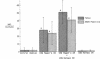Abstract
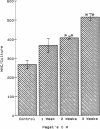
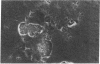
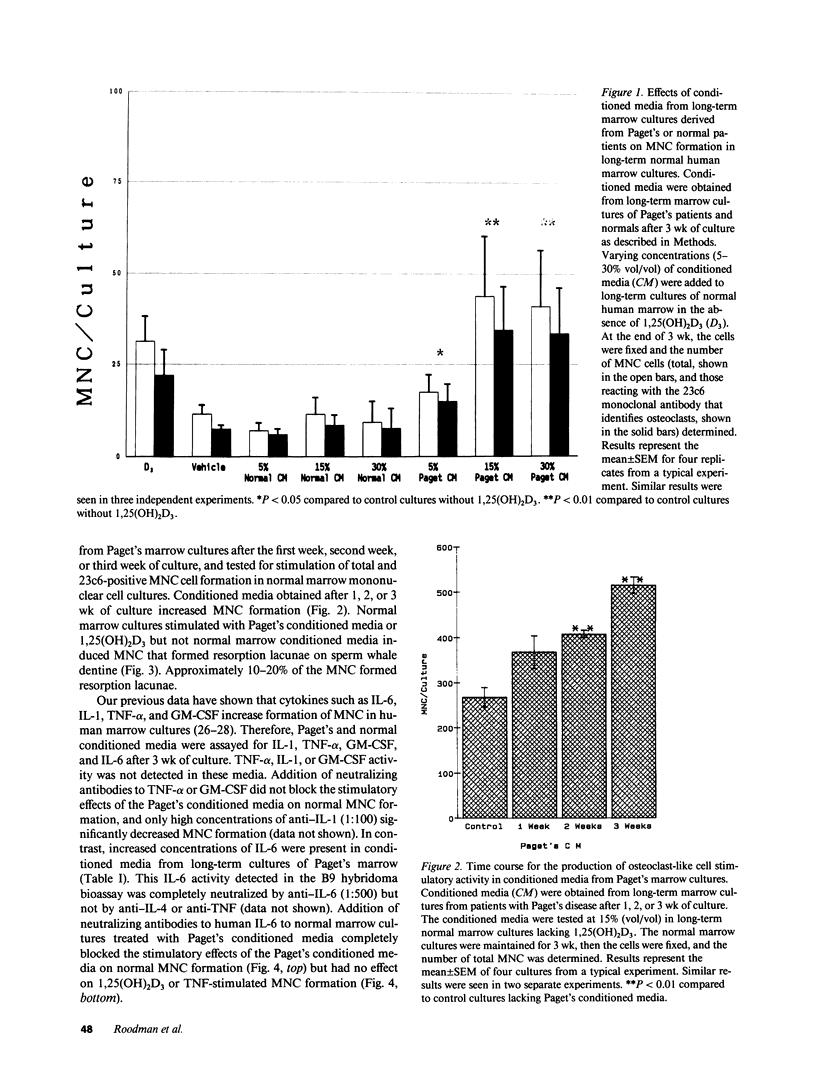
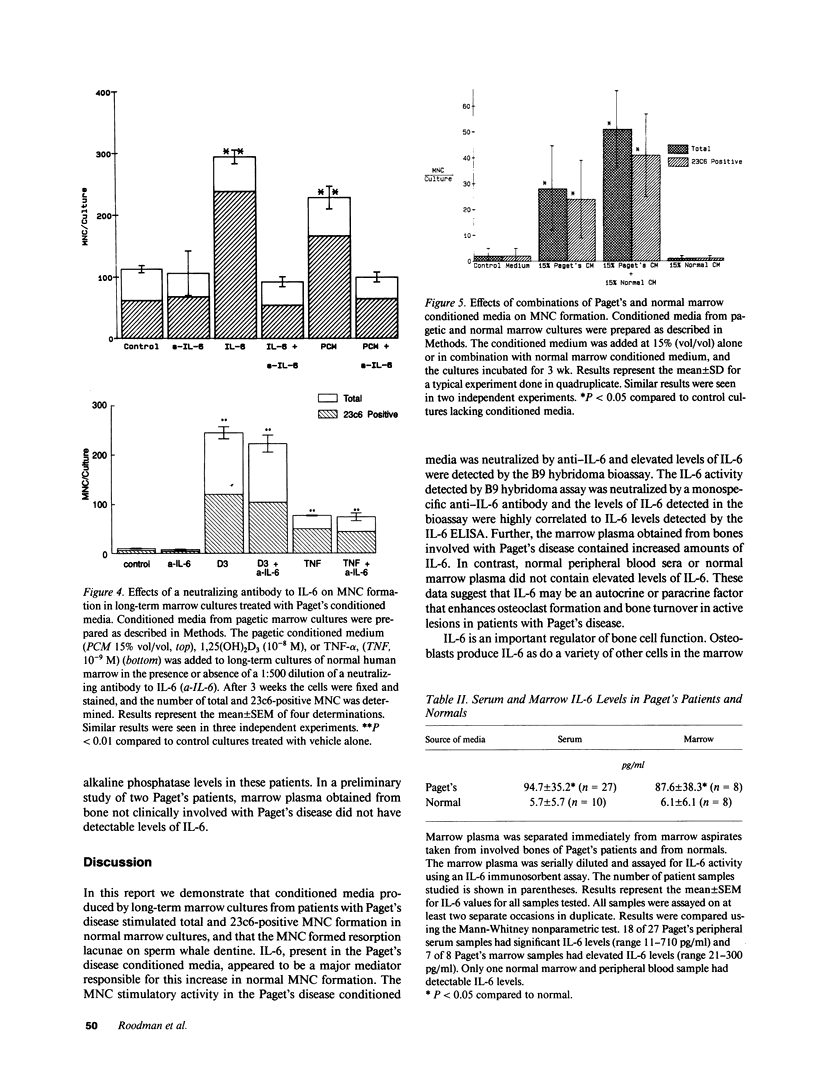
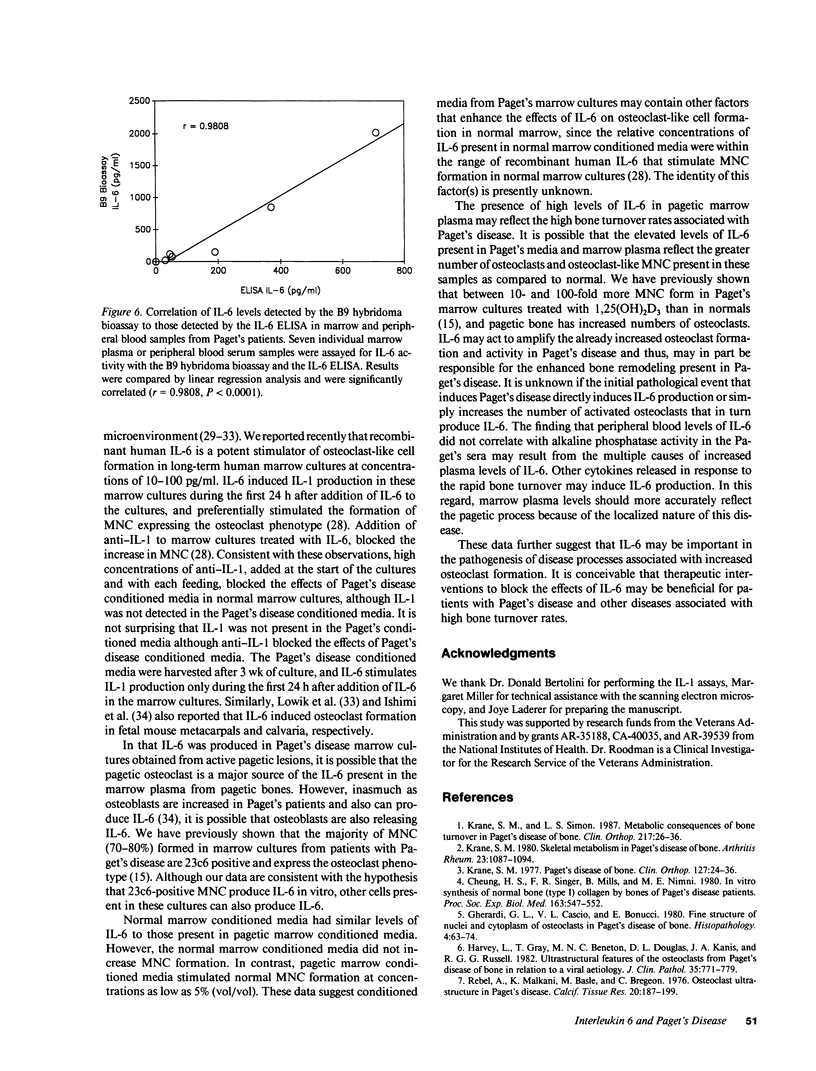
Pagetic osteoclasts are greatly increased in number and size and have increased numbers of nuclei per cell compared to normal osteoclasts. The mechanisms responsible for enhanced osteoclast formation in Paget's disease are unknown. We have used our recently described model system for pagetic osteoclast formation to evaluate culture media conditioned by these atypical multinucleated cells (MNC) to determine if pagetic osteoclasts produce an autocrine or paracrine factor that enhances osteoclast formation. Conditioned media from long-term bone marrow cultures from patients with Paget's disease stimulated osteoclast-like MNC formation in normal marrow cultures. At least part of this activity could be ascribed to interleukin 6 (IL-6). In contrast, conditioned media from normal marrow cultures contained lower levels of IL-6 and did not stimulate formation of osteoclast-like MNC. 7 of 8 bone marrow plasma samples taken from involved bones and 18 of 27 peripheral blood serum samples from Paget's patients had high levels of IL-6. Normal marrow plasma and peripheral blood serum had no or very low levels of IL-6. These results suggest that IL-6 produced by marrow and/or bone cells in patients with Paget's disease may be an autocrine/paracrine factor for pagetic osteoclasts.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., De Groot E. R., Schaap O. L., Lansdorp P. M. Production of hybridoma growth factor by human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1411–1416. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basle M. F., Russell W. C., Goswami K. K., Rebel A., Giraudon P., Wild F., Filmon R. Paramyxovirus antigens in osteoclasts from Paget's bone tissue detected by monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1985 Oct;66(Pt 10):2103–2110. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-10-2103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baslé M. F., Fournier J. G., Rozenblatt S., Rebel A., Bouteille M. Measles virus RNA detected in Paget's disease bone tissue by in situ hybridization. J Gen Virol. 1986 May;67(Pt 5):907–913. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-5-907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baslé M. F., Rebel A., Fournier J. G., Russell W. C., Malkani K. On the trail of paramyxoviruses in Paget's disease of bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987 Apr;(217):9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung H. S., Singer F. R., Mills B., Nimni M. E. In vitro synthesis of normal bone (Type I) collagen by bones of Paget's disease patients. