Abstract
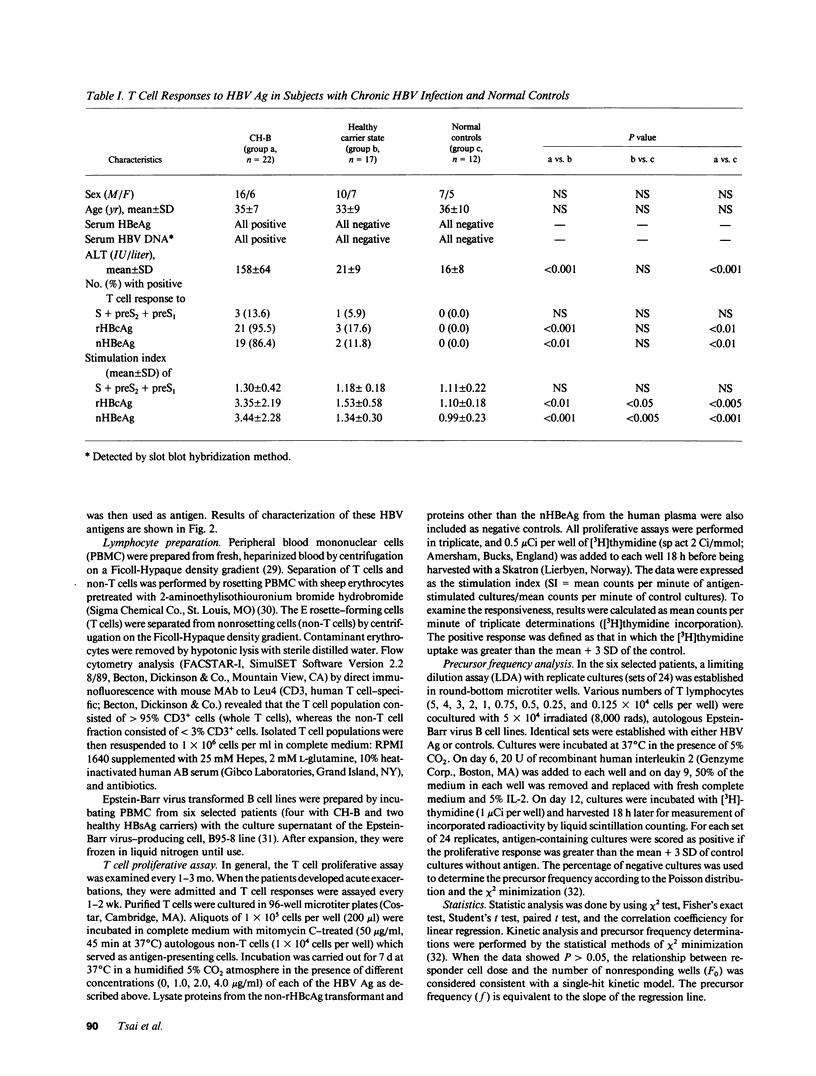
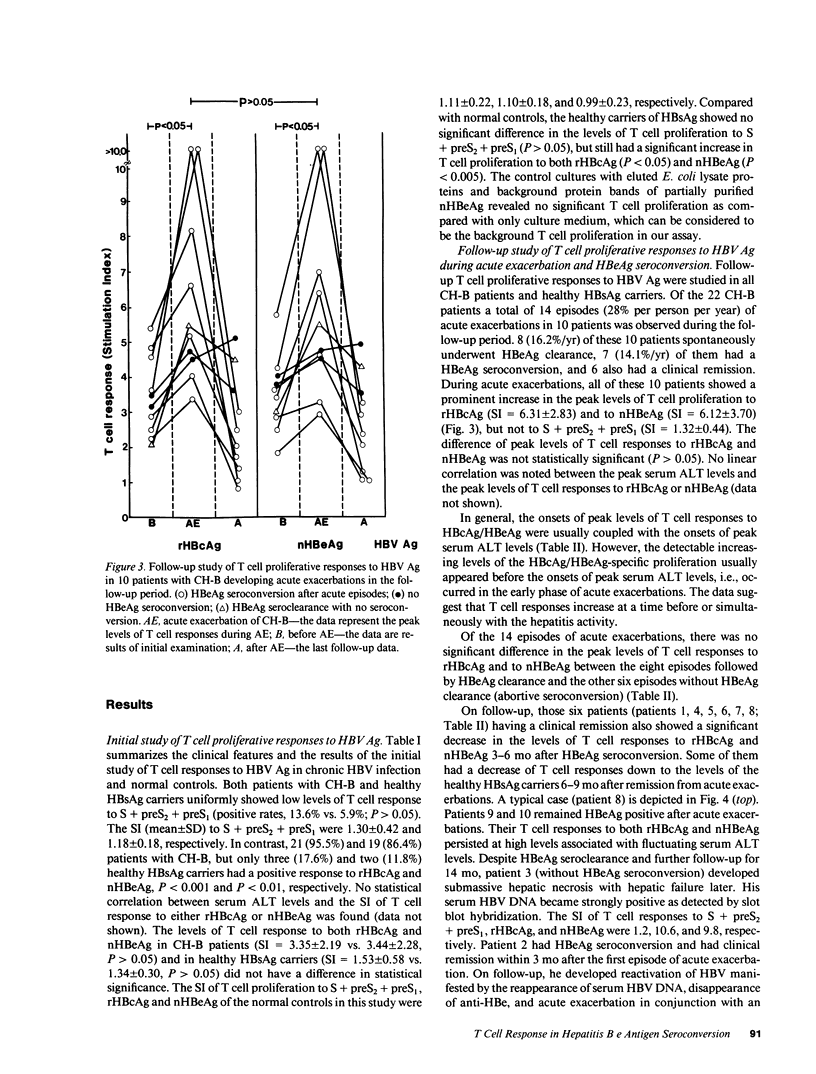
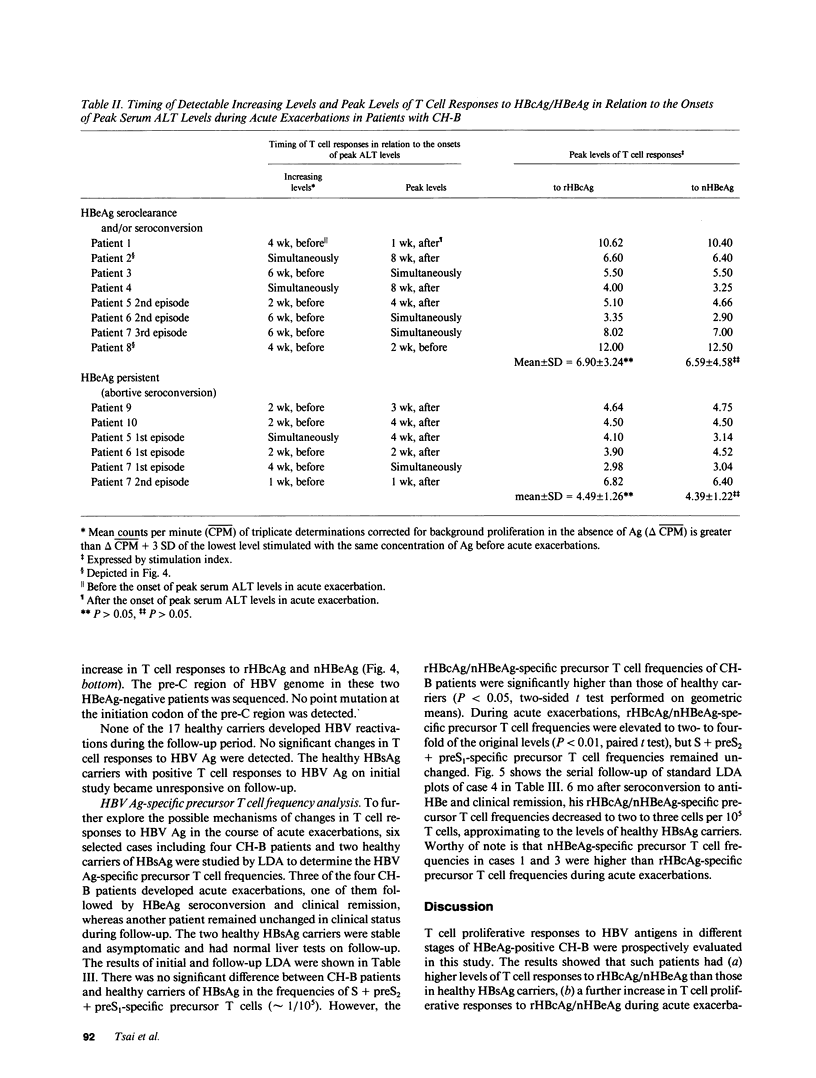
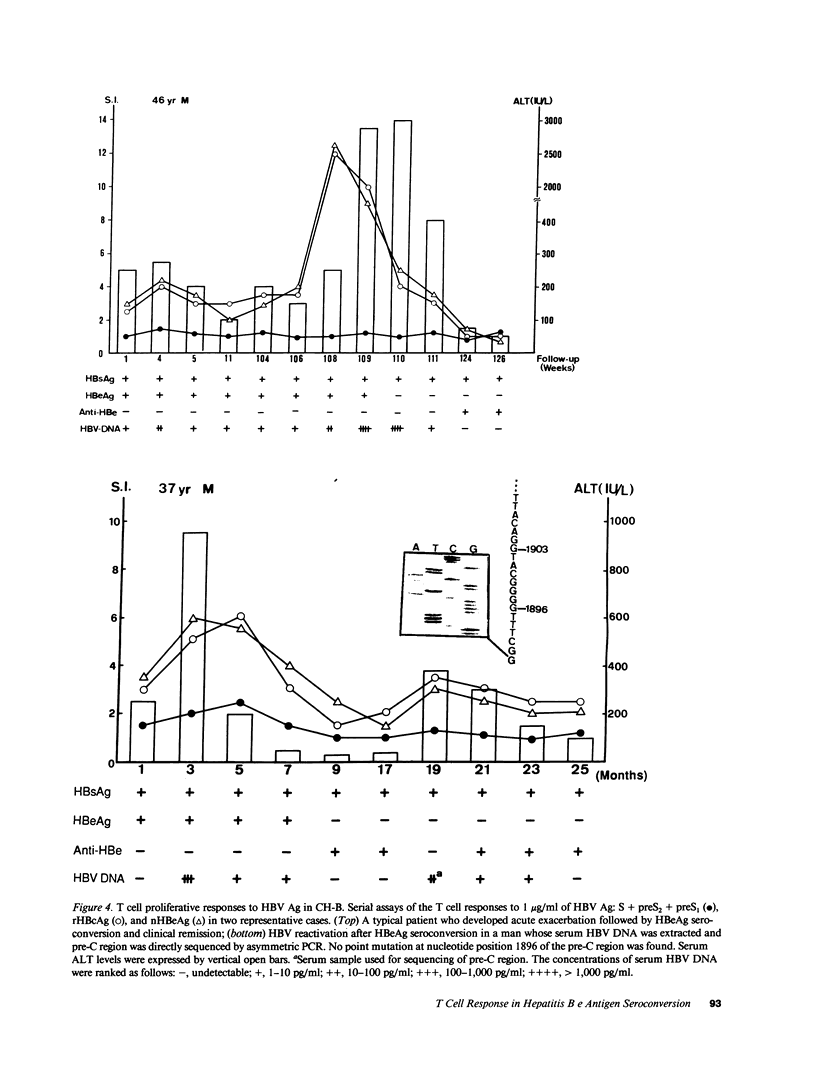
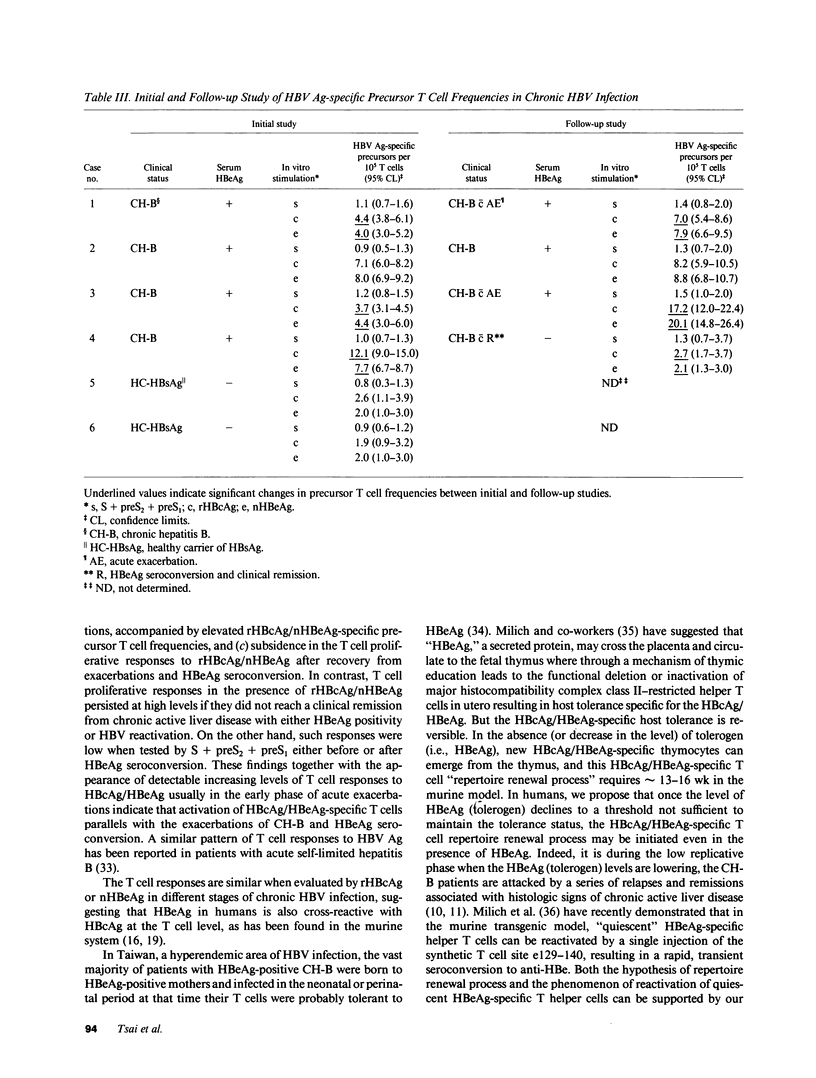
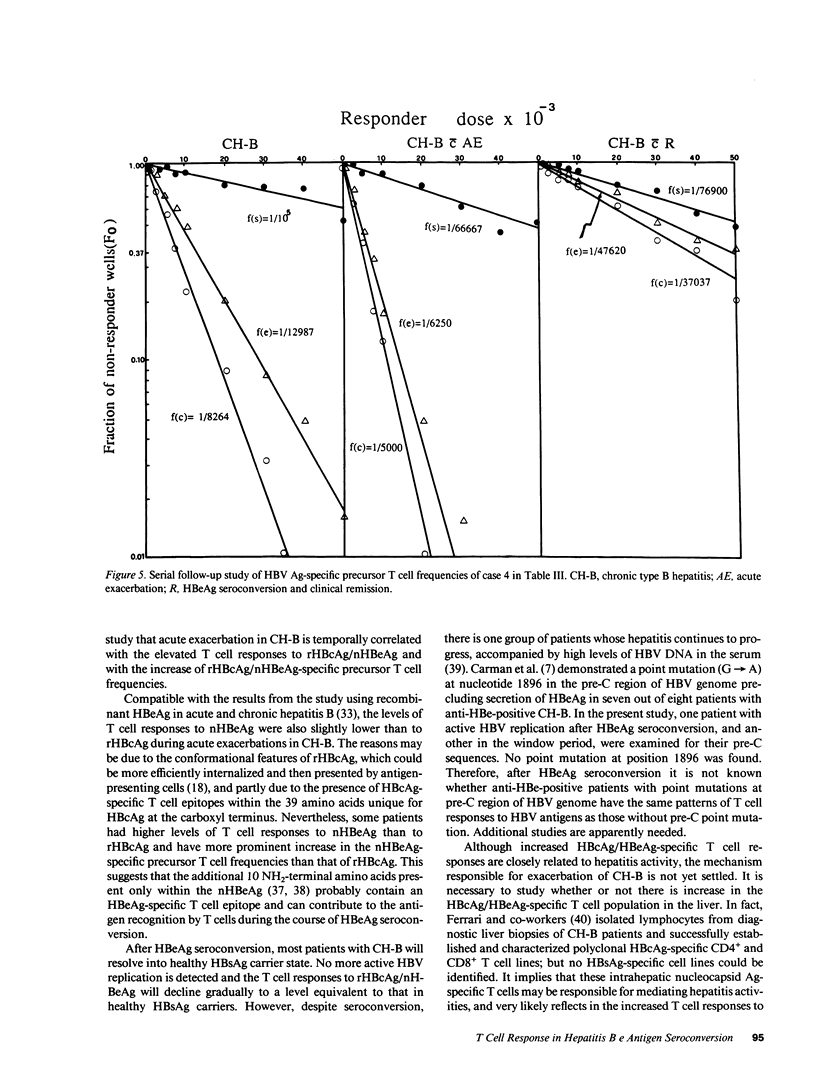
T cell proliferative responses to hepatitis B virus-encoded envelope antigen (S + preS2 + preS1), recombinant core antigen (HBcAg), and natural hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) were examined in 22 HBeAg-positive patients with chronic type B hepatitis and 17 healthy hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) carriers. The results showed that HBeAg-positive patients had (a) higher levels of T cell responses to HBcAg/HBeAg than those of healthy HBsAg carriers (P less than 0.001 and P less than 0.01, respectively); (b) a further increase in these T cell responses during acute exacerbations (P less than 0.05 and P less than 0.05, respectively); (c) subsidence in the T cell responses to HBcAg/HBeAg after recovery from acute exacerbations and HBeAg seroconversion, whereas the responses would persist at high levels if the patients did not enter a clinical remission; and (d) low levels of T cell responses to S + preS2 + preS1 either before or after HBeAg seroconversion. The appearance of increasing T cell responses to HBcAg/HBeAg usually occurred in the early phase of acute exacerbations. These findings imply that HBcAg/HBeAg-specific T cells play an important role in the exacerbations of chronic hepatitis B and in HBeAg seroconversion. HBcAg/HBeAg-specific precursor T cell frequencies were serially studied in selected cases by limiting dilution assay. Elevation (two- to fourfold) of HBcAg/HBeAg-specific precursor T cell frequencies contributed to the increase of HBcAg/HBeAg-specific T cell proliferation during acute exacerbations.