Abstract
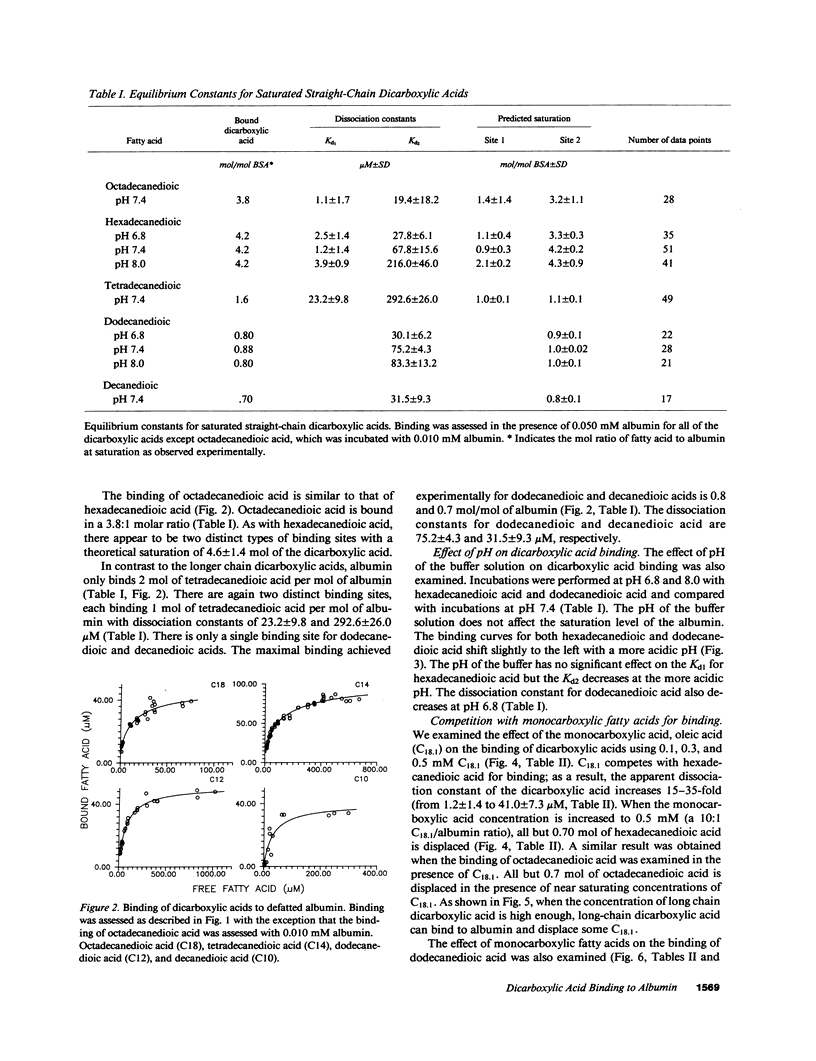
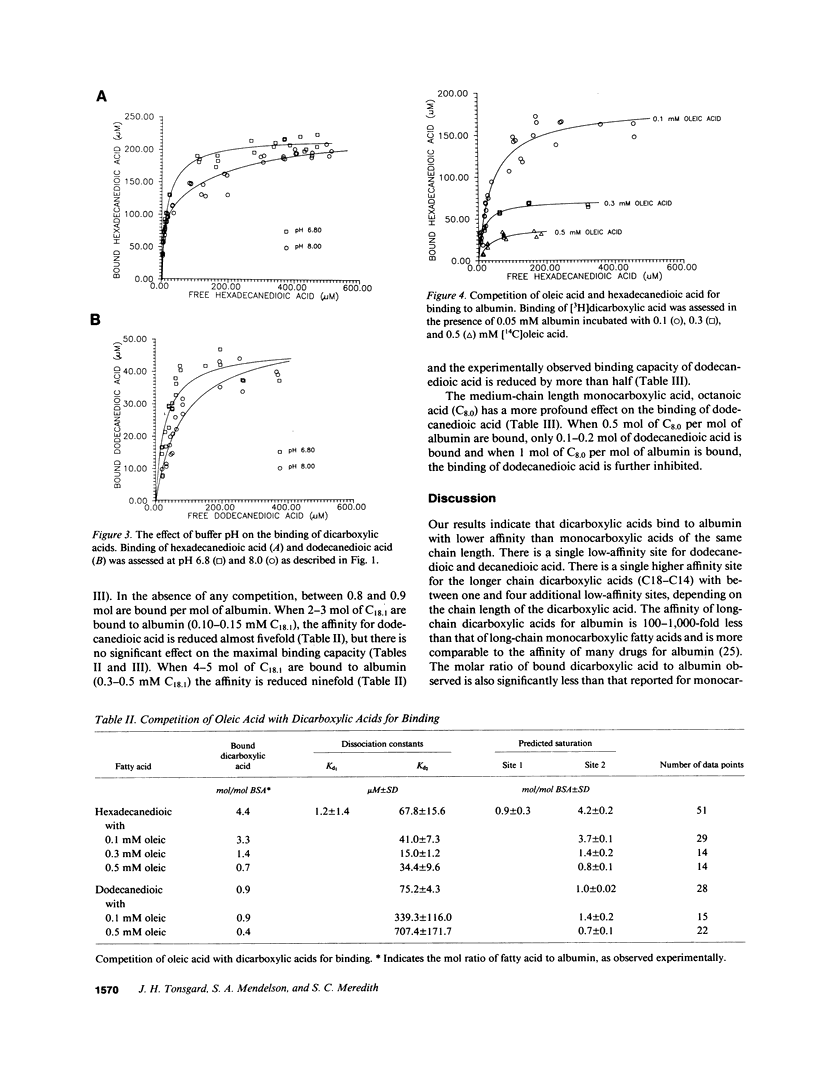
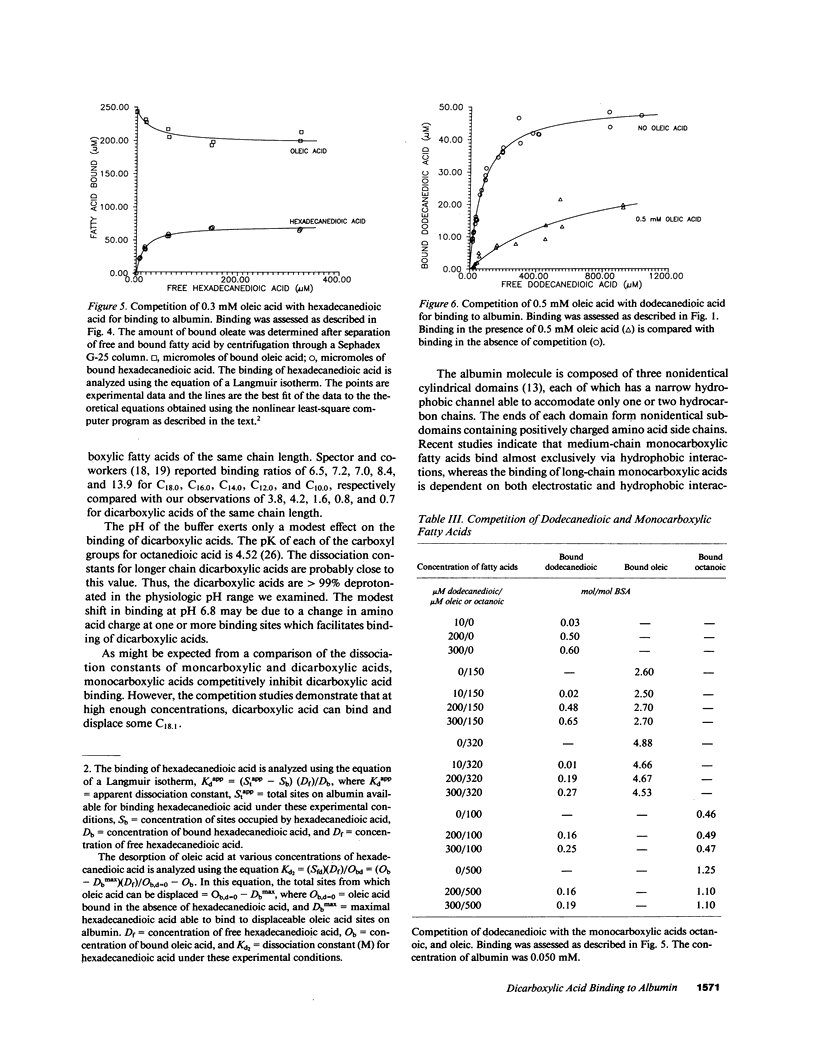
Dicarboxylic acids are prominent features of several diseases, including Reye's syndrome. Long-chain dicarboxylic acids have profound effects on the function and structure of isolated mitochondria, suggesting that they could contribute to the mitochondrial dysfunction in Reye's syndrome. Binding of fatty acids to albumin and the intracellular fatty acid-binding proteins is important in regulating the transport and metabolism of fatty acids and protects against the toxic effects of unbound fatty acids. We studied the binding of dicarboxylic acids to defatted albumin using equilibrium dialysis to assess to what extent dicarboxylic acids are likely to be bound in the plasma of patients. Dicarboxylic acids bind weakly to albumin in a molar ratio of 3.8, 4.2, 1.6, 0.8, and 0.7 to 1 for octadecanedioic, hexadecanedioic, tetradecanedioic, dodecanedioic, and decanedioic acid, respectively. The dissociation constants for long-chain dicarboxylic acids are 100-1,000-fold larger than those of comparable monocarboxylic acids. Oleate competes with dicarboxylic acid and reduces the moles of dicarboxylic acid bound per mol of albumin to less than 1. Octanoate inhibits dicarboxylic acid binding. Our observations indicate that in Reye's syndrome, substantial concentrations of dicarboxylic acids of patients may be free and potentially toxic to mitochondria and other cellular processes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashbrook J. D., Spectro A. A., Fletcher J. E. Medium chain fatty acid binding to human plasma albumin. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7038–7042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I. On the quantitative importance of omega-oxidation of fatty acids. