Abstract
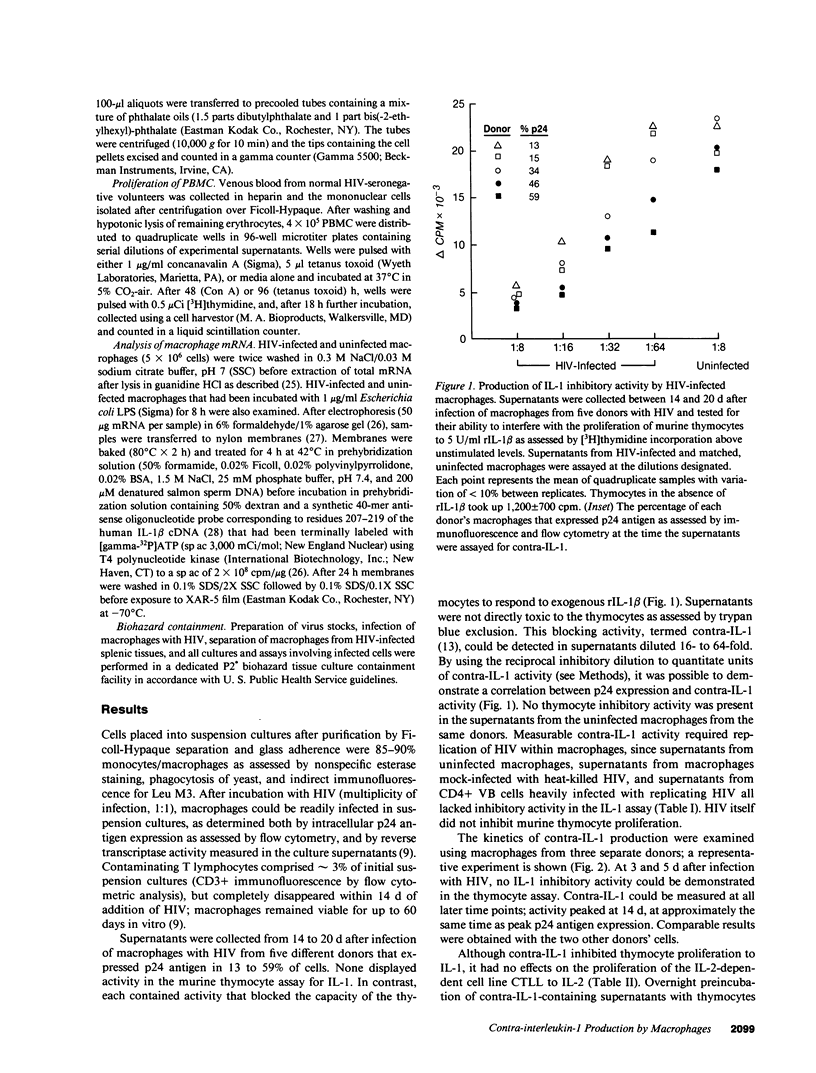
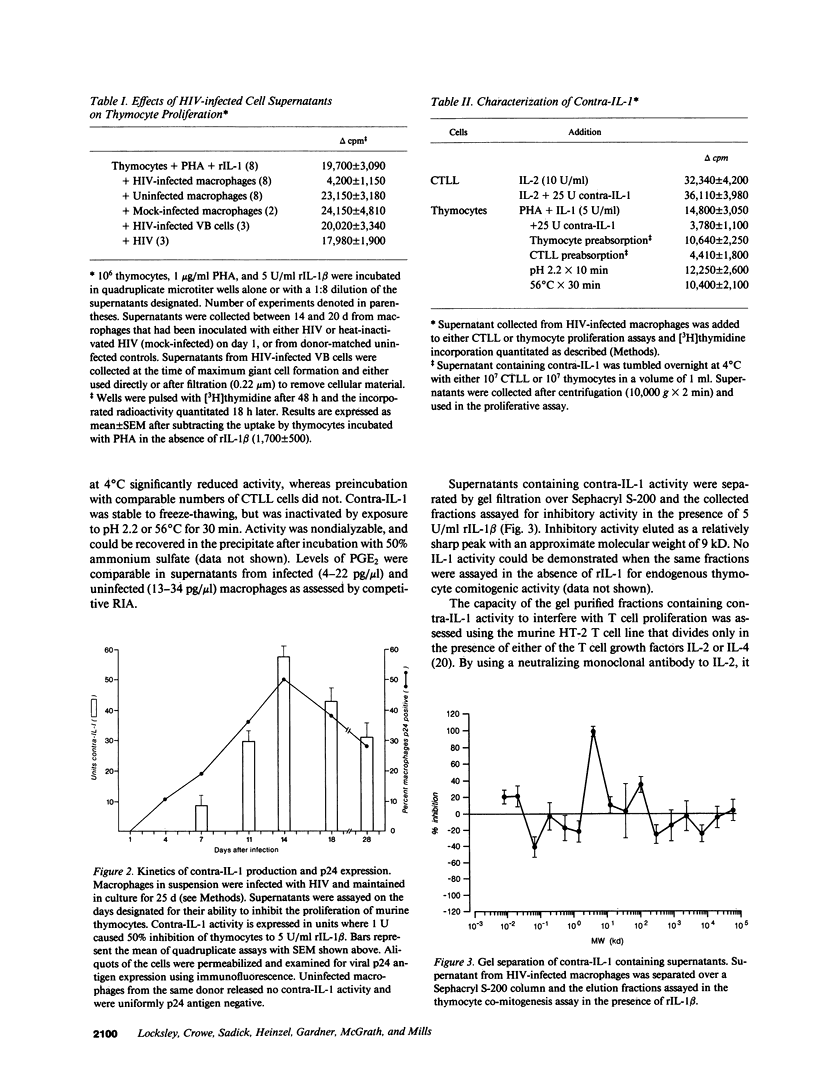
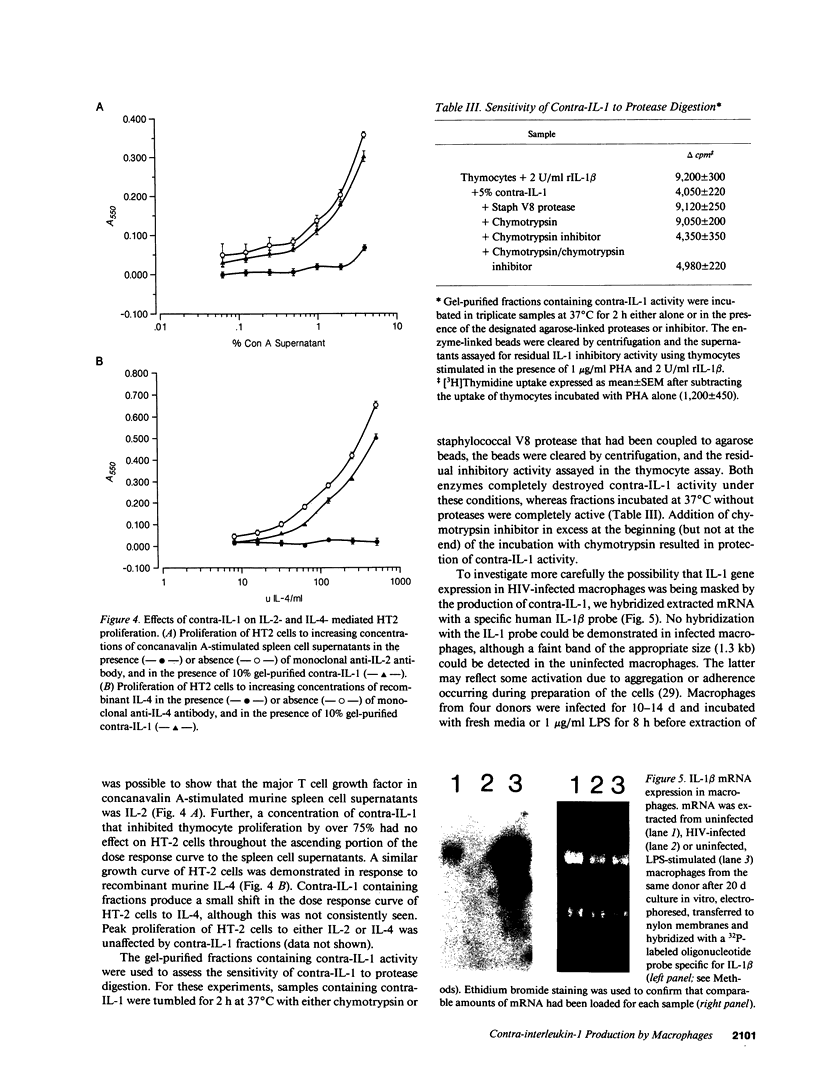
Infection of monocyte-macrophages with human immunodeficiency virus may be central to the pathogenesis of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. The ability of infected macrophages to prime T cells through IL-1 production was investigated in vitro. Purified human monocytes maintained in suspension culture were infected with strain HIV-DV. Intracellular expression of virus p24 antigen increased from undetectable levels immediately after infection to 13-59% of cells by 10-14 d; infected macrophages remained viable for up to 60 d. Supernatants collected between 14 and 20 d after infection were examined in the murine thymocyte co-mitogenesis assay and demonstrated to contain a potent IL-1 inhibitor, designated contra-IL-1. Contra-IL-1 activity was present in all supernatants examined after 4 d of infection, and peaked coincident with peak p24 antigen expression. Inhibitory activity was not present in uninfected cells. Contra-IL-1 activity eluted after gel filtration with an approximate molecular weight of 9 kD. Inhibitory activity was removed by exposure to heat or acid pH, or by incubation with chymotrypsin or staphylococcal V8 protease. Contra-IL-1 did not inhibit IL-2- or IL-4-dependent proliferation of murine T cell lines. Despite its ability to inhibit IL-1 activity, contra-IL-1 did not interfere with the binding of recombinant IL-1 beta to a fibroblast cell line. Contra-IL-1 inhibited the proliferation of normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells to both concanavalin A and tetanus toxoid; inhibition could be attenuated by the addition of exogenous IL-1. Messenger RNA extracted from infected macrophages was examined by Northern analysis for the presence of message to IL-1 beta. No message was apparent, suggesting that the presence of contra-IL-1 was not obscuring the concomitant release of IL-1. Infected macrophages stimulated with endotoxin generated readily detectable message for IL-1 beta. Spleen macrophages purified from two patients with AIDS complicated by immune thrombocytopenia spontaneously expressed p24 antigen in vitro and released contra-IL-1 activity into the media. Contra-IL-1 may contribute to the immune dysfunction of AIDS.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Massoni R. J. Effects of immune complexes on production by human monocytes of interleukin 1 or an interleukin 1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3868–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Rosenwasser L. J., Mucci S. F., Rich A., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Nucleotide sequence of human monocyte interleukin 1 precursor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsito D. V., Sanchez M. R., Baer R. L., Valentine F., Thorbecke G. J. Reduced Langerhans' cell Ia antigen and ATPase activity in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1984 May 17;310(20):1279–1282. