synthase phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2851–2855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahas N., Juhl H., Esmann V. Chromatographic characteristics and subcellular localization of synthase phosphatase, phosphorylase phosphatase and histone phosphatase in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;58(1-2):147–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00240614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuttali F. Q., Gannon M. C., Corbett V. A., Wheeler M. P. Insulin stimulation of heart glycogen synthase D phosphatase (protein phosphatase). J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6724–6729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oron Y., Galasko G., Larner J. Insulin action in intact mouse diaphragm. II. Inhibition of endogenous protein phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biochem. 1980 Nov 20;32(3):161–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00227443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M., Albertse E. C., Garlick P. J. Protein metabolism in skeletal muscle, diaphragm, and heart of diabetic rats. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):E604–E610. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.245.6.E604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Dose-response characteristics for effects of insulin on production and utilization of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):E630–E639. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.6.E630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R. Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strålfors P., Hiraga A., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. Purification and characterisation of the glycogen-bound form of protein phosphatase-1 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):295–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkenbach R. J., Hazen R., Larner J. Reversible inhibition of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase by insulin. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Feb 24;19(1):31–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00231232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


