Abstract
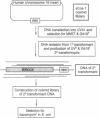
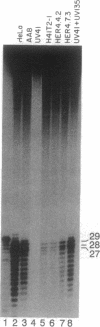
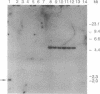
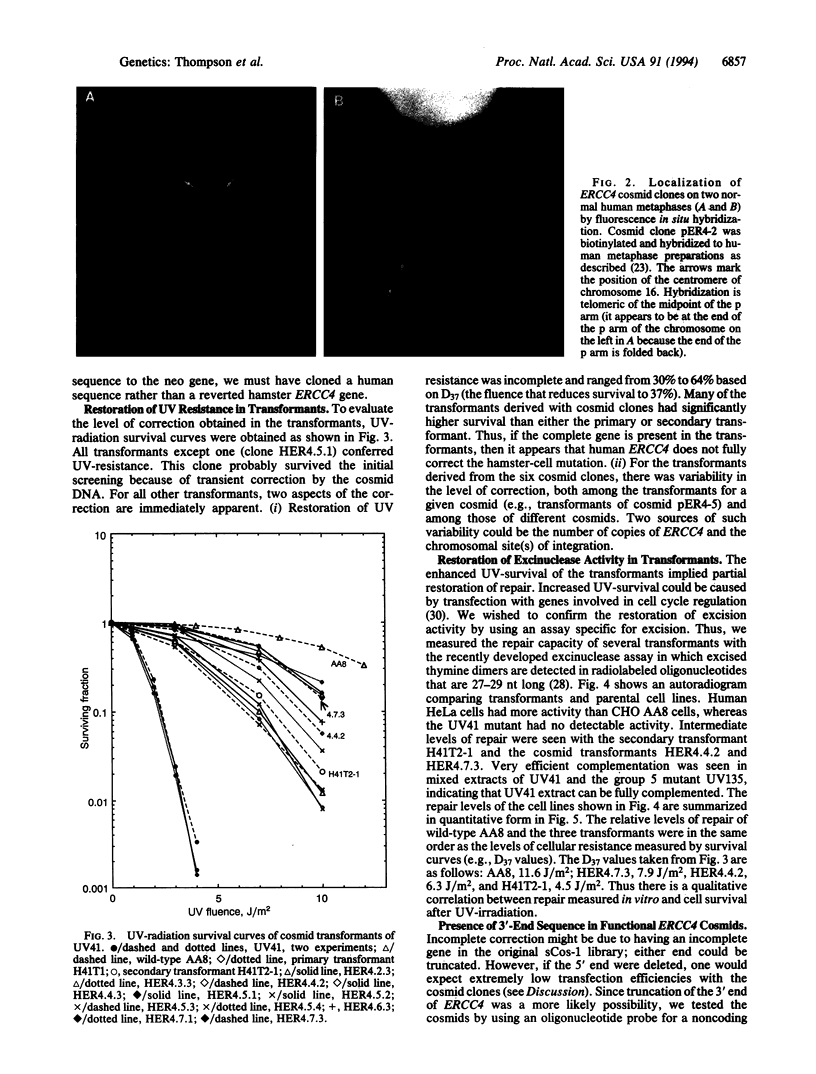
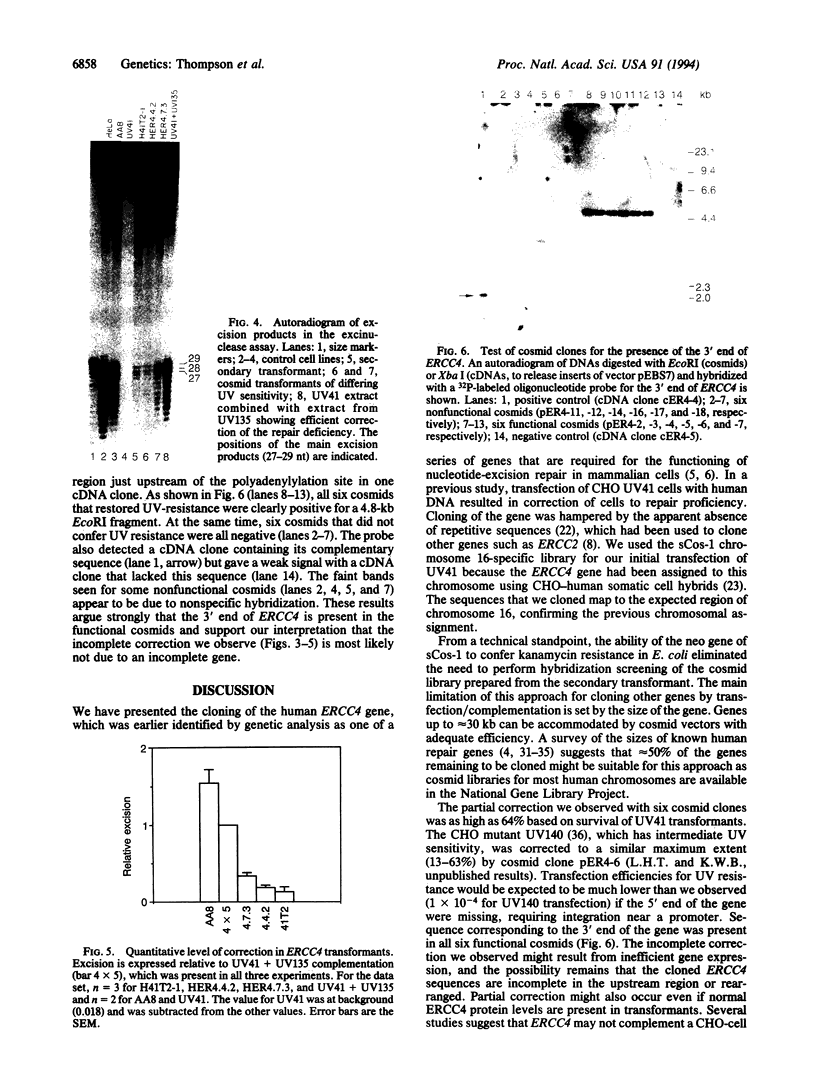
ERCC4 was previously identified in somatic cell hybrids as a human gene that corrects the nucleotide-excision-repair deficiency in mutant hamster cells. The cloning strategy for ERCC4 involved transfection of the repair-deficient hamster cell line UV41 with a human sCos-1 cosmid library derived from chromosome 16. Enhanced UV resistance was seen with one cosmid-library transformant and two secondary transformants of UV41. Cosmid clones carrying a functional ERCC4 gene were isolated from a library of a secondary transformant by selecting in Escherichia coli for expression of a linked neomycin-resistance gene that was present in the sCos-1 vector. The cosmids mapped to 16p13.13-p13.2, the location assigned to ERCC4 by using somatic cell hybrids. Upon transfection into UV41, six cosmid clones gave partial correction ranging from 30% to 64%, although all appeared to contain the complete gene. The capacity for in vitro excision of thymine dimers from a plasmid by transformant cell extracts correlated qualitatively with enhanced UV resistance.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggerstaff M., Szymkowski D. E., Wood R. D. Co-correction of the ERCC1, ERCC4 and xeroderma pigmentosum group F DNA repair defects in vitro. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3685–3692. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06043.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsaro C. M., Pearson M. L. Enhancing the efficiency of DNA-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Sep;7(5):603–616. doi: 10.1007/BF01549662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhanty A. M., Li M., Whitmore G. F. Isolation of Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants deficient in excision repair and mitomycin C bioactivation. Cancer Res. 1989 Jan 1;49(1):117–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhanty A. M., Rubin J. S., Whitmore G. F. Complementation of the DNA-repair defect in a CHO mutant by human DNA that lacks highly abundant repetitive sequences. Mutat Res. 1988 Nov;194(3):207–217. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(88)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Lewis K., Rothenberg B. E. High efficiency vectors for cosmid microcloning and genomic analysis. Gene. 1989 Jun 30;79(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flejter W. L., McDaniel L. D., Johns D., Friedberg E. C., Schultz R. A. Correction of xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group D mutant cell phenotypes by chromosome and gene transfer: involvement of the human ERCC2 DNA repair gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):261–265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H. Nucleotide excision repair. II: From yeast to mammals. Trends Genet. 1993 Jun;9(6):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90121-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoy C. A., Thompson L. H., Mooney C. L., Salazar E. P. Defective DNA cross-link removal in Chinese hamster cell mutants hypersensitive to bifunctional alkylating agents. Cancer Res. 1985 Apr;45(4):1737–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Svoboda D. L., Reardon J. T., Sancar A. Human nucleotide excision nuclease removes thymine dimers from DNA by incising the 22nd phosphodiester bond 5' and the 6th phosphodiester bond 3' to the photodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R., Peterson C. Expression cloning of a human DNA repair gene involved in xeroderma pigmentosum group C. Nature. 