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Apr;163(4):547–552. doi: 10.3181/00379727-163-40812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feyen J. H., Elford P., Di Padova F. E., Trechsel U. Interleukin-6 is produced by bone and modulated by parathyroid hormone. J Bone Miner Res. 1989 Aug;4(4):633–638. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650040422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherardi G., Lo Cascio V., Bonucci E. Fine structure of nuclei and cytoplasm of osteoclasts in Paget's disease of bone. Histopathology. 1980 Jan;4(1):63–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1980.tb02898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman G., Content J., Volckaert G., Derynck R., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Structural analysis of the sequence coding for an inducible 26-kDa protein in human fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):625–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey L., Gray T., Beneton M. N., Douglas D. L., Kanis J. A., Russell R. G. Ultrastructural features of the osteoclasts from Paget's disease of bone in relation to a viral aetiology. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jul;35(7):771–779. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.7.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Yasukawa K., Harada H., Taga T., Watanabe Y., Matsuda T., Kashiwamura S., Nakajima K., Koyama K., Iwamatsu A. Complementary DNA for a novel human interleukin (BSF-2) that induces B lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulin. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):73–76. doi: 10.1038/324073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton M. A., Lewis D., McNulty K., Pringle J. A., Chambers T. J. Monoclonal antibodies to osteoclastomas (giant cell bone tumors): definition of osteoclast-specific cellular antigens. Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 2):5663–5669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howatson A. F., Fornasier V. L. Microfilaments associated with Paget's disease of bone: comparison with nucleocapsids of measles virus and respiratory syncytial virus. Intervirology. 1982;18(3):150–159. doi: 10.1159/000149318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ida N., Sakurai S., Hosaka T., Hosoi K., Kunitomo T., Matsuura Y., Kohase M. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the measurement of human interleukin-6. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Oct 19;133(2):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90369-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimi Y., Miyaura C., Jin C. H., Akatsu T., Abe E., Nakamura Y., Yamaguchi A., Yoshiki S., Matsuda T., Hirano T. IL-6 is produced by osteoblasts and induces bone resorption. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3297–3303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Waddelow T. A., Caro J., Oliff A., Roodman G. D. Chronic exposure to tumor necrosis factor in vivo preferentially inhibits erythropoiesis in nude mice. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):130–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Hirano T. Molecular regulation of B lymphocyte response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:485–512. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krane S. M. Paget's disease of bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977;(127):24–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krane S. M., Simon L. S. Metabolic consequences of bone turnover in Paget's disease of bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987 Apr;(217):26–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krane S. M. Skeletal metabolism in Paget's disease of bone. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Oct;23(10):1087–1094. doi: 10.1002/art.1780231004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukita A., Chenu C., McManus L. M., Mundy G. R., Roodman G. D. Atypical multinucleated cells form in long-term marrow cultures from patients with Paget's disease. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1280–1286. doi: 10.1172/JCI114565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukita T., McManus L. M., Miller M., Civin C., Roodman G. D. Osteoclast-like cells formed in long-term human bone marrow cultures express a similar surface phenotype as authentic osteoclasts. Lab Invest. 1989 Apr;60(4):532–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara N., Bertolini D., Suda T., Akiyama Y., Roodman G. D. IL-6 stimulates osteoclast-like multinucleated cell formation in long term human marrow cultures by inducing IL-1 release. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4226–4230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löwik C. W., van der Pluijm G., Bloys H., Hoekman K., Bijvoet O. L., Aarden L. A., Papapoulos S. E. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) and PTH-like protein (PLP) stimulate interleukin-6 production by osteogenic cells: a possible role of interleukin-6 in osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1546–1552. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90851-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald B. R., Mundy G. R., Clark S., Wang E. A., Kuehl T. J., Stanley E. R., Roodman G. D. Effects of human recombinant CSF-GM and highly purified CSF-1 on the formation of multinucleated cells with osteoclast characteristics in long-term bone marrow cultures. J Bone Miner Res. 1986 Apr;1(2):227–233. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650010210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills B. G., Singer F. R. Nuclear inclusions in Paget's disease of bone. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):201–202. doi: 10.1126/science.959849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Chenu C., Bird A., Mundy G. R., Roodman G. D. Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor stimulate the formation of human osteoclastlike cells in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 1989 Feb;4(1):113–118. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650040116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebel A., Basle M., Pouplard A., Malkani K., Filmon R., Lepatezour A. Bone tissue in Paget's disease of bone. Ultrastructure and Immunocytology. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Oct;23(10):1104–1114. doi: 10.1002/art.1780231006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebel A., Malkani K., Baslé M., Bregeon C. Osteoclast ultrastructure in Paget's disease. Calcif Tissue Res. 1976 Apr 20;(2):187–199. doi: 10.1007/BF02546407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roodman G. D., Hutton J. J., Bollum F. J. DNA polymerase, thymidine kinase and DNA synthesis in erythropoietic mouse spleen cells separated on bovine serum albumin gradients. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 2;425(4):478–491. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer F. R., Mills B. G. Evidence for a viral etiology of Paget's disease of bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983 Sep;(178):245–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Kukita T., MacDonald B. R., Bird A., Mundy G. R., McManus L. M., Miller M., Boyde A., Jones S. J., Roodman G. D. Osteoclast-like cells form in long-term human bone marrow but not in peripheral blood cultures. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):543–550. doi: 10.1172/JCI113916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., MacDonald B. R., Hon J., Winkler M. E., Derynck R., Mundy G. R., Roodman G. D. Recombinant human transforming growth factor-alpha stimulates the formation of osteoclast-like cells in long-term human marrow cultures. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):894–898. doi: 10.1172/JCI112677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Ishikawa E., Ohmoto Y., Hirai Y. In vitro production of human interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta by peripheral blood mononuclear cells examined by sensitive sandwich enzyme immunoassay. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1527–1530. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Ruggieri R., Korn J. H., Revel M. Structure and expression of cDNA and genes for human interferon-beta-2, a distinct species inducible by growth-stimulatory cytokines. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2529–2537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04531.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]