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jul;19(5):585–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cistola D. P., Small D. M., Hamilton J. A. Carbon 13 NMR studies of saturated fatty acids bound to bovine serum albumin. II. Electrostatic interactions in individual fatty acid binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):10980–10985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatz J. F., Veerkamp J. H. A radiochemical procedure for the assay of fatty acid binding by proteins. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kritchevsky D., Davidson L. M., Kim H. K. Quantitation of serum lipids by a simple TLC-charring method. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Jun 14;46(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J. B., Sacchettini J. C., Laposata M., McQuillan J. J., Gordon J. I. Expression of rat intestinal fatty acid-binding protein in Escherichia coli. Purification and comparison of ligand binding characteristics with that of Escherichia coli-derived rat liver fatty acid-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5931–5937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng K. J., Andresen B. D., Hilty M. D., Bianchine J. R. Identification of long chain dicarboxylic acids in the serum of two patients with Reye's syndrome. J Chromatogr. 1983 Aug 12;276(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Manning J. A., Poppenhausen R. B., Ho W. K. A binding protein for fatty acids in cytosol of intestinal mucosa, liver, myocardium, and other tissues. Science. 1972 Jul 7;177(4043):56–58. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4043.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passi S., Picardo M., Nazzaro-Porro M., Breathnach A., Confaloni A. M., Serlupi-Crescenzi G. Antimitochondrial effect of saturated medium chain length (C8-C13) dicarboxylic acids. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Jan 1;33(1):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90376-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocchiccioli F., Aubourg P., Bougnères P. F. Medium- and long-chain dicarboxylic aciduria in patients with Zellweger syndrome and neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy. Pediatr Res. 1986 Jan;20(1):62–66. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198601000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A. Fatty acid binding to plasma albumin. J Lipid Res. 1975 May;16(3):165–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., John K., Fletcher J. E. Binding of long-chain fatty acids to bovine serum albumin. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):56–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starko K. M., Ray C. G., Dominguez L. B., Stromberg W. L., Woodall D. F. Reye's syndrome and salicylate use. Pediatrics. 1980 Dec;66(6):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonsgard J. H., Getz G. S. Effect of Reye's syndrome serum on isolated chinchilla liver mitochondria. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):816–825. doi: 10.1172/JCI112039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonsgard J. H. Serum dicarboxylic acids in patients with Reye syndrome. J Pediatr. 1986 Sep;109(3):440–445. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonsgard J. H. Urinary dicarboxylic acids in Reye syndrome. J Pediatr. 1985 Jul;107(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80619-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vianey-Liaud C., Divry P., Gregersen N., Mathieu M. The inborn errors of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1987;10 (Suppl 1):159–200. doi: 10.1007/BF01812855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojtczak L. Effect of long-chain fatty acids and acyl-CoA on mitochondrial permeability, transport, and energy-coupling processes. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1976 Dec;8(6):293–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00765158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka K., Tanigawara Y., Nakagawa T., Uno T. A pharmacokinetic analysis program (multi) for microcomputer. J Pharmacobiodyn. 1981 Nov;4(11):879–885. doi: 10.1248/bpb1978.4.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