1992 Sep 3;359(6390):70–73. doi: 10.1038/359070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P., Siciliano J., White B., Legerski R., Callen D., Reeders S., Siciliano M. J., Thompson L. H. Regional mapping of human DNA excision repair gene ERCC4 to chromosome 16p13.13-p13.2. Mutagenesis. 1993 May;8(3):199–205. doi: 10.1093/mutage/8.3.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudgett J. S., MacInnes M. A. Isolation of the functional human excision repair gene ERCC5 by intercosmid recombination. Genomics. 1990 Dec;8(4):623–633. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90248-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsu Y., Hattori K., Hayakawa H., Shimizu K., Sekiguchi M. Organization and expression of the human gene for O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase. Mutat Res. 1993 Jan;293(2):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(93)90063-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguiez P., Barnes D. E., Mohrenweiser H. W., Lindahl T. Structure of the human DNA ligase I gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3845–3850. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan A., Wood R. D. Identical defects in DNA repair in xeroderma pigmentosum group G and rodent ERCC group 5. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):185–188. doi: 10.1038/363185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon J. T., Thompson L. H., Sancar A. Excision repair in man and the molecular basis of xeroderma pigmentosum syndrome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:605–617. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riboni R., Botta E., Stefanini M., Numata M., Yasui A. Identification of the eleventh complementation group of UV-sensitive excision repair-defective rodent mutants. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 1;52(23):6690–6691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson C. N., Hochhauser D., Craig R., Rack K., Buckle V. J., Hickson I. D. Structure of the human DNA repair gene HAP1 and its localisation to chromosome 14q 11.2-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 11;20(17):4417–4421. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.17.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Tang M. S. Nucleotide excision repair. Photochem Photobiol. 1993 May;57(5):905–921. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1993.tb09233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh M. S., Jones C. J., Wood R. D., Lindahl T. DNA excision-repair defect of xeroderma pigmentosum prevents removal of a class of oxygen free radical-induced base lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6335–6339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Nouspikel T., Corlet J., Ucla C., Bairoch A., Clarkson S. G. Complementation of the DNA repair defect in xeroderma pigmentosum group G cells by a human cDNA related to yeast RAD2. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):182–185. doi: 10.1038/363182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanini M., Collins A. R., Riboni R., Klaude M., Botta E., Mitchell D. L., Nuzzo F. Novel Chinese hamster ultraviolet-sensitive mutants for excision repair form complementation groups 9 and 10. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):3965–3971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Satokata I., Ogita Z., Uchida T., Okada Y. Molecular cloning of a mouse DNA repair gene that complements the defect of group-A xeroderma pigmentosum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5512–5516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitz T., Eli D., Penner M., Bakhanashvili M., Naiman T., Timme T. L., Wood C. M., Moses R. E., Canaani D. Expression of the cDNA for the beta subunit of human casein kinase II confers partial UV resistance on xeroderma pigmentosum cells. Mutat Res. 1990 Jul;236(1):85–97. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Brookman K. W., Jones N. J., Allen S. A., Carrano A. V. Molecular cloning of the human XRCC1 gene, which corrects defective DNA strand break repair and sister chromatid exchange. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6160–6171. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Busch D. B., Brookman K., Mooney C. L., Glaser D. A. Genetic diversity of UV-sensitive DNA repair mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3734–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H. Somatic cell genetics approach to dissecting mammalian DNA repair. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1989;14(4):264–281. doi: 10.1002/em.2850140409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troelstra C., van Gool A., de Wit J., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. ERCC6, a member of a subfamily of putative helicases, is involved in Cockayne's syndrome and preferential repair of active genes. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):939–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90390-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen W., Stefanini M., Giliani S., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group H falls into complementation group D. Mutat Res. 1991 Sep;255(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(91)90054-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers M. A., Vyas P., Harris P. C., Simmons D. L., Higgs D. R. Structure of the human 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase gene and localization close to the 16p telomere. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3437–3441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber C. A., Salazar E. P., Stewart S. A., Thompson L. H. Molecular cloning and biological characterization of a human gene, ERCC2, that corrects the nucleotide excision repair defect in CHO UV5 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1137–1146. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeda G., van Ham R. C., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., van der Eb A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. A presumed DNA helicase encoded by ERCC-3 is involved in the human repair disorders xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne's syndrome. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):777–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90122-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zdzienicka M. Z., Roza L., Westerveld A., Bootsma D., Simons J. W. Biological and biochemical consequences of the human ERCC-1 repair gene after transfection into a repair-deficient CHO cell line. Mutat Res. 1987 Jan;183(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(87)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Westerveld A., Yasui A., Koken M. H., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Molecular characterization of the human excision repair gene ERCC-1: cDNA cloning and amino acid homology with the yeast DNA repair gene RAD10. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):913–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Vuuren A. J., Appeldoorn E., Odijk H., Yasui A., Jaspers N. G., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. Evidence for a repair enzyme complex involving ERCC1 and complementing activities of ERCC4, ERCC11 and xeroderma pigmentosum group F. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3693–3701. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]