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akahane Y., Yamanaka T., Suzuki H., Sugai Y., Tsuda F., Yotsumoto S., Omi S., Okamoto H., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Chronic active hepatitis with hepatitis B virus DNA and antibody against e antigen in the serum. Disturbed synthesis and secretion of e antigen from hepatocytes due to a point mutation in the precore region. Gastroenterology. 1990 Oct;99(4):1113–1119. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90632-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L. Y., Lin C. C., Chien C. S. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1129–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90585-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruss V., Gerlich W. H. Formation of transmembraneous hepatitis B e-antigen by cotranslational in vitro processing of the viral precore protein. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):268–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90266-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman W. F., Jacyna M. R., Hadziyannis S., Karayiannis P., McGarvey M. J., Makris A., Thomas H. C. Mutation preventing formation of hepatitis B e antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Lancet. 1989 Sep 9;2(8663):588–591. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. S., Lai M. Y., Lee S. C., Yang P. M., Sheu J. C., Sung J. L. Serum HBsAg, HBeAg, anti-HBe, and hepatitis B viral DNA in asymptomatic carriers in Taiwan. J Med Virol. 1986 May;19(1):87–94. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890190113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Ferrari C., Mondelli M. U. Hepatitis B virus structure and biology. Microb Pathog. 1989 May;6(5):311–325. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. M., Karayiannis P., Fowler M. J., Monjardino J., Liaw Y. F., Thomas H. C. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Taiwan: studies of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum. Hepatology. 1985 May-Jun;5(3):431–434. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. M., Liaw Y. F. Intrahepatic expression of HBcAg in chronic HBV hepatitis: lessons from molecular biology. Hepatology. 1990 Dec;12(6):1443–1445. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. L., Hoofnagle J. H., Waggoner J. G. Spontaneous reactivation of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology. 1984 Feb;86(2):230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Mondelli M. U., Penna A., Fiaccadori F., Chisari F. V. Functional characterization of cloned intrahepatic, hepatitis B virus nucleoprotein-specific helper T cell lines. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):539–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Penna A., Bertoletti A., Valli A., Antoni A. D., Giuberti T., Cavalli A., Petit M. A., Fiaccadori F. Cellular immune response to hepatitis B virus-encoded antigens in acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3442–3449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Penna A., Giuberti T., Tong M. J., Ribera E., Fiaccadori F., Chisari F. V. Intrahepatic, nucleocapsid antigen-specific T cells in chronic active hepatitis B. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2050–2058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields H. A., Bradley D. W., Davis C. L., Maynard J. E. Purification and partial characterization of hepatitis e antigen (HBeAg). Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):792–803. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.792-803.