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405173102002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M. A., Sandborg C. I., Calabia B. S., Andrews B. S., Friou G. J. Interleukin 1 inhibitor masks high interleukin 1 production in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Jan;42(1):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. M., Rosenstreich D. L. Mechanism of action of a human interleukin 1 inhibitor. Cell Immunol. 1987 Mar;105(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherwinski H. M., Schumacher J. H., Brown K. D., Mosmann T. R. Two types of mouse helper T cell clone. III. Further differences in lymphokine synthesis between Th1 and Th2 clones revealed by RNA hybridization, functionally monospecific bioassays, and monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1229–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colcher D., Schlom J. Purification and characterization of the RNA-directed DNA polymerase of a primate type-D retrovirus: Mason-Pfizer virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 30;607(3):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe S., Mills J., McGrath M. S. Quantitative immunocytofluorographic analysis of CD4 surface antigen expression and HIV infection of human peripheral blood monocyte/macrophages. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Summer;3(2):135–145. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Rosenwasser L. J., Wolff S. M. Demonstration of a circulating suppressor factor of thymocyte proliferation during endotoxin fever in humans. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2517–2519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower S. K., Call S. M., Gillis S., Urdal D. L. Similarity between the interleukin 1 receptors on a murine T-lymphoma cell line and on a murine fibroblast cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1060–1064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton M. J., Clark B. D., Collins K. L., Webb A. C., Rich A., Auron P. E. Transcriptional regulation of the human prointerleukin 1 beta gene. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3972–3979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhlbrigge R. C., Chaplin D. D., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Regulation of interleukin 1 gene expression by adherence and lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3799–3802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara H., Ellner J. J. Spontaneous production of a suppressor factor by the human macrophage-like cell line U937. I. Suppression of interleukin 1, interleukin 2, and mitogen-induced blastogenesis in mouse thymocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):181–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Betts R. F., Popovic M. Virus isolation from and identification of HTLV-III/LAV-producing cells in brain tissue from a patient with AIDS. JAMA. 1986 Nov 7;256(17):2365–2371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Kaplan M. H., Gallo R. C., Popovic M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):215–219. doi: 10.1126/science.3014648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haq A. U., Rinehart J. J., Maca R. D. The effect of gamma interferon on IL-1 secretion of in vitro differentiated human macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Dec;38(6):735–746. doi: 10.1002/jlb.38.6.