Abstract
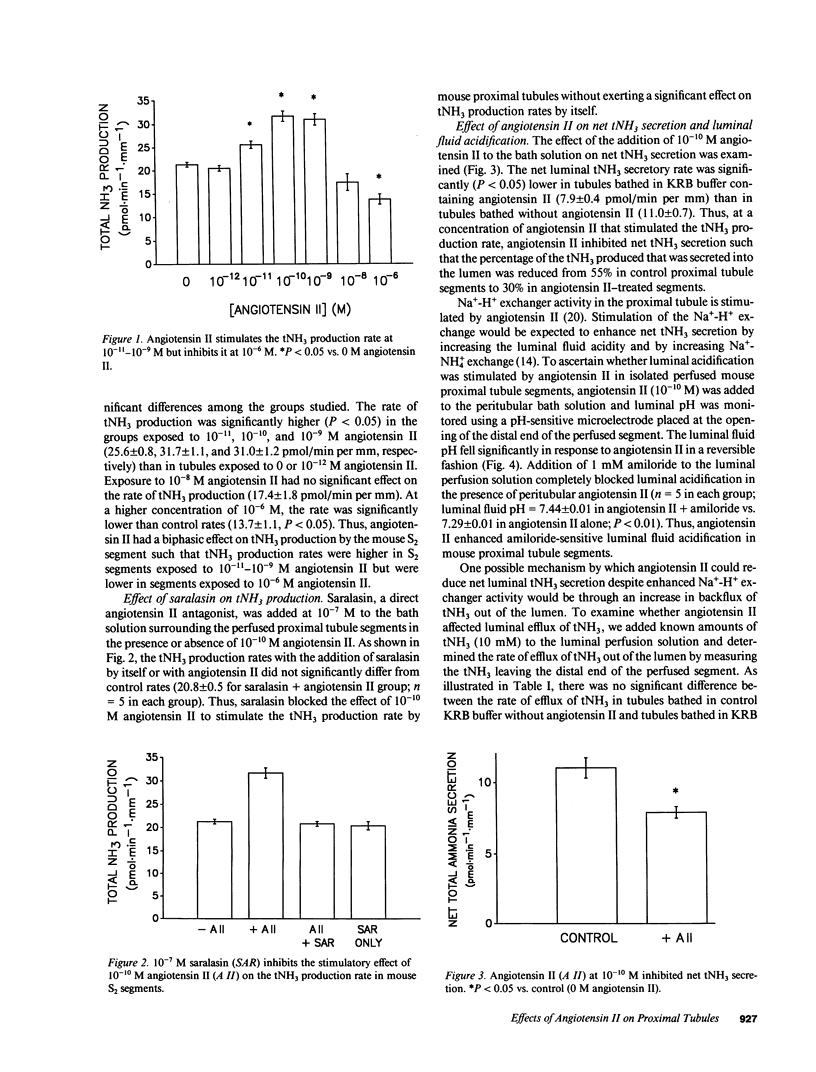
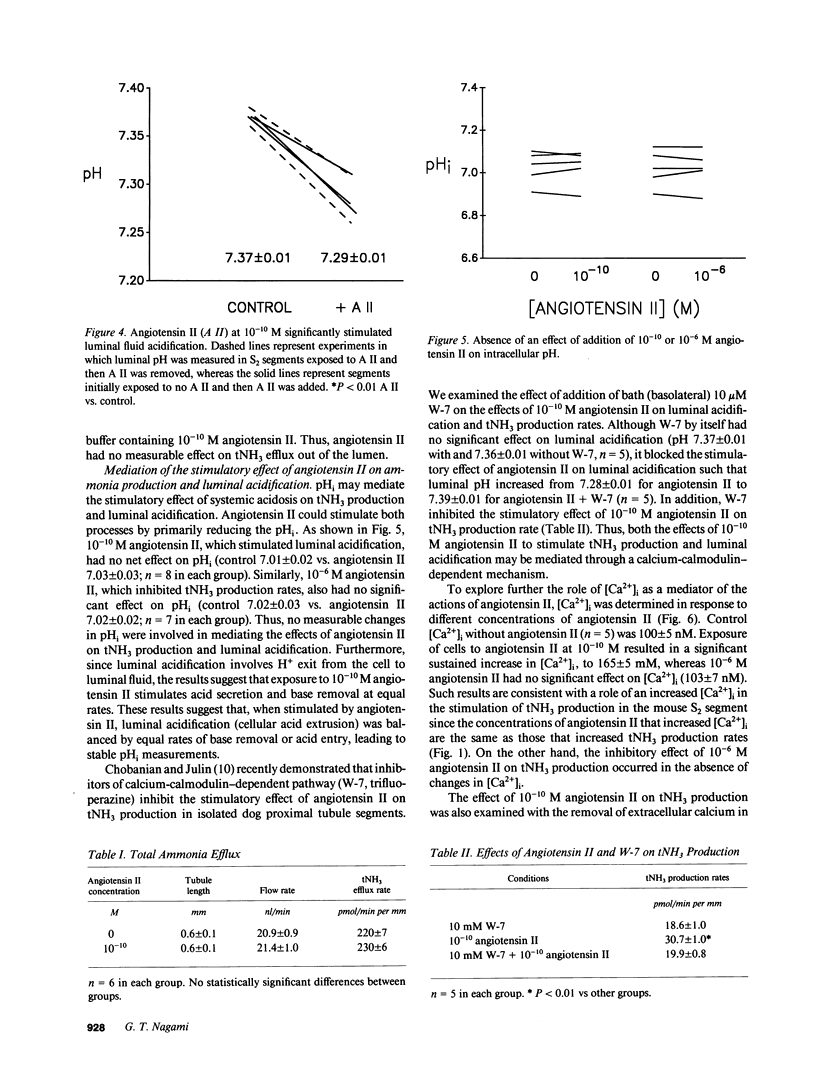
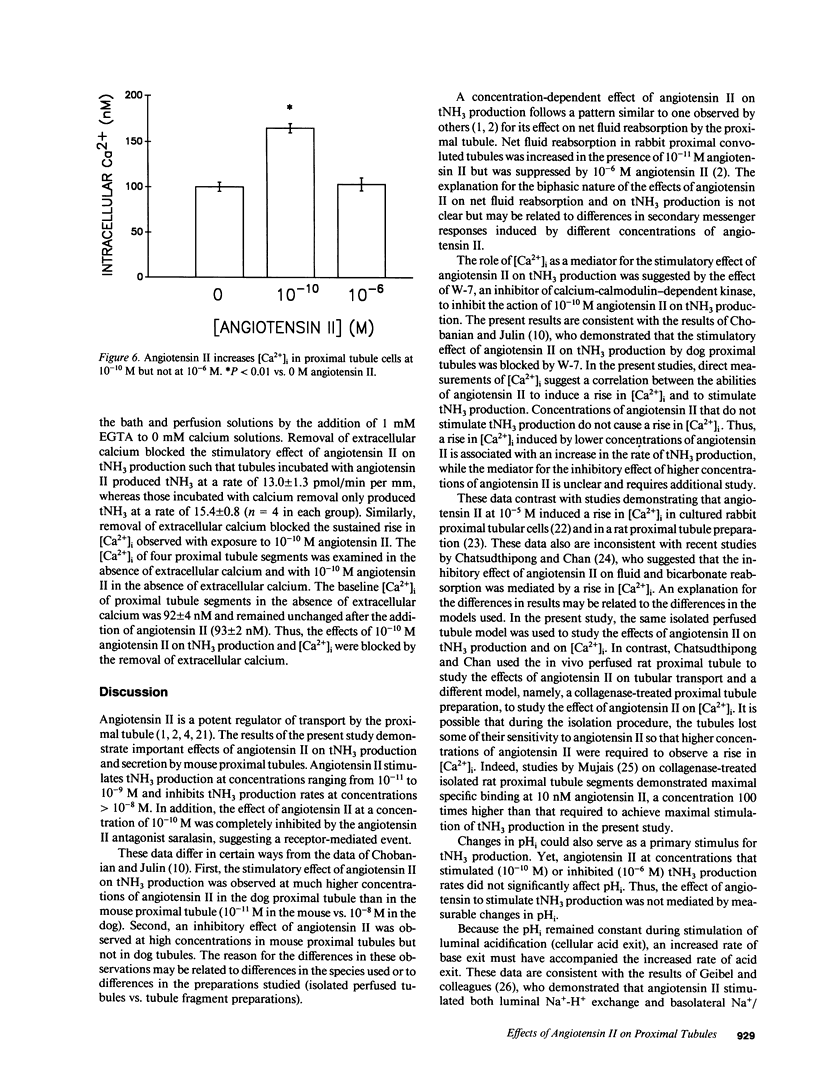
The effects of angiotensin II on total ammonia (tNH3) production and net secretion were investigated using in vitro microperfused mouse S2 proximal tubule segments incubated in Krebs-Ringer bicarbonate buffer containing 0.5 mM L-glutamine. Basolateral exposure of mouse S2 segments to 10(-11), 10(-10), and 10(-9) M angiotensin II stimulated tNH3 production rates by 23, 52, and 49%, respectively. Addition of 10(-6) M angiotensin II inhibited the tNH3 production rate by 34%. 10(-10) M angiotensin II inhibited net luminal secretion of tNH3 in the presence of enhanced luminal acidification and in the absence of altered luminal tNH3 efflux rates. Measurements of intracellular pH (pHi) and intracellular calcium concentration [( Ca2+]i) suggested that the effects of angiotensin II on tNH3 production were not mediated by changes in pHi but by the stimulatory effect of angiotensin II correlated with increased [Ca2+]i. Inhibition of the calcium-calmodulin-dependent pathway with W-7 blocked the stimulatory effect of 10(-10) M angiotensin II on tNH3 production and luminal acidification. These results indicate that angiotensin II has concentration-dependent effects on tNH3 production; that its action to stimulate tNH3 production may be mediated by rises in [Ca2+]i and the calcium-calmodulin pathway; and that angiotensin II, at concentrations that stimulate tNH3 production, inhibits net luminal ammonia secretion by a mechanism that is not mediated by diminished luminal acidification or by changes in luminal ammonia efflux rates.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown G., Douglas J. Effect of angiotensin II infusion in rats on Na,K-ATPase activity in renal cortical microsomal preparations. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Nov 15;275(1):236–243. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buerkert J., Martin D., Trigg D. Ammonium handling by superficial and juxtamedullary nephrons in the rat. Evidence for an ammonia shunt between the loop of Henle and the collecting duct. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):1–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI110581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatsudthipong V., Chan Y. L. Inhibitory effect of angiotensin II on renal tubular transport. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 2):F340–F346. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.3.F340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chobanian M. C., Julin C. M. Angiotensin II stimulates ammoniagenesis in canine renal proximal tubule segments. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jan;260(1 Pt 2):F19–F26. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.1.F19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filburn C. R., Harrison S. Parathyroid hormone regulation of cytosolic Ca2+ in rat proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):F545–F552. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.3.F545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLABMAN S., KOSE R. M., GIEBISCH G. Micropuncture study of ammonia excretion in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1963 Jul;205:127–132. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.1.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin J. L., Burg M. B., Knepper M. A. Ammonium replaces potassium in supporting sodium transport by the Na-K-ATPase of renal proximal straight tubules. Am J Physiol. 1985 Nov;249(5 Pt 2):F785–F788. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.5.F785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W., Burg M. B. Ammonia production by individual segments of the rat nephron. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):602–610. doi: 10.1172/JCI111250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES C. P., Jr, MAYSON J. S., OWEN E. E., ROBINSON R. R. A MICROPUNCTURE EVALUATION OF RENAL AMMONIA EXCRETION IN THE RAT. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jul;207:77–83. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. J., Navar L. G. Tubular transport responses to angiotensin. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 2):F621–F630. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.5.F621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. J., Young J. A. Dose-dependent stimulation and inhibition of proximal tubular sodium reabsorption by angiotensin II in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Jan 17;367(3):295–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00581370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Aronson P. S. Interaction of NH4+ and Li+ with the renal microvillus membrane Na+-H+ exchanger. Am J Physiol. 1981 Nov;241(5):C220–C226. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.241.5.C220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz I., Balaban R. S. Ammonium as a substrate for Na+-K+-ATPase in rabbit proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 2):F497–F502. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.3.F497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Cogan M. G. Angiotensin II stimulation of hydrogen ion secretion in the rat early proximal tubule. Modes of action, mechanism, and kinetics. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):601–607. doi: 10.1172/JCI113638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Cogan M. G. Angiotensin II: a potent regulator of acidification in the rat early proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):272–275. doi: 10.1172/JCI113059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mujais S. K., Kauffman S., Katz A. I. Angiotensin II binding sites in individual segments of the rat nephron. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):315–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI112293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagami G. T. Effect of bath and luminal potassium concentration on ammonia production and secretion by mouse proximal tubules perfused in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):32–39. doi: 10.1172/JCI114702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagami G. T., Kurokawa K. Regulation of ammonia production by mouse proximal tubules perfused in vitro. Effect of luminal perfusion. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):844–849. doi: 10.1172/JCI111781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagami G. T. Luminal secretion of ammonia in the mouse proximal tubule perfused in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):159–164. doi: 10.1172/JCI113287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagami G. T., Sonu C. M., Kurokawa K. Ammonia production by isolated mouse proximal tubules perfused in vitro. Effect of metabolic acidosis. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):124–129. doi: 10.1172/JCI112540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig P. A., Alpern R. J. Pathways for apical and basolateral membrane NH3 and NH4+ movement in rat proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):F587–F593. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.4.F587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajo I. M., Goldstein M. B., Sonnenberg H., Stinebaugh B. J., Wilson D. R., Halperin M. L. Sites of ammonia addition to tubular fluid in rats with chronic metabolic acidosis. Kidney Int. 1981 Sep;20(3):353–358. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Angiotensin II directly stimulates sodium transport in rabbit proximal convoluted tubules. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):507–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI111237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Dubinsky W. P., Fisher K., Steplock D., Dinh Q., Chang L., Shenolikar S. Regulation of reconstituted renal Na+/H+ exchanger by calcium-dependent protein kinases. J Membr Biol. 1988 Aug;103(3):237–244. doi: 10.1007/BF01993983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh C., Dubyak G., Douglas J. G. Relationship between phospholipase C activation and prostaglandin E2 and cyclic adenosine monophosphate production in rabbit tubular epithelial cells. Effects of angiotensin, bradykinin, and arginine vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):710–719. doi: 10.1172/JCI113376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