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadziyannis S. J., Lieberman H. M., Karvountzis G. G., Shafritz D. A. Analysis of liver disease, nuclear HBcAg, viral replication, and hepatitis B virus DNA in liver and serum of HBeAg Vs. anti-HBe positive carriers of hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 1983 Sep-Oct;3(5):656–662. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H. Chronic type B hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1983 Feb;84(2):422–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Shafritz D. A., Popper H. Chronic type B hepatitis and the "healthy" HBsAg carrier state. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):758–763. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. I., Chang M. H., Lee C. Y., Hsu H. Y., Chen J. S., Chen P. J., Chen D. S. Changes of serum hepatitis B virus DNA and aminotransferase levels during the course of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in children. Hepatology. 1990 Oct;12(4 Pt 1):657–660. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda K., Kanno A., Ohori H. Immunochemical characterization of hepatitis B e antigen subtypes, HBeAg/1 and HBeAg/2, in sera of hepatitis B virus carriers. J Med Virol. 1986 Nov;20(3):219–228. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890200304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R. Immune response to hepatitis B virus proteins: relevance of the murine model. Semin Liver Dis. 1991 May;11(2):93–112. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., Jones J. E., Hughes J. L., Price J., Raney A. K., McLachlan A. Is a function of the secreted hepatitis B e antigen to induce immunologic tolerance in utero? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6599–6603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., McLachlan A., Moriarty A., Thornton G. B. Immune response to hepatitis B virus core antigen (HBcAg): localization of T cell recognition sites within HBcAg/HBeAg. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1223–1231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., McLachlan A., Raney A. K., Houghten R., Thornton G. B., Maruyama T., Hughes J. L., Jones J. E. Autoantibody production in hepatitis B e antigen transgenic mice elicited with a self T-cell peptide and inhibited with nonself peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4348–4352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., McLachlan A., Stahl S., Wingfield P., Thornton G. B., Hughes J. L., Jones J. E. Comparative immunogenicity of hepatitis B virus core and E antigens. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3617–3624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills C. T., Lee E., Perrillo R. Relationship between histology, aminotransferase levels, and viral replication in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 1990 Aug;99(2):519–524. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondelli M., Tedder R. S., Ferns B., Pontisso P., Realdi G., Alberti A. Differential distribution of hepatitis B core and E antigens in hepatocytes: analysis by monoclonal antibodies. Hepatology. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):199–204. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrillo R. P., Schiff E. R., Davis G. L., Bodenheimer H. C., Jr, Lindsay K., Payne J., Dienstag J. L., O'Brien C., Tamburro C., Jacobson I. M. A randomized, controlled trial of interferon alfa-2b alone and after prednisone withdrawal for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. The Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 2;323(5):295–301. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008023230503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Shafritz D. A., Hoofnagle J. H. Relation of the hepatitis B virus carrier state to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):764–772. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Feldhaus J., Robins R. A. Single step separation of human T and B cells using AET treated srbc rosettes. J Immunol Methods. 1976;12(3-4):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su I. J., Lai M. Y., Hsu H. C., Chen D. S., Yang P. M., Chuang S. M., Sung J. L. Diverse virological, histopathological and prognostic implications of seroconversion from hepatitis B e antigen to anti-HBe in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 1986;3(2):182–189. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(86)80024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Imai M., Gotanda T., Sano T., Oinuma A., Mishiro S., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Hepatitis B e antigen polypeptides isolated from sera of individuals infected with hepatitis B virus: comparison with HBeAg polypeptide derived from Dane particles. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):49–57. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Machida A., Funatsu G., Nomura M., Usuda S., Aoyagi S., Tachibana K., Miyamoto H., Imai M., Nakamura T. Immunochemical structure of hepatitis B e antigen in the serum. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2903–2907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C. Limiting dilution assays for the determination of immunocompetent cell frequencies. I. Data analysis. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1614–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]