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heagy W., Kelley V. E., Strom T. B., Mayer K., Shapiro H. M., Mandel R., Finberg R. Decreased expression of human class II antigens on monocytes from patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Increased expression with interferon-gamma. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2089–2096. doi: 10.1172/JCI111633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. R., Pedersen N. C., Carlson J. R. Detection and differentiation by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus- and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retroviruslike clinical isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):424–430. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.424-430.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Pomerantz R. J., Kaplan J. C. Pathogenesis of infection with human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 30;317(5):278–286. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707303170505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Hirsch M. S. Infection of monocyte/macrophages by human T lymphotropic virus type III. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1712–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI112491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinerman E. S., Lachman L. B., Knowles R. D., Snyderman R., Cianciolo G. J. A synthetic peptide homologous to the envelope proteins of retroviruses inhibits monocyte-mediated killing by inactivating interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2329–2337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi Y., Miles S., Mitsuyasu R. T., Merrill J. E., Vinters H. V., Chen I. S. Dual infection of the central nervous system by AIDS viruses with distinct cellular tropisms. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.3646751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Hamberg S., Ohara J., Paul W. E., Abbas A. K. Heterogeneity of helper/inducer T lymphocytes. I. Lymphokine production and lymphokine responsiveness. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1774–1787. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Immunologic abnormalities in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:477–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao Z., Grimshaw R. S., Rosenstreich D. L. Identification of a specific interleukin 1 inhibitor in the urine of febrile patients. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):126–136. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Reyes G. R., McGrath M. S., Stein B. S., Engleman E. G. AIDS retrovirus induced cytopathology: giant cell formation and involvement of CD4 antigen. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1123–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.3010463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locksley R. M., Heinzel F. P., Shepard H. M., Agosti J., Eessalu T. E., Aggarwal B. B., Harlan J. M. Tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta differ in their capacities to generate interleukin 1 release from human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1891–1895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Jirik F., Kabouridis P., Tsoukas C., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Carson D. A. B cell stimulating factor 2/interleukin 6 is a costimulant for human thymocytes and T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1253–1258. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Tsoukas C. D., Fong S., Dinarello C. A., Carson D. A., Vaughan J. H. Release of lymphokines after infection with Epstein Barr virus in vitro. II. A monocyte-dependent inhibitor of interleukin 1 downregulates the production of interleukin 2 and interferon-gamma in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3643–3648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Tsoukas C. D., Robinson C. A., Dinarello C. A., Carson D. A., Vaughan J. H. Basis for defective responses of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid lymphocytes to anti-CD3 (T3) antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):713–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI112631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miossec P., Cavender D., Ziff M. Production of interleukin 1 by human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2486–2491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchmore A. V., Decker J. M. Evidence that recombinant IL 1 alpha exhibits lectin-like specificity and binds to homogeneous uromodulin via N-linked oligosaccharides. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2541–2546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Hillman J. K., Rubin B. Y., Kelly C. D., Jacobs J. L., Tyler L. W., Donelly D. M., Carriero S. M., Godbold J. H., Roberts R. B. Patients at risk for AIDS-related opportunistic infections. Clinical manifestations and impaired gamma interferon production. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 12;313(24):1504–1510. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512123132403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara J., Paul W. E. Production of a monoclonal antibody to and molecular characterization of B-cell stimulatory factor-1. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):333–336. doi: 10.1038/315333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Kohr W. J., Kuang W. J., Glaister D., Aggarwal B. B., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. Identification of human uromodulin as the Tamm-Horsfall urinary glycoprotein. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):83–88. doi: 10.1126/science.3453112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit A. J., Terpstra F. G., Miedema F. Human immunodeficiency virus infection down-regulates HLA class II expression and induces differentiation in promonocytic U937 cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1883–1889. doi: 10.1172/JCI113032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Zlotnik A., Espevik T., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Palladino M. A., Jr Tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin is a growth factor for thymocytes. Synergistic interactions with other cytokines. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1472–1478. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts N. J., Jr, Prill A. H., Mann T. N. Interleukin 1 and interleukin 1 inhibitor production by human macrophages exposed to influenza virus or respiratory syncytial virus. Respiratory syncytial virus is a potent inducer of inhibitor activity. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):511–519. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Rose R. M., Groopman J. E., Markham P. D., Gallo R. C. Human T lymphotropic virus type III infection of human alveolar macrophages. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):281–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scala G., Kuang Y. D., Hall R. E., Muchmore A. V., Oppenheim J. J. Accessory cell function of human B cells. I. Production of both interleukin 1-like activity and an interleukin 1 inhibitory factor by an EBV-transformed human B cell line. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1637–1652. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz T., Urbanska A., Gschnait F., Luger T. A. UV-irradiated epidermal cells produce a specific inhibitor of interleukin 1 activity. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1457–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Lowenthal J. W., Williamson K., Dayer J. M., MacDonald H. R. A urine inhibitor of interleukin 1 activity that blocks ligand binding. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1546–1549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., Assoian R. K. Transforming growth factor-beta: biological function and chemical structure. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):532–534. doi: 10.1126/science.3487831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler M. H., Eskin T. A., Benn S., Angerer R. C., Angerer L. M. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III infection of the central nervous system. A preliminary in situ analysis. JAMA. 1986 Nov 7;256(17):2360–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiku K., Tiku M. L., Liu S., Skosey J. L. Normal human neutrophils are a source of a specific interleukin 1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3686–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh L. J., Lander P. E., Seymour G. J., Powell R. N. Isolation and purification of ILS, an interleukin 1 inhibitor produced by human gingival epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 May;68(2):366–374. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. Continuous proliferation of murine antigen-specific helper T lymphocytes in culture. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1510–1519. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]