Abstract
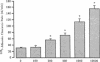
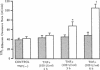
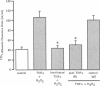
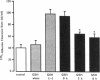
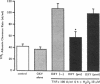
We examined the effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha) stimulation of endothelial cells on the increase in endothelial permeability induced by H2O2. Bovine pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (BPMVEC) were grown to confluence on a microporous filter and the 125I-albumin clearance rate across the monolayer was determined. Pretreatment with TNF alpha (100 U/ml) for 6 h had no direct effect on transendothelial 125I-albumin permeability. However, TNF alpha pretreatment enhanced the susceptibility of BPMVEC to H2O2; that is, H2O2 (10 microM) alone had no direct effect, whereas H2O2 increased 125I-albumin permeability more than threefold when added to monolayers pretreated for 6 h with TNF alpha. Determination of lactate dehydrogenase release indicated that increased permeability was not due to cytolysis. We measured the intracellular contents of GSH and catalase to determine their possible role in mediating the increased susceptibility to H2O2. TNF alpha treatment (100 U/ml for 6 h) decreased total GSH content and concomitantly increased the oxidized GSH content, but did not alter the cellular catalase activity. The role of GSH was examined by pretreating endothelial cells with 2 mM GSH for 3 h, which produced an 80% increase in intracellular GSH content. GSH repletion inhibited the increased sensitivity of the TNF alpha-treated endothelial cells to H2O2. We tested the effects of xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibition since XO activation may be a source of oxidants responsible for the decrease in cellular GSH content. Pretreatment with 0.5 mM oxypurinol attenuated the synergistic effect of TNF alpha and H2O2 on endothelial permeability. The results indicate that decreased oxidant buffering capacity secondary to TNF alpha-induced reduction in intracellular GSH content mediates the increased susceptibility of endothelial cells to H2O2. This mechanism may contribute to oxidant-dependent vascular endothelial injury in septicemia associated with TNF alpha release.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. D., Jr, Lauterburg B. H., Mitchell J. R. Plasma glutathione and glutathione disulfide in the rat: regulation and response to oxidative stress. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Dec;227(3):749–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERS R. F., Jr, SIZER I. W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo G., Mirabelli F., DiMonte D., Richelmi P., Thor H., Orrenius C., Orrenius S. Formation and reduction of glutathione-protein mixed disulfides during oxidative stress. A study with isolated hepatocytes and menadione (2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone). Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 15;36(8):1313–1320. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Mendrick D. L., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Identification of an inducible endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9238–9242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett J., Gerlach H., Nawroth P., Steinberg S., Godman G., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin increases permeability of endothelial cell monolayers by a mechanism involving regulatory G proteins. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1977–1991. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigham K. L., Meyrick B., Berry L. C., Jr, Repine J. E. Antioxidants protect cultured bovine lung endothelial cells from injury by endotoxin. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):840–850. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broudy V. C., Kaushansky K., Segal G. M., Harlan J. M., Adamson J. W. Tumor necrosis factor type alpha stimulates human endothelial cells to produce granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7467–7471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Camussi G., Baglioni C. Synthesis and release of platelet-activating factor by human vascular endothelial cells treated with tumor necrosis factor or interleukin 1 alpha. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11856–11861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra T., Baumgartner J. D., Grau G. E., Wu M. M., Lambert P. H., Schellekens J., Verhoef J., Glauser M. P. Prognostic values of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin-1, interferon-alpha, and interferon-gamma in the serum of patients with septic shock. Swiss-Dutch J5 Immunoglobulin Study Group. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):982–987. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. A., Chen M. J., Crooke S. T., Bomalaski J. S. Tumour necrosis factor (cachectin) induces phospholipase A2 activity and synthesis of a phospholipase A2-activating protein in endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):125–132. doi: 10.1042/bj2500125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Del Vecchio P. J., Minnear F. L., Burhop K. E., Selig W. M., Garcia J. G., Malik A. B. Measurement of albumin permeability across endothelial monolayers in vitro. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Mar;62(3):1076–1083. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.3.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Vecchio P. J., Ryan J. W., Chung A., Ryan U. S. Capillaries of the adrenal cortex possess aminopeptidase A and angiotensin-converting-enzyme activities. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):605–608. doi: 10.1042/bj1860605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneke S. M., Fanburg B. L. Regulation of cellular glutathione. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 1):L163–L173. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.4.L163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedl H. P., Till G. O., Ryan U. S., Ward P. A. Mediator-induced activation of xanthine oxidase in endothelial cells. FASEB J. 1989 Nov;3(13):2512–2518. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.13.2806779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. G., Siflinger-Birnboim A., Bizios R., Del Vecchio P. J., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Malik A. B. Thrombin-induced increase in albumin permeability across the endothelium. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jul;128(1):96–104. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs L. S., Lai L., Malik A. B. Tumor necrosis factor enhances the neutrophil-dependent increase in endothelial permeability. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Dec;145(3):496–500. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041450315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum S. E., Sun W. L. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha augments pulmonary arterial transendothelial albumin flux in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 1):L57–L67. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.258.2.L57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W. Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 15;106(1):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heflin A. C., Jr, Brigham K. L. Prevention by granulocyte depletion of increased vascular permeability of sheep lung following endotoxemia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1253–1260. doi: 10.1172/JCI110371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath C. J., Ferro T. J., Jesmok G., Malik A. B. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor increases pulmonary vascular permeability independent of neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9219–9223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaslovsky R. A., Horgan M. J., Lum H., McCandless B. K., Gilboa N., Wright S. D., Malik A. B. Pulmonary edema induced by phagocytosing neutrophils. Protective effect of monoclonal antibody against phagocyte CD18 integrin. Circ Res. 1990 Oct;67(4):795–802. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.4.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Graham D., Toy K., Lin L. S., Senyk G., Fendly B. M. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor causes activation of human granulocytes. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):640–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Wright S. C. Cytotoxic mechanism of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. FASEB J. 1990 Nov;4(14):3215–3223. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.14.2172061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcho Z., White J. E., Higgins P. J., Tsan M. F. Tumor necrosis factor enhances endothelial cell susceptibility to oxygen toxicity: role of glutathione. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Dec;5(6):556–562. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.6.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Neutrophil activation on biological surfaces. Massive secretion of hydrogen peroxide in response to products of macrophages and lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1550–1560. doi: 10.1172/JCI113241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Bank I., Handley D., Cassimeris J., Chess L., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1363–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips P. G., Tsan M. F. Direct staining and visualization of endothelial monolayers cultured on synthetic polycarbonate filters. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 May;36(5):551–554. doi: 10.1177/36.5.3356897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Lapierre L. A., Mendrick D. L., Fiers W., Rothlein R., Springer T. A. Overlapping patterns of activation of human endothelial cells by interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and immune interferon. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1893–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roten R., Markert M., Feihl F., Schaller M. D., Tagan M. C., Perret C. Plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Mar;143(3):590–592. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.3.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubin R., Elsas P. P., Fiers W., Dessein A. J. Recombinant human tumour necrosis factor (rTNF)2 enhances leukotriene biosynthesis in neutrophils and eosinophils stimulated with the Ca2+ ionophore A23187. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Nov;70(2):484–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royall J. A., Berkow R. L., Beckman J. S., Cunningham M. K., Matalon S., Freeman B. A. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 alpha increase vascular endothelial permeability. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):L399–L410. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.6.L399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuger L., Varani J., Marks R. M., Kunkel S. L., Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Cytotoxicity of tumor necrosis factor-alpha for human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):62–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer J. B., Treanor C. P., Del Vecchio P. J. Expression of bovine and mouse endothelial cell antioxidant enzymes following TNF-alpha exposure. Free Radic Biol Med. 1990;8(5):497–502. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(90)90064-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S., Peach M. J. Granulocytes and phorbol myristate acetate increase permeability to albumin of cultured endothelial monolayers and isolated perfused lungs. Role of oxygen radicals and granulocyte adherence. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jan;127(1):72–76. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiki Y., Meyrick B. O., Brigham K. L., Burr I. M. Endotoxin increases superoxide dismutase in cultured bovine pulmonary endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 1):C436–C440. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.4.C436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slungaard A., Vercellotti G. M., Walker G., Nelson R. D., Jacob H. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin stimulates eosinophil oxidant production and toxicity towards human endothelium. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):2025–2041. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.2025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Roederer M., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Intracellular thiols regulate activation of nuclear factor kappa B and transcription of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9943–9947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K. E., Ishizaka A., Larrick J. W., Raffin T. A. Tumor necrosis factor causes increased pulmonary permeability and edema. Comparison to septic acute lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jun;137(6):1364–1370. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.6.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K. E., Ishizaka A., Wu Z. H., Larrick J. W., Raffin T. A. Granulocyte depletion prevents tumor necrosis factor-mediated acute lung injury in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Nov;138(5):1300–1307. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.5.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada L. S., Beehler C. J., Banerjee A., Brown J. M., Grosso M. A., Harken A. H., McCord J. M., Repine J. E. Hyperoxia and self- or neutrophil-generated O2 metabolites inactivate xanthine oxidase. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Nov;65(5):2349–2353. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.5.2349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsan M. F., Danis E. H., Del Vecchio P. J., Rosano C. L. Enhancement of intracellular glutathione protects endothelial cells against oxidant damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):270–276. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80154-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsan M. F., White J. E., Rosano C. L. Modulation of endothelial GSH concentrations: effect of exogenous GSH and GSH monoethyl ester. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Mar;66(3):1029–1034. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.3.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Bendelow M. J., Sealey D. E., Kunkel S. L., Gannon D. E., Ryan U. S., Ward P. A. Tumor necrosis factor enhances susceptibility of vascular endothelial cells to neutrophil-mediated killing. Lab Invest. 1988 Aug;59(2):292–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Young J., LoBuglio A. F., Slivka A., Nimeh N. F. Role of hydrogen peroxide in neutrophil-mediated destruction of cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI110307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman R. J., Chan A., Leadon S. A. Oxidative damage in murine tumor cells treated in vitro by recombinant human tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Res. 1989 Apr 1;49(7):1644–1648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]