Abstract
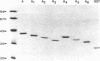
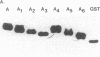
High-titer IgG autoantibodies to the La/SS-B ribonucleoprotein (RNP) are a hallmark of patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. Anti-La/SS-B-positive human sera bind to multiple epitopes on recombinant La/SS-B, although the initial response is against an immunodominant epitope within the first 107 NH2-terminal amino acids (aa). Sequence analysis has identified a striking homology between aa 88-101 in this NH2-terminal region of La/SS-B and a feline retroviral gag polypeptide suggesting the anti-La/SS-B response may be initiated by cross-reactivity with an exogenous agent. In the present study, detailed mapping of this NH2-terminal epitope, using recombinant La/SS-B purified from the expression of overlapping DNA fragments spanning aa 1-107, has shown that this immunodominant epitope is a complex conformational or discontinuous epitope dependent upon both aa 12-28 and 82-99 for expression, even though these regions share no homology with each other. This requirement questions the significance of the homology between La/SS-B and a retroviral gag polypeptide in the generation of the B cell response to La/SS-B and is in accord with the general concept that B cells recognize conformational epitopes on antigens rather than small linear peptide sequences. The finding also reinforces the notion that native autoantigen could be the initiator of the autoimmune response.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bini P., Chu J. L., Okolo C., Elkon K. Analysis of autoantibodies to recombinant La (SS-B) peptides in systemic lupus erythematosus and primary Sjogren's syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):325–333. doi: 10.1172/JCI114441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boire G., Craft J. Biochemical and immunological heterogeneity of the Ro ribonucleoprotein particles. Analysis with sera specific for the RohY5 particle. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):270–279. doi: 10.1172/JCI114150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. C., Kenan D., Martin B. J., Keene J. D. Genomic structure and amino acid sequence domains of the human La autoantigen. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18043–18051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Sullivan K. F., Machlin P. S., Cooke C. A., Kaiser D. A., Pollard T. D., Rothfield N. F., Cleveland D. W. Molecular cloning of cDNA for CENP-B, the major human centromere autoantigen. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):817–829. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K., Skelly S., Parnassa A., Moller W., Danho W., Weissbach H., Brot N. Identification and chemical synthesis of a ribosomal protein antigenic determinant in systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7419–7423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garry R. F. Extensive antigenic mimicry by retrovirus capsid proteins. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Dec;6(12):1361–1362. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J. A priori delineation of a peptide which mimics a discontinuous antigenic determinant. Mol Immunol. 1986 Jul;23(7):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldner H. H., Netter H. J., Szostecki C., Jaeger E., Will H. Human anti-p68 autoantibodies recognize a common epitope of U1 RNA containing small nuclear ribonucleoprotein and influenza B virus. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):819–829. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldner H. H., Netter H. J., Szostecki C., Lakomek H. J., Will H. Epitope mapping with a recombinant human 68-kDa (U1) ribonucleoprotein antigen reveals heterogeneous autoantibody profiles in human autoimmune sera. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):469–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets W. J., Hoet M. H., van Venrooij W. J. Epitope patterns of anti-RNP antibodies in rheumatic diseases. Evidence for an antigen-driven autoimmune response. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jun;33(6):834–841. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hang L., Slack J. H., Amundson C., Izui S., Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Induction of murine autoimmune disease by chronic polyclonal B cell activation. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):874–883. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L. Autoimmune phenomena in chronic chagasic cardiopathy. Parasitol Today. 1985 Jul;1(1):6–9. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(85)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff J. P., Roos G., Peebles C. L., Houghten R., Sullivan K. F., Tan E. M. Insights into native epitopes of proliferating cell nuclear antigen using recombinant DNA protein products. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):419–429. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury E. L., Ritacco V., Cossio P. M., Laguens R. P., Szarfman A., Diez C., Arana R. M. Circulating antibodies to peripheral nerve in American trypanosomiasis (Chagas' disease). Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Apr;36(1):8–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman D. M., Steinberg A. D. Systemic autoimmune disease arises from polyclonal B cell activation. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1755–1760. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohsaka H., Yamamoto K., Fujii H., Miura H., Miyasaka N., Nishioka K., Miyamoto T. Fine epitope mapping of the human SS-B/La protein. Identification of a distinct autoepitope homologous to a viral gag polyprotein. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1566–1574. doi: 10.1172/JCI114606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G., Jimenez S. A., Riggs E., Ziemnicka-Kotula D. Determination of an epitope of the diffuse systemic sclerosis marker antigen DNA topoisomerase I: sequence similarity with retroviral p30gag protein suggests a possible cause for autoimmunity in systemic sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8492–8496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeilage L. J., Macmillan E. M., Whittingham S. F. Mapping of epitopes on the La(SS-B) autoantigen of primary Sjögren's syndrome: identification of a cross-reactive epitope. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3829–3835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeilage L. J., Whittingham S., Jack I., MacKay I. R. Molecular analysis of the RNA and protein components recognized by anti-La(SS-B) autoantibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Dec;62(3):685–695. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Molecular mimicry and autoimmune disease. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):819–820. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90507-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Keene J. D. A human autoimmune protein associated with U1 RNA contains a region of homology that is cross-reactive with retroviral p30gag antigen. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rader M. D., Codding C., Reichlin M. Differences in the fine specificity of anti-Ro (SS-A) in relation to the presence of other precipitating autoantibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Dec;32(12):1563–1571. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsden D. A., Chen J., Miller F. W., Misener V., Bernstein R. M., Siminovitch K. A., Tsui F. W. Epitope mapping of the cloned human autoantigen, histidyl-tRNA synthetase. Analysis of the myositis-associated anti-Jo-1 autoimmune response. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2267–2272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauh A. J., Hornig H., Lührmann R. At least three distinct B cell epitopes reside in the C-terminal half of La protein, as determined by a recombinant DNA approach. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Dec;18(12):2049–2057. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. H., Pierani A., Chou C. H., Ng T., Nicastri C., Roeder R. G., Sthoeger Z. M. Epitopes of the p70 and p80 (Ku) lupus autoantigens. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2678–2686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair E. W., Pisetsky D. S., Reich C. F., Keene J. D. Analysis of autoantibody binding to different regions of the human La antigen expressed in recombinant fusion proteins. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4173–4180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess A. D., Peterson M. G., McNeilage L. J., Whittingham S., Coppel R. L. Characteristics and epitope mapping of a cloned human autoantigen La. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3212–3218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Chan E. K., Sullivan K. F., Rubin R. L. Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs): diagnostically specific immune markers and clues toward the understanding of systemic autoimmunity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 May;47(2):121–141. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. J., Jeffrey P. D. Polymyositis and molecular mimicry, a mechanism of autoimmunity. Lancet. 1986 Sep 13;2(8507):605–607. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Zabriskie J. B., McCarty M. Group A streptococcal antigens cross-reactive with myocardium. Purification of heart-reactive antibody and isolation and characterization of the streptococcal antigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):579–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]